What is the pathophysiology of auto PEEP?
Auto-PEEP is commonly found in acute severe asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or patients receiving inverse ratio ventilation. Factors predisposing to auto-PEEP include a reduction in expiratory time by increasing the respiratory rate, tidal volume or inspiratory time.
What factors increase the risk of auto PEEP?
Factors predisposing to auto-PEEP include a reduction in expiratory time by increasing the respiratory rate, tidal volume or inspiratory time. Auto-PEEP predisposes the patient to increased work of breathing, barotrauma, hemodynamic instability and difficulty in triggering the ventilator.
What are the causes of auto-PEEP in COPD?
Dynamic hyperinflation with intrinsic expiratory flow obstruction is the most common cause of auto-PEEP in COPD patients in whom alveolar collapse during expiration leads to air trapping.
What is auto-PEEP and why is it dangerous?
Auto-PEEP can cause severe respiratory and hemodynamic compromise. The presence of auto-PEEP should be suspected when airflow at end-exhalation is not zero.

How do you stop auto-PEEP?
The increased work of breathing resulting from auto-PEEP can be decreased by therapeutic measures to reduce the level of auto-PEEP, including bronchodilator therapy, employment of a large bore endotracheal tube, decreasing the minute ventilation by controlling fever or pain, and minimizing the ratio of inspiratory time ...
Does Auto-PEEP cause hypotension?
Auto-PEEP increases the work of breathing, worsens gas exchange, and increases intra-thoracic pressures which can cause decreased cardiac output and hypotension.
Is Auto-PEEP air trapping?
AutoPEEP may also be referred to as air-trapping, breath stacking, dynamic hyperinflation, inadvertent PEEP, or occult PEEP. AutoPEEP is a common phenomenon in mechanically ventilated patients with long expiratory time constants, for example patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or acute severe asthma.
What patients are at greatest risk for auto PEEP?
Auto-PEEP is commonly found in acute severe asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or patients receiving inverse ratio ventilation. Factors predisposing to auto-PEEP include a reduction in expiratory time by increasing the respiratory rate, tidal volume or inspiratory time.
What can you do with auto PEEP?
When intrinsic PEEP is diagnosed, the patient should temporarily be released from mechanical ventilation to allow for full expiration. The ventilator can then be adjusted to shorten inspiration by decreasing the set tidal volume, increasing the inspiratory flow rate, or reducing the frequency of respirations.
How much auto PEEP is too much?
When used, it is recommended to maintain extrinsic PEEP below 75% to 85% of the auto-PEEP. Again, the use of extrinsic PEEP to treat auto-PEEP has to be driven by strong clinical sense as not all patients will benefit from it and others will be harmed.
What does auto PEEP look like?
0:003:13Auto-PEEP (Medical Definition) | Air Trapping, Breath Stacking, Intrinsic ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAuto peep is a complication of mechanical ventilation that occurs when a positive pressure remainsMoreAuto peep is a complication of mechanical ventilation that occurs when a positive pressure remains in the alveoli.
What happens if PEEP is too high?
Increasing PEEP to 10 and higher resulted in significant declines in cardiac output. A PEEP of 15 and higher resulted in significant declines in oxygen delivery.
What is auto PEEP?
Intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure (auto-PEEP) is a common occurrence in patients with acute respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation. Auto-PEEP can cause severe respiratory and hemodynamic compromise. The presence of auto-PEEP should be suspected when airflow at end-exhalation is not zero. In patients receiving controlled mechanical ventilation, auto-PEEP can be estimated measuring the rise in airway pressure during an end-expiratory occlusion maneuver. In patients who trigger the ventilator or who are not connected to a ventilator, auto-PEEP can be estimated by simultaneous recordings of airflow and airway and esophageal pressure, respectively. The best technique to accurately measure auto-PEEP in patients who actively recruit their expiratory muscle remains controversial. Strategies that may reduce auto-PEEP include reduction of minute ventilation, use of small tidal volumes and prolongation of the time available for exhalation. In patients in whom auto-PEEP is caused by expiratory flow limitation, the application of low-levels of external PEEP can reduce dyspnea, reduce work of breathing, improve patient-ventilator interaction and cardiac function, all without worsening hyperinflation. Neurally adjusted ventilatory assist, a novel strategy of ventilatory assist, may improve patient-ventilator interaction in patients with auto-PEEP.
