
Parathyroid hormone is a protein made by the parathyroid gland under the control of serum calcium activity. Intermittent PTH stimulation increases osteoblast activity, although PTH is bifunctional and mediates bone matrix degradation at higher concentrations. Click to see full answer.
What increases osteoblast activity Quizlet?
Nov 15, 2021 · Parathyroid hormone is responsible for increasing osteoclast activity to release more calcium into the bloodstream. What is osteoblastic disease? Bone Damage The new bone-forming, or osteoblastic lesions, causes the bone to become weak and deformed. Osteoblastic lesions are more frequently seen in spread of prostate, bladder, and stomach cancer.
What happens when osteoblastic bone formation exceeds osteoclastic bone resorption?
Feb 25, 2020 · What causes increased osteoblastic activity? Intermittent PTH stimulation increases osteoblast activity , although PTH is bifunctional and mediates bone matrix degradation at higher concentrations. In mice, mutations that reduce the efficiency of ACTH-induced glucocorticoid production in the adrenals cause the skeleton to become dense …
How does cancer affect osteoblast and osteoclast activity?
Nov 15, 2021 · What causes increased osteoblastic activity? Without enough vitamin D, your bloodstream will not properly take up the calcium in milk, calcium supplements, or other sources. Low levels of vitamin D will also trigger a series of …
Does osteoblastic activity increase or decrease calcium?
Mar 29, 2020 · What increases osteoblast activity? Parathyroid hormone is a protein made by the parathyroid gland under the control of serum calcium activity. Intermittent PTH stimulation increases osteoblast activity, although PTH is bifunctional and mediates bone matrix degradation at higher concentrations. Click to see full answer.
What increases the activity of osteoblasts?
Intermittent PTH stimulation increases osteoblast activity, although PTH is bifunctional and mediates bone matrix degradation at higher concentrations.
What factors affect osteoblastic and osteoclastic activity?
What affects osteoblast and osteoclast activity? Gravity, Mechanical stress, Calcitonin and parathyroid hormone levels, and blood calcium level.
What stimulates osteoblasts to become active?
The forward signaling mediated by EPH (OC-OB) stimulates osteoblast differentiation and induces bone formation; the reverse signaling mediated by Ephrin (OB-OC) inhibits bone resorption.Mar 2, 2018
What causes increased osteoclast activity?
Low levels of calcium stimulates the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from chief cells of the parathyroid gland. In addition to its effects on kidney and intestine, PTH increases the number and activity of osteoclasts.
What hormone is responsible for osteoblast?
Thyroxine, a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland promotes osteoblastic activity and the synthesis of bone matrix.
Does osteoblast activity increase blood calcium?
Of the possible answers, only increased osteoclast activity would result in higher blood calcium levels. Increased osteoblast activity, decreased parathyroid hormone, and increased calcitonin would all result in lower blood calcium levels.
What causes osteoblastic?
Osteolytic and osteoblastic metastatic bone disease occur because the different cancer cells secrete factors that interact with the naturally occurring cells in the bone and cause bone destruction, new bone formation, or both.
Which hormone increases osteoblast activity to release more calcium ions into the bloodstream?
Parathyroid hormone is responsible for increasing osteoclast activity to release more calcium into the bloodstream.
When do osteoblasts become active?
Osteoblasts are present throughout life, but their activity is highest during embryonic skeletal formation and growth. In an adult organism, osteoblasts are activated when there is need to regenerate a defect or when the bone matrix has been depleted [6].Sep 26, 2016
What does osteoblastic activity mean?
An osteoblast is a cell that develops bone. Bone mass is maintained by a balance between the activity of osteoblasts that form bone and other cells called osteoclasts that remove bone.
Does T3 cause osteoporosis?
The thyroid releases 2 hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). If you have hyperthyroidism—that is, your body produces too much T4—you have an increased risk of developing osteoporosis because being hyperthyroid can trigger an imbalance of bone-eroding activity by the osteoclasts.Mar 9, 2020
Does vitamin D increased osteoclast activity?
In co-culture studies of osteoblasts and hematopoietic cells, active metabolites of vitamin D has been shown to stimulate osteoclastogenesis. This stimulation has been shown to be an increase in RANKL production and consequently osteoclast stimulation.Oct 11, 2016
What are the pathways that affect osteoclasts?
Osteoblasts can affect osteoclast formation, differentiation or apoptosis through several pathways, such as OPG/RANKL/RANK, LGR4/RANKL/RANK, Ephrin2/ephB4 and Fas/FasL pathways . In addition, cytokine released from the resorbed bone matrix, such as TGF-β and IGF-1 also affects the activity of osteoblasts.
Where do osteochondrocytes come from?
Osteochondroprogenitor cells are progenitor cells that arise from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in the bone marrow. They have the ability to differentiate into osteoblasts or chondrocytes depending on the signalling molecules they are exposed to, giving rise to either bone or cartilage respectively.
What hormones are released by calcium?
Low levels of calcium stimulates the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from chief cells of the parathyroid gland. In addition to its effects on kidney and intestine, PTH increases the number and activity of osteoclasts. What stem cells develop into osteoblasts?
