What could increase gravity on Earth?
The Earth can increase its gravity by several methods. In fact the Earth can increase its gravity by using for method. One of the methods, by which the earth can increase its gravitation, is to decrease the speed of its rotation.
What does gravity allow us to do on Earth?
The answer is gravity: an invisible force that pulls objects toward each other. Earth’s gravity is what keeps you on the ground and what makes things fall. So, the closer objects are to each other, the stronger their gravitational pull is. Earth’s gravity comes from all its mass.
How does gravity effect things on Earth?
Top 6 things about gravity
- Gravity is by far the weakest force we know. Gravity only attracts – there’s no negative version of the force to push things apart. ...
- Gravity and weight are not the same thing. Astronauts on the space station float, and sometimes we lazily say they are in zero gravity. ...
- Gravity makes waves that move at light speed. ...
What really causes gravity?
When a mass is present in the above space-time it distorts it so that whilst it remains true that travelling through space causes you to travel through time, travelling through time now causes you to move (accelerate) through space. In other words just by existing, you are compelled to move through space - this is gravity.

Is gravity caused by the Earth spinning?
gravity is caused by the Earth spinning. gravity affects things while they are falling but stops when they reach the ground. It does not operate on things that are moving upwards.
What force causes gravity?
In Newtonian mechanics, mass is what causes gravitational "pull". It is a pull,and only a pull, between any two masses and all masses.
Can we create gravity?
At present, there is no confirmed technique that can simulate gravity other than actual mass or acceleration.
Does time create gravity?
In a sense, it's no. Gravity does NOT warp the flow of time. It's the other way around the warping of time causes gravity.
What are two things that can cause gravitational force?
Any object with mass generates a gravitational pull. So, there is a gravitational force of attraction between every object. The amount of gravitational force between two objects will depend on two things: the masses of the two objects and the distance between them.
What causes gravity according to Einstein?
GETTING A GRIP ON GRAVITY Einstein's general theory of relativity explains gravity as a distortion of space (or more precisely, spacetime) caused by the presence of matter or energy. A massive object generates a gravitational field by warping the geometry of the surrounding spacetime.
Does the strong nuclear force cause gravity?
1) Gravity is due to the relativistic effects of the strong force causing increases in mass and a comparable contraction of space in the atomic nucleus, diluted by the greater atomic volume.
What is an example of the force of gravity?
Some examples of the force of gravity include: The force that holds the gases in the sun. The force that causes a ball you throw in the air to come down again. The force that causes a car to coast downhill even when you aren't stepping on the gas.
What Causes Gravity ?
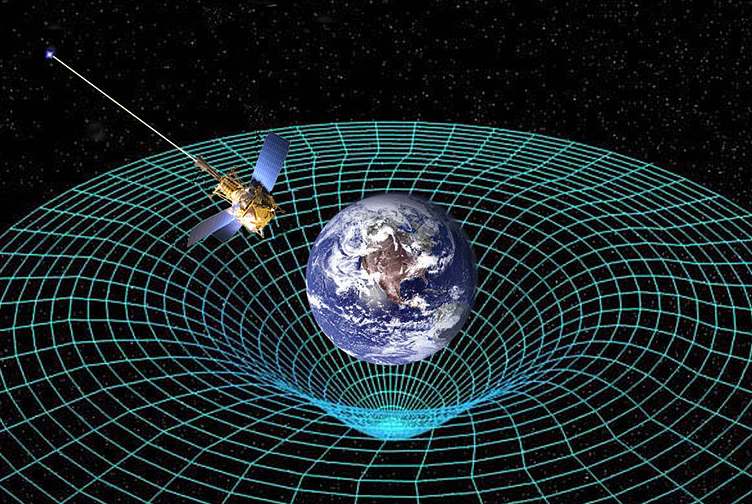
In his theory of relativity, Sir Albert Einstein postulated that gravity is more than a force. According to him gravity is a curvature in the space-time continuum. Because the rubber sheet is distorted by the large ball's weight, this description is commonly seen as a heavy ball lying on a rubber sheet, with smaller balls sinking in towards the heavier object. Although the curvature of space-time cannot be observed directly in reality, it may be seen in the movements of things. Because the space it is travelling through is bent toward that object, every object under the influence of another celestial body's gravity is influenced.
