
What is the treatment for the FOP disease?
Treatment
- Early detection is the best way to lessen the progression of the disorder, but not to treat the disease. ...
- Lessening the progression by avoiding bumps and falls.
- There are different medical measures to increase pulmonary function, decrease respiratory compromise, and prevent pneumonia and influenza. ...
What are symptoms of FOP?
Symptoms of the genetic condition include:
- Episodes of muscle swelling and inflammation followed by rapid ossification after trauma to a muscle
- Difficulty speaking and eating as mouth becomes affected
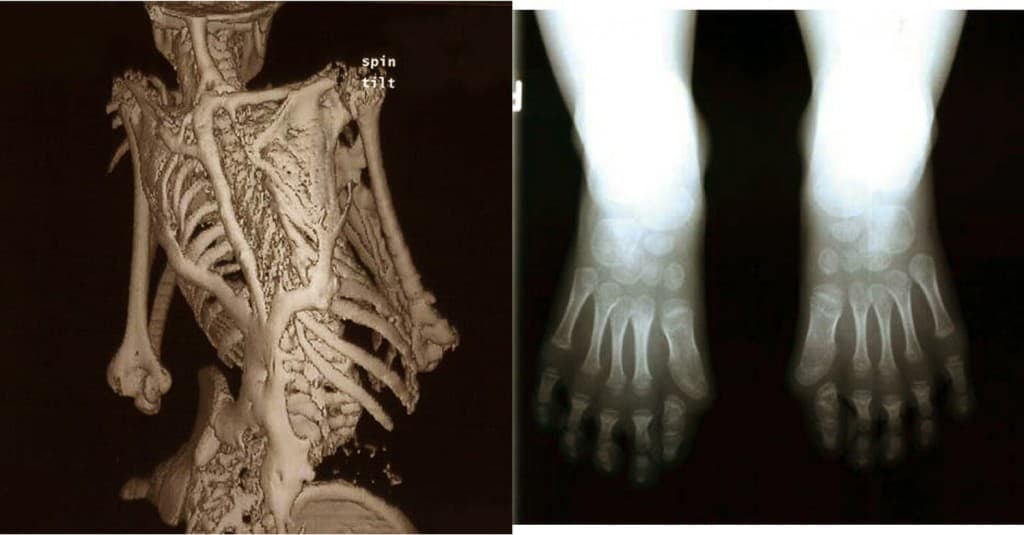
- Malformed big toes present at birth: This abnormality often helps distinguish FOP from other musculoskeletal conditions
What causes fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva?
Objectives:
- Describe the etiology of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva.
- Review the common presentation of a patient with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva.
- Identify the various investigations required for diagnosing fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva.
How many people have fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva?
This condition occurs in about 1 in 1,600,000 newborns and about 800 people worldwide are known to have FOP. [1] [2] Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is characterized by the gradual replacement of muscle tissue and connective tissue (such as tendons and ligaments) by bone, restricting movement.

Are you born with FOP?
FOP is the most disabling condition of ectopic skeletogenesis. Children who have FOP appear normal at birth except for congenital malformations of the great toes (Figures 1 and 3).
Can FOP be passed down?
FOP is a rare condition, occurring at a population frequency of about one per 2 million, and can be inherited by autosomal dominant inheritance, although most cases are sporadic new mutations in the affected person. A child carrying the FOP-causing mutation is usually born following an uneventful pregnancy.
What is the life expectancy of FOP?
The median estimated lifespan of individuals with FOP is approximately 56 years of age.
How do you get FOP?
FOP is caused by a mutation in the ACVR1 gene. This gene is involved in growth and development of bones. The mutation allows them to grow unchecked. The gene can be inherited from one parent, but in most cases of FOP, it's a new mutation in a person with no family history of the disease.
How is fibrodysplasia ossificans inherited?
This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder. Most cases of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva result from new variants in the gene. These cases occur in people with no history of the disorder in their family.
What percent of people have FOP?
Q - How many people have FOP? A - It is estimated that FOP affects about 3,500 people worldwide or approximately one in two million people.
Can you get FOP at any age?
The HO in FOP normally presents between birth and 26 years of age, with presentation in the first decade being the most common. There are a few case reports of patients presenting with FOP in their late forties, but age 54 is the oldest presentation reported in the literature to date [9].
Is fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva a genetic disorder?
Overview. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is a rare genetic disorder that causes soft tissues to transform permanently into bone. These bones grow abnormally in the muscles, tendons, ligaments and other connective tissues, forming bridges of extra bone across the joints.
What is the FOP mutation?
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva ( FOP ), sometimes referred to as Münchmeyer disease, is an extremely rare connective tissue disease resulting from a mutation of the ACVR1 gene.
What is FOP in medical terms?
FOP was originally called myositis ossificans progressiva and was thought to be caused by muscular inflammation ( myositis) that caused bone formation. The disease was renamed by Victor A. McKusick in 1970 following the discovery that soft tissue other than muscles (e.g. ligaments) were also affected by the disease process.
