...
Hearing Loss in Adults
- Loud noises.
- Heredity.
- Head injury.
- Infection.
- Illness.
- Certain prescription drugs.
- Circulatory problems such as high blood pressure.
Common Causes
List of symptoms, according to expert
- Needing things repeated
- Thinking people are not speaking clearly or are mumbling
- Difficulty during phone conversations
- Unable to keep up when watching TV
- Becoming quiet in social situations
- Feeling drained and exhausted after conversing with other people
Related Conditions
Top 3 Herbs for hearing loss
- Echinacea. Also known as “coneflowers,” echinacea is a flower commonly found growing in North America. ...
- Ginger. This common ingredient in a lot of Eastern dishes has a hidden restorative property. ...
- Turmeric. Another supposed “superfood,” turmeric is also commonly used in the Eastern hemisphere for its medicinal values.
What are signs of losing hearing?
The NIA notes that hearing loss can be treated successfully through:
- Wearing hearing aids
- Using assistive-listening devices
- Undergoing surgery to implant a small electronic device near the ear
How to treat hearing loss naturally?
Most of us will lose some of our ability to hear as we age. But hearing loss may pose a previously overlooked risk, according to recently published research. Three separate studies found that older adults with hearing loss may be “more sedentary and more ...
How do you fix hearing loss?
Can you fix hearing loss?
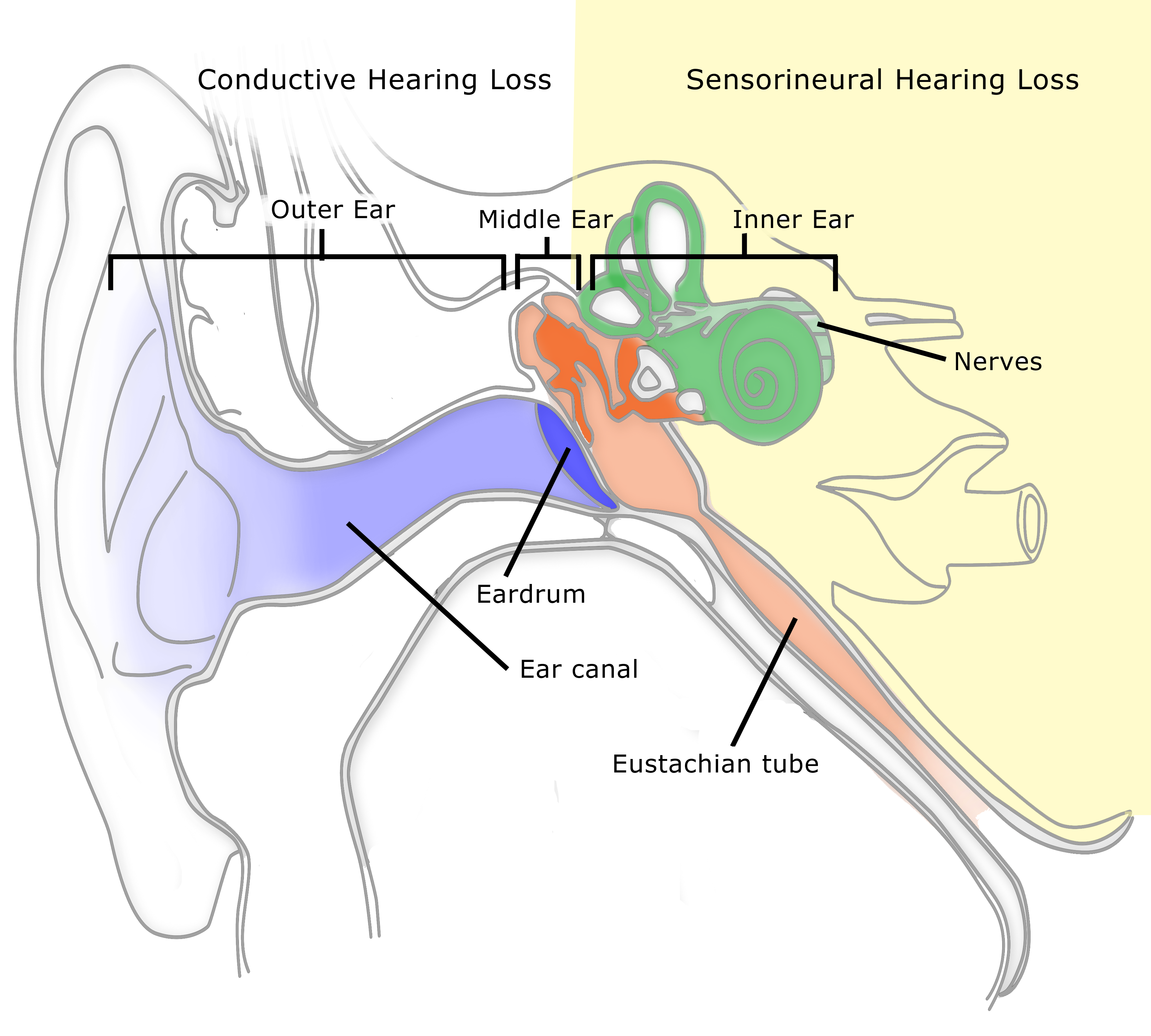
What are the 4 types of hearing loss?
