What are the symptoms of an inflamed trachea?
SymptomsAsthma (wheezing)Bluish tint to skin color, or in the mucous membrane of nose or mouth.Coughing or hoarseness.Coughing up blood.Difficulty breathing.Frequent cases of pneumonia or other upper respiratory infections.Respiratory distress.Shortness of breath.More items...
Which diseases or disorders affect the trachea?
The trachea can be felt in the front of the neck. Several types of malignant (cancerous) and benign (noncancerous) tracheal diseases include tracheal and bronchial tumors, tracheal stenosis, and tracheobronchomalacia.
What does it mean if your trachea is swollen?
Epiglottitis is inflammation and swelling of the epiglottis. It's often caused by an infection, but can also sometimes happen as a result of a throat injury. The epiglottis is a flap of tissue that sits beneath the tongue at the back of the throat.
How do you treat an inflamed trachea?
Treatment methods It's recommended that you drink plenty of fluids. You may also take over-the-counter pain medications and cough suppressants. Some find that a humidifier is useful in helping them to breathe more easily and loosening the mucus in their lungs.
What causes tracheitis in adults?
Causes. Bacterial tracheitis is most often caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It often follows a viral upper respiratory infection.
What does an irritated trachea feel like?
Pain or a scratchy sensation in the throat. Pain that worsens with swallowing or talking. Difficulty swallowing. Sore, swollen glands in your neck or jaw.
What are the signs and symptoms of tracheitis?
What are the symptoms of bacterial tracheitis?high fever.deep severe cough.difficulty breathing.wheezing.nasal flaring.cyanosis, a blue tinge to their skin.
How long can tracheitis last?
The term acute bronchitis and tracheitis defines a self-limited (1 to 3 weeks) inflammation of the large airways of the lung that extends to the tertiary bronchi (Fig. 96-1 ). In patients with a primary symptom of cough (Chapter 83), the diagnosis is made if there is no clinical or radiologic evidence of pneumonia.
Does asthma affect trachea?
Asthma affects the airways, which begin just below the throat as a single tube called the trachea. The trachea is situated immediately in front of the esophagus, the passageway that connects the throat with the stomach.
How does COPD affect the trachea?
In people with COPD, the trachea gets narrower when you breathe out. It's thought that the cartilage that makes up the trachea is weaker in someone with COPD. Narrowing of the trachea was seen in people with COPD whether their condition was stable or was in a flare-up.
How do you tell if your trachea is damaged?
SymptomsWheezing, coughing or shortness of breath, including difficulty breathing.A high-pitched squeal coming from your lungs when inhaling.Frequent bouts of pneumonia or upper respiratory infections.Asthma that doesn't respond well to treatment.Chest congestion.Pauses in breathing (apnea)More items...
Overview
Your trachea (windpipe) moves the air you breathe in through your nose and mouth to your lungs. When you have tracheal stenosis, inflammation or scar tissue in your trachea makes it more difficult for air to get through and for you to breathe.
Symptoms and Causes
Many tracheal stenosis symptoms are the same for children and adults. Here are some symptoms children and adults have in common:
Diagnosis and Tests
Healthcare providers use several tests to diagnose tracheal stenosis and decide how to treat it. Those tests might include:
Management and Treatment
Tracheal stenosis is usually treated with surgery. Healthcare providers consider several factors before deciding on your treatment options. Those factors include:
Prevention
Unfortunately, the most common cause of tracheal stenosis is intubation, which is a life-saving medical treatment that can’t be anticipated or avoided.
Living With
You might start by asking your healthcare provider how your surgery will affect you. Every surgery to treat tracheal stenosis will have different post-surgery care. Your healthcare provider will have information about your next steps.
What is the trachea?