What is Gravity ?
Gravity is the force that pulls items toward the centre of a planet or other entity. All of the planets are kept in orbit around the sun by gravity. Gravity exists in everything that has mass. Gravity is stronger for heavier objects. Gravity weakens with distance as well. As a result, the stronger the gravitational force of two things, the closer they are to each other. The gravity of the earth is caused by all of its mass. Its whole mass exerts a cumulative gravitational force on the entire mass of your body. That is what gives you heft. And if you were on a planet with a lower mass than earth, you would weigh less. The value of gravity on the surface of earth is 9.8 m/s2.
What is the gravity of the Earth?
Earth's gravity is what keeps you on the ground and what makes things fall. An animation of gravity at work. Albert Einstein described gravity as a curve in space that wraps around an object—such as a star or a planet. If another object is nearby, it is pulled into the curve. Image credit: NASA.
What else does gravity do?
Why do you land on the ground when you jump up instead of floating off into space? Why do things fall down when you throw them or drop them? The answer is gravity: an invisible force that pulls objects toward each other. Earth's gravity is what keeps you on the ground and what makes things fall.
What holds the planets in orbit around the Sun?
Gravity is what holds the planets in orbit around the sun and what keeps the moon in orbit around Earth. The gravitational pull of the moon pulls the seas towards it, causing the ocean tides. Gravity creates stars and planets by pulling together the material from which they are made.
Why is gravity important?
Gravity is very important to us. We could not live on Earth without it. The sun's gravity keeps Earth in orbit around it, keeping us at a comfortable distance to enjoy the sun's light and warmth. It holds down our atmosphere and the air we need to breathe.
What would happen if we were on a planet with less mass than Earth?
That's what gives you weight. And if you were on a planet with less mass than Earth, you would weigh less than you do here. Image credit: NASA. You exert the same gravitational force on Earth that it does on you.
Which color has stronger gravity?
Areas in blue have slightly weaker gravity and areas in red have slightly stronger gravity. Image credit: NASA/University of Texas Center for Space Research. GRACE detects tiny changes in gravity over time. These changes have revealed important details about our planet.
Does gravity come from mass?
Image credit: NASA. Anything that has mass also has gravity. Objects with more mass have more gravity. Gravity also gets weaker with distance. So, the closer objects are to each other, the stronger their gravitational pull is. Earth's gravity comes from all its mass.
What is the gravity of the Earth?
The gravity of Earth, denoted by g, is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation (from mass distribution within Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation ). In SI units this acceleration is measured in metres per second squared ...
How much gravity is on Earth?
Gravity on the Earth's surface varies by around 0.7%, from 9.7639 m/s 2 on the Nevado Huascarán mountain in Peru to 9.8337 m/s 2 at the surface of the Arctic Ocean. In large cities, it ranges from 9.7806 in Kuala Lumpur, Mexico City, and Singapore to 9.825 in Oslo and Helsinki .
Why is gravity different at different latitudes?
The second major reason for the difference in gravity at different latitudes is that the Earth's equatorial bulge (itself also caused by centrifugal force from rotation) causes objects at the Equator to be farther from the planet's centre than objects at the poles. Because the force due to gravitational attraction between two bodies (the Earth and the object being weighed) varies inversely with the square of the distance between them, an object at the Equator experiences a weaker gravitational pull than an object on the pole.
How fast is the Earth's gravitational force?
Near Earth's surface, gravitational acceleration is approximately 9.81 m/s 2 (32.2 ft/s 2 ), which means that, ignoring the effects of air resistance, the speed of an object falling freely will increase by about 9.81 metres (32.2 ft) per second every second. This quantity is sometimes referred to informally as little g (in contrast, the gravitational constant G is referred to as big G ).
