The primary contributors to heat in the core are the decay of radioactive elements, leftover heat from planetary formation, and heat released as the liquid outer core solidifies near its boundary with the inner core. Unlike the mineral -rich crust and mantle
Mantle
The mantle is a layer inside a terrestrial planet and some other rocky planetary bodies. For a mantle to form, the planetary body must be large enough to have undergone the process of planetary differentiation by density. The mantle lies between the core below and the crust above.
What causes the earths core to become very hot?
There's the heat that comes from radioactive decay, the heat caused by differentiation, or the friction generated by heavy objects being pulled to the core, and the heat that's left over from the initial formation of the planet. But in the end, scientists are unsure exactly how hot the Earth's core is.
Why the Earths interior is so very hot?
There are several reasons why the earth's interior is so much hotter than its surface. First, the earth was formed through gravitational compression of many particles; a portion of that original heat remains, trapped beneath the crust. Second, some of the heat in the middle layers of the interior are...
What heats the earths core?
What causes heat at the Earth's core? There are three main sources of heat in the deep earth: (1) heat from when the planet formed and accreted, which has not yet been lost; (2) frictional heating, caused by denser core material sinking to the center of the planet; and (3) heat from the decay of radioactive elements. Click to see full answer.
What does the heat from the earth's core do?
It also keeps the planet's atmosphere in place and helps animals to find their way around. The heat escaping from the core also makes material move around in different layers of our planet - from the rocky mantle to the rigid plates on the surface, where you and I live.
See more
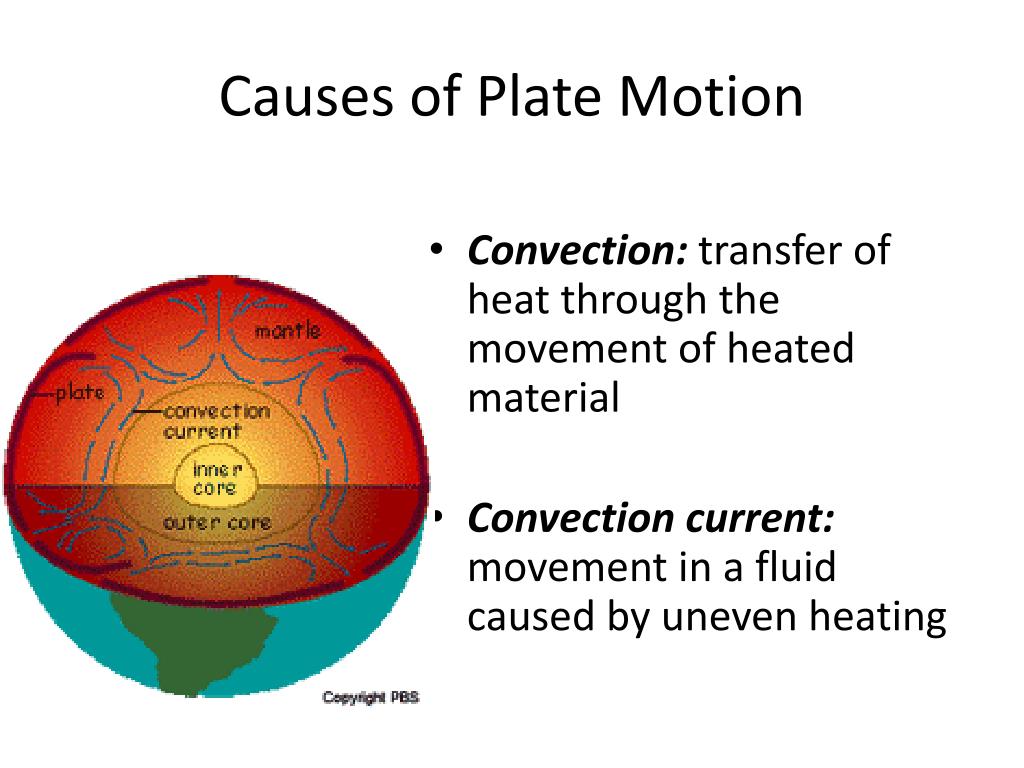
What is the source of heat in the Earth's interior?
For all this, however, Marone says, the vast majority of the heat in Earth's interior—up to 90 percent—is fueled by the decaying of radioactive isotopes like Potassium 40, Uranium 238, 235, and Thorium 232 contained within the mantle. These isotopes radiate heat as they shed excess energy and move toward stability. "The amount of heat caused by this radiation is almost the same as the total heat measured emanating from the Earth."
How hot is the Earth?