The Four Types of Hearing LossSensorineural Hearing Loss.Conductive Hearing Loss.Mixed Hearing Loss.Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder.Talk to Your Audiologist.
What causes unequal hearing loss?
The causes of asymmetrical hearing loss are normally the same as for hearing loss in general such as ageing (age-related hearing loss), noise (noise-induced hearing loss), genetic causes (genetic hearing loss), drugs and injuries to the head or the ear.
What are the main causes of hearing loss?
Causes of hearing loss include:Damage to the inner ear. ... Gradual buildup of earwax. ... Ear infection and abnormal bone growths or tumors. ... Ruptured eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation).
What are the five classification of hearing loss?
Degree of hearing loss. Hearing loss can be classified according to the severity or degree of the disease. Hearing losses between 26 and 40 dB are considered mild, 41 and 55 dB moderate, 56 and 70 dB moderately severe, 71 and 90 dB severe, and greater than 91 dB profound (Table 1) [5, 6].
Is it normal to have different hearing in each ear?
Yes, for many people, the left and right ears handle sound a little differently. If you have hearing loss, one ear probably has more than the other—but even more than that, since birth, your ears have been partial to different sounds. Scientists have discovered that the left and right ears process sound differently.
Why is hearing different in each ear?
Earwax. Cerumen impaction, or compressed earwax, can also lead to differing levels of hearing loss in each ear. Earwax build up that affects hearing, causes pain and must be treated by a physician is pretty common—it affects six percent of the U.S. population.
What are 3 types of hearing loss?
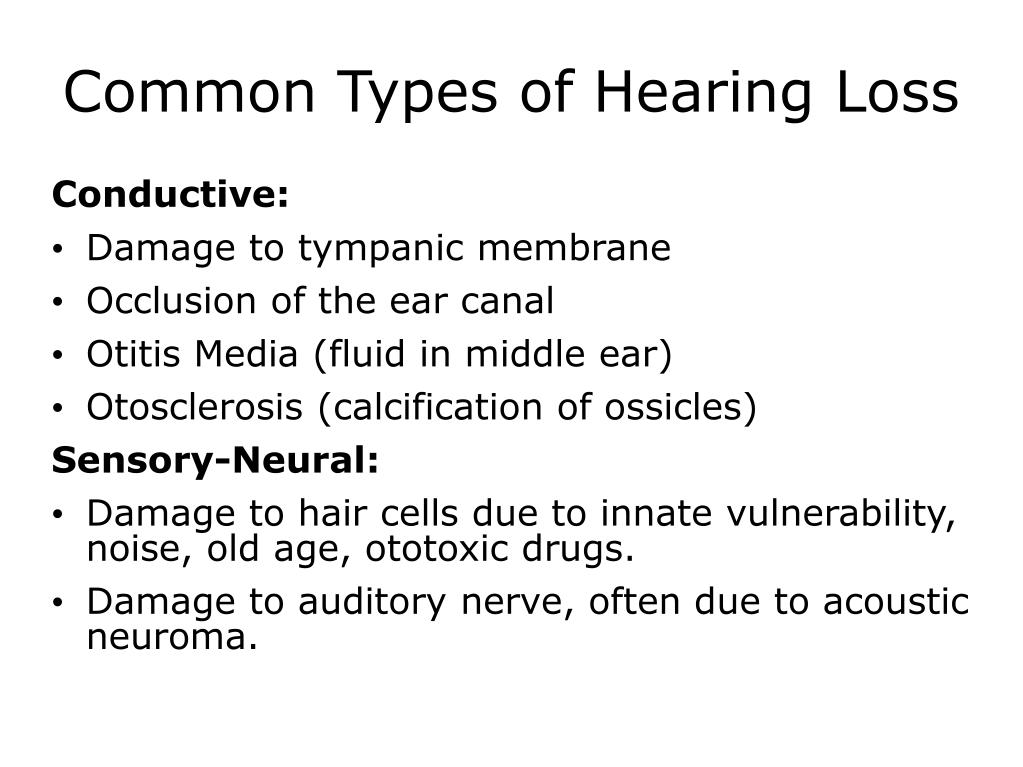
Hearing loss affects people of all ages and can be caused by many different factors. The three basic categories of hearing loss are sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss. Here is what patients should know about each type.
What is the most common form of hearing loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss. It occurs when the inner ear nerves and hair cells are damaged — perhaps due to age, noise damage or something else. Sensorineural hearing loss impacts the pathways from your inner ear to your brain.
What is the most common cause of sudden hearing loss?
Most cases of sudden hearing loss are viral, and most patients are treated with steroids. Patients with mild degrees of hearing loss usually recover.
What's the difference between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound conduction is impeded through the external ear, the middle ear, or both. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is a problem within the cochlea or the neural pathway to the auditory cortex.
