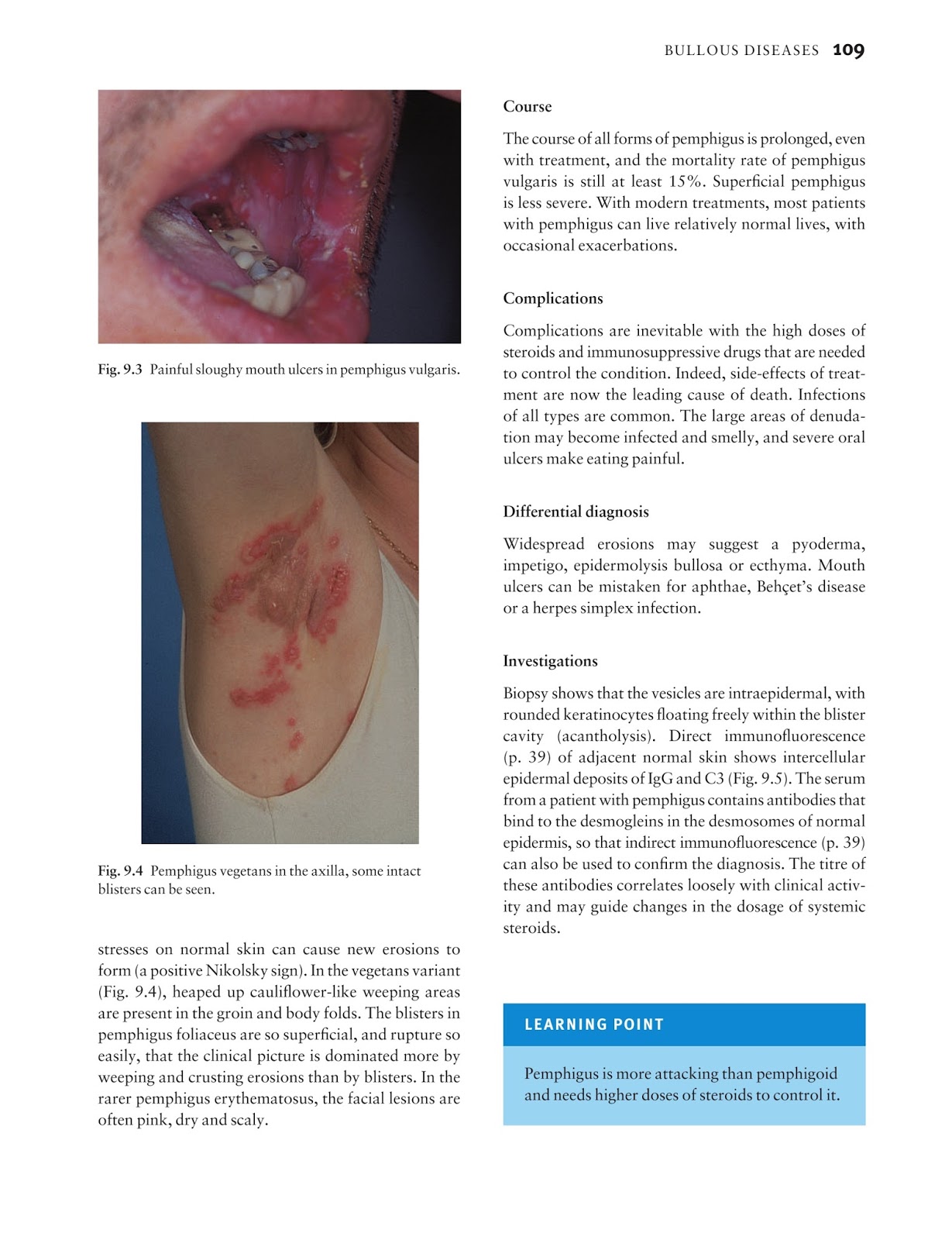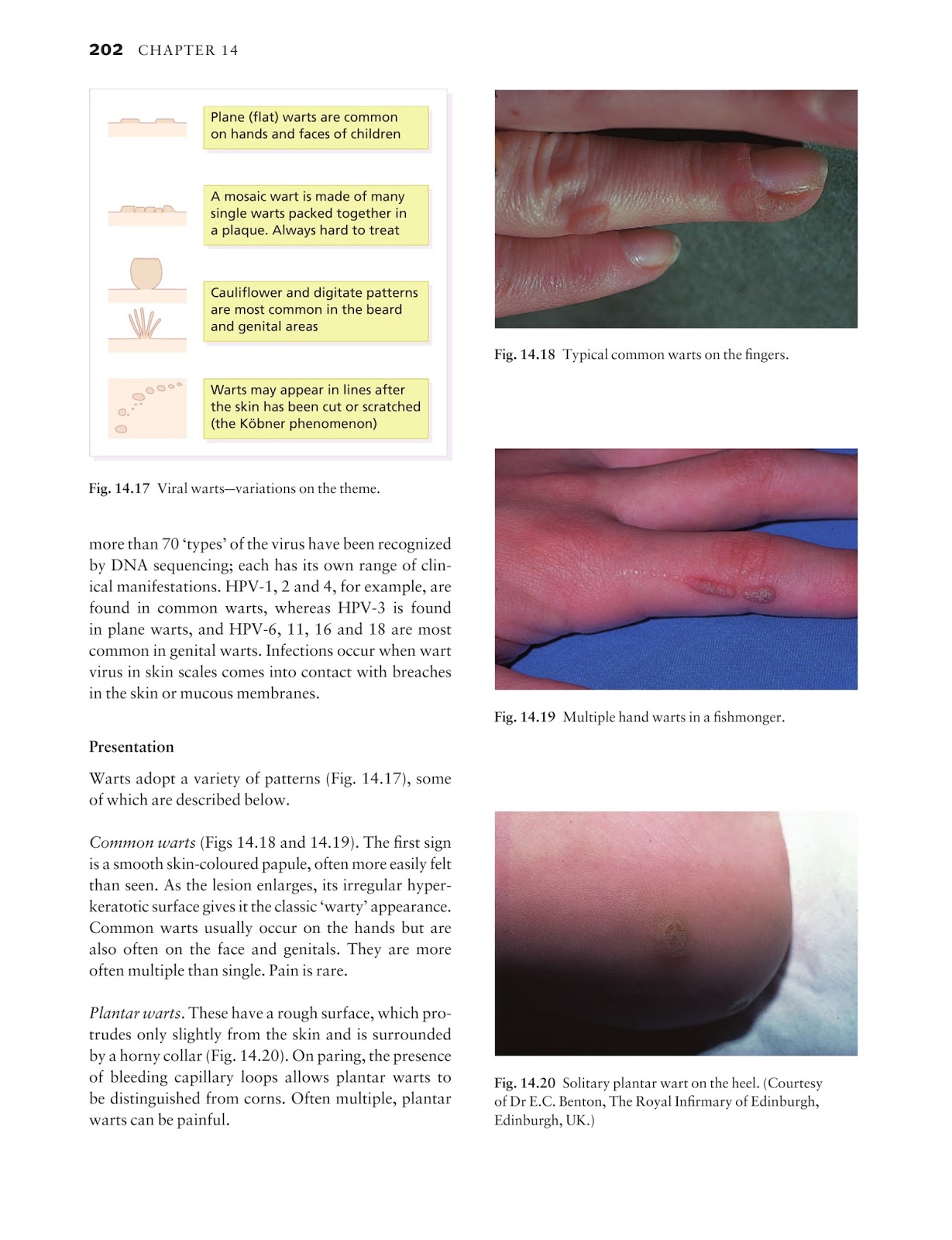
Causes
How to Treat Dysphagia
- Method 1 Method 1 of 3: Diagnosing Dysphagia Download Article. Visit your doctor if you notice symptoms of dysphagia. ...