What is fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva?
It is the only known medical condition where one organ system changes into another. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva is caused by a mutation of the gene ACVR1.
What is the term for a disease that causes soft tissue to regrow?
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. The effects of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva , a disease which causes damaged soft tissue to regrow as bone. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva ( FOP ), sometimes referred to as Münchmeyer disease, is an extremely rare connective tissue disease resulting from a mutation of the ACVR1 gene.
How many cases of FOP are there in the world?
As of 2017#N#[update]#N#, approximately 800 cases of FOP have been confirmed worldwide making FOP one of the rarest diseases known. The estimated incidence of FOP is 0.5 cases per million people and affects all ethnicities.
How to tell if you have a FOP?
Another telltale sign of FOP is a shortened great toe with a malformed distal first metatarsal and a missing or abnormal first phalanx and/or interphalangeal joint.
What age do you get FOP?
The first "flare-up" that leads to the formation of FOP bone usually occurs before the age of 10.
What is the cause of FOP?
FOP is caused by a mutation in the ACVR1 gene. This gene is involved in growth and development of bones. The mutation allows them to grow unchecked. The gene can be inherited from one parent, but in most cases of FOP, it’s a new mutation in a person with no family history of the disease.
Why is it so hard to eat with FOP?
Limited movement of the jaw can make it hard to eat, which can lead to malnutrition and weight loss. Talking can also be difficult. About half of people with FOP experience hearing impairment. Poor blood flow can lead to pooling of the blood in the arms or legs, causing visible swelling.
What is the misdiagnosis rate for FOP?
The diagnosis can be confirmed with genetic testing. The misdiagnosis rate could be as high as 80 percent. The most common misdiagnoses are cancer, aggressive juvenile fibromatosis, and fibrous dysplasia. Early on, the symptom that can distinguish FOP from these other conditions is a malformed big toe.
How to tell if you have a FOP?
Diagnosis depends on medical history and clinical examination. Symptoms of FOP include: malformations of the big toe. spontaneous flare-ups of inflammation or soft tissue swelling. increased flare-ups after injury, viral illness, or immunizations. difficulty moving . frequent injury due to falling.
How rare is FOP?
FOP is extremely rare. There are 800 confirmed cases worldwide, with 285 of them in the United States. Gender, ethnicity, and race play no role. Unless you have a parent with FOP, there’s no way to assess your risk of developing the condition.
Can a deformed spine cause respiratory infection?
The spine can become deformed or fused. Limited mobility may cause balance and coordination problems that can lead to injury due to falling. Even a minor injury can cause more inflammation and bone growth. Bone growth in the chest can restrict breathing, increasing the risk of respiratory infection.
Is there a cure for FOP?
It’s the only recognized condition that causes one organ system to morph into another. There’s no cure for this chronic, progressive disorder. The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms. Continue reading to learn more about FOP and why early diagnosis is crucial, plus tips for raising awareness of this condition.
Who is the scientist who discovered the genetic mutation that causes FOP?
In April 2006, an international team of researchers led by Eileen M. Shore, PhD and Frederick Kaplan MD of the University of Pennsylvania, published results of research identifying the genetic mutation that causes FOP.
What are the symptoms of FOP?
All individuals with classic FOP have malformations of the great toes and, in approximately 50% of patients, the thumbs. These changes in the skeleton are present at birth (congenital) and are the first clinical signs of this disorder. The most common skeletal malformation associated with FOP is a shortened great toe with a malformed distal first metatarsal and a missing or abnormal first phalanx and/or interphalangeal joint. Other malformations of the toes and fingers may include inward turning of the great toe toward the other toes (hallux valgus), abnormally short fingers and toes (microdactyly), and/or permanent fixation of the fifth finger in a bent position (clinodactyly). Other congenital signs of FOP include proximal medial tibial osteochondromas, malformation of the upper part of the spinal column (cervical vertebrae), and an abnormally short broad neck of the bone in the thigh that extends from the knee to the pelvis (femur).
What is a FOP?
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is a very rare genetic connective tissue disorder characterized by the abnormal development of bone in areas of the body where bone is not normally present (heterotopic ossification), such as the ligaments, tendons, and skeletal muscles. Specifically, this disorder causes the body’s skeletal muscles and soft connective tissues to undergo a metamorphosis, essentially a transformation into bone, progressively locking joints in place and making movement difficult or impossible. Patients with FOP have malformed big toes that are present at birth (congenital). Other skeletal malformations may occur. The abnormal episodic development of bone at multiple soft tissue sites frequently leads to stiffness in affected areas, limited movement, and eventual ankylosis (fusion) of affected joints (neck, back, shoulders, elbows, hips knees, wrists, ankles, jaw – often in that order).
Why should biopsies be avoided when FOP is suspected?
