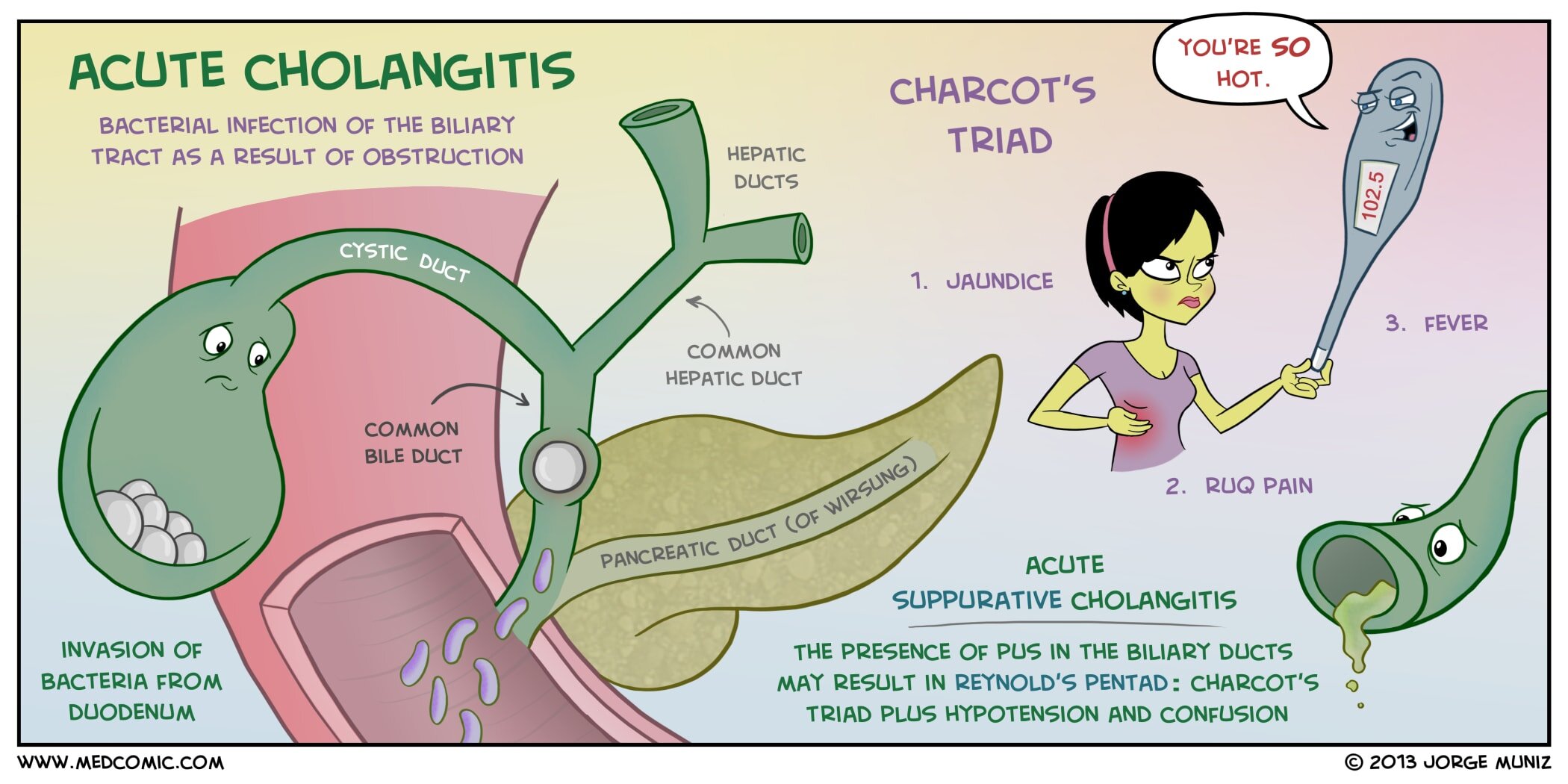
Cholangitis may also be caused when you have:
- A backflow of bacteria from your small intestine
- A blood infection (bacteremia)
- A test done to check your liver or gallbladder (such as a test where a thin tube or endoscope is put into your body)
What are the signs and symptoms of acute cholangitis?
