
What is the difference between basal cell and squamous cell?
• The shapes of basal cells vary from cubic to columnar while that of squamous cells is flat-shape. • Basal cells usually form the first single layer of cells, which lies on the basement membrane, whereas squamous cell are usually found on the basal cells.
How serious is a basal cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma is a very slow growing type of non-melanoma skin cancer. This type of skin cancer needs to be treated and has a high cure rate. If left untreated , basal cell carcinomas can become quite large, cause disfigurement, and in rare cases, spread to other parts of the body and cause death.
How dangerous is squamous cell skin cancers?
Untreated squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can destroy nearby healthy tissue, spread to the lymph nodes or other organs, and may be fatal, although this is uncommon. The risk of aggressive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin may be increased in cases where the cancer: Is particularly large or deep Involves the mucous membranes, such as the lips
What are the signs of basal cell carcinoma?
Warning Signs of Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Sore That Won’t Heal. Most people notice a problem when they have a sore that just won’t heal. ...
- Irritated Patch of Skin. In some instances, a small reddish patch of skin can be a warning sign of skin cancer. ...
- Shiny Nodule or Bump. You may suddenly notice that a small nodule or bump has appeared on your skin. ...
- Pink Colored Growth. ...
- Scar-Like Patch of Skin. ...
See more
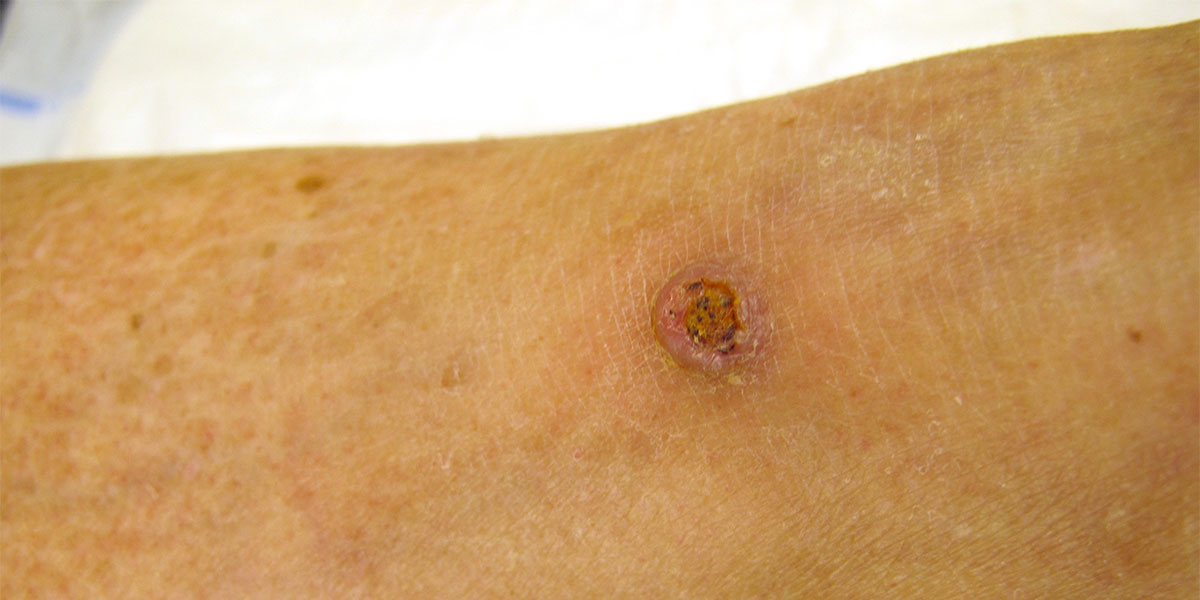
What is the most common cause of squamous cell carcinoma?
Most squamous cell carcinomas of the skin result from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from sunlight or from tanning beds or lamps.
Why is basal and squamous cancer so common?
Basal and squamous cell skin cancers are the most common types of skin cancer. They start in the top layer of skin (the epidermis), and are often related to sun exposure.
