Pioneering research was conducted on demand characteristics by Martin Orne
Martin Theodore Orne
Martin Theodore Orne was a professor of psychiatry and psychology at the University of Pennsylvania. Orne is best known for his pioneering research into demand characteristics, illustrating the weakness of informing participants that they are taking part in a psychology experim…
What is a demand characteristics in psychology?
In a psychological experiment, a demand characteristic is a subtle cue that makes participants aware of what the experimenter expects to find or how participants are expected to behave. Demand characteristics can change the outcome of an experiment because participants will often alter their behavior to conform to expectations. 1
What is the problem with demand characteristics in research?
These cues can lead participants to change their behaviors or responses based on what they think the research is about. Demand characteristics are problematic because they can bias your research findings. They commonly occur in psychology experiments and social sciences studies because these involve human participants.
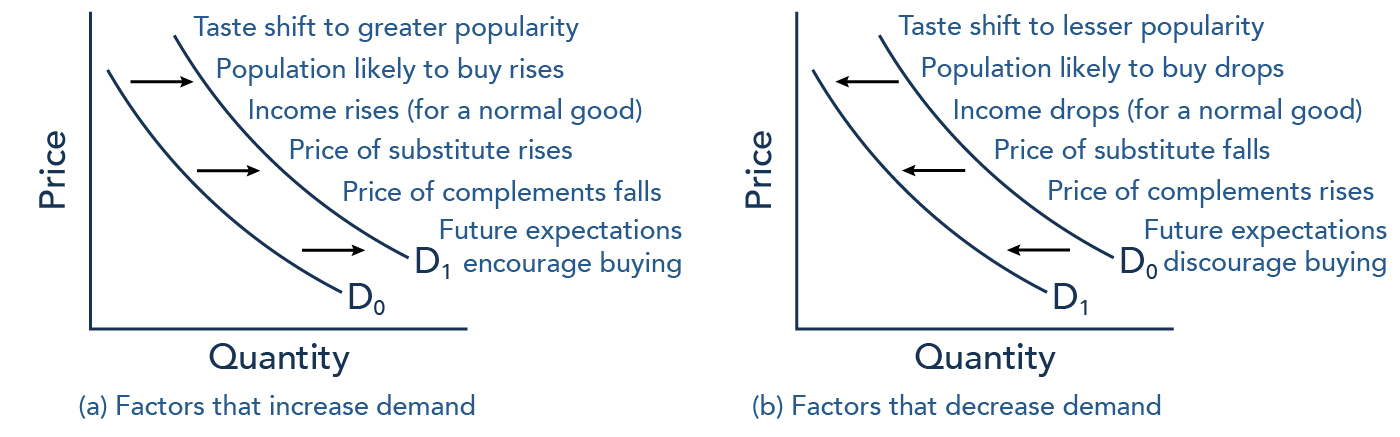
What are the factors that change demand?
Other things that change demand include tastes and preferences, the composition or size of the population, the prices of related goods, and even expectations. A change in any one of the underlying factors that determine what quantity people are willing to buy at a given price will cause a shift in demand.
How does the price of a good affect its demand?
While it is clear that the price of a good affects the quantity demanded, it is also true that expectations about the future price—or expectations about tastes and preferences, income, and so on—can affect demand. For example, if people hear that a hurricane is coming, they may rush to the store to buy flashlight batteries and bottled water.

How do you avoid demand characteristics?
You can control demand characteristics by taking a few precautions in your research design and materials. Use these measures: Deception: Hide the purpose of the study from participants. Between-groups design: Give each participant only one independent variable treatment.
What are demand characteristics in social psychology?
Demand Characteristics Definition Demand characteristics are any aspect of an experiment that may reveal the hypothesis being tested or that may cue participants as to what behaviors are expected.
What are demand characteristics in marketing?
A demand characteristic is used to describe specific cues in experimental research that may inadvertently influence a participant's response or behavior in an experiment.
What is a demand characteristic example?
Examples of common demand characteristics Common demand characteristics include: Rumors of the study – any information, true or false, circulated about the experiment outside of the experiment itself. Setting of the laboratory – the location where the experiment is being performed, if it is significant.
What are the four characteristics of demand?
Terms in this set (19)What are the characteristics of demand? ... Combination of desire, ability, and willingness. ... A change in price causes a change in the quantity demanded. ... Quantity demanded at each and every possible price that might prevail in the market at a given time.More items...
How can we control for demand characteristics quizlet?
How do blind/double procedures control for demand characteristics?...Ask participants not to tell others about the study.Complete study quickly.Use participants from different locations.
What are demand characteristics in psychology quizlet?
What is a demand characteristics? It is when a participant in a study forms an interpretation of the purpose of an experiment and subconsciously changes their behavior to fit that behavior.
What is demand characteristics and what techniques do psychologists use to this problem?