The signs and symptoms of acute cholangitis are often similar to that of gallstones and can include:
- Back pain 5
- Chills
- Clay-colored stools
- Darkened urine
- Fever 5
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Nausea
- Pain below the shoulder blade
- Right upper quadrant or middle abdominal pain that is sharp, crampy or dull
- Vomiting 5
What are the causes of cholelithiasis?
The risk of developing cholelithiasis increases manifold if:
- Your age is above 40 years.
- You have a family history of cholelithiasis.
- You have undergone an organ transplant or bone marrow transplant.
- You are diabetic.
- You have cirrhosis of the liver.
- You have undergone bariatric surgery and have experienced excessive weight loss as a result of it.
How to treat primary sclerosing cholangitis?
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Diagnosis. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) uses a dye to highlight the bile ducts and pancreatic duct on X-ray images.
- Treatment. ...
- Clinical trials. ...
- Lifestyle and home remedies. ...
- Alternative medicine. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
What causes enlarged bile duct and how to treat it?
The following are some of the most common causes of biliary obstruction:
- gallstones, which are the most common cause
- inflammation of the bile ducts
- trauma
- a biliary stricture, which is an abnormal narrowing of the duct
- cysts
- parasites
- enlarged lymph nodes
- pancreatitis
- an injury related to gallbladder or liver surgery
- tumors that have reached the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, or bile ducts

How do you prevent cholangitis?
Can primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) be prevented?Quit smoking, stop drinking alcohol and stop using illegal drugs.Take all medicines as directed by your doctor.Eat a healthy, well balanced diet.Get regular exercise, such as walking.
What bacteria causes cholangitis?
Bacteria that commonly cause cholangitis are Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Enterococcus, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, and anaerobes. Although most infections are polymicrobial, this situation may not always prevail.
What happens when you have cholangitis?
But in primary biliary cholangitis, they mistakenly destroy the healthy cells lining the small bile ducts in the liver. Inflammation in the smallest ducts spreads and eventually damages other cells in the liver. As the cells die, they're replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis) that can lead to cirrhosis.
Can a virus cause cholangitis?
Viral cholangitis occurs in several distinct settings, including chronic viral hepatitis caused by hepatitis B and C, in association with systemic viral infection in immunocompromised patients and direct invasion by systemic viruses in neonates.
How do you get cholangitis?
What causes cholangitis? In most cases cholangitis is caused by a blocked duct somewhere in your bile duct system. The blockage is most commonly caused by gallstones or sludge impacting the bile ducts. Autoimmune disease such as primary sclerosing cholangitis may affect the system.
Can cholangitis be cured?
There's no cure for primary biliary cholangitis, but medications are available to help slow the progression of the disease and prevent complications.
Is cholangitis fatal?
Acute cholangitis is a potentially life-threatening systemic disease resulting from a combination of infection and obstruction of the biliary tree, secondary to different underlying etiologies. Common causes of cholangitis (eg, gallstones, benign and malignant biliary strictures) are well known.
Is cholangitis an emergency?
Conclusions. Cholangitis is a life-threatening infection that carries a high likelihood of poor outcomes if not treated early and aggressively in the emergency department.
Is cholangitis hereditary?
Inheritance. The inheritance pattern of primary sclerosing cholangitis is unknown because many genetic and environmental factors are likely to be involved. This condition tends to cluster in families, however, and having an affected family member is a risk factor for developing the disease.
What antibiotics are used to treat cholangitis?
The initial choice should be piperacillin-tazobactam, ticarcillin-clavulanate, ceftriaxone plus metronidazole or ampicillin-sulbactam. If the patient is sensitive to penicillin, ciprofloxacin plus metronidazole, carbapenems or gentamicin plus metronidazole are good choices[25].
Can cholangitis cause sepsis?
Sepsis from cholangitis can be particularly severe because there is no endothelial lining between the bile canaliculi and the capillary system in the liver. Elevated intraductal pressure leads to bacteremia and about 50% of the patients have positive blood cultures.
What part of the body itches with liver problems?
Symptoms of itching with liver disease Itching associated with liver disease tends to be worse in the late evening and during the night. Some people may itch in one area, such as a limb, the soles of their feet, or the palms of their hands, while others experience an all-over itch.
Which antibiotic is best for cholangitis?