Who is most at risk for basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma?
Age over 50: Most BCCs appear in people over age 50. Fair skin: People with fair skin have an increased risk. Male gender: Men are more likely to develop BCC. Chronic infections and skin inflammation from burns, scars and other conditions.
How do you get basal cell skin cancer?
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or from a tanning bed are the main cause of basal cell carcinoma. When UV rays hit your skin, over time, they can damage the DNA in your skin cells. The DNA holds the code for the way these cells grow. Over time, damage to the DNA can cause cancer to form.
Why do I keep getting squamous cell carcinoma?
These factors increase your SCC risk: Unprotected exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Weakened immune system due to illness or certain immunosuppressive medications. History of skin cancer including basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
What are five risk factors for basal and squamous cell carcinoma?
Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Risk FactorsUltraviolet (UV) light exposure. ... Having light-colored skin. ... Being older. ... Being male. ... Exposure to certain chemicals. ... Radiation exposure. ... Previous skin cancer. ... Long-term or severe skin inflammation or injury.More items...•
What are the warning signs of basal cell carcinoma?
SymptomsA shiny, skin-colored bump that's translucent, meaning you can see a bit through the surface. ... A brown, black or blue lesion — or a lesion with dark spots — with a slightly raised, translucent border.A flat, scaly patch with a raised edge. ... A white, waxy, scar-like lesion without a clearly defined border.
Why do I keep getting basal cell?
Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight, as well as from man-made sources such as tanning beds.
How can you prevent squamous cell carcinoma?
The best way to prevent squamous cell skin cancer is to consistently shield your skin from sunlight — every day.apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with a minimum of 30 sun protection factor (SPF)reapply sunscreen every two hours if you're sweating or swimming.stay in the shade.wear protective hats and clothing.
What organs does squamous cell carcinoma affect?
If left untreated, squamous cell carcinoma can spread to nearby lymph nodes, bones or distant organs (such as the lungs or liver). Normal squamous tissue usually appears flat. When this tissue develops cancer it can appear as round masses that are can be flat, raised, or ulcerated.
What kills basal cell carcinoma?
Cryotherapy (cryosurgery) Cryotherapy is used most often for pre-cancerous conditions such as actinic keratosis and for small basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. For this treatment, the doctor applies liquid nitrogen to the tumor to freeze and kill the cells.
What are the chances of dying from squamous cell carcinoma?
Compared with skin BCCs, skin SCCs not only are more likely to metastasize but also to cause mortality. Although the case-fatality rate is only approximately 1%, the national NMSC mortality figures equal or exceed those for melanoma, which is far more lethal but less common.
Which is more serious squamous or basal cell?
Though not as common as basal cell (about one million new cases a year), squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread (metastasize). Treated early, the cure rate is over 90%, but metastases occur in 1%–5% of cases. After it has metastasized, it's very difficult to treat.
Can basal cell carcinoma turn into squamous cell?
One type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells, which make skin cells that continuously push older cells toward the surface. As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, where a skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma can occur.
Why do I have so many basal cell carcinomas?
Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight, as well as from man-made sources such as tanning beds.
What is the difference between basal cell and squamous cell cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma most commonly appears as a pearly white, dome-shaped papule with prominent telangiectatic surface vessels. Squamous cell carcinoma most commonly appears as a firm, smooth, or hyperkeratotic papule or plaque, often with central ulceration.
Where does basal cell cancer start?
These cancers start in the basal cell layer, which is the lower part of the epidermis. These cancers usually develop on sun-exposed areas, especially the face, head, and neck. They tend to grow slowly. It’s very rare for a basal cell cancer to spread to other parts of the body. But if it's left untreated, basal cell cancer can grow ...
Where does squamous cell carcinoma start?
These cancers start in the flat cells in the upper (outer) part of the epidermis. These cancers commonly appear on sun-exposed areas of the body such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands.
Where do skin cancers start?
