
What are the main causes of tachycardia?
What are the Main Causes of Tachycardia?
- Heart diseases- coronary heart diseases, heart valve disease, infections and tumors in heart, heart failure, heart attack
- Abnormalities in the heart present since birth
- Lifestyle factors- consumption of alcohol, cocaine, other drugs and smoking
- Fever
- Hypertensive disease
- Hyperthyroidism
- Reaction to certain medicines
- Imbalances caused by electrolyte
What can cause increased fetal heart rate?
What causes high fetal heart rate? There are a number of maternal conditions that increase the likelihood of tachycardia in the fetus . Hyperthyroidism secondary to thyroid stimulating antibodies, fever associated with systemic infections and substance abuse may result in an increase in the fetal heart rate above the normal range.
What causes low heart rate in fetus?
What Causes A Low Fetal Heart Rate? There are various factors that can play a part in an abnormal fetal heart rate. Some of those factors include: Underlying conditions in the mother, including infection, fever, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, adverse reaction to anesthesia (including epidural medication), or any other health issue that may ...
What causes an irregular heartbeat in a fetus?
Overview
- Types. In general, heart arrhythmias are grouped by the speed of the heart rate. ...
- Fast heartbeat (tachycardia) Atrial fibrillation (A-fib). ...
- Slow heartbeat (bradycardia) Although a heart rate below 60 beats a minute while at rest is considered bradycardia, a low resting heart rate doesn't always signal a problem.
- Premature heartbeats. ...

What does fetal tachycardia indicate?
Fetal tachyarrhythmia is an abnormally fast fetal heart rate. In some cases the fast heartbeat may also have an irregular rhythm. Tachyarrhythmia is one of several types of fetal cardiac arrhythmias, congenital heart conditions involving an abnormal heartbeat. The condition is also sometimes referred to as tachycardia.
What causes a fetal heart rate to be high?
The fetal heart rate may change as your baby responds to conditions in your uterus. An abnormal fetal heart rate may mean that your baby is not getting enough oxygen or that there are other problems.
How do you fix fetal tachycardia?
Maternal transplacental short-duration intravenous magnesium treatment should be considered as first-line therapy. Transplacental propranolol, lidocaine, mexiletine, flecainide, sotalol, and amiodarone have all been used for fetal treatment of ventricular tachycardia.
Can fetal tachycardia go away?
SVT typically resolves before or after birth, either by itself or with medical therapy. Sometimes treatment is needed during the first year or so of life, and for a small number of patients, beyond their first year. If SVT goes away in the fetus or in the first year of life, it may return again around puberty.
What happens if baby's heart rate is too high?
If the heart beats too fast, contractions are shallow and not enough blood is pumped with each heartbeat. As a result, the fetus can go into heart failure. The most common form of this condition is called supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), in which the heart rate can be faster than 200 beats per minute.
Can stress cause high fetal heart rate?
Previous studies had shown that stress and anxiety during pregnancy could cause fetal abnormalities. In their article, Monk and colleagues reported that the fetuses of anxious pregnant women were more likely to have elevated heart rates and increased stress when exposed to stressors than fetuses of non-anxious women.
Is 170 bpm too high for fetus?
A normal fetal heart rate (FHR) usually ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute (bpm) in the in utero period. It is measurable sonographically from around 6 weeks and the normal range varies during gestation, increasing to around 170 bpm at 10 weeks and decreasing from then to around 130 bpm at term.
Is fetal tachycardia an indication for C section?
Fetal arrhythmia can be missed as a diagnosis, potentially leading to suboptimal management. Cases Three cases are described where detection of fetal tachycardia >200 beats per minute (bpm) at 36, 40, and 38 weeks gestation resulted in emergency cesarean section for presumed fetal distress.
Does fetal heart rate indicate Downs Syndrome?
Down syndrome can be detected early on in pregnancy with a blood screening of the mother. In the past, parents worried that fetal heart rate or a white spot (echogenic intracardiac foci) on an ultrasound may be related to Down syndrome, but these factors are not necessarily associated with a Down syndrome diagnosis.
Is 180 too high for fetal heart rate?
The normal fetal heart rate is between 120 and 160 beats per minute. Typically, an abnormally fast heart rate is over 200 beats per minute.
How common is fetal SVT?
Fetal SVT is defined as 1:1 atrioventricular activity of the FHR exceeding 200 bpm. It accounts for 60–80% of the fetal tachyarrhythmias with prevalence ranging from 1/1000 to 1/25 000 pregnancies.
What are the conditions that cause fetal tachycardia?