Does auto-peep help with dyspnea?
In patients in whom auto-PEEP is caused by expiratory flow limitation, the application of low-levels of external PEEP can reduce dyspnea , reduce work of breathing, improve patient-ventilator interaction and cardiac function, all without worsening hyperinflation.
What is auto PEEP?
Intrinsic or auto-PEEP is a complication of mechanically ventilated patients. [8] Usually, passive exhalation will permit complete emptying of the air in the lungs until lung pressure equalized with atmospheric pressure, but in some cases the lungs may not completely deflate, leaving air trapped inside the lung at the end of exhalation which generates a positive pressure that remains in the lungs. This pressure is called auto or intrinsic PEEP. When this process repeatedly happens with each respiratory cycle, the amount of air trapping increases with each breath and consequently the intrathoracic pressure increases pathologically, compressing the RA and decreasing VR causing hypotension, as well as increasing plateau pressure (intra-alveolar pressure) and causing barotrauma. The increased air trapping also will make it harder for the patient to bring new air in, increasing the work of breathing, which increases oxygen consumption and CO2 production, thereby increasing the need for ventilation, increasing respiratory rate, and worsening auto-PEEP in a vicious cycle.
What is PEEP in medical terms?
Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is a value that can be set up in patients receiving invasive or non-invasive mechanical ventilation. This activity reviews the indications, contraindications, complications, and other key elements of the use of PEEP in the clinical setting as relates to the essential points needed by members of an interprofessional team managing the care of patients requiring assisted ventilation.
How does extrinsic PEEP affect oxygenation?
The application of extrinsic PEEP will, therefore, have a direct impact on oxygenation and an indirect impact on ventilation. By opening up airways, the alveolar surface increases, creating more areas for gas exchange and somewhat improving ventilation.
What causes mucus plugs to close?
Airway inflammation and mucus plugs generate dynamic airflow obstruction as a forced expiratory effort will increase the pressure around the airway leading to closure around the plugs or inflamed area and trapping air in the alveoli that are dependent on that airway.
How does CPAP work?
Continuous positive airway pressure therapy (CPAP), although not an interchangeable term, works by delivering a constant pressure, which at the time of exhalation works in the same way as PEEP.
What is the positive end-expiratory pressure?
Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is the positive pressure that will remain in the airways at the end of the respiratory cycle (end of exhalation) that is greater than the atmospheric pressure in mechanically ventilated patients. [1]
How to tell if air is trapped in a ventilator?
This can be easily checked by looking at the volume curve in the ventilator display. If this curve fails to go back to zero, then it is a sign that air is being trapped. [9]
What is intra-pulmonary EEP?
Intrinsic PEEP occurs when the expiratory time is shorter than the time needed to fully deflate the lungs, preventing the lung and chest wall from reaching an elastic equilibrium point
Why disconnect the ETT circuit?
Disconnect the circuit from the ETT to observe for a prolonged exhalation and audible wheeze. Resolved hypotension and decreased Pplat on reconnection suggests that dynamic hyperinflation causing high PEEPi was present
Does PEEPI increase with Pplat?
Plateau pressure (Pplat) will also tend to increase as PEEPi increases, but this could also occur due to decreased lung compliance so increased PEEPi cannot be assumed
How to reduce auto-peep?
The increased work of breathing resulting from auto-PEEP can be decreased by therapeutic measures to reduce the level of auto-PEEP, including bronchodilator therapy, employment of a large bore endotracheal tube, decreasing the minute ventilation by controlling fever or pain, and minimizing the ratio of inspiratory time to expiratory time by increasing the inspiratory flow rate or using nondistensable tubing in the ventilator circuit.
What is auto-peep in airflow limitation?
The auto-PEEP that occurs in patients with airflow limitation is a direct result of critical closure of the airways.
Why does end-expiratory lung volume exceed FRC?
Instead, end-expiratory lung volume may exceed predicted functional residual capacity (FRC), because the rate of lung emptying is slowed and expiration is interrupted by the next inspiratory effort before the patient has exhaled to the static relaxation volume.
What is the recoil pressure of the respiratory system?