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin , called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
What is the earliest form of squamous cell carcinoma?
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also called Bowen disease, is the earliest form of squamous cell skin cancer. “In situ” means that the cells of these cancers are still only in the epidermis (the upper layer of the skin) and have not invaded into deeper layers.
What are the different types of skin cancer?
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer: 1 Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper (outer) part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer (also called squamous cell carcinoma ). 2 Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skin’s surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas. 3 Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the body’s natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
What is the name of the cell that moves up the epidermis?
These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skin’s surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
What is a dome shaped tumor?
Keratoacanthomas are dome-shaped tumors that are found on sun-exposed skin. They may start out growing quickly, but their growth usually slows down. Many keratoacanthomas shrink or even go away on their own over time without any treatment. But some continue to grow, and a few may even spread to other parts of the body. They can be hard to tell apart from squamous cell skin cancer, and their growth is often hard to predict, so many skin cancer experts recommend treating them (typically with surgery).
Why is skin cancer risk higher for whites than for blacks?
This is because melanin helps protect against UV radiation. People with dark skin have more melanin. People with fair (light-colored) skin that freckles or burns easily are at extra high risk.
Is sunlight a cause of cancer?
Sunlight is the main source of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which can damage the genes in your skin cells. UV light is thought to be the major risk factor for most skin cancers. Tanning lamps and booths are another source of UV radiation. People with high levels of exposure to UV light are at greater risk for skin cancer.
Can scars cause cancer?
Scars from bad burns, areas of skin over bad bone infections, and skin damaged by certain skin diseases are more likely to develop skin cancer; but this risk is fairly small.
Can radiation cause skin cancer?
People who have had radiation treatment have a higher risk of getting skin cancer in the area that was treated. This can be a problem for children who have had cancer treatment.
Does arsenic cause cancer?
Exposure to large amounts of arsenic increases the risk of skin cancer. Arsenic is a heavy metal used to make some insecticides. It is also found in well water in some areas. Workers exposed to industrial tar, coal, paraffin, and certain types of oil may have an increased risk, too.
Can you get cancer from sun exposure?
Scientists have found that certain people are more likely than others to develop skin cancer after sun exposure. In these people, certain parts of the normal cells are more sensitive to being damaged by sunlight.
Where does basal cell carcinoma occur?
Studies reveal that 80% of skin cancers develop from basal cancer cells. The basal cell skin cancer generally develops on the neck and head while also being found anywhere on the skin. Furthermore, the disease is usually caused by the sun’s ultraviolet rays or develops in people who have taken radiation therapy many years ago. Basal cell carcinoma grows relatively slowly and hardly spreads to other parts of the body.
What causes skin cancer?
The mutations that occur in the skin cell DNA causes skin cancer. Such changes cause abnormal cells to multiply uncontrollably. When this occurs in squamous cells, it gives rise to squamous cell cancer. DNA mutations are generally caused by UV radiation found in the sun, tanning lamps, and beds.
What are the different types of skin cancer?
Primarily, there are four types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell cancer, and melanoma, but basal and squamous cell cancer are the most common types. Let’s find out more about these diseases.
How long does squamous cell carcinoma last?
Also, the condition may be fatal sometimes. If detected early, the five-year squamous cell carcinoma survival rate is 99%. Even if the cancer is spread to the nearby organs, the squamous cell carcinoma treatment can be done through a combination of surgery and radiation treatment.
What does it mean when you have a bump on your skin?
A change in the skin might be the first sign of the presence of basal cancer cells. The changes may include a bump or sore that won’t heal. The following can be a few symptoms of the disease:
Can tanning beds cause cancer?
Refrain the use of tanning beds: Many people generally don’t know tanning beds emit ultraviolet rays that cause cancer.
Does UV light cause cancer?
As we read, exposure to UV radiation increases the risk of cancer. Still, it is pretty shocking to know that less exposure to sunlight or tanning lamps also increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
What are the factors that increase the risk of basal cell carcinoma?