Biopsies should be avoided when FOP is suspected because these tests may result in rapid bone formation in those areas where tissue is removed. Intramuscular injections (e.g., immunizations) must be avoided, and dental therapy should preclude injections of local anesthetics and stretching of the jaw. In addition, individuals should avoid any situations, such as falls, that may cause blunt trauma, since trauma may cause abnormal bone development in most cases. Various viral illnesses including influenza and influenza-like illnesses may provoke flare-ups of the condition.
How many people have FOP?
FOP is a very rare inherited connective tissue disorder that was first identified in the 18th century. Of an estimated 4000 affected individuals worldwide, there are approximately 900 known patients. This disorder affects both genders and all ethnicities.
What are the congenital signs of FOP?
Other congenital signs of FOP include proximal medial tibial osteochondromas, malformation of the upper part of the spinal column (cervical vertebrae), and an abnormally short broad neck of the bone in the thigh that extends from the knee to the pelvis (femur).
When does FOP flare up?
Episodic flare-ups (inflammatory soft tissue swellings) of FOP usually begin during early childhood and progress throughout life. Most cases of FOP occur as the result of a sporadic new mutation and the genetic mutation that results in this disorder has been identified.
Where does FOP start?
FOP often starts in early childhood. It begins around the shoulders and neck , then works its way down through the rest of the body. As you get older, bone replaces more and more of soft tissue, but how quickly that happens varies from person to person.
How to tell if you have FOP?
Usually it's found during a physical exam when the doctor looks for the two main signs -- the short and inward-pointing toes and the tumorlike growths on the shoulders, back, and neck. Your doctor can make sure it’s FOP with a blood test that looks for the glitch in the gene that causes it.
What is the condition where the body breaks down?
Sometimes you need flexibility and strength. Other times you need hardness and structure. In a rare condition called fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP), this system breaks down. Your body’s soft tissues -- muscles, ligaments, and tendons -- turn into bone and form a second skeleton outside your normal one.
Can bone grow too much?
But with this problem in your gene, bone grows too often and too much. In most cases, you don’t get FOP -- which is also known as myositis ossificans progressive -- from your parents. That happens sometimes, but more often, there’s a change in your genes during your lifetime that causes it.
Overview
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva is an extremely rare connective tissue disease in which fibrous connective tissue such as muscle, tendons, and ligaments turn into bone tissue. It is the only known medical condition where one organ system changes into another. It is a severe, disabling disorder with no current cure or treatment.
Signs and symptoms
For unknown reasons, children born with FOP often have malformed big toes, sometimes missing a joint or, in other cases, simply presenting with a notable lump at the minor joint. The first "flare-up" that leads to the formation of FOP bone usually occurs before the age of 10. The bone growth generally progresses from the top of the body downward, just as bones grow in fetuses. A child with FOP will typically develop additional bones starting at the neck, then at the shoulders, arms…
Causes
FOP is caused by an autosomal dominant allele on chromosome 2q23-24. The allele has variable expressivity, but complete penetrance. Most cases are caused by spontaneous mutation in the gametes; most people with FOP cannot or choose not to have children. A similar but less catastrophic disease is fibrous dysplasia, which is caused by a post-zygotic mutation.
Genetics
FOP is an autosomal dominant disorder. Thus, a child of an affected heterozygous parent and an unaffected parent has a 50% probability of being affected. Two affected individuals can produce unaffected children. Two unaffected individuals can produce an affected offspring as a result of the mutation of the gene. The homozygous dominant form is more severe than th…
Diagnosis
Generally, FOP can be diagnosed with radiographs. Early diagnosis of this disorder through radiology is very important to avoid unnecessary invasive investigations like biopsies. The smallest or trivial trauma or intramuscular injections can amplify progression of the disease through inflammation hence the favorability of radiology. Clinicians should be aware of this rare entity, as it is frequently misdiagnosed as cancer or other benign entities such as infection, resul…
Treatment
There is no cure or approved treatment for FOP. Attempts to surgically remove bone in a FOP patient may result in explosive growth of new bone. While undergoing anesthesia, people with FOP may encounter difficulties with intubation, restrictive pulmonary disease, and changes in the electrical conduction system of the heart. Activities that increase the risk of falling or soft tissue injury should be avoided, as even minor trauma may provoke heterotopic bone formation.
Epidemiology
As of 2017 , approximately 800 cases of FOP have been confirmed worldwide making FOP one of the rarest diseases known. The estimated incidence of FOP is 0.5 cases per million people and affects all ethnicities.
History
Medical reports describing individuals affected by FOP date back to Dr. Guy Patin in 1648. FOP was originally called myositis ossificans progressiva and was thought to be caused by muscular inflammation (myositis) that caused bone formation. The disease was renamed by Victor A. McKusick in 1970 following the discovery that soft tissue other than muscles (e.g. ligaments) we…