Demand characteristics are aspects of experiments that may give away the research purpose to participants. Social desirability bias is when participants automatically try to respond in ways that make them seem likeable in a study, even if it means misrepresenting how they truly feel.
What is the difference between social desirability and demand characteristics?
The second major difference is that social desirability bias is generally associated specifically w/ responses to questionnaires, whereas demand characteristics can reflect any aspect of the behavior involved in an experiment.
How does demand characteristics affect validity?
Demand characteristics are a issue, as the participants may behave in a way to support the hypothesis, making the results less valid. Conversely, the participant may deliberately try to disrupt the results, a phenomenon known as the 'screw-you' effect.
What are demand characteristics?
In research, demand characteristics are cues that might indicate the aim of a study to participants. These cues can lead to participants changing...
Why do demand characteristics matter in research?
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that can affect the outcomes of the study. They can invalidate studies by providing an...
How do I prevent demand characteristics?
You can control demand characteristics by taking a few precautions in your research design and materials. Use these measures: Deception: Hide...
What’s the difference between demand characteristics and social desirability bias?
Demand characteristics are aspects of experiments that may give away the research purpose to participants. Social desirability bias is when part...
What are the types of extraneous variables?
There are 4 main types of extraneous variables : Demand characteristics : environmental cues that encourage participants to conform to researchers...
What is demand characteristic?
In a psychological experiment, a demand characteristic is a subtle cue that makes participants aware of what the experimenter expects to find or how participants are expected to behave. Demand characteristics can change the outcome of an experiment because participants will often alter their behavior to conform to expectations. 1 .
What was the purpose of Asch's conformity experiment?
In Asch's conformity experiment, participants were told that they were taking part in a vision experiment. In reality, the researchers were interested in the role that social pressure plays in conformity. By disguising the true intentions of the experiment, researchers are able to minimize the possibility of demand characteristics. 3
What did the researchers examine in one classic experiment published in the journal Psychosomatic Medicine?
In one classic experiment published in the journal Psychosomatic Medicine, researchers examined whether demand characteristics and expectations could influence menstrual cycle symptoms reported by study participants. 2
What influenced the reporting of symptoms?
The researchers concluded that the reporting of symptoms was influenced by the demand characteristics as well as social expectations . In other words, people who thought that the researchers wanted to hear about some of the stereotypical symptoms of PMS and menstrual issues were more likely to say that they had experienced such negative symptoms while having their periods. 2
What is the most common approach to minimize the impact of demand characteristics?
Researchers typically rely on a number of different strategies to minimize the impact of demand characteristics. Deception is a very common approach. This involves telling participants that the study is looking at one thing when it is really looking at something else altogether.
Why do researchers do double blind studies?
In other cases, researchers will minimize the contact that they have with study subjects. A double-blind study is a method used in which neither the participants nor the researchers interacting with them are aware of the condition to which the participants have been assigned. Having people who are not aware of the experimenter's hypothesis collect the data from participants helps reduce the chances that the subjects will guess what the study is about. 4
Does Verywell Mind use peer reviewed sources?
Verywell Mind uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
What does the presence of demand characteristics in a study suggest?
Presence of demand characteristics in a study suggest that there is a high risk that participants will change their natural behaviour in line with their interpretation of the aims of a stud y, in turn affecting how they respond in any tasks they are set.
Why is repeated measures study design more likely to present the problem of demand characteristics?
A repeated measures study design is more likely to present the problem of demand characteristics, as participants will be take part in all conditions of the experiment, which could give them enough information to consider the ‘real’ purpose of the study.
What is bias in behavior?
This bias in participants’ behaviour occurs when they note aspects of the study that have to do with particular social norms or expectations, and in turn present themselves in what they deem a socially acceptable fashion.
What are demand characteristics?
The most common definition of demand characteristics out there goes something like, “demand characteristics are when participants are aware of the aim of the research and change their behaviour in a way to fit what the researcher expects.” I see this in so many textbooks.
What is the meaning of "whose work demand characteristics originated"?
For a more complex version, you can refer to Orne’s definition, in whose work demand characteristics originated ( source ): “the totality of cues and mutual expectations which inhere in a social context…which serve to influence the behaviour and/or self-reported experience of the research receiver” (Orne, 2000).
Law of demand
The law of demand establishes a negative relationship between the magnitude of the demand for a good and the price it receives in the market. Thus, the more a good or service costs, the lower its demand will tend to be; and for the same reasons as a good or service is in high demand, its price will tend to rise.
Types of demand
Market demand represents the amount of goods that the market can consume.
Elasticity of demand
Demand is elastic, that is, it is not continuous and uniform but changes over time . Thus, we can speak of an elastic and an inelastic demand, according to the calculation expressed in absolute terms of the specific formula of elasticity: Ƞ p = Δ% Q D ÷ Δ% P, where Q D is the quantity demanded and P the price of the product.
