
Why is denaturation important and how is it caused?
Denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the quaternary structure, tertiary structure, and secondary structure which is present in their native state, by application of some external stress or compound such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt, an organic solvent, radiation or heat. If proteins in a living cell are denatured, this results in disruption of cell activity and possibly cell death. Protein denaturation is also a consequence of cell death. D
What does denaturation mean and why is it important?
The way proteins change their structure in the presence of certain chemicals, acids or bases – protein denaturation – plays a key role in many important biological processes. And the way proteins interact with various simple molecules is essential to finding new drugs.
What is Protein denaturing and why is it bad?
- For proteins to be utilized by the body, they need to be metabolized, or broken down to amino acids.
- We have enzymes or proteases to break down protein molecules into amino acid residues that are further utilized by the human body.
- When partially digested food reach the gut, the acidic environment is already going to have an impact on the struc
What denatures enzymes and why?
What is the best supplement for pancreas?
- Amylase. This class of digestive enzyme is needed to help break down carbohydrates and sugars.
- Lipase. This digestive enzyme category is pivotal to digestion of oils and fats.
- Protease. These digestive enzymes are necessary for the breakdown of proteins.
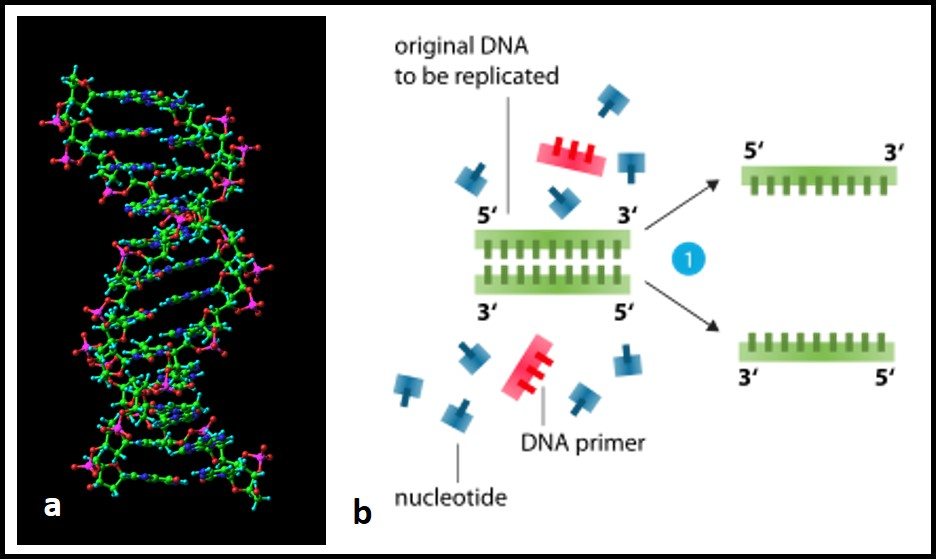
At what temperature does DNA denature?
approximately 90°C(i) Denaturation by Temperature: If a DNA solution is heated to approximately 90°C or above there will be enough kinetic energy to denature the DNA completely causing it to separate into single strands. This denaturation is very abrupt and is accelerated by chemical reagents like urea and formamide.
Why does DNA denature at high temperature?
DNA melting temperature Specifically, adenine bases pair with thymine bases and guanine bases pair with cytosine bases. Heating a DNA sample disrupts these hydrogen bonds, thus “unwinding” the double helix and denaturing the DNA.
What are some factors that can lead to protein denaturation?
A wide variety of reagents and conditions, such as heat, organic compounds, pH changes, and heavy metal ions can cause protein denaturation.
What causes DNA melting?
In bacteria, the DnaA protein may be responsible for melting origin DNA, and also for loading the helicase onto the melted ssDNA. For eukaryotic viruses, the Large T and E1 helicases are competent to melt the origin DNA and subsequently unwind the DNA by steric exclusion.
How does DNA denaturation work?
If the temperature is slowly decreased in the solution where the DNA had been denatured, the DNA chains will spontaneously reanneal and the original double helix structure is restored. This process can be followed in a spectrophotometer at 260 nm and the temperature/absorbency relationship can be described by a curve that is the opposite of the denaturation curve shown in Fig. 6.14. The DNA renaturation resulting from slow cooling is called reannealing. When the complementary strands meet, they completely reconstitute the double helix.
What temperature is DNA denaturation?
Double strand DNA denaturation of the sperm and FISH probes is carried out after incubation at high temperature (70°C–74°C). After denaturation, both DNAs are coincubated and hybridized to form a duplex of complementary strands.
What happens to DNA when it is unwinded?
DNA unwinding is initiated only if a functional oligomeric helicase is formed. Significantly, partial dissociation of the oligomeric helicase during unwinding leaves an inactive Rep monomer, resulting in a stalled complex. This stalled complex can be resolved in two ways.