A fetal tachycardia can be associated with many maternal, as well as fetal conditions, which include: maternal. maternal hyperthyroidism. maternal medications. maternal tachycardia (e.g. systemic infection) fetal. in utero infection. in utero hypoxia. fetal anemia.
What is fetal tachycardia?
Fetal tachycardia is an abnormal increase in the fetal heart rate. It is variably defined as a heart rate above 160-180 beats per minute (bpm) and typically ranges between 170-220 bpm (higher rates can occur with tachyarrhythmias). On this page:
Where do abnormal electrical impulses originate?
In the majority of cases, the abnormal electrical impulses originate from the atria.
What is fetal sinus tachycardia?
Fetal sinus tachycardia is most commonly seen in cases related to maternal conditions, such as Graves’ disease or infection, or secondary to drug use. The fetal heart rate is usually less than 200 bpm and tends to resolve once the precipitating condition is corrected or exposure eliminated. In this type of tachycardia, there is 1-to-1, atrial-to-ventricular conduction with origin from the sinus node.
What is the BPM of fetal tachycardia?
Fetal tachycardia is defined as a heart rate greater than 160-180 beats per minute (bpm). This rapid rate may have a regular or irregular rhythm which may be intermittent or sustained. A sustained fetal tachyarrhythmia is uncommon, affecting fewer than 1% of all pregnancies.
What is the best treatment for sinus tachycardia secondary to hyperthyroidism?
Sinus tachycardia secondary to maternal hyperthyroidism can be managed with antithyroid medications such as methimazole. Antibiotics are necessary for maternal systemic infections and acetaminophen can be used short-term to reduce maternal fever and subsequently to normalize the fetal heart rate.
What is the fetal heart rate?
The fetal heart rate is usually less than 200 bpm and tends to resolve once the precipitating condition is corrected or exposure eliminated. In this type of tachycardia, there is 1-to-1, atrial-to-ventricular conduction with origin from the sinus node.
Why do we need fetal echocardiogram?
A detailed fetal echocardiogram is also warranted to firmly establish the rate and rhythm, confirm normal cardiac anatomy and assess any hemodynamic consequences related to the tachycardia. In addition to standard two-dimensional imaging and color flow mapping, M-mode and pulsed Doppler are critical for the characterization of a fetal arrhythmia.
Is fetal tachycardia benign?
The outcome of pregnancies complicated by fetal tachycardia is related to the underlying cause of the arrhythmia. PACs and PVCs are benign and the prognosis is excellent. In cases where these extrasystoles result in SVT and in utero medical therapy is successful, a favorable outcome is also expected. The majority of these infants are treated with antiarrhythmic agents for 12 months and about 80% will not require any intervention beyond that first year.
Can PACs cause SVT?
Although PACs and PVCs can trigger the onset of SVT, they are benign without significant sequelae in the majority of cases. A fetal echocardiogram should be obtained when these extra beats are detected to exclude associated heart anomalies and to confirm the diagnosis. Smoking, alcohol, and ingestion of caffeine-containing products should be eliminated. Serial surveillance with office auscultation or ultrasound examination every 1-2 weeks is recommended in these cases until no further extrasystoles are detected. If a fetal tachycardia is discovered on follow-up assessments, repeat fetal echocardiography and consultation with pediatric cardiology is advised.
What is fetal tachycardia?
Fetal tachycardia is an important cause of fetal morbidity and mortality. 1 2 Reliable diagnosis in utero has been possible only since the introduction of ultrasound examination of the fetal heart. 2 3 In the early days little thought was given to the mechanism of tachycardia, and treatment involved maternal administration of drugs fashionable at the time for treating supraventricular tachycardia in infants and children. Drug treatment was often followed by a return to sinus rhythm, which was interpreted as a response to treatment. However, the natural history of fetal tachycardia was, and remains, unknown.
How fast does a tachycardia occur in a neonate?
In the neonate, orthodromic atrioventricular reentry is usually faster than atrial ectopic tachycardia or permanent junctional reciprocating tachycardia, but in the fetus most tachycardias occur at about 240 beats/min.
What is supraventricular tachycardia?
The term supraventricular tachycardia covers a wide variety of tachycardia mechanisms. Many are caused by reentry and others are automatic; some are confined to the atria and others involve the atria and the ventricles. The introduction of drugs with more specific actions and, more recently, of radiofrequency ablation, ...
Is fetal tachycardia spontaneous?
However, the natural history of fetal tachycardia was, and remains, unknown. Resolution of tachycardia, sometimes many days after institution of treatment, may be spontaneous rather than a response to treatment. Digoxin was the mainstay of treatment and verapamil was often the second choice. Both of these drugs exert their main effect on ...
Is fetal tachycardia a cause of mortality?