What is osteoblastic lesions?
The most current malignant osteoblastic lesions are bone metastases from prostate cancer. These lesions are associated with a deregulation of osteoblast activities, the specialized bone forming cells. Click to see full answer.
How does bone mass maintain its mass?
Bone mass is maintained by a balance between the activity of osteoblasts that form bone and other cells called osteoclasts that break it down . Beside above, what are blastic lesions? Bone metastases result in lesions or injury to the bone tissue.
What is the balance between osteoblasts and osteoclastic bone?
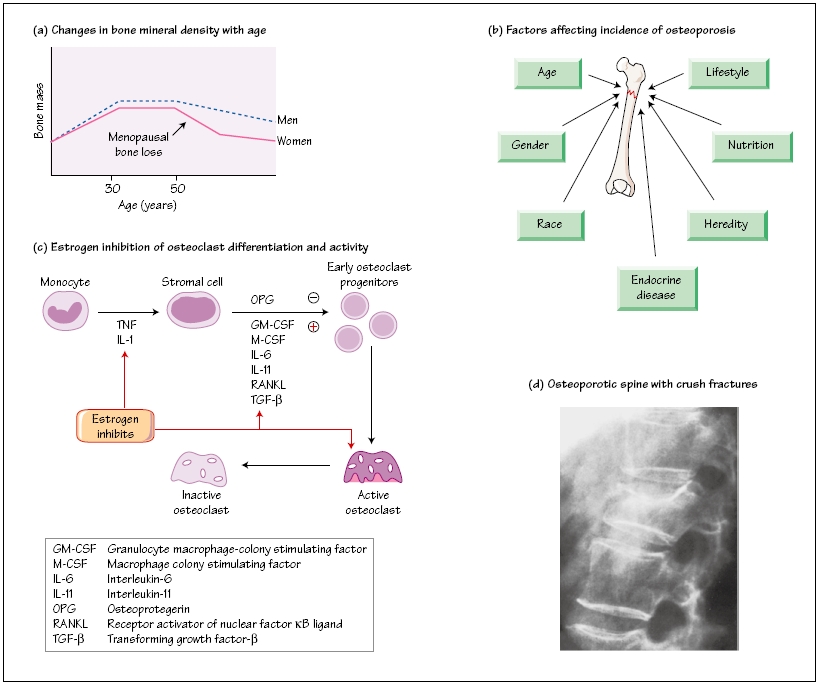
The bone tissue in humans is renewed and reconstructed continuously with a dynamic balance between osteoblastic bone formation and osteoclastic bone resorption . Osteoclasts, the only cells with bone resorption function in vivo, maintain the balance of bone metabolism by cooperating with osteoblasts that are responsible for bone formation ( 1 ). During the process of osteoclast maturation, two hematopoietic factors, macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF, also called CSF-1) and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL), are required ( 2, 3 ). Osteoclast differentiation and activation research have focused on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor and TNF-like proteins, such as receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B (RANK), RANKL, and osteoprotegerin (OPG). The binding of RANKL to its receptor RANK activates signaling pathways that ultimately lead to osteoclastogenesis; however, this process can be suppressed by OPG, which is a soluble “decoy receptor” for RANKL ( 4, 5 ).
What is the cause of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease characterized by a loss of bone mass and the destruction of bone microstructure, leading to fragility and fractures ( 22 ). It is considered to be a multifactorial disease potentially caused by genetic mutations, endocrine disorders, and nutritional deficiency.
What is the mechanism of bone metastases and bone destruction found in cancer?
The mechanism of bone metastases and bone destruction found in cancer is also related to the direct activation of osteoclasts by RANKL , which is secreted by cancer cells ( 15, 16 ). In addition, high expression of RANK (the RANKL receptor) on the osteoclast surface is an important factor in Paget’s disease ( 17 ).
Which enzyme is secreted by osteoclasts during bone resorption?
Cathepsin K , which is specifically expressed and secreted by activated osteoclasts during bone resorption, is a key enzyme in the degradation of critical proteins in the bone matrix, including type I collagens ( 86 ). Bone resorption can be inhibited by the removal of cathepsin K from osteoclasts.
Which cells are responsible for bone resorption?
Osteoclasts, the only cells with bone resorption functions in vivo, maintain the balance of bone metabolism by cooperating with osteoblasts, which are responsible for bone formation. Excessive activity of osteoclasts causes many diseases such as osteoporosis, periprosthetic osteolysis, bone tumors, and Paget’s disease.
Is wear particle osteolysis periprosthetic?
Although the mechanism of wear particle-induced peri prosthetic osteolysis is not clear, it is generally agreed that the excessive activation of osteoclasts caused by wear particles plays a critical role in this process ( 10 – 12 ).
Which cytokine is most important for osteoclasts?
TNF-α is stimulated by activated T cells, macrophages, and synovial cells under inflammatory conditions and is the most critical inflammatory cytokine, causing excessive activation of osteoclasts ( 106, 107 ). The expression of TNF-α has several effects on osteoclastogenesis.