How does gravity decrease with altitude?
Gravity decreases with altitude as one rises above the Earth's surface because greater altitude means greater distance from the Earth's centre. All other things being equal, an increase in altitude from sea level to 9,000 metres (30,000 ft) causes a weight decrease of about 0.29%.
What is the color of the Earth's gravity?
Gravity of Earth. Earth's gravity measured by NASA GRACE mission, showing deviations from the theoretical gravity of an idealized, smooth Earth, the so-called Earth ellipsoid. Red shows the areas where gravity is stronger than the smooth, standard value, and blue reveals areas where gravity is weaker.
What is the standard acceleration of the Earth?
In 1901 the third General Conference on Weights and Measures defined a standard gravitational acceleration for the surface of the Earth: gn = 9.80665 m/s 2. It was based on measurements done at the Pavillon de Breteuil near Paris in 1888, with a theoretical correction applied in order to convert to a latitude of 45° at sea level. This definition is thus not a value of any particular place or carefully worked out average, but an agreement for a value to use if a better actual local value is not known or not important. It is also used to define the units kilogram force and pound force .
Why do scientists map the Earth's gravity?
Because scientists can't see, feel, or directly observe gravitational forces, they map the Earth's gravity using a mathematical model that describes an imaginary spherical surface called the geoid. The geoid represents oceans as smooth, continuous surfaces unaffected by tides, winds, or currents.
How can scientists map gravity?
Scientists can map gravity anywhere on the Earth's surface by measuring tiny changes in distance between the two satellites as each of them speeds up and slows down in response to gravitational force. Archived at NASA's Physical Oceanography Distributed Active Archive Center (PO.DAAC) in Pasadena, California, and the GeoForschungZentrum Information ...
What are the dark blue areas on the Earth's gravity map?
Dark blue areas show areas with lower than normal gravity, such as the Indian Ocean (far right of image) and the Congo river basin in Africa. Dark red areas indicate areas with higher than normal gravity. The long red bump protruding from the lower left side of the image indicates the Andes Mountains in South America, while the red bump on the upper right side of the image indicates the Himalayan mountains in Asia. (Image prepared by The University of Texas Center for Space Research as part of a collaborative data analysis effort with the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the GeoForschungsZentrum in Potsdam, Germany)
How can scientists determine changes in the Earth's gravity?
By measuring changes in the distance between the GRACE mission's lead satellite and trailing satellite , scientists can determine changes in the Earth's gravity. (Image courtesy of NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory)
What did Newton describe gravity?
Using the word "gravitas" (Latin for "weight"), he described the fundamental force that keeps objects anchored to the Earth. Since then, scientists have used maps of the Earth's gravity to design drainage systems, lay out road networks, and survey land surfaces. But Newton probably didn't imagine that gravity could reveal new information about ...
How far apart are the satellites in Grace?
GRACE relies on two identical satellites, each about the size of a car. As the satellites fly approximately 220 kilometers (137 miles) apart, one following the other, a microwave ranging system monitors the distance between them to within a micron -- smaller than a red blood cell.
When was the gravity experiment launched?
Launched in March 2002 as a joint venture between NASA and the Deutsches Zentrum fuer Luft und Raumfahrt (German Aerospace Center), the mission was implemented through collaboration ...
How does gravity affect us?
Gravity. The average person probably doesn’t think about it on a daily basis, but yet gravity affects our every move. Because of gravity, we fall down (not up), objects crash to the floor, and we don’t go flying off into space when we jump in the air. The old adage, “everything that goes up must come down” makes perfect sense to everyone ...
Why is gravity affected by objects?
Any object ‘caught’ in another celestial body’s gravity is affected because the space it is moving through is curved toward that object. It is similar to the way a coin would spiral down one of those penny slot cyclone machines you see at tourist shops, or the way bicycles spiral around a velodrome.
What is the relationship between the mass of two objects?