Does sensorineural hearing loss get worse?
Does sensorineural hearing loss get worse? SNHL often progresses over time if it's caused by age-related or genetic factors. If it's caused by a sudden loud noise or environmental factors, symptoms will likely plateau if you avoid the cause of hearing damage.
What are the different types of hearing loss?
There are four types of hearing loss: Hearing loss caused by something that stops sounds from getting through the outer or middle ear. This type of hearing loss can often be treated with medicine or surgery. Hearing loss that occurs when there is a problem in the way the inner ear or hearing nerve works.
Why is sound not organized in the brain?
Hearing loss that occurs when sound enters the ear normally, but because of damage to the inner ear or the hearing nerve, sound isn’t organized in a way that the brain can understand. For more information, visit the National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. .
What are the bones that send the movement of the eardrum to the inner ear?
three small bones called ossicles that send the movement of the eardrum to the inner ear. Inner Ear. The inner ear is made up of: the snail shaped organ for hearing known as the cochlea. the semicircular canals that help with balance. the nerves that go to the brain. Auditory (ear) Nerve.
What is the part of the ear that separates the outer and middle ear?
the part we see on the sides of our heads, known as pinna. the ear canal. the eardrum, sometimes called the tympanic membrane, which separates the outer and middle ear. Middle Ear. The middle ear is made up of: the eardrum. three small bones called ossicles that send the movement of the eardrum to the inner ear.
What are the organs of the inner ear?
Inner Ear#N#The inner ear is made up of: 1 the snail shaped organ for hearing known as the cochlea 2 the semicircular canals that help with balance 3 the nerves that go to the brain
What does "stable" mean in hearing?
Fluctuating or Stable. Hearing loss gets either better or worse over time (fluctuating) or stays the same over time (stable). Congenital or Acquired/Delayed Onset. Hearing loss is present at birth (congenital) or appears sometime later in life (acquired or delayed onset).
Which nerve sends sound information from the ear to the brain?
Auditory (ear) Nerve. This nerve sends sound information from the ear to the brain. Auditory (Hearing) System. The auditory pathway processes sound information as it travels from the ear to the brain so that our brain pathways are part of our hearing.
What are the different types of hearing loss?
The three basic categories of hearing loss are sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss. Here is what patients should know about each type.
Where does hearing loss occur?
