
What is arterial occlusion?
Arterial occlusion is a condition involving partial or complete blockage of blood flow through an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to body tissues [1] [2]. An occlusion of arteries disrupts oxygen and blood supply to tissues, leading to ischemia. [1]
What causes acute peripheral arterial occlusion (Aro)?
Acute peripheral arterial occlusion may result from: Rupture and thrombosis of an atherosclerotic plaque Embolus from the heart or thoracic or abdominal aorta
What causes arterial occlusion in the shoulder?
Arterial occlusion is usually caused by atherosclerosis or compression of an artery, such as the subclavian artery in thoracic outlet syndrome. Arterial occlusion can manifest as a deep, constant pain in the shoulder, or it can lead to ischemic pain with exercise. 30,63
What causes retinal artery occlusion?
Homocystinuria (a hereditary disorder that prevents your body from processing the amino acid methionine; this leads to an excess accumulatio of homocysteine in the blood and urine) Most retinal artery occlusion patients are in their 60s, and are more commonly men than women.
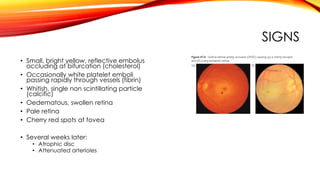
What is the most common cause of acute arterial occlusion?
Acute arterial occlusion is most commonly related to acute thrombosis of a diseased but previously patent, often atherosclerotic artery [10] but can also be due to acute thrombosis of a stent or graft, dissection of an artery, direct trauma to an artery, or the result of an embolus from a proximal source lodging into a ...
What is the most common cause of arterial disease?
Peripheral artery disease is often caused by a buildup of fatty, cholesterol-containing deposits (plaques) on artery walls. This process is called atherosclerosis. It reduces blood flow through the arteries. Atherosclerosis affects arteries throughout the body.
What are the signs of arterial occlusion?
The symptoms of lower extremity arterial occlusive disease include:Pain in the calves or thighs while walking.Pain in the feet at rest.Coolness of legs and feet.Poor healing of wounds in the extremity.Ulcers of the feet and legs.Black discoloration of the toes or skin (gangrene)
What are the 5 P's of arterial occlusion?
The traditional 5 P's of acute ischemia in a limb (ie, pain, paresthesia, pallor, pulselessness, poikilothermia) are not clinically reliable; they may manifest only in the late stages of compartment syndrome, by which time extensive and irreversible soft tissue damage may have taken place.
What foods cause clogged arteries?
The study, published Aug. 13 in Science, suggests that consuming food rich in saturated fat and choline - a nutrient found in red meat, eggs and dairy products - increases the number of metabolites that build plaques in the arteries.
What does a blocked artery feel like?
The symptoms of an artery blockage include chest pain and tightness, and shortness of breath. Imagine driving through a tunnel. On Monday, you encounter a pile of rubble. There is a narrow gap, big enough to drive through.
How do you fix arterial occlusion?
Possible treatments for acute arterial occlusion include:Dissolving or removing a blood clot. A tube (catheter) may be put into an artery in the groin to dissolve the clot. ... Angioplasty. ... Stenting. ... Endarterectomy. ... Peripheral bypass surgery.
How do you treat arterial occlusion?
Treatment. Treatment consists of embolectomy (catheter or surgical), thrombolysis, or bypass surgery. The decision to do surgical thromboembolectomy vs thrombolysis is based on the severity of ischemia, the extent or location of the thrombus, and the general medical condition of the patient.
How is arterial occlusion diagnosed?
If doctors suspect a blockage in an arm artery, they measure systolic blood pressure in both arms. Pressure that is consistently higher in one arm suggests a blockage in the arm with lower blood pressure, and occlusive peripheral arterial disease is diagnosed. Pulse assessment is also useful to assess blood flow.
When is arterial occlusion an emergency?
Acute arterial occlusion is serious. It occurs when blood flow in a leg artery stops suddenly. If blood flow to the toe, foot, or leg is completely blocked, the tissue begins to die.
Is an arterial occlusion painful?
Acute peripheral arterial occlusion is characterized by severe pain, cold sensation, paresthesias (or anesthesia), pallor, and pulselessness in the affected extremity. Treatment consists of embolectomy, thrombolysis, or bypass surgery.
Which patient is most at risk for peripheral vascular disease?
Who is at risk for peripheral vascular disease?Age (especially older than age 50)History of heart disease.Male gender.Postmenopausal women.Family history of high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or peripheral vascular disease.