- Method 2 Method 2 of 3: Getting Medical Treatment Download Article. Get emergency medical care if you’re having trouble breathing. ...
- Method 3 Method 3 of 3: Making Dietary Changes Download Article. ...
Symptoms
There are two types of dysphagia 'high' dysphagia and 'low'dysphagia. The first one is also known as oropharingeal dysphagia while the second one is also called esophageal dysphagia. Most of the neurological problems which lead to 'high' dysphagia are cured by medications or surgical procedures but not to a full extend.
Prevention
What are some causes of dysphagia?
- a condition that affects the nervous system, such as a stroke, head injury, multiple sclerosis or dementia.
- cancer – such as mouth cancer or oesophageal cancer.
- gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) – where stomach acid leaks back up into the oesophagus.
Complications
Symptoms may include: Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) Odynophagia (pain when swallowing) Heartburn. Feeling that food is stuck in the esophagus. Chest pain from esophageal spasms. Choking. Dysphonia (hoarseness or voice loss) Regurgitation (the return of partially digested food from the stomach to the mouth)
How to treat dysphagia naturally?
Is there a cure for dysphagia?
What is the most common cause of dysphagia?
What are the signs and symptoms of esophageal dysphagia?

Can dysphagia be intermittent?
Dysphagia due to benign stricturing (and resulting spasm) is often intermittent for months or years before it becomes fixed and progressive. When they is any narrowing of the esophagus (or inflammation), sudden obstruction can be caused when a lump of food becomes stuck.
Is occasional dysphagia normal?
Occasional difficulty swallowing, such as when you eat too fast or don't chew your food well enough, usually isn't cause for concern. But persistent dysphagia can be a serious medical condition requiring treatment.
What is episodic dysphagia?
Sudden, episodic dysphagia is associated with a lower esophageal mucosal ring, known as a Schatski ring. A Schatski ring often becomes symptomatic with the swallowing of a bolus of meat and is also known as the "steak-house syndrome." A hiatal hernia is often found in association with a Schatski ring.
What are 4 potential causes of dysphagia?
Causes of dysphagia a condition that affects the nervous system, such as a stroke, head injury, multiple sclerosis or dementia. cancer – such as mouth cancer or oesophageal cancer. gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) – where stomach acid leaks back up into the oesophagus.
When should I worry about dysphagia?
You should see your doctor to determine the cause of your swallowing difficulties. Call a doctor right away if you're also having trouble breathing or think something might be stuck in your throat. If you have sudden muscle weakness or paralysis and can't swallow at all, call 911 or go to the emergency room.
Can dysphagia be caused by anxiety?
Some cases of dysphagia are due to structural abnormalities or disease, and some are considered functional, where there is no apparent physical cause. Psychiatric reasons for dysphagia include anxiety disorders, phobias, somatic symptom disorder, and more.
What are the red flags in dysphagia?
Nasal regurgitation, drooling, coughing or choking during meals are relevant and may be suggestive of an oropharyngeal disorder. Systemic review should include weakness and any associated fatigue, tremor and speech disturbance. There may also be shortness of breath or a hoarse voice.
What is Plummer Vinson syndrome?
Plummer-Vinson syndrome is a condition that can occur in people with long-term (chronic) iron deficiency anemia. People with this condition have problems swallowing due to small, thin growths of tissue that partially block the upper food pipe (esophagus).
What are some of the neurological causes of dysphagia?
Some neurological causes of dysphagia include:a stroke.neurological conditions that cause damage to the brain and nervous system over time, including Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, dementia, and motor neurone disease.brain tumours.myasthenia gravis – a rare condition that causes your muscles to become weak.
Can dysphagia go away?
Many cases of dysphagia can be improved with treatment, but a cure isn't always possible. Treatments for dysphagia include: speech and language therapy to learn new swallowing techniques. changing the consistency of food and liquids to make them safer to swallow.
What is the best medicine for dysphagia?
Your gastroenterologist may prescribe corticosteroids, antacids, proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs), and muscle relaxants to treat the cause of your esophageal dysphagia.