This type of hearing loss occurs in the outer or middle ear where sound waves are not able to carry all the way through to the inner ear. Sound may be blocked by earwax or a foreign object located in the ear canal; the middle ear space may be impacted with fluid, infection or a bone abnormality; or the eardrum may have been injured.
Can hearing loss discriminate?
Hearing problems don’t discriminate and can affect people at any stage of life. Don’t suffer in silence with hearing loss. Our center’s physicians are among the finest and most highly skilled otologists and neurotologists (ear, nose and throat doctors) in the world.
Can hearing aids help with hearing loss?
It can be a result of aging, exposure to loud noise, injury, disease, certain drugs or an inherited condition. This type of hearing loss is typically not medically or surgically treatable; however, many people with this type of loss find that hearing aids can be beneficial.
Can hearing loss be reversed?
In some people, conductive hearing loss may be reversed through medical or surgical intervention. Conductive hearing loss is most common in children who may have recurrent ear infections or who insert foreign objects into their ear canal.
What are the three types of hearing loss?
Hearing loss is defined as one of three types: Conductive (involves outer or middle ear) Sensorineural (involves inner ear) Mixed (combination of the two) Aging and chronic exposure to loud noises both contribute to hearing loss.
What causes hearing loss in the middle ear?
In the outer or middle ear, any of these can cause hearing loss. Ruptured eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation). Loud blasts of noise, sudden changes in pressure, poking your eardrum with an object and infection can cause your eardrum to rupture and affect your hearing.
What is the name of the eardrum that connects the middle ear to the inner ear?
Anvil (incus) — in the middle of the chain of bones. Stirrup (stapes) — attached to the membrane-covered opening that connects the middle ear with the inner ear (oval window) The vibration of the eardrum triggers a chain of vibrations through the bones.
How does the vestibular nerve affect the sense of balance?
They convert the motion into electrical signals that are transmitted along the vestibular nerve to the brain. This sensory information enables you to maintain your sense of balance. Traveling to the brain. Electrical impulses travel along the auditory nerve and pass through several information-processing centers.
What is the role of the cochlea in hearing?
Inner ear. The inner ear contains a group of interconnected, fluid-filled chambers. The snail-shaped chamber, called the cochlea (KOK-lee-uh), plays a role in hearing. Sound vibrations from the bones of the middle ear are transferred to the fluids of the cochlea.
What is the middle ear?
The middle ear is an air-filled cavity that holds a chain of three bones: the hammer (malleus), the anvil (incus) and the stirrup (stapes). These bones are separated from the outer ear by the eardrum (tympanic membrane), which vibrates when struck by a sound wave.
What are the parts of the ear?
The ear is made up of three primary parts: the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. Each section is composed of structures that play distinct roles in the process of converting sound waves into signals that go to the brain. Outer ear. The outer ear is composed of the visible part of the ear (pinna) and the ear canal.
What is conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss is due to problems with the ear canal, ear drum, or middle ear and its little bones (the malleus, incus, and stapes).
What is the treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss?
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL), presumed to be of viral origin, is an otologic emergency that is medically treated with corticosteroids. Corticosteroids may also be used to reduce cochlea hair cell swelling and inflammation after exposure to loud noise.
What is amplification in hearing aids?
Amplification may be a solution with the use of a bone-conduction hearing aid, or a surgically implanted, osseointegrated device (for example, the Baha or Ponto System), or a conventional hearing aid, depending on the status of the hearing nerve. Antibiotic or antifungal medications are used to treat chronic ear infections, or chronic middle fluid.
What is ear infection?
Ear infection (otitis media – an infection of the middle ear in which an accumulation of fluid may interfere with the movement of the eardrum and ossicles) Allergies. Poor Eustachian tube function. Perforated eardrum. Benign tumors.
Can a head trauma cause ear leakage?
Sensorineural hearing loss can occur from head trauma or abrupt changes in air pressure (e.g., airplane descent), which can cause inner ear fluid compartment rupture or leakage, which can be toxic to the inner ear. There has been variable success with emergency surgery when this happens.
Do audiologists take care of conductive components?