The initial choice should be piperacillin-tazobactam, ticarcillin-clavulanate, ceftriaxone plus metronidazole or ampicillin-sulbactam. If the patient is sensitive to penicillin, ciprofloxacin plus metronidazole, carbapenems or gentamicin plus metronidazole are good choices[25].
Can cholangitis cause sepsis?
Sepsis from cholangitis can be particularly severe because there is no endothelial lining between the bile canaliculi and the capillary system in the liver. Elevated intraductal pressure leads to bacteremia and about 50% of the patients have positive blood cultures.
What triggers PSC?
An immune system reaction to an infection or toxin may trigger the disease in people who are genetically predisposed to it. A large proportion of people with primary sclerosing cholangitis also have inflammatory bowel disease, an umbrella term that includes ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
What is autoimmune Cholangiopathy?
Autoimmune cholangitis (AIC) or autoimmune cholangiopathy is a chronic inflammation of liver and a variant syndrome of autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). It is an “outlier” (findings that are inconsistent with the definite diagnosis of AIH) rather than an “overlap” (features of AIH and another liver disease) syndrome.
What is cholangitis in the liver?
Cholangitis is inflammation (swelling and redness) in the bile duct. The American Liver Foundation notes that cholangitis is a type of liver disease. It can also be broken down more specifically and known as the following: primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)
What are the symptoms of cholangitis?
vomiting. back pain. pain below the shoulder blades. dull pain or cramps in the upper right side. sharp or dull pain in the middle of the stomach. low blood pressure. confusion. yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice) Your doctor may find signs of cholangitis in other parts of the body.
Why is my bile duct hard?
Chronic cholangitis may be an autoimmune disease. This means that your body’s own immune system mistakenly attacks the bile ducts. This causes inflammation. Over time, inflammation can trigger scars or the growth of hard tissue inside the bile ducts. The scarring makes the ducts hard and narrow.
What side of the body does cholangitis hurt?
If you have chronic cholangitis for a long time, you may have: pain in the upper right side. night sweats. swollen feet and ankles. darkening of the skin ( hyperpigmentation) muscle pain. bone or joint pain. bloating (fluid in the stomach area) fat deposits ( xanthomas) in the skin around the eyes and eyelids.
Why do balloon dilations help cholangitis?
Balloon dilation may be used to open up the ducts and increase bile flow. This helps to improve and prevent symptoms. You may need endoscopic therapy several times to treat cholangitis. You may have full or local anesthesia (numbing) before the procedure.
How do you know if you have cholangitis?
Some early symptoms of chronic cholangitis may include: tiredness and fatigue. itchy skin. dry eyes.
How many types of cholangitis are there?
There are two main types of cholangitis:
What causes cholangitis in the bile duct?
Acute cholangitis occurs most commonly from bacterial infection of the bile ducts. For the development of acute cholangitis, there must be obstruction of biliary flow. Complete obstruction can lead to increased biliary pressure, which frequently leads to bacteremia.[5] The most common cause of biliary obstruction is caused by choledocholithiasis. Other causes include benign or malignant strictures of biliary ducts, pancreatic cancer, ampullary adenoma or cancer, porta hepatis tumor, parasites (Clonorchis sinensis, Fasciola hepatica), roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides), tapeworm (Taenia saginata),[6] biliary sludge deposits due to biliary stent obstruction, gallstone impaction in the neck of the gallbladder or the cystic duct leading to compression on common bile or common hepatic duct known as Mirizzi syndrome, peri-ampullary diverticulum of the duodenum leading to biliary obstruction known as Lemmel syndrome and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). [3]
What is ascending cholangitis?
Acute cholangitis, also known as ascending cholangitis, is a life-threatening condition that is caused by an ascending bacterial infection of the biliary tree. Delay in diagnosis and treatment can lead to septic shock. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of acute cholangitis and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in the care of patients with this condition.
What is the name of the condition that causes a biliary tree to swell?
Acute cholangitis, also known as ascending cholangitis, is a life-threatening condition caused by an ascending bacterial infection of the biliary tree.[1] Choledocholithiasis is the most common cause, with infection-causing stones in the common bile duct leading to partial or complete obstruction of the biliary system.[2] The diagnosis is made by clinical presentation, abnormal laboratory results, and imaging studies implying infection and biliary obstruction.[3]
What is the best imaging for ascending cholangitis?