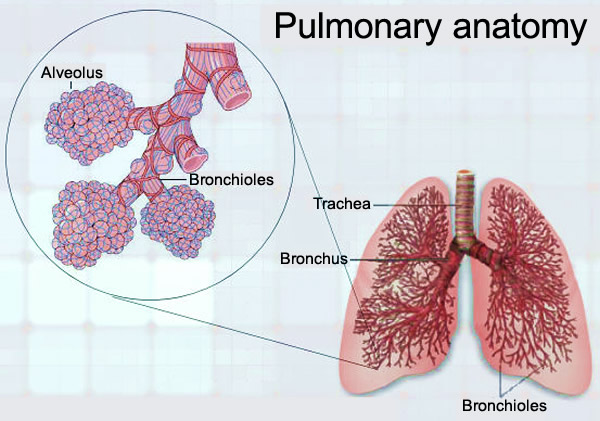
Your trachea is also known as your windpipe. It’s an important part of your body’s airway system. When you inhale air through your nose or mouth, it travels through your larynx, or voice box, and down your trachea. Your trachea branches into two tubes, called your bronchi, which deliver air to your lungs. In addition, your trachea allows carbon ...
What is the condition where the trachea allows carbon dioxide to leave the body?
In addition, your trachea allows carbon dioxide-rich air to leave your body when you exhale. Tracheitis is an infection of your trachea. When caused by bacteria, it’s known as bacterial tracheitis. This condition is rare and typically affects young children. If it isn’t treated quickly enough, it can lead to life-threatening complications.
How to tell if a child has tracheitis?
If your child develops bacterial tracheitis, it will likely happen after they’ve contracted an upper respiratory infection (URI), such as the common cold. Their initial symptoms may include cough, runny nose, and low-grade fever. After two to five days, they may develop more symptoms of infection and airway obstruction. These can include: 1 high fever 2 deep severe cough 3 difficulty breathing 4 wheezing 5 nasal flaring 6 cyanosis, a blue tinge to their skin
How to help a child breathe?
Your child’s doctor will also focus on clearing your child’s airway. They may need to insert an endotracheal tube into your child’s trachea to help them breath. This procedure is known as intubation. Once the tube is positioned, your child’s doctor will connect it a ventilator. This can help improve your child’s lung function while they recover from their infection.
What test is used to test for bacteria in a child's throat?
These may include: A nasopharyngeal culture, which is a sample of secretions from the uppermost part of your child’s throat to test if bacteria are present. A tracheal culture, which is a sample ...
Why does my child make a loud noise when he breathes?
Your child may also develop stridor. This is a high-pitched sound when they breathe. It’s often a sign of a serious infection and partial airway obstruction. This can be life threatening.
How long does it take for a child to get a bacterial tracheitis?
Their initial symptoms may include cough, runny nose, and low-grade fever. After two to five days, they may develop more symptoms of infection and airway obstruction.
What Are The Causes Of Tracheal Infection?
Tracheal infection is mostly caused due to bacteria . There are number of bacterial pathogens which may cause infection of trachea. Usually tracheal infection is secondary infection that occurs after an attack of viral infection in the upper respiratory tract. It may develop after viral influenza and common cold infection. Following a viral upper respiratory tract infection, bacteria can easily invade the larynx and trachea causing inflammatory changes and swelling.
Why does swallowing food hurt?
Pain while swallowing food. This is because the food pipe and wind pipe are close to each other.
Is tracheal infection common in adults?
Tracheal infection is not as common in adults as it is in children. Bacterial tracheitis is commonly seen in children as the length of trachea is short and therefore bacteria are able to easily invade its tissue. It causes inflammation and swelling blocking the air passage partially or completely.
What causes a tracheal stenosis?
Tracheal stenosis is most commonly caused by inflammation and scarring that follows intubation, insertion of a breathing tube into the trachea during surgery , or when there is the need for mechanical ventilation (respirator). It can also be caused by:
What are the two most common tracheal disorders?
The two most common tracheal disorders are tracheal stenosis and tracheomalacia:
What is a tracheobronchial stent?
Tracheobronchial airway stent: The trachea is propped open with a thin metallic expandable stent placed into the airway through a bronchoscope.
What is the condition where the cartilage in the wall of the trachea softens?
Tracheomalacia is a condition in which the cartilage in the wall of the trachea softens resulting in a floppy or weak airway that collapses with breathing and makes breathing difficult.
What is tracheal reconstruction?