Audiologists recommend taking care of the conductive component first. There have been times when the addition of the conductive component made the person a better hearing aid candidate, by flattening out the audiogram for example, while the underlying sensorineural component presented a high-frequency loss. However, the emphasis would still be on treating medically what can be treated. Generally, you would expect positive results.
What is the most common type of hearing loss?
Hearing aids may help people with sensorineural hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss: Conductive hearing loss, also called conduction deafness, occurs when sound waves can’t reach the inner ear.
Why do people with high frequency hearing loss hear high pitched sounds?
High-frequency deafness is typically caused by aging and damage to hair cells in the inner ear .
What is mixed hearing loss?
Mixed hearing loss: Mixed hearing loss refers to a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. It occurs when there is damage to the inner ear and the middle or outer ear. Mixed hearing loss is treated on a case-by-case basis.
What is prelingual deafness?
A person with prelingual deafness experienced hearing loss before learning how to speak. Postligual hearing loss develops after a person has learned to speak. Acquired or congenital. Congenital hearing loss refers to children who are born with hearing loss.
What is the difference between progressive and sudden hearing loss?
Hearing loss can also be: Sudden or progressive. Sudden hearing loss is when hearing loss develops very quickly; progressive hearing loss develops over time. Unilateral or bilateral. Unilateral hearing loss, also called single-sided hearing loss, describes hearing loss in one ear only.
What are the best ways to treat hearing loss?
There are effective treatments for hearing loss, including hearing aids, cochlear implants, medicine and surgery. Physicians usually treat sensorineural hearing loss, the most common type, with hearing aids. However, those who have damage to their outer or middle ear may require medical treatment.
What does it mean when you have high frequency hearing loss?
Those with high-frequency hearing loss often feel their hearing is muffled or that they can hear but not understand people speaking. Fluctuating or stable. Fluctuating hearing loss occurs when the degree of hearing loss changes over time. Stable hearing loss doesn’t get better or worse.
What is the most common cause of middle ear hearing loss?
This is a particular problem in young children but also affects adults. Otitis media affects the health and function of the eardrum and the ossicular chain; it is the most common cause of middle ear hearing loss.
Why do I lose my hearing at birth?
present at birth. Noticeable hearing loss will only arise if the entrance to the ear canal is obstructed or closed up preventing sound entry.
Why does my eardrum rupture?
Perforations of the eardrum are usually due to middle ear inflammation/infection (otitis media) usually resulting in a discharge from the middle ear into the ear canal as well as hearing loss. A blow to the side of the head, especially against the pinna , can cause the eardrum to rupture.
What is the chain of bones in the middle ear?
The chain of three tiny bones in the middle ear ( ossicles or ossicular chain) transmit sound vibrations from the outer ear to the cochlea in the inner ear. These tiny bones can suffer dislocation from head trauma such as in a road traffic accident or in contact sports such as boxing or rugby.
What is the most common condition that affects the ossicular chain?
Apart from the effects of middle ear inflammation and infection, the most common condition affecting the ossicular chain in adults is otosclerosis. This is a hereditary condition but, because it doesn’t appear in every generation of an affected family, the genetic connection is often not obvious.
What is the eardrum?
The eardrum is a delicate membrane which divides the outer from the middle ear, so it’s really part of both. The eardrum, as part of the outer ear, can easily be affected by infection or inflammation of the ear canal (otitis externa).
What is mixed hearing loss?
Mixed hearing loss. When there is both a conductive and sensorineural loss, this is called a mixed hearing loss. The onset of a hearing loss can be sudden (within a few days), rapid (within a few months) or slowly progressive (over years rather than months). Sudden hearing loss is classified as a medical emergency and should always have urgent, ...
Ailments of the Outer Ear (Conductive Losses)
Infection – Causes irritation, swelling and pain but usually does not cause any hearing loss unless untreated.
Ailments of the Middle Ear: (Conductive Losses)
Infection – The middle ear structures can be damaged by infection resulting from bacteria
Ailments of the Inner Ear: (Sensorineural Loss)
Presbycusis – Deterioration of the hair cells in the inner ear due to aging. It is the most common ailment of the inner ear.