The first-line imaging study of choice is abdominal ultrasonography. It is highly sensitive and specific in examing the gallbladder and investigating for biliary duct dilatation. A classic finding of ascending cholangitis is the thickening of the walls of the bile ducts, dilatation of biliary ducts, including the common bile duct, as well as evidence of cholelithiasis and pyogenic material. It can help differentiate intrahepatic versus extrahepatic obstruction. However, a normal abdominal sonogram does not necessarily rule out ascending cholangitis. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) can be performed as an adjunct to investigate co-existing pathologies such as hepatic/pancreatic tumors, metastasis, or hepatic abscess.[20] Dilated intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts, as well as inflammation of the biliary tree, can be appreciated. Another advantage is CT that can help to investigate differential diagnoses, including diverticulitis and pyelonephritis. One major disadvantage is that CT has poor sensitivity for the diagnosis of choledocholithiasis.
What causes bile duct stones?
Primary bile duct stones are thought to be caused by the biliary infection itself, with both processes leading to ascending infection throughout the biliary system. [12][13][10]
What is the most sensitive modalities for detecting common bile duct stones?
The most sensitive modalities for detecting common bile duct stones are magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). MRCP is a noninvasive imaging study that can detect the cause and the level of biliary obstruction, including choledocholithiasis, strictures, and biliary dilatations. [16][20] ERCP is essential to both diagnosis and treatment as it detects the site of obstruction and helps in drainage of the biliary tree and for retrieval of biopsy and culture specimens from the biliary system. ERCP should be used in patients with high clinical suspicion and those that will benefit from therapeutic intervention. [21]
How common is cholelithiasis?
Cholangitis is relatively uncommon. On average, in the United States, there are less than 200,000 cases of acute cholangitis annually. The average age of individuals affected is 50 to 60 years old. Males and females are affected equally.[3] In hospitalized patients with gallstone disease, 6% to 9% are diagnosed with acute cholangitis in the United States.[6] The prevalence of cholelithiasis varies among different ethnicities. It is more prevalent in Native Americans and Hispanics, less so among Whites, and is far less common in Asians and African Americans.[9] In addition, Asian populations and countries with intestinal parasites and individuals with sickle cell disease are at increased risk.
What is acute cholangitis?
Severe acute cholangitis is acute cholangitis associated with at least one of cardiovascular, neurological, respiratory, renal, hepatic and/or haematological dysfunction. 10-20% of patients also present with the additional features of hypotension due to septic shock and mental confusion - the Reynolds' pentad.
What is the cause of cholecystitis?
Acute cholecystitis is an acute inflammatory disease of the gallbladder, often caused by gallstones; however, many factors (eg, ischaemia, motility disorders, chemical injury, infections by micro-organism, protozoon and parasites, collagen disease and allergic reactions) are also involved. The term hepatic fever was used for ...
What is the name of the syndrome that causes fever, jaundice, and abdominal pain?
Acute obstructive cholangitis was defined by Reynolds and Dargan in 1959 as a syndrome consisting of lethargy or mental confusion and shock, as well as fever, jaundice, and abdominal pain caused by biliary obstruction. These five symptoms were then called Reynolds' pentad.
How many people develop cholangitis after ERCP?
Approximately 1% of patients develop cholangitis after ERCP.
When should a sample of bile fluid be sent for culture?
If bile fluid is available (eg, biliary drainage through intervention has occurred), a sample should be sent for culture.
Can a history of gallstones be a diagnosis?
A history of gallstones, CBD stones, recent cholecystectomy, ERCP or other invasive procedures, HIV or AIDS may assist the diagnosis. Some patients present with several attacks, usually in association with untreated biliary stones (recurrent pyogenic cholangitis).
Can cholangitis be caused by liver fluke?
More than one organism may be involved. Outside the UK, cholangitis can be caused by roundworm and liver fluke. NB: primary sclerosing cholangitis is an aetiologically unrelated idiopathic condition which is dealt with in a separate article.
What is cholangitis caused by?
In most cases, cholangitis is caused by a bacterial infection.
Who is at risk for cholangitis?
