
The electron affinity of an element depends mainly upon the following factors:
- Nuclear Charge. More the nuclear charge of the atom more strongly will it attract an additional electron. ...
- Atomic size. The smaller the size of the atom smaller will be the distance between the extra electron and the nucleus. ...
- Electronic Configuration. ...
What is electron affinity and how does it increase?
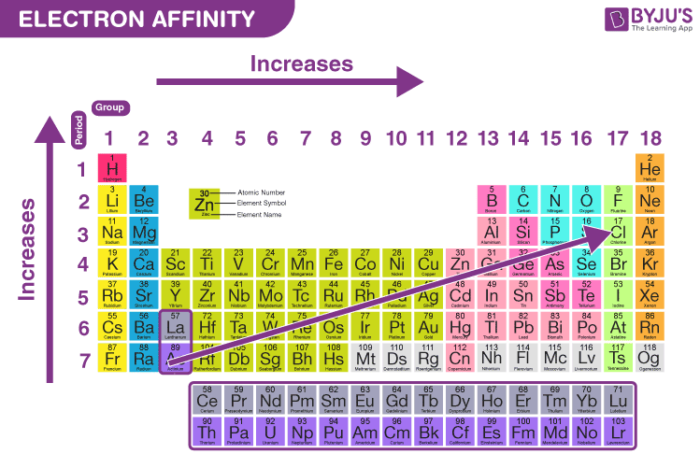
It increases moving down a column or group and also increases moving from left to right across a row or period (except for the noble gases). The value may be either positive or negative. A negative electron affinity means energy must be input in order to attach an electron to the ion.
What are some examples of electron affinity?
Other theoretical concepts that use electron affinity include electronic chemical potential and chemical hardness. Another example, a molecule or atom that has a more positive value of electron affinity than another is often called an electron acceptor and the less positive an electron donor. Together they may undergo charge-transfer reactions.
What does it mean when electron affinity is negative?
If the value of electron affinity or Eea is negative, it means energy is required to attach an electron. Negative values are seen for the nitrogen atom and also for most captures of second electrons. For a negative value, the electron capture is an endothermic process:
Who discovered electron affinity in chemistry?
Who discovered electron affinity? Electron Affinity was a concept that was discovered of 1901 in view of the discovery of electron negativity by Linus Carl Pauling. Electron Affinity is the amount of change in energy when an electron in a gaseous state is applied to a neutral atom.

What causes electron affinity trend?
Electron affinity increases from left to right within a period. This is caused by the decrease in atomic radius. Electron affinity decreases from top to bottom within a group. This is caused by the increase in atomic radius.
What affects electron affinity?
The three factors affecting the electron affinity of a molecule are Nuclear Charge, Atomic Size, and Electronic Configuration. Nuclear Charge: The greater the nuclear charge, the greater will be the attraction of the incoming electron. This will result in a larger value of electron affinity.
What does the electron affinity of an element depend on?
There are two factors that can affect electron affinity. These are atomic size and nuclear charge.
How do you explain electron affinity?
Electron affinity is the energy change that results from adding an electron to a gaseous atom. For example, when a fluorine atom in the gaseous state gains an electron to form F⁻(g), the associated energy change is -328 kJ/mol.
Why does electron affinity decrease with increase in atomic size?
An increase in atomic size leads to a decrease in electron affinity because the incoming electron is added further away from the nucleus, i.e. on a higher energy level. As you go down a group, the outermost electrons are located further and further away from the nucleus.
How does size of atomic affect electron affinity?
The smaller the atom is, the closer the outermost shell is; therefore, it is a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the incoming electron. That means the electron affinity is higher for smaller atoms.
Is electron affinity same as electronegativity?
Electronegativity is defined as a chemical property which decides the propensity of an atom to attract an electron. In the year 1932, Linus Pauling proposed the concept of electronegativity. Electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy liberated when a molecule or neutral atom acquires an electron from outside.
What is the relationship between electron affinity and ionization energy?
The main difference between electron affinity and ionization energy is that electron affinity gives the amount of energy released when an atom gains an electron whereas ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
What element has the highest electron affinity?
ChlorineWhich Element Has the Highest Electron Affinity? Chlorine has the highest electron affinity among the elements. Its high affinity can be attributed to its large atomic radius, or size. Because chlorine's outermost orbital is 3p, its electrons have a large amount of space to share with an incoming electron.