Variations in demand
The demand may vary according to its internal laws and external conditions, according to two different models of variation:
Claimants and bidders
The economic exchange occurs when the applicant agrees with the offeror.
Demand curve
Historical trends in demand can and are usually represented by graphs, especially curves that allow the visualization of the upward or downward trend in consumption and therefore in demand for a given good or sector.
Lawsuit in law
In legal matters, the term “demand” has another meaning: any act of initiation of proceedings , that is, the first real step in the sense of a legal dispute.
What is complementary good?
A complement refers to a complementary good or service used in conjunction with another good or service. Usually, the complementary good has little to no value when consumed alone, but when combined with another good or service, it adds to the overall value of the offering. An increase in the price of complementary goods leads to a decrease in the demand for given commodity and vice-versa. For example, if the price of a complementary good like condensed milk increases, then demand for given commodities as coffee will slightly fall as it will be relatively costlier to use both the goods together. So, demand for a given commodity is inversely affected by change in price of complementary goods.
How does income affect demand?
The demand for goods and services also depends on the incomes of the people. The greater the incomes, the greater their demand will be. However, the effect of change in income on demand depends on the nature of the commodity under consideration. If a specific good is a normal good, then an increase in income leads to rise in its demand, while a decrease in income reduces the demand. But if the given commodity is an inferior good, an increase in income will then reduce the demand, and a decrease in income leads to rise in demand.
What factors influence the demand for goods?
Another factor which influences the demand for goods is consumers’ expectations with regard to future prices of the goods.If the price of a certain commodity is expected to increase in near future, the consumer will buy more of that commodity than what they normally buy. In that situation, they won't have to pay a higher price in the future. If the price of petrol is expected to rise in the next few days, people will rush for fuel. Similarly, when the consumers expect that in the future the prices of goods will fall, then in the present they will postpone a part of the consumption of goods with the result that their present demand for goods will decrease.
What is demand curve?
The demand curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded for a given period of time. The demand curve will move downward from the left to the right, which expresses the law of demand: As the price of a given commodity increases, the quantity demanded decreases (all else being equal). When the price of commodities decreases, the quantity demanded will then increase.
How does the market affect demand for a good?
The market’s demand for a good is influenced by adding up the individual demands of the present as well as prospective consumers of a good at various possible prices. The greater the number of consumers of a good, the greater the market demand for it. The increase in consumers can happen when more and more favored substitute goods than a specific commodity. Then the number of substitute’s buyers will rise. When the seller expands to a new market to distribute goods, or when there is a growth in the population, the demand for a specific good can also escalate.
What is demand in economics?
In economics, demand is a fundamental concept that refers to a consumer's desire to purchase goods and services and willingness to pay a price for them. Demand, along with supply, determines the actual prices of goods and the volume of goods that changes hands in a market.
What is a substitute in economics?
A substitute, or substitute good in economics is a product or service a consumer sees as the same or similar to another product. An increase in the price of substitute will lead to an increase in the demand for given commodity and vice-versa. For example, if the price of a substitute good like tea increases, the demand for a commodity such as coffee will rise as coffee will become relatively cheaper than tea. So, demand for a given commodity is directly affected by change in price of substitute goods.
How does price affect demand?
If people learn that the price of a good like coffee is likely to rise in the future, they may head for the store to stock up on coffee now. These changes in demand are shown as shifts in the curve. Therefore, a shift in demand happens when a change in some economic factor other than price causes a different quantity to be demanded at every price.
What is demand curve?
A demand curve or a supply curve is a relationship between two, and only two, variables: quantity on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis. The assumption behind a demand curve or a supply curve is that no relevant economic factors, other than the product’s price, are changing. Economists call this assumption ceteris paribus, a Latin phrase meaning “other things being equal”. If all else is not held equal, then the laws of supply and demand will not necessarily hold. The rest of this article explores what happens when other factors aren't held constant.
Why is the quantity demanded increased?
For example, in recent years as the price of tablet computers has fallen, the quantity demanded has increased because of the law of demand. Since people are purchasing tablets, there has been a decrease in demand for laptops, which can be shown graphically as a leftward shift in the demand curve for laptops. A higher price for a substitute good has the reverse effect.
Why does demand curve shift?
Demand curves can shift. Changes in factors like average income and preferences can cause an entire demand curve to shift right or left. This causes a higher or lower quantity to be demanded at a given price.
What would happen if the demand curve was to the left?
A decrease in incomes would have the opposite effect, causing the demand curve to shift to the left, toward . People have less money on average, so they are less likely to buy a car at a given price, decreasing the quantity demanded.
What does "other things being equal" mean?
Economists call this assumption ceteris paribus, a Latin phrase meaning “other things being equal”. If all else is not held equal, then the laws of supply and demand will not necessarily hold. The rest of this article explores what happens when other factors aren't held constant.
What are the factors that shift demand curves?
Other things that change demand include tastes and preferences, the composition or size of the population, the prices of related goods, and even expectations.