At the very center, it is believed temperatures exceed 11,000 degrees Fahrenheit , hotter than the surface of the sun.
How does Marone explain the process of gravitational heat?
In a gravitational sorting process called differentiation, the denser, heavier parts were drawn to the center, and the less dense areas were displaced outwards. The friction created by this process generated considerable heat, which, like the original heat, still has not fully dissipated.
How thick is the Earth's crust?
A cross-section of the Earth reveals three concentric layers. Around the outside, a thin, hard crust ranging from 10 to 100 kilometers thick. Under that, a donut-shaped mantle 2,900 kilometers thick. Instead of dough, it consists of viscous molten rock that flows very slowly, on a geological time scale. "It moves about as fast as your fingernails grow," Marone explains.
Where is the most of the Earth's heat stored?
Most of Earth's heat is stored in the mantle, Marone says, and there are four sources that keep it hot. First, there's the heat left over from when gravity first condensed a planet from the cloud of hot gases and particles in pre-Earth space. As the molten ball cooled, some 4 billion years ago, the outside hardened and formed a crust. The mantle is still cooling down.
What is the outer core of the Earth?
"The inner part is about the size of our moon," Marone says, "and has a density of essentially steel." The outer core surrounding it is an ocean of liquid metal 2,300 kilometers thick. The Earth's rotation makes this ocean flow and swirl, and the moving metal generates the planet's magnetic field.
Where is radioactivity found?
Radioactivity is present not only in the mantle, but in the rocks of Earth's crust. For example, Marone explains, a 1-kilogram block of granite on the surface emanates a tiny but measurable amount of heat (about as much as a .000000001 watt light bulb) through radioactive decay.
What is the source of heat in the Earth's interior?
For all this, however, Marone says, the vast majority of the heat in Earth's interior—up to 90 percent—is fueled by the decaying of radioactive isotopes like Potassium 40, Uranium 238, 235, and Thorium 232 contained within the mantle. These isotopes radiate heat as they shed excess energy and move toward stability. "The amount of heat caused by this radiation is almost the same as the total heat measured emanating from the Earth."
How hot is the Earth?
At the very center, it is believed temperatures exceed 11,000 degrees Fahrenheit , hotter than the surface of the sun.
How thick is the mantle of the Earth?
Under that, a donut-shaped mantle 2,900 kilometers thick. Instead of dough, it consists of viscous molten rock that flows very slowly, on a geological time scale. "It moves about as fast as your fingernails grow," Marone explains. At the center of the Earth lies a two-part core.
How does Marone explain the process of gravitational heat?
In a gravitational sorting process called differentiation, the denser, heavier parts were drawn to the center, and the less dense areas were displaced outwards. The friction created by this process generated considerable heat, which, like the original heat, still has not fully dissipated.
How hot is the Earth's center?
At the very center, it is believed temperatures exceed 11,000 degrees Fahrenheit, hotter than the surface of the sun. A cross-section of the Earth reveals three concentric layers. Around the outside, a thin, hard crust ranging from 10 to 100 kilometers thick. Under that, a donut-shaped mantle 2,900 kilometers thick.
What is the outer core of the Earth?
The outer core surrounding it is an ocean of liquid metal 2,300 kilometers thick. The Earth's rotation makes this ocean flow and swirl, and the moving metal generates the planet's magnetic field.
Why do radioactive isotopes radiate heat?
These isotopes radiate heat as they shed excess energy and move toward stability. "The amount of heat caused by this radiation is almost the same as the total heat measured emanating from the Earth.". Radioactivity is present not only in the mantle, but in the rocks of Earth's crust.
What are the effects of heat on the Earth?
These phenomena, ultimately driven by Earth’s internal heat, have far-reaching effects on other parts of the Earth system, including wind patterns and airborne particles in the atmosphere, and species ranges in the biosphere.
How are human activities influenced by Earth's internal heat?
The use of Earth’s internal heat as a renewable energy source can decrease the burning of fossil fuels and the impact of humans on the Earth system. Hover over or click on the icons to learn more about these human causes of change and how they influence the Earth system.
How hot is the Earth?
After 4.5 billion years, the inside of the Earth is still very hot (in the core, approximately 3,800°C – 6,000°C), and we experience phenomena generated by this heat, including earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building. While Earth’s internal heat is the energy sources for processes like plate tectonics and parts of the rock cycle, ...
How long ago was the Earth formed?
Adapted from the USGS. Most of Earth’s internal heat is left over from when our planet formed, about 4.5 billion years ago. Earth and the other planets in the solar system first began to take shape as countless smaller bodies collided and clumped together. The energy of those violent collisions transformed into heat energy.