At normal end-expiration, the static recoil pressure of the respiratory system is zero, whereas a positive value is observed in patients with dynamic hyperinflation. 24 This positive recoil pressure has been termed auto-PEEP (positive end-expiratory pressure) or intrinsic-PEEP.
Is PEEP registered on ventilator pressure manometer?
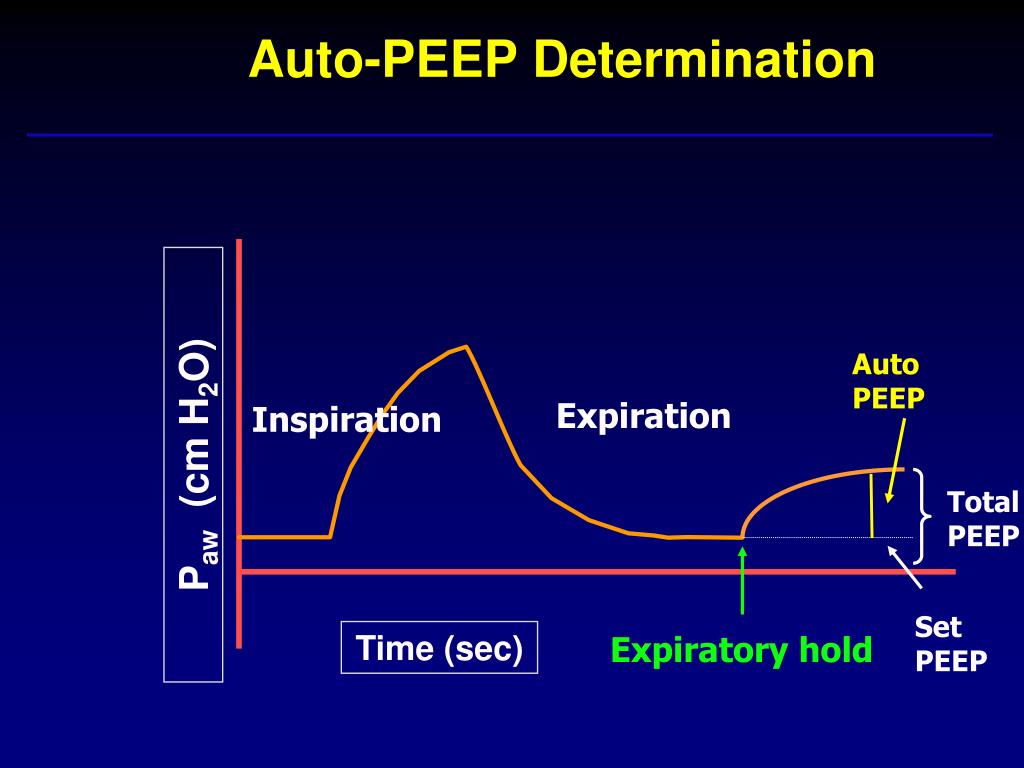
In patients receiving mechanical ventilation, it has been termed occult-PEEP, because, unlike externally applied PEEP, it is not registered on the ventilator pressure manometer, since the latter is open to atmosphere. If, however, the expiratory port of the ventilator circuit is occluded immediately before the onset of the next breath, the pressure in the lungs and ventilator circuit will equilibrate and the level of auto-PEEP will be displayed on the ventilator manometer.
Does hyperinflation decrease alveolar pressure?
In the presence of hyperinflation, however, to achieve a decrease in alveolar pressure below ambient pressure, a much greater decrease in pleural pressure is required; this greater decrease in pleural pressure is analogous to the further stretching of an already hyperextended spring.
Can external PEEP reduce breathing?
It has also been suggested that this increased work of breathing can be decreased by the application of external PEEP.
What is the difference between PEEPtot and PEEPe?
The difference between PEEPtot and PEEPe corresponds with the intrinsic PEEP (PEEPi), and is also known as AutoPEEP (1). AutoPEEP may also be referred to as a ir-trapping, breath stacking, dynamic hyperinflation, inadvertent PEEP, or occult PEEP.
Can autopeep affect mechanical ventilation?
AutoPEEP can potentially interfere with weaning from mechanical ventilation. Caregivers should monitor whether AutoPEEP is occurring during ventilation, and set their ventilation control parameters accordingly to avoid the negative consequences of AutoPEEP.