Factors that increase your risk of basal cell carcinoma include: Chronic sun exposure. A lot of time spent in the sun — or in commercial tanning beds — increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma. The threat is greater if you live in a sunny or high-altitude location, both of which expose you to more UV radiation.
Where does basal cell carcinoma develop?
Basal cell carcinoma usually develops on sun-exposed parts of your body, especially your head and neck. Less often, basal cell carcinoma can develop on parts of your body usually protected from the sun, such as the genitals.
What is a pink bump on the skin?
Basal cell carcinoma appears as a change in the skin, such as a growth or a sore that won't heal. These changes in the skin (lesions) usually have one of the following characteristics: A pearly white, skin-colored or pink bump that is translucent, meaning you can see a bit through the surface.
What is the name of the cancer that is most often found on the face?
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that most often develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun, such as the face. On brown and Black skin, basal cell carcinoma often looks like a bump that's brown or glossy black and has a rolled border.
What is the name of the cancer that occurs when a cell moves upward?
As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, where a skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma can occur. Melanoma, another type of skin cancer, arises in the pigment cells (melanocytes). Basal cell carcinoma occurs when one of the skin's basal cells develops a mutation in its DNA.
What is basal cell carcinoma?
Overview. Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that most often develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun. This photograph shows a basal cell carcinoma that affects the skin on the lower eyelid. Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer.
When does basal cell carcinoma become more common?
But it can also affect younger adults and is becoming more common in people in their 20s and 30s. A personal or family history of skin cancer.
Why do basal cells have mutations?
Most basal cell carcinomas are thought to be caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight and commercial tanning beds.
Where does basal cell carcinoma start?
Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells —a type of cell within the skin that produces new skin cells as old ones die off. Basal cell carcinoma often appears as a slightly transparent bump on the skin, though it can take other forms.
What is the treatment for basal cell carcinoma?
There are several basal cell carcinoma treatment options available to patients, including Mohs micrographic surgery, excisional surgery, electrosurgery, cryosurgery, and laser surgery. These treatments all have one thing in common: the word surgery.
What is the most common type of skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the two most common types of skin cancers. According to the American Cancer Society, over 5 million cases of basal cell and squamous cell cancers are diagnosed every year.
Where does squamous cell carcinoma occur?
Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the thin, flat squamous cells that make up the outer layer of the skin. Squamous cells are found all over the body, and this type of cancer can occur anywhere squamous cells are found. Though this form of skin cancer is not usually life-threatening, one major difference between basal cell and squamous cell cancers is that squamous cell cancer are more likely to grow deeper into the layers of your skin and spread to other parts of the body. While still relatively uncommon, it is considered an aggressive form of cancer, if left untreated.
Is basal cell cancer life threatening?
Though this form of skin cancer is not usually life-threatening, one major difference between basal cell and squamous cell cancers is that squamous cell cancer are more likely to grow deeper into the layers of your skin and spread to other parts of the body.
Is squamous cell carcinoma invasive?
Traditional treatment options—including Mohs—has involved invasive incisions that cut through healthy tissue, leading to a lengthy recovery and unsightly scarring. Sensus Healthcare is changing all that with a non-surgical treatment option— the SRT-100™.
Why is basal cell carcinoma increasing?
Rates of basal cell carcinoma have been increasing. Experts believe this is due to more sun exposure, longer lives, and better skin cancer detection methods. ( 4) This type of cancer begins in the skin’s basal cells, which are found in the outermost layer, the epidermis.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the basal cells?
The type of skin cancer you develop depends on the type of cell it started in. For example, if the cancer begins in the round basal cells below the skin’s surface, it’s known as basal cell skin cancer.
What are the most common types of skin cancer?
The three most common types of skin cancer are, in order from most to least: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma , and melanoma . While these make up most of the cases, there are other, rarer forms of cancer that can also affect the skin.
What is AK in skin?