What elements are losing heat?
Since its formation, the Earth has been losing heat to space. Certain elements, known as radioactive elements such as potassium, uranium, and thorium, break down through a process known as radioactive decay, and release energy. This radioactive decay in Earth’s crust and mantle continuously adds heat and slows the cooling of the Earth.
What is the core of the Earth made of?
The friction of the iron moving down through the other material generated even more heat. As denser material sank, layers formed inside the Earth: A core primarily made of iron, the less dense mantle, and even less dense crust (to learn more about the structure of the Earth, visit the plate tectonics page).
What is the importance of internal heat?
Global Change Infographic. Earth’s internal heat contributes to the energy budget , specifically the energy available on Earth that drives system processes in the geosphere. Earth’s internal heat is an essential part of How the Earth System Works. Click the image on the left to open the Understanding Global Change Infographic.
Why is the Earth under pressure?
The Earth is under immense pressure due to the tidal forces exerted by the Sun, the Moon, and the other planets in the Solar System. When you include the fact that it is also rotating the Earth’s core is under immense pressure. This pressure basically keeps the core hot in the same way as a pressure cooker. It also helps to minimize the heat it ...
What is the last known source of heat?
The last known source of heat is the radioactive decay of elements in the inner part of the Earth. The Earth is pretty old at 4 billion years old and there are still things we don’t completely understand about its formation.
Why do we have explored further into space than we have explored the depths of the Earth?
It interesting that we have explored further into space than we have explored the depths of the Earth. The main reason for that is the pressure and the heat. We know through seismography that temperatures in the inner parts of the Earth actually exceed the surface temperature of the Sun! That is pretty hot.
How does gravity affect the Earth?
We do know that gravity played a role pulling in more matter and compressing it to form the Earth. When you have matter colliding at high velocities like it did in the early stages of the Solar System’s development all that kinetic energy has to go somewhere. In the case of Earth that energy was turned into heat.
Does the Earth have a nuclear engine?
In short the Earth has a nuclear engine inside it. It is thank to the continous nuclear fission of elements in the Earth’s interior that replaces the heat the Earth loses keeping it nice and hot. This fission process occurs in the form of radioactive decay. It also creates the convection currents in the mantle that drive plate tectonics.
How much heat does the Earth produce?
The average heat flow from the earth's surface is 87mW/m 2 – that is, 1/10,000th of the energy received from the sun, meaning the earth emits a total of 47 terawatts, the equivalent of several thousand nuclear power plants. The source of the earth's heat has long remained a mystery, but we now know that most of it is the result of radioactivity.
How hot is the Earth?
Earth generates heat. The deeper you go, the higher the temperature. At 25km down, temperatures rise as high as 750°C; at the core, it is said to be 4,000°C. Humans have been making use of hot springs as far back as antiquity, and today we use geothermal technology to heat our apartments. Volcanic eruptions, geysers and earthquakes are all signs of the Earth's internal powerhouse.
How do geoneutrinos form?
Geoneutrinos mainly arise from heavy elements with very long half-lives, whose properties are now thoroughly understood through lab studies: chiefly uranium, thorium and potassium. The decay of one uranium-238 nucleus, for example, releases an average of 6 neutrinos, and 52 megaelectronvolts of energy carried by the released particles that then lodge in matter and deposit heat. Each neutrino carries around two megaelectronvolts of energy. According to standardized measures, one megaelectronvolt is equivalent to 1.6 10 -13 joules, so it would take around 10 25 decays per second to reach the earth's total heat. The question is, can these neutrinos be detected?
What is the name of the particles that are found in the Earth's deepest layers?
These kinds of particles are called geoneutrinos, and they provide an original way to investigate the depths of the Earth.
How long did it take for the Big Bang to form?
The Big Bang produced matter in the form of protons, neutrons, electrons, and neutrinos. It took around 370,000 years for the first atoms to form—protons attracted electrons, producing hydrogen. Other, heavier nuclei, like deuterium and helium, ...
How did stars form?
First, stars were born and heavy nuclei formed via accretion in their fiery crucible. This process, called stellar nucleosynthesis, took billions of years. Then, when the stars died, these elements spread out across space to be captured in the form of planets. The earth's composition is therefore highly complex.
What is inside the bowels of the Earth?
Inside the bowels of the earth is an entire panoply of elements, arranged within various onion-like layers. We know little about the inside of our planet. The deepest mines reach down 10km at the most, while the earth has a radius of 6,500km. Scientific knowledge of deeper levels has been obtained through seismic measurements.