If you have had gallstones, you are at greater risk for cholangitis. Other risk factors include:
How is cholangitis diagnosed?
The pain from cholangitis can feel a lot like the pain from gallstones.
What causes cholanitis in the liver?
Cholangitis may also be caused when you have: A backflow of bacteria from your small intestine. A blood infection (bacteremia) A test done to check your liver or gallbladder (such as a test where a thin tube or endoscope is put into your body) The infection causes pressure to build up in your bile duct system.
Why is my bile duct blocked?
The blockage may be from: Cholangitis may also be caused when you have: A test done to check your liver or gallbladder (such as a test where a thin tube or endoscope is put into your body) The infection causes pressure to build up in your bile duct system.
How to drain bile ducts?
To drain your bile duct using ERCP, a long, thin, flexible tube (endoscope) is put in your mouth. The scope goes down your food pipe (esophagus) and into your stomach. It passes into the first part of your small intestine (the duodenum) and into the bile ducts.
How long do you stay in the hospital for cholangitis?
If you have cholangitis, you will likely be in the hospital for a few days. You will be given fluids by IV (intravenous) line through a vein. You will also have pain medicine and bacteria-fighting medicine (antibiotics).
What is cholangitis caused by?
Acute cholangitis is bacterial infection of the extra-hepatic biliary system. As it is caused by gallstones blocking the common bile duct in most of the cases, its prevalence is greater in ethnicities with high prevalence of gallstones. Biliary obstruction of any cause is the main predisposing factor. Diagnosis is established by the presence of clinical features, laboratory results and imaging studies. The treatment modalities include administration of intravenous fluid, antibiotics, and drainage of the bile duct. The outcome is good if the treatment is started early, otherwise it could be grave.
What are the most common pathogens in cholangitis?
The most frequently found pathogens isolated in acute cholangitis are coliform organisms[12,13]. These include Escherechia coli(25%-50%), Klebsiella species(15%-20%), Enterococcusspecies (10%-20%) and Enterobacterspecies (5%-10%). Sometimes, anaerobic bacteria like Bacteroids fragilis and Clostridium perfringens can also cause acute cholangitis, particularly in patients with previous biliary surgery and in the elderly population[14]. Parasitic infestation of the biliary system by the liver flukes Clonorchis sinensis, Opisthorchis viverriniand Opisthorchis felineusand the roundworm Ascaris lumbricoidesmay lead to cholangitis[15].
What causes biliary obstruction?
Other causes of obstruction include benign or malignant stricture of the bile duct or hepatic ducts, pancreatic cancer, ampullary adenoma or cancer, porta hepatis tumor or metastasis, biliary stent obstruction (due to microbial biofilm formation, biliary sludge deposition and duodenal reflux of food content), primary sclerosing cholangitis, amyloid deposition in the biliary system[3], Mirizzi syndrome (gallstone impacted in cystic duct or neck of the gall bladder causing compression on common bile duct or common hepatic duct), Lemmel’s syndrome (peri-ampullary diverticulum causing distal biliary obstruction), round worm (Ascaris lumbricoides) or tapeworm (Taenia saginata) infestation of the bile duct[4], acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (commonly known as AIDS) cholangiopathy and strictured bilioenteric anastomoses[5]. Choledochocele and narrow-caliber bile duct are other risk factors for acute cholangitis. Recently, there was an outbreak of cholangitis due to carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae(CRE) as a result of exposure to contaminated duodenoscope[6]. Post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) acute cholangitis can occur in 0.5% to 2.4% cases (Figure (Figure11)[7]. As cholelithiasis is the most important risk factor, the same risk factors may play important roles in the development of acute cholangitis, particularly high fat (triglyceride) intake, sedentary life styles, obesity and rapid weight loss. Heavy alcohol consumption may lead to cirrhosis of the liver, which is a risk factor for gallstone formation.
Why is biliary obstruction important?
Biliary obstruction is an important factor in the pathogenesis of cholangitis. When bile flow occurs, presence of bacteria in the bile is not that significant because bacterial concentration does not increase and the intraductal pressure does not increase. Normally, there are different defensive mechanisms to prevent cholangitis. The bile salts have bacteriostatic activity and the biliary epithelium secretes IgA and mucous which probably act as anti-adherent factors. Kupffer cells on the biliary epithelium and the tight junction between the cholangiocytes prevent translocation of bacteria from the hepatobiliary system into the portal venous system. Normal bile flow flushes out any bacteria into the duodenum.