Tracheal resection and reconstruction: The area of tracheal scarring and constriction is cut away (resected), and the two remaining ends of the trachea sewn back together resulting in an unobstructed airway.
What is the procedure for tracheal narrowing?
Laser bronchoscopy: Through a bronchoscope, scar tissue is burned away with a laser beam; the procedure provides short-term but immediate relief of the obstruction. Tracheobronchial airway stent: The tracheal narrowing is propped open with a fine metallic expandable stent inserted into the airway through a bronchoscope.
What is a balloon tracheal dilation?
Bronchoscopic tracheal dilation: Through a bronchoscope (a light used to examine the inside of the airway), a balloon or tracheal dilator is used to widen (stretch) the trachea, providing immediate relief of the airway obstruction and allowing the thoracic surgeon to precisely identify the extent and severity of the narrowing.
What is tracheitis inflammation?
Tracheitis is called inflammation in the mucous membrane of the trachea, which can occur in both acute and chronic forms.
What causes acute banal tracheitis?
Primary acute banal tracheitis is most often caused by exposure to colds (general and local cooling, high humidity in the cold season), creating favorable conditions for the activation of conditionally pathogenic local microbiota, as well as increased content of dust, corrosive gases, toxic vapors and all sorts of allergens. Contributing factors may be chronic heart and lung diseases leading to congestion and hyperemia of the upper respiratory tract mucosa, weakening of the nutritional status, low immunity after infectious diseases or HIV infection. In children, exudative diathesis, rickets, dystrophy, as well as poor living conditions can act as contributing factors that cause tracheitis. Most often, acute tracheitis occurs in children and the elderly in the spring and autumn periods.
What is the name of the virus that infects the mucous membrane of the larynx?
Adenoviruses and respiratory syncytial viruses first infect the mucous membrane of the larynx, viral laryngitis develops, if the disease is not treated, viruses infect the tracheal membrane, a cough characteristic of tracheitis appears.
How to prevent tracheitis during pregnancy?
The only reliable way to prevent tracheitis during pregnancy is prevention , that is, the maximum restriction of contact with patients, sneezing, coughing people who can be found in public places and hospitals.
How is tracheitis determined?
Tracheitis and bronchitis, in addition to standard diagnostic methods, is determined using an auscultatory test: the patient takes a deep breath and then a sharp exhalation. With narrowed bronchi, the exhalation is literally “heard” by a typical bronchial whistle.
How long does tracheitis last?
However, with complex intensive treatment, patients with chronic tracheitis recover no later than one month after the onset of the disease .
When does tracheitis occur?
Most often, acute tracheitis occurs in children and the elderly in the spring and autumn periods. Acute banal tracheitis is characterized by hyperemia of the mucous membrane, which is covered by mucus, sometimes forming separate lumps.
What are the diseases of the trachea and airways?
We have a special interest in these conditions, including tracheal stenosis, tracheal and airway tumors, tracheoesophageal fistula, and tracheomalacia.
What is the most common tracheal tumor?
The most common primary tracheal tumors are squamous cell carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma. Patients often have cough, wheezing, stridor, and hemoptysis (coughing up blood). Evaluation includes a CT scan and bronchoscopy, during which the exact location and character of the tumor is determined. Bronchoscopy can be "flexible" (where the ...
What causes shortness of breath and coughing?
The normal trachea (windpipe) brings air from the mouth and nose to the lungs ( Figure 1 ). Tracheal stenosis is a narrowing of the trachea that can cause shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and stridor ( Figure 2 ). The most common cause is prolonged intubation or tracheostomy, when a tube is used to assist with breathing via a mechanical ventilator. It can also be caused by inflammatory or immunologic diseases. Another cause is idiopathic tracheal stenosis, which occurs mostly in women for unknown reasons.
What is a weakness in the membranous trachea?
Tracheomalacia is a weakness in the membranous (back) trachea and change in the shape of the cartilaginous (front) trachea ( Figure 6 ). When patients with tracheomalacia exhale, the membranous trachea bows towards the cartilaginous trachea, obstructing the airway. This abnormality often extends to the bilateral mainstem bronchi, ...
