What is a keratoma in horses?
A keratoma is a rare benign tumor of the inner layer of keratin-producing epidermal hoof wall cells that forms inside a horse's foot. As the tumor slowly grows, it expands and separates the hoof wall laminae, causing pain and lameness.
How to remove a tumor in a horse’s hoof?
The tumor and overlying hoof wall requires surgical removal, under local or general anesthesia, as required by the individual case. Parallel cuts are made in the hoof wall on either side of the tumor, and the section of hoof wall is carefully prised away from the underlying sensitive laminae up to the level of the coronet.
What are keratinized hoofs?
It consists of abnormal masses of keratin (the main substance of hoof), which is deposited between the hoof wall and the underlying pedal bone. What causes them? We don’t know for sure, but they are thought to result from trauma or inflammation of the cells that produce horn.
How do I know if my horse has a tumor?
The first thing to be noticed may be signs of bulging of the hoof wall at the coronet. Lameness develops, to a speed and degree depending upon the size, position and speed of growth of the tumor and may appear as sudden onset or chronically-progressive lameness.

What is a Keratoma?
A keratoma is a benign mass made up of keratin that is situated between the hoof wall and distal phalanx.
What is Keratoma surgery?
Surgical removal of a keratoma involves first identifying the exact site of the tumour, followed by removal of an area of outer hoof wall, using an electrical burr. This allows access to the tumour, located between the hoof wall and the deeper sensitive tissues.
How long does a hoof abscess take to burst?
Most abscesses rupture within a few days, but some can take 2-3 weeks to rupture. Stubborn hoof abscesses may need to be radiographed to see if the infection can be visualized and to confirm the proper diagnosis.
What is Quittor in a horse?
What is quittor? Quittor is an old term for a condition that involves death and destruction (necrosis) of the collateral cartilages of the foot (see our information sheet on sidebones), following an infection in the foot (see our information sheet on pus in the foot).
What is another name for a Keratoma?
Keratoma: An area of hardened skin, usually called a callus which is usually a response to frictional trauma to the skin.
What is a Keratoma Milady?
Keratoma – callus. Mole – small brownish spot or blemish. Skin tag – small brown or flesh-colored outgrowth of the skin.
Can you turn a horse out with an abscess?
While many vets and farriers will recommend stabling the horse during treatment, some owners continue to turn their horses out while protecting the dressing with a thick plastic bag secured with thick strong tape. Take care not to cause a pressure sore when taping over the hoof covering.
Should you pop an abscess on a horse?
To heal an abscess in horses, it's best for the farrier or vet to identify where the abscess is, open it up and allow the infection to drain. However, some abscesses rupture on their own during home treatment. Other more severe cases may need to be drained surgically with the help of your vet and/or farrier.
Why does my horse keep getting hoof abscesses?
An abscess occurs when bacteria get trapped inside the hoof. Nails, screws and glass may damage the hoof and leave behind bacteria. Horseshoe nails inside the white line (where the hoof wall meets the sole) may allow bacteria to enter. Poor hoof quality may allow bacteria to enter the deeper parts of the hoof.
What is sand crack in horses?
Sand cracks are vertical splits in the front of a horse's hoof and they run from the coronary band downwards. Any vertical split in the hoof tends to get called a sand crack, even if it is just a superficial, cosmetic flaw.
Why is my horse Quidding?
When teeth are diseased, in disrepair, or missing, horses will sometimes drop feedstuffs from the mouth in the midst of chewing it, a behavior known commonly as “quidding.” A similar condition, called “cud dropping,” has been noted in cattle but is not related to dental health.
What are the symptoms of a quittor?
In the early stages of quittor, it may present as pain and swelling over the affected region. In severe cases it is characterised by pus discharging tracts (sinuses) from or above the coronary band. Lameness will also be a common factor.
How long does it take for an abscess to drain on its own?
If the abscess opens on its own and drains, and the infection seems to clear up in a couple of days, your body should heal on its own. If it doesn't, it's time to call your doctor's office. If you have tooth pain and you suspect there may be an infection, call your dentist.
Do abscesses burst on their own?
