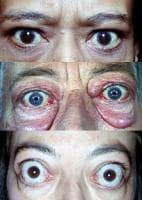
Mar 05, · Exophthalmos
Bulging Eyes
Protrusion of one or both eyes from the sockets.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine, and then triiodothyronine which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body. It is a glycoprotein hormone produced by thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland, which regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid. In 1916, Bennett M. Allen and Philip E. Smith found that the pituitary …
Full Answer
Why does hyperthyroidism cause exophthalmos?
If a person's immune system attacks the thyroid gland, it may react by producing extra hormones. The autoimmune antibodies can attack the muscles and soft tissue surrounding the eyes, which can cause them to protrude from the sockets.
What is the cause of exophthalmos in Graves disease?
In adults, the most common cause of unilateral and bilateral exophthalmos is thyroid-associated eye disease, such as Graves-related ophthalmopathy. In children, orbital cellulitis is the most common cause, whereas bilateral exophthalmos is most likely due to neuroblastoma and leukemia.
What disease commonly causes exophthalmos?
Exophthalmos, also known as proptosis, is a medical term for a bulging or protruding eyeball or eyeballs. It's most often caused by thyroid eye disease.
Which thyroid causes exophthalmos?
Thyroid Eye Disease Anyone can get Graves' disease, but it typically affects women before age 40. With thyroid eye disease, your immune system -- the body's defense against germs -- attacks tissue around the eyes. This causes them to swell and push forward, giving them a "bulging" appearance.
What is an exophthalmos?
Exophthalmos (also called exophthalmus, exophthalmia, proptosis, or exorbitism) is a bulging of the eye anteriorly out of the orbit. Exophthalmos can be either bilateral (as is often seen in Graves' disease) or unilateral (as is often seen in an orbital tumor).
What is characterized by exophthalmos?
exophthalmos, also spelled exophthalmus, also called proptosis, abnormal protrusion of one or both eyeballs. The most common cause for unilateral or bilateral exophthalmos is thyroid eye disease, or Graves ophthalmopathy.
What is the difference between exophthalmos and proptosis?
Proptosis can describe any organ that is displaced forward, while exophthalmos refers to only the eyes. Proptosis can include any directional forward displacement.
Does Graves disease cause hyperthyroidism?
Graves' disease is an immune system disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism). Although a number of disorders may result in hyperthyroidism, Graves' disease is a common cause.
Why does hyperthyroidism cause proptosis?
Proptosis is spontaneous decompression resulting from enlargement of the extraocular muscles and adipose tissue, as well as orbital fat deposits and the infiltration of orbital tissues by GAGs and leukocytes (Figure 2). TAO is the most common cause of unilateral and bilateral proptosis in adults.
What is the difference between exophthalmos and Enophthalmos?
Enophthalmos is a posterior displacement of the eyeball within the orbit. It is due to either enlargement of the bony orbit and/or reduction of the orbital content, this in relation to each other. It should not be confused with its opposite, exophthalmos, which is the anterior displacement of the eye.
What is Graves ophthalmopathy?
What is Graves' orbitopathy? Graves' orbitopathy is an autoimmune condition characterized by swelling of the tissue in the orbit (the area around the eyes), creating bulging of the eyes. It is commonly referred to as thyroid eye disease.
What is the pathophysiology of Graves disease?
Graves, MD, circa 1830s, is an autoimmune disease characterized by hyperthyroidism due to circulating autoantibodies. Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSIs) bind to and activate thyrotropin receptors, causing the thyroid gland to grow and the thyroid follicles to increase synthesis of thyroid hormone.
How do you prevent bulging eyes in Graves disease?
Thyroid eye disease, also known as Graves' eye disease, is an autoimmune condition in which the body's immune system attacks the fat and muscle tissue within the eye socket, causing inflammation. Keeping the head elevated at night and selenium supplements may help reduce swelling if it is not severe.
Why does hyperthyroidism cause proptosis?
Proptosis is spontaneous decompression resulting from enlargement of the extraocular muscles and adipose tissue, as well as orbital fat deposits and the infiltration of orbital tissues by GAGs and leukocytes (Figure 2). TAO is the most common cause of unilateral and bilateral proptosis in adults.
What is difference between proptosis and exophthalmos?
Proptosis can describe any organ that is displaced forward, while exophthalmos refers to only the eyes. Proptosis can include any directional forward displacement.
How to tell if your eye is protruding?
A physician can normally notice a protruding eye by looking at it, but as exophthalmos is normally a sign of some disease or condition, tests will be needed to find the cause. A blood test to see if the thyroid gland is functioning properly. Measurement of the degree of protrusion, using an exophthalmometer.
What is Graves disease?
Graves’ disease affects the thyroid gland. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disease that causes hyperthyroidism. A person with hyperthyroidism has an overactive thyroid gland that produces excess hormones and causes it to grow. The thyroid is in the neck, below the Adam’s apple.
What causes a bulging eyeball?
Graves' disease and thyroid disorders. Common cause. Other causes. Diagnosis. Treatment. Complications. Outlook. Exophthalmos describes a condition where the eyeball protrudes from the eye socket, making it appear to bulge. It can affect one or both eyes.
Why do my eyes protrude from my sockets?
If a person’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland, it may react by producing extra hormones. The autoimmune antibodies can attack the muscles and soft tissue surrounding the eyes, which can cause them to protrude from the sockets. This can lead to:
How does eyelid surgery work?
Eyelid surgery: This works by protecting the cornea and outer eyeball from damage.
What is the condition where the area above the cornea becomes inflamed due to abnormal tearing and blinking?