What causes arterial disease?
It is primarily caused by the buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries, which is called atherosclerosis. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.
What are the warning signs of peripheral vascular disease?
Peripheral Vascular Disease SymptomsButtock pain.Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs.Burning or aching pain in the feet or toes while resting.A sore on a leg or a foot that will not heal.One or both legs or feet feeling cold or changing color (pale, bluish, dark reddish)Loss of hair on the legs.Impotence.
What is the life expectancy of someone with peripheral artery disease?
If left untreated, PAD can result in the need for a major amputation of the foot or leg. This is most concerning because the life expectancy for 60% of PAD amputee patients is only 2 to 5 years.
What is the primary symptom of peripheral arterial disease?
The most common symptom of lower-extremity peripheral artery disease is painful muscle cramping in the hips, thighs or calves when walking, climbing stairs or exercising. The pain of PAD often goes away when you stop exercising, although this may take a few minutes.
What is a thrombus occlusion?
Arterial occlusion by embolus or thrombus (see Table 21.4) is a well-documented neonatal cause of focal and multifocal parenchymal defects. a Often it has been difficult by clinical imaging or even pathological criteria to distinguish between a thrombotic and embolic process. As noted earlier, the lesions have been observed principally in the regions of the middle (and sometimes anterior) cerebral arteries (see Figs. 21.1 and 21.2 ).
What is acute ischemia?
Patients with acute ischemia, in contradistinction, usually present with an acute abdomen and often have a deranged metabolic status and other concomitant medical conditions (e.g., shock, cardiac disease, sepsis).
What is a vascular stenosis after liver transplant?
Hepatic artery stenosis is one of the most common vascular complications after liver transplantation. Most commonly the stenosis occurs in the donor arteries ( Fig. 77-8 ). Hepatic artery stenosis may cause graft ischemia, with deterioration of liver function and formation of biliary strictures.
Is pan a primary or secondary cause?
PAN is a cause of secondary , not primary, vasculitis of the nervous system, usually the peripheral nervous system. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978032344592450144X.
How to know if you have an arterial occlusion?
If you have diabetes or poor blood circulation, check your feet daily for wounds, sores, blisters, and color changes. Call your healthcare provider right away if you notice problems. If you smoke, stop smoking.
What is the procedure to bypass a blocked artery?
The material that blocks the artery is then removed from artery walls. Peripheral bypass surgery. A natural or manmade graft is used to bypass the blocked part of the artery.
What is the condition that reduces blood flow to the legs and feet?
You are more likely to have this condition if you have peripheral arterial disease (PAD). With PAD, leg arteries are narrowed. This reduces blood flow to your legs and feet.
What is it called when blood flow stops in your leg?
If blood flow to your toe, foot, or leg is completely blocked, the tissue begins to die. This is called gangrene. If this happens, medical care is needed right away to restore blood flow and possibly save your leg.
What causes a peripheral artery to occlude?
Peripheral arteries may be acutely occluded by a thrombus, an embolus, aortic dissection, or acute compartment syndrome. Acute peripheral arterial occlusion may result from: Rupture and thrombosis of an atherosclerotic plaque.
What is angina pectoris?
Test your knowledge. Angina Pectoris. Angina pectoris is usually described as chest discomfort rather than as chest “pain.”. The symptoms of angina pectoris may be a vague, barely troublesome ache or may rapidly become a severe, intense precordial crushing sensation.
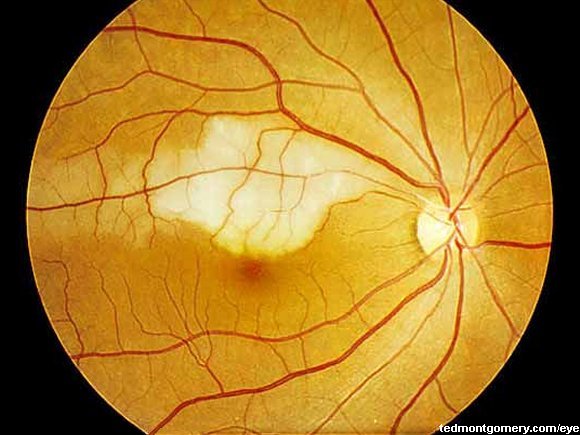
What is retinal artery occlusion?