What is DNA unwinding?
A DNA unwinding element (DUE) is an A + T-rich sequence ranging from 30 to > 100 bp in length in which the duplex DNA is prone to unpairing (also called melting or unwinding).
How much DNA is found in mammals?
Finally, a third fraction of the DNA that in mammals comprises about 60% of total DNA, corresponds to sequences only found in one to three copies ( single copy DNA) that anneal very slowly. In bacteria, almost all the DNA exists as single copy DNA. Hybridization.
What is the name of the fragments of DNA that are repeated many times?
In mammalian DNA preparations, fragments exist that are repeated many times (presenting hundreds of thousands to millions of copies), which are called highly repetitive DNA segments. Portions of highly repetitive DNA of more than 6 bp in length are also designated as satellite DNAs.
Why is the annealing time shorter?
When a given DNA has segments with the same sequence (repetitive sequences), the annealing time is shorter because the chance that one chain meets a complementary one is greater. In contrast, DNA sections with unique sequences require a longer time to find its complementary strand to reform the double helix.
When preparations of double-stranded DNA are denatured and allowed to renature, the rate of
When preparations of double-stranded DNA are denatured and allowed to renature, the rate of renaturation can give valuable information about the complexity of the DNA if there are repetitive sequences in the DNA, it shows less complexity in comparison to its total length, but the complexity is equal to its total length if all sequences are unique.
What happens when DNA is heated to 90°C?
If a DNA solution is heated to approximately 90°C or above there will be enough kinetic energy to denature the DNA completely causing it to separate into single strands. This denaturation is very abrupt and is accelerated by chemical reagents like urea and formamide.
What is the temperature at which DNA is melted?
It is defined as temperature at which 50% of the DNA is melted.
What does the abruptness of the transition mean?
The abruptness of the transition indicates that the DNA double helix is highly cooperative structure, held together by many reinforcing bonds. The melting of DNA can be followed spectrophotometrically by monitoring the absorbance of DNA at 260 nm. T m is analogous to the melting point of crystal. The T m value depends on the nature of the DNA.
Why does DNA have a high viscosity?
The solutions of native DNA exhibit high viscosity because of the relatively rigid double helical, long and rod like character of DNA molecule. Denaturation causes a marked decrease in viscosity. If melted DNA is cooled it is possible to reassociate the separated strands, a process known as renaturation.
Does rapid cooling reverse denaturation?
DNA (50-60%) is renatured. Rapid cooling does not rever se denaturation, but if the cooled solution is again heated and then cooled slowly, renaturation takes place.
Does DNA have a T-m or G-C?
In fact, the T m of DNA from many species varies linearly with G—C content. This relationship between T m and G—C content arises due to guanine and cytosine form three hydrogen bonds when base paired, whereas adenine and thymine form only two. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is Denaturation of DNA
During the replication of DNA and other different phenomenon in which active participation of DNA is observed with the separation of strands of DNA double helix.
Renaturation of DNA
Segregated strands of DNA start to anneal immediately when temperature drops below the T m value. This annealing cycle is often called as renaturation. The property of denaturation and renaturation is very important for the optimum biological functioning of the DNA.
Thermal Denaturation of DNA
DNA can be denatured through heat and this process is same as melting. The sample is heated until the DNA unwinding and the separation of two strands. When the strands have been separated, the DNA will then, at that point be allowed to reach a steady temperature.
DNA Denaturation through NaOH Treatment
Besides heating the DNA sample, Chemicals like NaOH can also be used to achieve denaturation of DNA. A specific concentration of NaOH can be utilized to denature DNA. As the amount of NaOH utilized is lowered, the denaturation will take longer time than expected – yet the DNA can in any case be completely denatured.
DNA Denaturation through Salt
A high amount of salt in the medium will make DNA normally denature, given the right ratio of salt. DNA denaturation using salt is like denaturation using organic solvents. generally, DNA denaturation using salt can’t be renatured.
Which PCR step causes the denaturation of double stranded DNA
Separation of DNA strands take place in denaturation step of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) which is described in the following steps:
Effect of urea on DNA denaturation
Like Thermal and pH induced denaturation of DNA, Urea also possess the capability to denature DNA. Urea in high amounts addresses a problematic condition for nucleic acid structures. Since urea is hydrogen-bond donor as well as acceptor, it can undoubtedly denature nucleic acids.
What is DNA denaturation?
DNA denaturation is the process of breaking down the DNA molecule, generally for the purposes of comparison or sequencing. As with many laboratory techniques, there are a variety of ways to denature DNA -- and each of them tend to be better for specific applications. The top three methods of DNA denaturation are heat, NaOH treatment, and salt.
How does DNA denature?