What is a TEF in a trachea?
Thoracotomy. A tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is an abnormal connection between the trachea and esophagus. These are usually caused by complications of intubation, trauma, or operations such as esophagectomy or laryngectomy. Patients can become very ill due to infected fluid from the esophagus contaminating the lungs.
How to diagnose tracheobronchomalacia?
Tracheomalacia and tracheobronchomalacia are often diagnosed after a long evaluation for shortness of breath, cough, or multiple pulmonary infections. Evaluation starts with a CT scan with images taken during both inhalation and exhalation, and bronchoscopy. The Interventional Pulmonology team often places temporary Y stents to keep the airway open and determine whether surgery is likely to improve symptoms more permanently. The Y stents cannot be left in place for long periods of time.
What causes tracheobronchitis?
Causes and risk factors. Tracheobronchitis is generally caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Viral infections will pass on their own, whereas bacterial infections may require antibiotic treatment. The condition can also be caused by an allergic reaction, so you should avoid known allergens.
What happens when your bronchial lungs are inflamed?
The windpipe and bronchi both carry air to the lungs, so when they become inflamed it usually results in some difficulty breathing and a severe cough.
Why do I have difficulty breathing?
Tracheobronchitis occurs when the windpipe or bronchi become inflamed. This is usually due to a viral or bacterial infection, but it can also be the result of some kind of irritant, such as cigarette smoke. The windpipe and bronchi both carry air to the lungs, so when they become inflamed it usually results in some difficulty breathing ...
What are the two types of bronchitis?
There are two types of bronchitis — acute and chronic. Tracheobronchitis is usually acute, which means the symptoms can be treated to make you more comfortable, but the infection itself usually passes naturally. If the condition is caused by a bacterial infection, then antibiotics may be needed. Chronic bronchitis is caused by extended exposure ...
How long does tracheobronchitis last?
The outlook for a person with acute tracheobronchitis is very good. The condition usually lasts between one and two weeks and often passes by itself. Even in cases where the condition is caused by a bacterial infection, if antibiotics are prescribed promptly, the symptoms should still be eliminated within one to two weeks.
How to predict life expectancy of bronchitis?
There is no way to predict life expectancy in chronic bronchitis, but regular exercise, a healthy diet, and medical treatments can all help to relieve the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Last medically reviewed on February 1, 2018.
What is the risk of bronchitis?
People who smoke or work in environments where they’re exposed to excessive dust or fumes are at increased risk of developing chronic bronchitis.

Epidemiology
- Overall tracheitis on its own is not a common condition. It often arises as neighboring respiratory infections spread to involves the trachea as well. Tracheitis affects small children more frequently because their windpipes are smaller in size and shape. As a result of inflammation, the trachea …
Causes
- There are various causes of tracheitis and infections are by far the most common. The trachea is broad tract that leads from the larynx (voice box) and then divides into the two bronchi, which in turn lead to the lungs. The trachea has C-shaped cartilages which keeps it open. Unlike with other parts of the respiratory tract, especially the bronchi, it cannot widen and narrow to a large degre…
Symptoms
- Tracheitis may be accompanied by infection of the neighboring parts of the respiratory tract and these symptoms may therefore also be present. The first symptoms associated with tracheitis appear within a few days after contracting the infection. Viral infections may also be accompanied by non-specific symptoms like fatigue while bacterial infections usually present m…
Prognosis
- Symptoms worsen with time, particularly with bacterial infections that do not resolve spontaneously and require medical treatment.
Diagnosis
- The healthcare provider examines the breathing in a simple setting. The breathing is usually difficult and labored as a result of inflamed and swollen windpipe. Further tests are carried out to find out the reason of chest congestion and difficulty in breathing. These tests may include checking blood oxygen levels and taking culture from trachea and/or nasal passage to check fo…
Treatment
- The treatment for tracheitis depends on the cause. Viral infections usually do not require any treatment although in severe cases supportive measures are advised. Bacterial infections on the other hand usually requires antibiotics to eradicate the bacteria. The condition should be monitored carefully as a repeat course of antibiotics may be required in severe cases which do …