Retinal artery occlusion is usually associated with sudden painless loss of vision in one eye. The area of the retina affected by the blocked vessels determines the area and extent of visual loss. The main artery supplying blood to the eye is the ophthalmic artery; when it is blocked, it produces the most damage.
Why does a retinal artery occlusion last for a few seconds?
The retinal artery occlusion may be transient and last for only a few seconds or minutes if the blockage breaks up and restores. blood flow to the retina, or it may be permanent.
What is the name of the artery that blocks the retina?
A blockage in the main artery in the retina is called central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO), which often results in severe loss of vision. However, about 25% of people who develop CRAO have an extra artery called a cilioretinal artery in their eyes.
What is the term for the loss of vision due to the lack of oxygen in the retina?
Retinal artery occlusion refers to blockage of the retinal artery carrying oxygen to the nerve cells in the retina at the back of the eye. The lack of oxygen delivery to the retina may result in severe loss of vision.
What causes blood to flow to the retina?
blood flow to the retina, or it may be permanent. Common risk factors include: Carotid artery disease. Atherosclerosis (fatty deposits in the arteries) Faulty heart valves (valvular heart disease) Tumors in the heart (myxoma) Abnormal heart rhythms such as atrial fibrillation. Diabetes.
How to treat crao clots?
Lowering the intraocular pressure with medication . Ocular massage with a thumb to dislodge the clot. However, for any treatment to be potentially effective in CRAO, it must be deployed within a short time window, probably within 4 to 6 hours after symptoms begin .
What is CRAO in vision?
When CRAO occurs, having a cilioretinal artery can greatly lessen the chances of damage to your central vision, as long as the cilioretinal artery is not affected. A blockage in a smaller artery is called branch retinal artery occlusion (BRAO); this may cause a loss of a section of your visual field, such as your vision to one side.
Overview
Arterial occlusion is a condition involving partial or complete blockage of blood flow through an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to body tissues. An occlusion of arteries disrupts oxygen and blood supply to tissues, leading to ischemia. Depending on the extent of ischemia, symptoms of arterial occlusion range from simple soreness and pain that can be relieved with rest, to a lack of sensation or paralysis that could require amputation.
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of arterial occlusion depend on several factors, including the location, extent, and onset of blockage. Normally, the blockage should affect approximately 70% of the artery for symptoms to become noticeable. Symptoms can be less severe during gradual narrowing, as this allows time for the widening of existing vessels and the formation of new ones (collateral vessels), allowing blood to still reach the area. Symptoms in this case will simply be in…
Types of arterial occlusion
Commonly observed types of arterial occlusion include thrombosis, atherosclerosis, and embolism.
An embolism involves the occlusion of blood vessels by an embolus. Arterial occlusion by an embolus is termed 'arterial embolism'. An embolus is an agent that blocks blood flow by physically obstructing blood vessels. This includes gas bubbles, fatty deposits, amniotic fluid, blo…
Diseases of arterial occlusion
The pathophysiology of diseases of arterial occlusion depends on the type of occlusion, the severity of blockage, and the location of the occluded artery. Common diseases of arterial occlusion include Coronary Artery Disease, Peripheral Artery Disease, and Pulmonary Embolism.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) results from the stenosis of coronary arteries by an atherosclerotic plaque. The coronary arteries perfuse the cardiomyocytes located within the myocardium. Cardio…
Complications
Diseases of arterial occlusion may progress into life-threatening conditions with improper prevention or management. Myocardial infarction, gangrene, and ischemic stroke are among the complications of severe arterial occlusion.
A myocardial infarction (MI), or heart attack, arises from complete occlusion of a coronary artery. The most frequent cause of MI is the rupturing of an atherosclerotic plaque formed in CAD. Plaq…
Diagnosis
There are several methods of diagnosing arterial occlusion, ranging from straightforward setups like exercise testing, to advanced scanning equipment such as ultrasonic duplex scanning or Multi-Detector Coronary Tomography (MDCT) angiography.
Exercise testing is a simplistic, non-invasive method of diagnosing intermittent claudication. Blood pressure measurements at the suspected area can be taken before and after exercise, as some …
Treatment
Treatment for arterial occlusion varies depending on the extent of blockage. In severe cases, surgical intervention is needed to remove the blockage from the affected artery. Currently, there are 3 types of surgical approaches, including surgical bypass, endarterectomy, and embolectomy. If surgery is not required, blood-thinning medication may be prescribed.
A surgical bypass is a procedure performed to treat CAD. This procedure involves bypassing the …