How do you fix dysphagia?
Try eating smaller, more frequent meals. Cut your food into smaller pieces, chew food thoroughly and eat more slowly. If you have difficulty swallowing liquids, there are products you can buy to thicken liquids. Trying foods with different textures to see if some cause you more trouble.
Will dysphagia go away?
Many cases of dysphagia can be improved with treatment, but a cure isn't always possible. Treatments for dysphagia include: speech and language therapy to learn new swallowing techniques. changing the consistency of food and liquids to make them safer to swallow.
What can be mistaken for dysphagia?
Odynophagia, which is often confused with dysphagia, is pain with swallowing.
Can dysphagia be benign?
Dysphagia has both benign and malignant causes. A prospective study was conducted on 220 patients using endoscopy, biopsies, and barium swallow. It was found that malignancy is an important cause of dysphagia in the elderly.
Is it possible to recover from dysphagia?
Outside of a few special cases, dysphagia is often temporary and most dysphagic stroke survivors recover fully. Working with experts, like dieticians and speech pathologists, can help survivors manage their dysphagia and improve their ability to swallow safely.
Why is my esophagus narrowing?
Esophagus narrowing and blockages: Esophageal cancer, a tumor or a swollen thyroid gland can constrict the esophagus ( make it narrower). A narrowed esophagus can make swallowing a challenge. Some people develop webs or Schatzki rings (pieces of tissue inside the esophagus). This tissue narrows the tube and makes it hard to swallow chunks of food. Disorders of the opening of the esophagus can also contribute to difficulty swallowing such as cricopharyngeal hypertrophy. Swallowing can be difficult or impossible if anything is stuck in your throat.
What is swallowing disorder?
Dysphagia is simply defined as a swallowing disorder. It can occur in any of the three phases of swallowing: Oral. Pharyngeal. Esophageal. Dysphagia is often noted in stroke survivors and can affect the oral and/or pharyngeal phase of swallowing. The patient may cough or choke while attempting to swallow saliva, liquids, or food.
What is the tube that carries food and water to your stomach?
The esophagus is a muscular tube in your throat that carries food and water to your stomach. Swallowing problems can be mild or severe. The treatment varies depending on what’s causing the problem. Sometimes, doctors can prescribe medication to help you swallow.
Why does my esophagus have scars?
Scarring from acid reflux: Scar tissue can form in your esophagus as a result of GERD (acid reflux disease). GERD can lead to Barrett’s esophagus (irritation in the esophagus lining).
What is esophageal dysphagia?
Esophageal dysphagia: This is a problem of the esophagus. This can be caused when something blocks or compresses the esophagus, there’s a muscular disorder or there are pouches in the esophagus .
What causes swallowing difficulties?
Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ( ALS) and stroke can lead to swallowing difficulties. Muscle disorders: Myasthenia gravis (an autoimmune condition) and muscular dystrophy affect muscles all over the body.
What is modified barium swallow?
Modified barium swallow: During this test, a speech therapist gives you different foods and liquids to chew and swallow. The food will be covered with barium, a minty tasting liquid or pasty material.
Why does eosinophilic oesophagitis cause swallowing problems?
eosinophilic oesophagitis – a type of white blood cell (eosinophil) builds up in the lining of the oesophagus due to a reaction to foods, allergens or acid reflux; the build-up damages the lining of the oesophagus and causes swallowing difficulties.
Why is swallowing difficult?
Obstruction. Conditions that cause an obstruction in the throat or a narrowing of the oesophagus (the tube that carries food from your mouth to the stomach) can make swallowing difficult. Some causes of obstruction and narrowing include: mouth cancer or throat cancer, such as laryngeal cancer or oesophageal cancer – once these cancers are treated, ...
Why is dysphagia so common in elderly people?
The muscles used for swallowing can become weaker with age. This may explain why dysphagia is relatively common in elderly people.