Is electron affinity the same as ionization energy?
Chemical Bond Energy Considerations Ionization energy: the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom. Electron affinity: the energy change when a neutral atom attracts an electron to become a negative ion.
Why does electronegativity increase across a period?
Electronegativity increases across a period because the number of charges on the nucleus increases. That attracts the bonding pair of electrons more strongly.
1. As we move down the group of the periodic table, electron affinity increase or decrease? If so, w...
As we move down the group on the periodic table, electron affinity tends to decrease. There are three reasons associated with why it tends to decre...
2. Why the Halogens show high electron affinity?
Electron affinity reflects the ability of an atom to accept an electron. The halogens show high electron affinity due to their small size. It has a...
3. What does Electron Affinity mean in simple words?
In chemistry, electron affinity simply means the energy that is released when an electron is added to a neutral atom, which then forms a negatively...
4. How should I study Electron Affinity?
To study Electron Affinity, you will need two things: a good study schedule and high-quality study materials. Vedantu has already provided the stud...
5. Where can I find more resources to study Electron Affinity?
You can find more resources to study Electron Affinity on the Vedantu website and app. This page contains a detailed explanation of electron affini...
What are some examples of electron affinity?
Other theoretical concepts that use electron affinity include electronic chemical potential and chemical hardness . Another example, a molecule or atom that has a more positive value of electron affinity than another is often called an electron acceptor and the less positive an electron donor.
Why do groups 17 and 18 have more energy?
This is caused by the filling of the valence shell of the atom; a group 17 atom releases more energy than a group 1 atom on gaining an electron because it obtains a filled valence shell and therefore is more stable. In group 18, the valence shell is full, meaning that added electrons are unstable, tending to be ejected very quickly.
Is electron affinity a function of electronic structure?
The electron affinity of molecules is a complicated function of their electronic structure. For instance the electron affinity for benzene is negative, as is that of naphthalene, while those of anthracene, phenanthrene and pyrene are positive. In silico experiments show that the electron affinity of hexacyanobenzene surpasses that of fullerene.
Why do we use electron affinity?
Even so, electron affinity has practical applications. It is used to measure chemical hardness , a measure of how charged and readily polarized Lewis acids and bases are. It's also used to predict electronic chemical potential. The primary use of electron affinity values is to determine whether an atom or molecule will act as an electron acceptor or an electron donor and whether a pair of reactants will participate in charge-transfer reactions.
What is the primary use of electron affinity values?
The primary use of electron affinity values is to determine whether an atom or molecule will act as an electron acceptor or an electron donor and whether a pair of reactants will participate in charge-transfer reactions.
What is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom?
Electron affinity reflects the ability of an atom to accept an electron. It is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. Atoms with stronger effective nuclear charge have greater electron affinity. The reaction that occurs when an atom takes an electron may be represented as: X + e − → X − + energy.
What does it mean when an electron is negative?
Sometimes the values are given in terms of magnitudes relative to each other. If the value of electron affinity or Eea is negative, it means energy is required to attach an electron.
Which element has a completely filled valence electron shell?
The exception is the noble gases, which are in the last column of the table. Each of these elements has a completely filled valence electron shell and an electron affinity approaching zero. Nonmetals typically have higher electron affinity values than metals. Chlorine strongly attracts electrons.
Is electron capture endothermic or exothermic?
A negative electron affinity means energy must be input in order to attach an electron to the ion. Here, electron capture is an endothermic process. If electron affinity is positive, the process is exothermic and occurs spontaneously.
What happens when a molecule is a good electron acceptor?
When a molecule (or group) that is a good electron donor comes into contact with a molecule (or group) that is a good electron acceptor, the donor may transfer some of its charge to the acceptor. This forms a charge-transfer complex, which, in effect, is a molecular dipole-dipole interaction. The potential energy of this interaction is proportional to the difference between the ionization potential of the donor and the electron affinity of the acceptor.
How are radical anion compounds formed?
A radical anion is formed due to the addition of an electron to a molecule. It is rather stable if the molecule possesses a positive electron affinity (EA). These compounds are aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, and aldehydes
What is the thermal stability of PFCs?
The thermal stability and chemical inertness of PFCs reflect a combination of the strength of the C─F bond, low polarizability and strong electro-attracting character of fluorine (which reinforces the C─C backbone), and of the compact, repellent electron shield provided by the fluorine atoms.
What is the reduction of aromatic compounds?