Fetal tachycardia is an important cause of fetal morbidity and mortality. 1. , 2 Reliable diagnosis in utero has been possible only since the introduction of ultrasound examination of the fetal heart. 2. ,
Is tachycardia prenatal or postnatal?
The mechanisms of tachycardia occurring prenatally are likely to be similar to those presenting postnatally. Although previous reports have failed to differentiate or investigate the underlying cause of tachycardia, most separate atrial flutter (very rapid atrial rate with atrioventricular block) from supraventricular tachycardia (with a 1:1 atrioventricular relation). Knowledge of the mechanism of tachycardia is potentially important as it will define both the response to treatment and prognosis.
What causes fetal tachycardia?
Some other warning signs of the fetal tachycardia are caused by thyrotoxicosis or anemia of the mother. Serious causes of the symptoms include congenital heart defect (also known as chiroamnionitis) and fetal arrhythmia. It is interesting to know that the excessive fetal movements can cause the problem too. Usually mothers are happy about the fetal ...
Why does fetal tachycardia last longer?
One of the most common causes of the problem is maternal fever that leads to maternal ketosis. The parents thinking about the fetal tachycardia symptoms should know that the anxiety and the dehydration of the mother can also be a contributing factor.
What is the normal heart rate for a 30 week pregnant woman?
Fetal Tachycardia Symptoms – Causes and Manifestation. No parent ever wants to think about the fetal tachycardia symptoms. It is good to know that the normal heart rate of the baby during the 30 th week of pregnancy is of 120-160 bpm and at term the heart rate is supposed to be of 110-150 bpm.
Does fetal tachycardia increase heart rate?
It is important to remember that fetal tachycardia isn’t associated with increased heart rate during activity or excretion. Nonetheless the parents should be looking for some other signs and symptoms, such as excessive fatigue or sleepiness of the baby.
Can fetal tachycardia cause fuzziness?
In the same time when thinking about fetal tachycardia symptoms you should expect to see fuzziness and there could be changes when the baby is doing some kind of activity. The truth is that there aren’t too many symptoms that would indicate the problem.
What is fetal tachycardia?
Fetal Tachycardia (FT) is described as increase in baseline fetal heart rate (FHR) above 160bpm. Mild fetal tachycardia is described as 161-180bpm and severe tachycardia is defined as greater than 180bpm for at least three minutes. The fetal tachycardia causes include maternal fever, dehydration or anxiety, maternal ketosis, medications like anticholinergic medications, sympathomimetic medications like terbutaline, fetal movement, preterm fetus, maternal thyrotoxicosis and maternal anaemia1. Fetal tachycardia is considered significant (any range >160-180bpm) in the presence of maternal pyrexia as Chorioamnionitis is suspected. Fetal arrhythmia or congenital defect is associated with FHR more than 200 bpm. Baseline FHR tachycardia represents an increase in sympathetic and or a decrease in parasympathetic autonomic nervous system tone1.
What is considered significant in fetal tachycardia?
Fetal tachycardia is considered significant (any range >160-180bpm) in the presence of maternal pyrexia as Chorioamnionitis is suspected. Fetal arrhythmia or congenital defect is associated with FHR more than 200 bpm.
Can fetal tachycardia cause decreased variability?
We know that fetal hypoxia, congenital heart anomalies and fetal tachycardia itself can cause decreased variability so one can argue that fetal tachycardia with reduced variability is not a reassuring sign and may warrant delivery.
Is fetal tachycardia preceded by deceleration?
Hence clinicians may face another dilemma in cases where fetal tachycardia is not preceded by deceleration in the absence of maternal fever.
Why does tachycardia occur in pregnant women?
Unbalanced nutrition of a pregnant woman, lack of vitamins and nutrients. Tachycardia in the fetus can be caused by blood loss in the mother or taking medications. For reasons that directly affect the embryo developing in the womb, include: Intrauterine infection or hypoxia. Anemia.
How to diagnose tachycardia in a pregnant woman?
To detect violations of the heart rhythm in the baby, use ultrasound, echocardiography of the embryo and radiographic diagnosis.
Why is it important to monitor the heart during pregnancy?
That is why during pregnancy it is very important to monitor the indices of the sinus rhythm of the heart. If in the resting state there is an increased palpitation, then this indicates a disorder of the sinus part, which forms conductive impulses. The pregnant woman experiences heart palpitations, but the body temperature remains within the normal range. Tachycardia in the fetus during pregnancy can be either sinus or caused by various tachyarrhythmias.
How to tell if a woman has tachycardia?