A small skin abscess may drain naturally, or simply shrink, dry up and disappear without any treatment. However, larger abscesses may need to be treated with antibiotics to clear the infection, and the pus may need to be drained.
How long should I poultice hoof abscess?
The poultice should be maintained until there is no new discharge for several days and the horse is comfortable. Normally this takes 5-7 days. Following this the hole may need to be packed to prevent dirt entering the hole and re-infecting the hoof.
How do you draw out a hoof abscess?
There are two methods to draw out a hoof abscess. You can use warm water and Epsom salts in a bucket and soak your horse's foot daily. You can also use a drawing salve or poultice pad wrap/bandage on the hoof.
Why do horses get keratoma?
The exact cause of keratoma in horses is unknown. It was originally thought that an injury caused a keratoma to form. However, there are several documented cases where no injury or irritation has occurred. Inflammation of the coronary band is also a possible cause of a keratoma.
How to remove keratoma from horse?
Surgical removal of the tumor will be necessary to ensure that the contours of the hoof wall do not become more deformed. A section of the outer hoof wall will have to be removed so that underlying keratoma can be easily accessed. Depending on exactly where the keratoma is located, your horse may be given local anesthetic that will numb the foot and the horse can remain standing. In other cases, a general anesthetic is necessary and the horse will be completely out and unable to stand. All abnormal cells of the tumor must be removed to prevent the keratoma from growing back.
What is Keratoma?
The tumor begins to form when there is something that alters the normal division of the keratin cells. The tumor begins to increase in size between the outer hoof wall and the pedal bone. The tumor has a keratin core.
How long does it take for a horse's hoof to heal after surgery?
It can take between 6-12 months for the hoof wall to grow back out.
What happens if a horse is lame?
Generally, your horse will exhibit mild lameness that comes and goes. That lameness will progressively worsen as the keratoma grows. If you notice intermittent lameness in your horse, speak with your veterinarian and have a thorough physical examination completed.
How long after keratoma removal can you exercise?
About 30 days to 45 days after surgical removal of the keratoma, light exercise is generally acceptable. However, always consult your veterinarian before changing any part of your horse’s routine.
Why do horses need antibiotics?
Your horse will be put on antibiotics to fight any infections that might occur post-surgery. Be sure to give all medications as directed and consult your veterinarian if you have any questions regarding side-effects or dosage instructions.
What happens when a horse has a keratoma?
However, when horses have an underlying keratoma it will cause the abscess to keep recurring.
Where does keratoma come from?
A keratoma is a benign tumor of the hoof that grows inside the horse's foot. It originates from the keratin-containing tissue, usually underneath the coronet , and between the hoof wall and third phalanx. As the size of the keratoma increases, it will exert pressure on the horse's sensitive laminae and surrounding structures in the hoof, causing pain and lameness.
How long does it take for a keratoma to heal?
Prolonged post-surgical care is required, since the hoof takes at least 10 to 12 months to grow back. Frequent bandage changes are required, with wound dressings applied regularly to control bleeding and infection. A special shoe is often applied to help stabilize the weakened hoof during the recovery period.
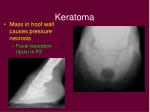
What causes radiolucency on the third phalanx?
Radiographs - Visible semicircular to circular well-demarcated area of radiolucency along the solar margin of the third phalanx, caused by pressure necrosis fromt he karatoma.
How to diagnose keratomas?
Keratomas are diagnosed based on history (of recurring abscesses in the same foot), clinical signs, and radiographs of the foot. Radiographs will show the appearance of an indentation in the coffin bone inside the hoof, due to the loss of calcium in the bone.
How long does it take for a dog's hoof to grow back?
Good, however it can take up to a year before regrowth of the hoof.
Do keratomas grow back?
Once removed, keratomas don't usually grow back, and since they are a benign tumor, they don't spread.
Pathophysiology
Some controversy exists in the literature regarding the precise etiology and pathophysiology of keratomas.
Timecourse
Often a prolonged history with intermittent flare-ups initially thought to be simple recurrent foot abscessation.
This article is available in full to registered subscribers
Sign up now to obtain ten tokens to view any ten Vetlexicon articles, images, sounds or videos, or Login