The reduction of aromatic compounds by dissolving metals is an extremely useful transformation. Because of the much higher electron affinity of arene substrates over the products, the formation of partially reduced compounds is generally favored under such reducing conditions. Although the first example of the partial reduction of an arene with sodium in ammonia was reported by Wooster and Godfrey <1937JA596>, this reaction has been extensively developed by Birch and is now known as the Birch reaction <1991COS (8)489>. Since the reduction involves two electron transfers and two protonation steps, the exact pathway followed will depend on the substitution pattern of the aromatic ring, the choice of the metal, and the proton source. Thus, the mechanism involving radicals, radical-anions, and anions might be more subtle than the simple general reaction pattern summarized in Scheme 12. Furthermore, iron impurities contained in ammonia have been shown to be a major cause for the lack of reproducible results in several reductions.
Why does electron affinity decrease from right to left?
The opposite trend holds true as well, electron affinity decreases from right to left and down the groups because the electrons are located farther away from the nucleus and therefore have less attraction .
Why does the electron affinity of an atom depend upon the initial addition of an electron to a neutral atom?
The initial addition of an electron to a neutral atom, the first electron affinity, will always have negative energy. This is because energy is released when an electron is added to a neutral atom. The ion is now negative, and more energy is necessary when an electron is ...
Why is the electron affinity of nonmetals negative?
This is because nonmetals have enough energy to form negatively charged ions, anions. This means that the electron affinity value of nonmetals is typically negative. Nonmetals have more electron affinity than metals do because ...
What is the electron affinity trend?
The electron affinity trend describes the trend across the periodic table and describes how much energy in an atom is released or spent when an electron is added to a neutral atom or the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral atom. The electron affinity trend describes how as one follows the periodic table left ...
How are reactivity and electron affinity related?
Reactivity and electron affinity are tightly correlated, with the reactivity of an element increasing as the electron affinity increases. In other words, the greater an element’s tendency to gain electrons, the more reactive the element is.
Why do metals lose electrons?
The addition of an electron to a metal element requires energy. This is because metals don’t exert a very strong pull on their valence electrons and are therefore lose electrons in the valence shell rather easily, becoming cations. For this reason, many metals have very low electron affinities. ADVERTISEMENT.
Why are neutrons used in chemistry?
The neutrons are used as a point of comparison to find the mass of electrons and protons. “We’re protons and electrons/ Residing in one nucleus.”. — Afeefa. Electrons are about 1800 times smaller than either neutrons or protons, and they have a negative charge.
Overview
The electron affinity (Eea) of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is attached to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form an anion.
X(g) + e → X (g) + energy
Note that this is not the same as the enthalpy change of electron capture ionization, which is defined as negative when energy is released. In other words, the enthalpy change and the electr…
Measurement and use of electron affinity
This property is used to measure atoms and molecules in the gaseous state only, since in a solid or liquid state their energy levels would be changed by contact with other atoms or molecules.
A list of the electron affinities was used by Robert S. Mulliken to develop an electronegativity scale for atoms, equal to the average of the electrons affinity and ionization potential. Other theoretical concepts that use electron affinity include electronic chemical potential and chemical hardness. …
Electron affinities of the elements
Although Eea varies greatly across the periodic table, some patterns emerge. Generally, nonmetals have more positive Eea than metals. Atoms whose anions are more stable than neutral atoms have a greater Eea. Chlorine most strongly attracts extra electrons; neon most weakly attracts an extra electron. The electron affinities of the noble gases have not been conclusively measured, s…
Molecular electron affinities
The electron affinity of molecules is a complicated function of their electronic structure. For instance the electron affinity for benzene is negative, as is that of naphthalene, while those of anthracene, phenanthrene and pyrene are positive. In silico experiments show that the electron affinity of hexacyanobenzene surpasses that of fullerene.
"Electron affinity" as defined in solid state physics
In the field of solid state physics, the electron affinity is defined differently than in chemistry and atomic physics. For a semiconductor-vacuum interface (that is, the surface of a semiconductor), electron affinity, typically denoted by EEA or χ, is defined as the energy obtained by moving an electron from the vacuum just outside the semiconductor to the bottom of the conduction band just inside th…
See also
• Ionization energy — a closely related concept describing the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom or molecule
• One-electron reduction
• Electron-capture mass spectrometry
External links
• Electron affinity, definition from the IUPAC Gold Book