We know from Isaac Newton and his law of gravitation that any two objects in the Universe exert a force of attraction on each other. This relationship is based on the mass of the two objects and the distance between them. The greater the mass of the two objects and the shorter the distance between them, the stronger the pull ...
How are gravitational waves generated?
Another idea is that gravitational waves are generated when an object is accelerated by an external force, but these waves have never been directly detected , either. Our understanding of gravity breaks down at both the very small and the very big: at the level of atoms and molecules, gravity just stops working.
What episode of Astronomy Cast is gravity?
We’ve also recorded an entire episode of Astronomy Cast all about Gravity. Listen here, Episode 102 : Gravity.
Who explained gravity as a force?
A demonstration of gravity with balls on a rubber sheet. Credit: Stanford University. With his theory of relativity, Albert Einstein explained how gravity is more than just a force: it is a curvature in the space-time continuum.
Is gravity a particle?
Besides being a characteristic of space, gravity is also a force (but it is the weakest of the four forces), and it might be a particle, too.
What causes gravity on Earth?
So, in short, the earth's mass causes it to have gravity.
What is Newton's law of gravity?
This is described by Newton's Law of Gravity. Why masses cause gravity, we do not know. So, in short, the earth's mass causes it to have gravity. Anything that has mass will have gravity ( Exhibit a phenomemon called gravitation) not just black holes.
Does everything have mass?
The exciting thing is that everything has mass! Even us, but our mass, like some tens of KGs, are too small to create a gravitational pull, to pull other things , even just a centimeter away.

Overview
The gravity of Earth, denoted by g, is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation (from mass distribution within Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation). It is a vector (physics) quantity, whose direction coincides with a plumb bob and strength or magnitude is given by the norm .
In SI units this acceleration is expressed in metres per second squared (in symbols, m/s or m·s ) or …
Variation in magnitude
A non-rotating perfect sphere of uniform mass density, or whose density varies solely with distance from the centre (spherical symmetry), would produce a gravitational field of uniform magnitude at all points on its surface. The Earth is rotating and is also not spherically symmetric; rather, it is slightly flatter at the poles while bulging at the Equator: an oblate spheroid. There are consequentl…
Direction
Gravity acceleration is a vector quantity, with direction in addition to magnitude. In a spherically symmetric Earth, gravity would point directly towards the sphere's centre. As the Earth's figure is slightly flatter, there are consequently significant deviations in the direction of gravity: essentially the difference between geodetic latitude and geocentric latitude. Smaller deviations, called vertical deflection, ar…
Comparative values worldwide
Tools exist for calculating the strength of gravity at various cities around the world. The effect of latitude can be clearly seen with gravity in high-latitude cities: Anchorage (9.826 m/s ), Helsinki (9.825 m/s ), being about 0.5% greater than that in cities near the equator: Kuala Lumpur (9.776 m/s ). The effect of altitude can be seen in Mexico City (9.776 m/s ; altitude 2,240 metres (7,350 ft)), and by comparing Denver (9.798 m/s ; 1,616 metres (5,302 ft)) with Washington, D.C. (9.80…
Mathematical models
If the terrain is at sea level, we can estimate, for the Geodetic Reference System 1980, , the acceleration at latitude :
This is the International Gravity Formula 1967, the 1967 Geodetic Reference System Formula, Helmert's equation or Clairaut's formula.
An alternative formula for g as a function of latitude is the WGS (World Geodetic System) 84 Elli…
Estimating g from the law of universal gravitation
From the law of universal gravitation, the force on a body acted upon by Earth's gravitational force is given by
where r is the distance between the centre of the Earth and the body (see below), and here we take to be the mass of the Earth and m to be the mass of the body.
Additionally, Newton's second law, F = ma, where m is mass and a is acceleration, here tells us t…
Measurement
The measurement of Earth's gravity is called gravimetry.
See also
• Figure of the Earth
• Geopotential
• Gravity (Gravitation)
• Gravity anomaly, Bouguer anomaly
• Gravitation of the Moon