What is grade 2 cholangitis?
Grade II is moderate acute cholangitis. Patients do not have any organ dysfunction and do not respond to the initial antibiotic treatment. Any two of the five conditions should be present: (1) leukocytosis (WBC > 12000/cmm) or leukopenia (WBC < 4000/cmm); (2) high temperature (≥ 39 °C); (3) elderly (age > 75 years); (4) hyperbilirubinemia (total bilirubin ≥ 5 mg/dL); and (5) hypoalbuminemia (< 0.7 × lower limit of normal).
What are the two clinical factors that determine the severity of acute cholangitis?
Severity of acute cholangitis: two clinical factors determine the severity of acute cholangitis: (1) response to initial medical treatment; and (2) organ dysfunction[1].
Is cholangitis a serious medical condition?
Core tip:Acute cholangitis is a serious medical problem unless treated early. High clinical suspicion is essential to diagnose this condition. The different diagnostic criteria, treatment options, including different modalities of biliary drainage, and prognosis are described in this article.
What cells are involved in biliary cholangitis?
The liver inflammation seen in primary biliary cholangitis starts when certain types of white blood cells called T cells (T lymphocytes) start to collect in the liver. Normally, these immune cells detect and help defend against germs, such as bacteria and viruses.
How long does it take for biliary cholangitis to develop?
The disease may be diagnosed when blood tests are done for other reasons, such as routine testing. Symptoms eventually develop over the next 5 to 20 years.
What happens when biliary cholangitis is destroyed?
Inflammation in the smallest ducts spreads and eventually damages other cells in the liver. As the cells die, they're replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis) that can lead to cirrhosis.
What happens when bile ducts are damaged?
When bile ducts become damaged, bile can back up into the liver, causing damage to liver cells. This damage can lead to liver failure. Primary biliary cholangitis, previously called primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic disease in which the bile ducts in your liver are slowly destroyed. Bile is a fluid made in your liver.
Why does my abdomen have fluid?
Buildup of fluid in the abdomen due to liver failure (ascites)
Can biliary cholangitis be treated?
At this time, there's no cure for primary biliary cholangitis, but medication can slow liver damage, especially if treatment begins early.
Why is my spleen swollen?
Your spleen can become swollen with white blood cells and platelets because your body no longer filters toxins out of the bloodstream as it should.
How do doctors diagnose biliary cholangitis?
How do doctors diagnose primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)? To diagnose PBC, a doctor will ask about your medical and family history, do a physical exam, order blood tests and other medical tests. Doctors use a blood test to look for a specific substance in the blood called anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA).
What is the name of the disease that affects the liver?
Primary biliary cholangitis (P BC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a disease that harms the liver’s ability to function. It is chronic, which means it lasts for a long time or regularly comes back. In people with PBC, the bile ducts become injured, then inflamed, and eventually permanently damaged.
Why do doctors believe PBC is caused by the immune system?
In PBC, doctors believe the immune system damages the bile ducts.
What causes PBC in family?
In addition, infections, smoking and exposure to certain chemicals may play a role in triggering PBC. PBC also tends to occur more commonly among family members. If one member of a family has PBC, the other family members are at an increased risk. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
How to treat PBC?
Because doctors do not know the cause of PBC, it cannot be prevented. However, you can take steps to lessen liver damage, including: 1 Quit smoking, stop drinking alcohol and stop using illegal drugs 2 Take all medicines as directed by your doctor. 3 Eat a healthy, well balanced diet. 4 Get regular exercise, such as walking.
Can PBC cause autoimmune disease?
While there is not a known cause, some people with PBC also have other related autoimmune diseases. These conditions include autoimmune hepatitis, thyroid diseases, scleroderma, Raynaud’s diseases, Sjogren’s syndrome and celiac disease. Frequent urinary tract infections are also often seen in patients with PBC.
Can cirrhosis cause liver failure?
Cirrhosis makes it hard for the liver to function properly. PBC is progressive, meaning it gets worse over time. If it is not treated, cir rhosis can cause liver failure and even death. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.