Actinic Keratosis. Actinic keratosis (AK), also known as solar keratosis, is a precancerous lesion that can develop into squamous cell carcinoma. The condition is caused by excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun or indoor tanning. AK may look like a small, dry, scaly, or crusty patch of skin.
How many people die from basal cell carcinoma?
Though it’s rare, basal cell carcinoma can be life-threatening. Experts believe that about 2,000 people in the United States die each year from basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. (4) Some risk factors that increase your chances of having a basal cell carcinoma include: ( 7, 8)
Where does squamous cell carcinoma start?
This type of cancer starts in flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. It commonly crops up on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and hands. It can also develop on scars or chronic sores. Squamous cell carcinomas may develop from precancerous skin spots, known as actinic keratosis (AK).
What does a cancer look like?
These cancers might look like: (2,6) A firm, red bump. A flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface. A sore that heals and then reopens. People with lighter skin are more at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma, but the skin cancer can also affect those with darker skin. (2) Other risk factors include: ( 10)
What are the factors that increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma?
Factors that may increase your risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include: Fair skin. Anyone, regardless of skin color, can get squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. However, having less pigment (melanin) in your skin provides less protection from damaging UV radiation.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the basal cells?
One type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells, which make skin cells that continuously push older cells toward the surface. As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, where a skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma can occur. Melanoma, another type of skin cancer, ...
What is the risk of precancerous skin lesions?
Having a precancerous skin lesion, such as actinic keratosis or Bowen's disease, increases your risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
How to tell if you have squamous cell carcinoma?
Signs and symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin include: A firm, red nodule. A flat sore with a scaly crust. A new sore or raised area on an old scar or ulcer. A rough, scaly patch on your lip that may evolve to an open sore. A red sore or rough patch inside your mouth.
Where does squamous cell carcinoma occur?
But it can occur anywhere on your body, including inside your mouth, the bottoms of your feet and on your genitals.
What are the risks of a weakened immune system?
Weakened immune system. People with weakened immune systems have an increased risk of skin cancer. This includes people who have leukemia or lymphoma and those who take medications that suppress the immune system, such as those who have undergone organ transplants.
Where does skin cancer develop?
Where skin cancer develops. Skin cancer begins in the cells that make up the outer layer (epidermis) of your skin. One type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells, which make skin cells that continuously push older cells toward the surface. As new cells move upward, they become flattened squamous cells, ...

Overview
Symptoms
- Basal cell carcinoma usually develops on sun-exposed parts of your body, especially your head and neck. Less often, basal cell carcinoma can develop on parts of your body usually protected from the sun, such as the genitals. Basal cell carcinoma appears as a change in the skin, such as a growth or a sore that won't heal. These changes in the skin (lesions) usually have one of the fo…
Causes
- Basal cell carcinoma occurs when one of the skin's basal cells develops a mutation in its DNA. Basal cells are found at the bottom of the epidermis — the outermost layer of skin. Basal cells produce new skin cells. As new skin cells are produced, they push older cells toward the skin's surface, where the old cells die and are sloughed off. The proc...
Risk Factors
- Factors that increase your risk of basal cell carcinoma include: 1. Chronic sun exposure. A lot of time spent in the sun — or in commercial tanning beds — increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma. The threat is greater if you live in a sunny or high-altitude location, both of which expose you to more UVradiation. Severe sunburns also increase your risk. 2. Radiation therapy.R…
Complications
- Complications of basal cell carcinoma can include: 1. A risk of recurrence.Basal cell carcinomas commonly recur, even after successful treatment. 2. An increased risk of other types of skin cancer.A history of basal cell carcinoma may also increase the chance of developing other types of skin cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma. 3. Cancer that spreads beyond the skin.Very r…
Prevention
- To reduce your risk of basal cell carcinoma you can: 1. Avoid the sun during the middle of the day.In many places, the sun's rays are strongest between about 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Schedule outdoor activities for other times of the day, even during winter or when the sky is cloudy. 2. Wear sunscreen year-round.Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on clou…