DNA can be denatured through heat in a process that is very similar to melting. Heat is applied until the DNA has unwound itself and separated into two single strands. Once the strands have been separated, the DNA will then be cooled back down to a stable temperature.
What are the three methods of DNA denaturation?
The top three methods of DNA denaturation are heat, NaOH treatment, and salt. Each of these methods will break the bonds between strands, but may do so with a greater degree of accuracy or lessened disruption.
How long does it take for DNA to denature?
A certain concentration of NaOH can be used to denature DNA safely, often in as little as one minute.
How does salt affect DNA?
A high concentration of salt will cause DNA to naturally denature, given the right concentration of salt. DNA denaturation with salts are similar to denaturation through the use of organic solvents. In general, DNA denaturation through salt cannot be renatured. Salt is often used in addition to an acid for the full denaturation of DNA, and it may also be used in conjunction with heat. Salt is not usually used as the sole process of denaturation -- it's usually used alongside other chemicals such as isopropanol and ethanol. This process is able to be used on larger volumes of DNA, which makes it less useful for highly accurate and specific work, but more useful for scaling up and processing DNA in larger quantities.
Is salt used in DNA?
Salt is not usually used as the sole process of denaturation -- it's usually used alongside other chemicals such as isopropanol and ethanol. This process is able to be used on larger volumes of DNA, which makes it less useful for highly accurate and specific work, but more useful for scaling up and processing DNA in larger quantities.
Is DNA melting accurate?
Though DNA melting is a fairly simple and straightforward process, it is generally not used when accuracy is required. Heated DNA denaturation is considered to be less accurate than DNA sequencing and is used for more broad scope applications. This type of denaturation may also be used within the polymerase chain reaction.
What is DNA denaturation?
In general the process of “denaturation” or “denaturing the biomolecule” encourage losing the structure. For example, denaturation of protein or DNA loses various levels of structure.
Techniques to Denature DNA
One of the most common techniques to denature, (theoretically or more precisely) to unwind the dsDNA is by heat. And is commonly practiced in routine lab experiments. At higher heat or temperature >90℃, hydrogen bonds between dsDNA break and produce two separate single strands.
Applications of DNA denaturation
Many different assays use the “process” DNA denaturation for various purposes and studies.
Wrapping up
Unlike NaOH, the majority of chemical denaturants work in PCR with heat, meaning it alters the melting temperature. Denaturing DNA has significant importance in the downstream application, however, to get good results, DNA should denature completely.
What is denaturation in biology?
Note 2: Denaturation can occur when proteins and nucleic acids are subjected to elevated temperature or to extremes of pH, or to nonphysiological concentrations of salt, organic solvents, urea, or other chemical agents.
Why do amino acids denaturate?
Protein denaturation due to pH. Denaturation can also be caused by changes in the pH which can affect the chemistry of the amino acids and their residues. The ionizable groups in amino acids are able to become ionized when changes in pH occur. A pH change to more acidic or more basic conditions can induce unfolding.
How are nucleic acids synthesized?
Nucleic acids (including RNA and DNA) are nucleotide polymers synthesized by polymerase enzymes during either transcription or DNA replication . Following 5'-3' synthesis of the backbone, individual nitrogenous bases are capable of interacting with one another via hydrogen bonding, thus allowing for the formation of higher-order structures. Nucleic acid denaturation occurs when hydrogen bonding between nucleotides is disrupted, and results in the separation of previously annealed strands. For example, denaturation of DNA due to high temperatures results in the disruption of Watson and Crick base pairs and the separation of the double stranded helix into two single strands. Nucleic acid strands are capable of re-annealling when " normal " conditions are restored, but if restoration occurs too quickly, the nucleic acid strands may re-anneal imperfectly resulting in the improper pairing of bases.
What happens to albumin in eggs?
(Top) The protein albumin in the egg white undergoes denaturation and loss of solubility when the egg is cooked. (Bottom) Paperclips provide a visual analogy to help with the conceptualization of the denaturation process.
What is the effect of temperature on enzyme activity?
Denaturation (biochemistry) The effects of temperature on enzyme activity. Top - increasing temperature increases the rate of reaction ( Q10 coefficient ). Middle - the fraction of folded and functional enzyme decreases above its denaturation temperature. Bottom - consequently, an enzyme's optimal rate of reaction is at an intermediate temperature.
What are the characteristics of denatured proteins?
Denatured proteins can exhibit a wide range of characteristics, from conformational change and loss of solubility to aggregation due to the exposure of hydrophobic groups. Denatured proteins lose their 3D structure and therefore cannot function.
Which method of denaturation provides faster denaturation?
Studies comparing different denaturation methods such as heating, beads mill of different bead sizes, probe sonification, and chemical denaturation show that chemical denaturation can provide quicker denaturation compared to the other physical denaturation methods described.