What is the tube that carries food from mouth to stomach called?
mouth or throat – known as oropharyngeal dysphagia. oesophagus (the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach) – known as oesophageal dysphagia. Some causes of dysphagia are explained here.
What is the name of the disease where the immune system attacks the body's natural defence system?
scleroderma – where the immune system (the body's natural defence system) attacks healthy tissue, leading to a stiffening of the throat and oesophagus muscles. achalasia – where muscles in the oesophagus lose their ability to relax and open to allow food or liquid to enter the stomach.
What causes dysphagia in the brain?
Some neurological causes of dysphagia include: a stroke. neurological conditions that cause damage to the brain and nervous system over time, including Parkinson's disease , ...
What is the term for something you're born with?
The term "congenital" refers to something you're born with. Developmental conditions affect the way you develop. Congenital or developmental conditions that may cause dysphagia include: learning disabilities – where learning, understanding, and communicating are difficult.
What is the inflammation of the esophagus that can be caused by acid reflux?
Esophagitis: Esophagitis is inflammation of the esophagus that can be caused by acid reflux or certain medications. Learn more about the types of esophagitis and their treatments.
What is it called when you feel something stuck in your throat?
Esophageal dysphagia is the feeling that something is stuck in your throat. This condition is caused by: spasms in the lower esophagus, such as diffuse spasms or the inability of the esophageal sphincter to relax. tightness in the lower esophagus due to an intermittent narrowing of the esophageal ring.
Why is it so hard to swallow without choking?
Oropharyngeal dysphagia is caused by disorders of the nerves and muscles in the throat. These disorders weaken the muscles, making it difficult for a person to swallow without choking or gagging. The causes of oropharyngeal dysphagia are conditions that primarily affect the nervous system such as: multiple sclerosis.
What is the name of the condition where you can't swallow?
People who have a hard time swallowing may choke on their food or liquid when trying to swallow. Dysphagia is a another medical name for difficulty swallowing. This symptom isn’t always indicative of a medical condition.
What is a thyroid nodule?
Thyroid nodule: A thyroid nodule is a lump that can develop in your thyroid gland. It can be solid or filled with fluid. You can have a single nodule or a cluster of nodules. Learn what causes thyroid nodules and how they are treated.
What are the phases of swallowing?
Types of dysphagia. Swallowing occurs in four phases: oral preparatory, oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal. Swallowing difficulty can be broken down into two categories: oropharyngeal (which includes the first three phases) and esophageal.
What causes stomach pain when swallowing?
In other words, there are lots of things that can go wrong and lead to problems swallowing. Some conditions include: Acid reflux and GERD: Acid reflux symptoms are caused when stomach contents flow up from the stomach back into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn, stomach pain, and burping.
What are the clinical features of esophageal motility disorders?
The clinical significance of esophageal and esophagogastric disorders include motility abnormalities, obstructive lesions, and a combination of the two. Two of the best-known esophageal motility disordersare diffuse esophageal spasm and achalasia. Diffuse esophageal spasm is characterized by high-pressure, repetitive, simultaneous (rather than peristaltic) contractions in the smooth muscle portion of the esophagus, resulting in pain and spasm as well as dysphagia. Regurgitation may occur because of the un-coordinated swallowing. The principal symptom of achalasia is dysphagia. The lower esophageal sphincter is hypertensive and fails to relax completely with swallowing. To compound the problem, peristaltic activity is absent. The degree of dysphagia occurring with achalasia is variable with occasional patients recognizing their symptoms only in retrospect. When chest pain accompanies the typical findings of achalasia, the syndrome of "vigorous achalasia," with a hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter and high-pressure esophageal contractions, is often present. Dysphagia due to motor abnormalities can also occur in diabetes mellitus and scleroderma. In both these entities, there are weak or absent esophageal contractions with ineffective peristalsis.
What does it mean when you feel fullness in your esophagus?