People with exophthalmos are more likely to develop conjunctivitis, and especially superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis, in which the area above the cornea becomes inflamed due abnormal tearing and blinking.
What does it mean when your eyes are bulging?
Overall, the first step for any individual who notices bulging eyes is to seek medical care. Remember, exophthalmos is a sign that something more is going on, in or around the eye or within the brain.
How do goiters form?
Goiters form by increase of thyroid hormone being produced and correctly stop production when levels normalized (McCance, K. L., & Huether, S. E. (2019). Exophthalmos is caused by T cell secretion and inflammatory cytokines are produced which causes a reaction of the hypertrophy and hyperplasia of fibroblast cells.
What is the function of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland’s main function is to produce hormones such as thyroid hormone and iodine hormones T4 &T3. It maintains homeostasis throughout the body. Thyroid gland is made up of two lobes of squamous epithelial cells called follicle (Marieb, E. N., & Hoehn, K. (2007). Follicle cells store a thyroid globin protein called colloid. Colloid is an amber sticky substance that attaches to the iodine hormones thyroxine binding globulins (TBG). Then T4 and T3 bind to the receptor cells and enter the nucleus (Marieb, E. N., & Hoehn, K. (2007). When the blood levels decrease thyroid hormone send message to release more thyroid stimulating hormone. When this happens thyroid hormone levels increased it inhibits Hypothalamic Adenoypophyseal axis ( Marieb, E. N., & Hoehn, K. (2007). This increases the metabolic demand for the body functions.
How to diagnose Graves disease?
The condition of Graves Disease is diagnosed by lab tests and clinical symptoms. The patient will have a positive thyrotropin receptor antibodies test. Also, clinicians may perform an iodine scan of the thyroid gland to look at the gland where the iodine is absorbed (McCance, K. L., & Huether, S. E. (2019). The patient will experience weight loss, heat intolerance, warm moist skin, menstrual irregularities, exophthalmos. Other contributing factors are celiac disease, anxiety. Goiters form by increase of thyroid hormone being produced and correctly stop production when levels normalized (McCance, K. L., & Huether, S. E. (2019). Exophthalmos is caused by T cell secretion and inflammatory cytokines are produced which causes a reaction of the hypertrophy and hyperplasia of fibroblast cells. This makes the fibroblast cells to secrete glycosaminoglycans this causes the swelling of the muscle and connective tissue around the eye socket and the eye to bulge. Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism present similar in nature. Labs test will be conducted to confirm the diagnosis of hypothyroidism. The clinical presentation is different from hyperthyroidism such as, constipation, bradycardia, loss of hair, cold intolerance McCance, K. L., & Huether, S. E. (2019).
What is the protein that stores thyroid hormones?
Follicle cells store a thyroid globin protein called colloid. Colloid is an amber sticky substance that attaches to the iodine hormones thyroxine binding globulins (TBG). Then T4 and T3 bind to the receptor cells and enter the nucleus (Marieb, E. N., & Hoehn, K. (2007).
What is the role of environmental factors in disease?
This is classified as an autoimmune type II hypersensitivity which affects the lymphocytes and the antibodies against the Thyroid stimulating hormone sites (McCance, K. L., & Huether, S. E. (2019).
What Does Bulging Eyes (Exophthalmos) Indicate?
Exophthalmus or bulging eyes is most commonly a symptom of a thyroid disorder called Grave's disease, but may have other causes as well.
What are the symptoms of bulging eyes?
Depending on the cause, symptoms that may accompany bulging eyes may include: Eye pain. Changes in visual clarity or sharpness. Double vision. Decreased fields of vision. Temporary vision loss or blackout periods. Foreign body sensation. Dry, gritty eyes.
What is the best treatment for bulging eyes?
Treatment for bulging eyes (exophthalmos) depends on the cause and is aimed at reversing the problem and minimizing damage to the eye. Teprotumumab (Tepezza) is used to treat thyroid eye disease in adults. Ophthalmic lubricants are used to prevent complications from dry eyes.
What is the best treatment for thyroid disease?
Corticosteroids. Stop smoking. Radiotherapy for the active stage of thyroid eye disease. Chemotherapy for cancerous causes. Antibiotics for infectious causes. Surgery in severe cases. Orbital decompression surgery, in which a small amount of bone is removed from 1 or both eye sockets.
What Causes Exophthalmos?
There are a few different causes of exophthalmos. Here are some for reference.
What is the best treatment for thyroid ophthalmopathy?
With thyroid associated ophthalmopathy, patients may use propylthiouracil (an oral medication for hyperthyroidism) followed by surgery, propylthiouracil and then radioactive iodine, or any one of them alone. 4 Methimazole and teprotumumab are also available.
What happens if you leave your left eye protruding?
While the symptoms may just be uncomfortable at first, if you leave exophthalmos untreated for too long, it can lead to serious damage and vision loss.
Why does my eye protrude out of its orbit?
Exophthalmos is the protrusion of the eye anteriorly out of its orbit, which happens because of an increase in orbital contents within your eye’s rigid bony orbit. 1
Why do my eyes feel sore?
If you have inflamed and red bulging eyes that feel painful, you may be dealing with exophthalmos. Your eyes may also be tearful and sensitive to light.
What causes forward displacement of the eye socket?
But there are other signs, as well. An infection of the soft tissues in the eye sockets can also cause the forward displacement of your eyes. 5.
What to do if your eyes are bulging?
If you notice that one or both of your eyes is bulging, talk to your doctor to get a blood test and have your eyes checked out. There may be an underlying cause for concern, such as an underlying medical condition.