Signs of tachycardia in the fetus during pregnancy. The signs of this pathology look like an increased heart rate in a woman. By increased heart rate means a rhythm of more than 120 beats per minute in a woman, the embryo heart rhythm reaches 170-220 strokes.
What are the symptoms of tachycardia during pregnancy?
Another sign of tachycardia during pregnancy is the numbness of different parts of the body in a woman, chest pain, anxiety.
When is sinus tachycardia observed?
Severe sinus tachycardia is observed in the last trimester of pregnancy, when the embryo is practically formed. Rapid heart rate is explained by intensive gas exchange of the baby. In order to diagnose tachyarrhythmia in the fetus, it is necessary to conduct echocardiography, ultrasound and radiographic examination.
Why is ventricular tachycardia treated only in hospital?
With ventricular tachycardia due to the syndrome of the extended QT interval , treatment is performed only in a hospital setting and with extreme caution. This is because some drugs contribute to the lengthening of the interval, which causes arrhythmia.
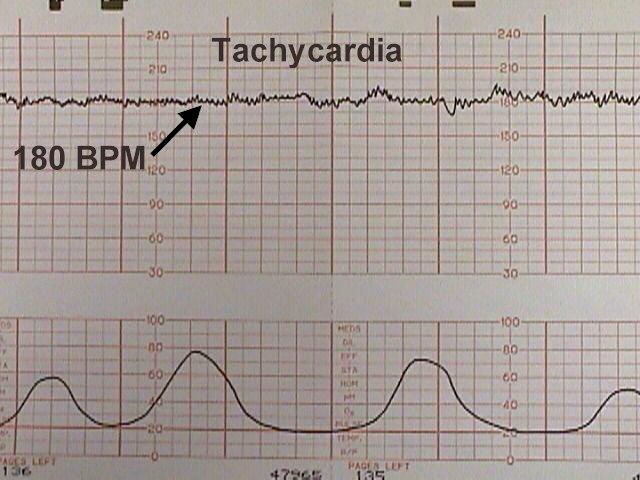
Pathology
Radiographic Features
- An M-modeDoppler study is best for assessment of heart rate. It is recommended that the sampling line intercepts both the atrial and ventricular walls, thereby allowing simultaneous assessment of both ventricular and atrial contractility. Ultrasound may also show evidence of associated complications, such as signs of hydrops fetalis.
Treatment and Prognosis
- The long-term prognosis for most fetuses diagnosed with sinus tachycardia is generally good, with the abnormal rhythm resolving spontaneously during the first year of life in the majority of cases5. Treatment options (if required) include transplacental administration of antiarrhythmic drugs.
Differential Diagnosis
- Considerations include: 1. fetal premature atrial contraction(s): transient and not sustained 2. fetal premature ventricular contraction(s): transient and not sustained
What Every Clinician Should Know
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
- The diagnosis of fetal tachycardia is usually made during office auscultation or at the time of an ultrasound scan. A fetal heart rate of over 160-180 bpm requires a thorough maternal history and examination, screening for potential precipitating factors. A history of leakage of fluid per vagina or uterine tenderness on palpation may indicate intrauterine infection. Fetal tachycardia in labor …
Management
- Extrinsic causes of fetal tachycardia should be identified and treated appropriately. Sinus tachycardia secondary to maternal hyperthyroidism can be managed with antithyroid medications such as methimazole. Antibiotics are necessary for maternal systemic infections and acetaminophen can be used short-term to reduce maternal fever and subsequently to normalize …
Complications
- The major risks of fetal tachycardia are hemodynamic compromise, development of hydrops and intrauterine fetal death. The best strategy to avoid these complications is to identify and treat maternal conditions causing fetal sinus tachycardia and to deliver term pregnancies or medically manage preterm pregnancies with fetal tachyarrhythmias that have features associated with a p…
Prognosis and Outcome
- The outcome of pregnancies complicated by fetal tachycardia is related to the underlying cause of the arrhythmia. PACs and PVCs are benign and the prognosis is excellent. In cases where these extrasystoles result in SVT and in utero medical therapy is successful, a favorable outcome is also expected. The majority of these infants are treated with antiarrhythmic agents for 12 month…
What Is The Evidence For Specific Management and Treatment Recommendations
- Cuneo, BF. “Treatment of fetal tachycardia”. Heart Rhythm. vol. 5. 2008. pp. 1216-8. (Review of the treatment options for fetal tachycardia.) Lopriore, E, Aziz, MI, Nagel, HT, Blom, NA, Rozendaal, L. “Long-term neurodevelopmental outcome after fetal arrhythmia”. Am J Obstet Gynecol. vol. 201. 2009. pp. 46.e1-5. (One of few studies looking at neurodevelopment outcomes of tachyarrhythm…