Dysphagia means difficulty swallowing. For this diagnosis it is critical that related symptoms be associated with the act of swallowing of a liquid or solid bolus. When unassociated with swallowing, the sensation of fullness in the upper esophagus suggests globus hystericus, which is distinct from dysphagia. Globus hystericus is often a sign of a functional disorder, but it may also represent an abnormality of the pharyngeal or upper esophageal musculature.
What is the cause of esophageal dysphagia?
Esophageal dysphagiaoccurs when there is difficulty with the passage of solid or liquid material through the esophagus , specifically the region between the upper and lower esophageal sphincter. It results from either abnormal motility of this segment of the esophagus or physical impairment to passage (obstruction). The mechanisms mediating normal esophageal peristalsis are not fully understood, but require smoothly coordinated muscular contraction in one segment with muscular relaxation in adjacent segments.
What causes paraesophageal lesions?
Causes include thyromegaly, mediastinal neoplasia, left atrial enlargement, anomalous aorta, and prior surgery or radiation. In such cases, dysphagia, while a sign of esophageal dysfunction, becomes a sign of primary disease in another organ.
What are the four categories of dysphagia?
Dysphagia can be classified into four categories, based on the location of the swallowing impairment: oropharyngeal, esophageal, esophagogastric, and paraesophageal (Figure 82.1). These four types occur in four separate but continuous anatomic areas. Table 82.2lists the causes of these types of dysphagia; associated symptoms are given in Table 82.3.
Why is it important to have a careful history of dysphagia?
A careful history is of critical importance in the evaluation of the patient with dysphagia because approximately 80% of esophageal disorders can be diagnosed by history alone.
When does dysphagia occur?
When physical obstruction causes dysphagia, the swallowing difficulty for solids is always greater and occurs earlier than for liquids. Symptomatic dysphagia for solids generally occurs when the esophageal lumen is narrowed to less than 12 mm. Dysphagia for liquids may occur when dysphagia for solids arises, or it may not occur until later when the esophageal lumen is narrowed by half or more.
How to diagnose RA swallowing?
In regards to how doctors should approach the assessment and management of swallowing disorders in RA, one way to begin is by understanding where the symptoms are localizing. The doctor could start by asking the patient about mouth and throat dryness, difficulty swallowing and hoarseness. If present, it is important to take a systemic approach and to make a proper, timely referral for further instrumental examination. Currently, the most effective standard for assessment of difficulty swallowing is modified barium swallow, a fluoroscopic procedure designed to determine whether food or liquid is entering an individual’s lungs. Other key examinations include pharyngeal and/or esophageal high-resolution manometry and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. “Once the specific impairments of the swallow have been identified, the treatment plan can be designed to target the specific problem to maximize and optimize swallow” said Dr. Azola.
How many people with dysphagia have sought professional help?
Only 46% of the participants with dysphagia had ever sought professional help, and symptom improvement was observed among 74% of these individuals.
Why is patient education important for swallowing disorders?
Similarly, patient education regarding swallowing disorders in RA is important, so that they can know what signs and symptoms to look for. And if patients do start showing abnormal signs and symptoms, they need to be specific when describing them to their doctor, as there are numerous potential causes.
What is RA in the body?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term autoimmune disorder, typically results in warm, swollen, stiff and painful joints. Aside from pain in the joints and other tissues, oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal motility disorders are also common in patients with RA. In fact, difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, ...
What is FindATopDoc?
FindATopDoc is a trusted resource for patients to find the top doctors in their area. Be visible and accessible with your up to date contact information, certified patients reviews and online appointment booking functionality.
Is dysphagia common in RA?
From doctors’ point of view on dysphagia in RA, the findings from this particular study suggest that the prevalence of swallowing disorders is quite common in RA. Additionally, the findings align with what is seen in medical practice today and in the knowledge on dysphagia at large.
Does dysphagia affect quality of life?
Eating, in general, is an important part of health and well-being. And when dysphagia is present, it can have a significant impact on nutritional status, a negative impact on quality of life, as well as increase morbidity and mortality. It is known that the aging population has a significantly increased prevalence of swallowing disorders ...