What are the causes of reversible and irreversible cell injury?
Factors like hypoxia/ischemia, extreme temperatures, radiation, chemical agents, infectious agents, immune responses, nutrition, and genetics are causes for irreversible cell injuries. What are the Similarities Between Reversible and Irreversible Cell Injury?
What are the causes of injury to a cell?
Other causes for injury to a cell may include intracellular accumulations of carbohydrates, such as in the lysosomal storage disease known as mannosidosis. Furthermore, oxygen deficiency due to anemia, blunt force trauma, toxins, and drugs can all cause either reversible or irreversible injury to a cell and even an entire organ or tissue.
What are the two types of cell injury?
Cell injury can be mainly divided into two types: reversible and irreversible cell injury. Reversible cell injury results in morphological and cellular changes that could be reversed if the stress is taken off. Irreversible cell injury results in complete cell death and normal cellular conditions cannot be achieved even if the stress is relieved .
How do you recognize a cell undergoing reversible cell injury?
A cell undergoing reversible cell injury can be recognized by cellular swelling and the changes in the lipid concentrations in cells. Cellular swelling occurs in response to ion imbalances or due to mechanical injury caused on the plasma membrane. This will affect the transport process across membranes resulting in cellular injury.
What are some examples of irreversible cell injury?
What causes cell and tissue injury?
What is caseous necrosis?
Why does coagulation necrosis occur?
What is the term for cell death caused by irreversible injury?
What happens when a cell is injured?
What causes a yellow-white mixture of dead debris to accumulate?
See 4 more
About this website
What are the seven causes of reversible cell injury?
Oxygen deprivation, Physical agents, Chemical agents and drugs, Immunologic reactions, Infectious agents, Nutritional imbalances, Genetic derangement.
What are the main causes of cell injury?
Physical agents capable of causing cell injury include mechanical trauma, extremes of temperature (burns and deep cold), sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, radiation, and electric shock.
What causes permanent cell injury?
In principle, cell injury can occur due to the following factors: Excessive or overly prolonged normal stimuli. Action of toxins and other adverse influences that could inhibit the vital cell functions (e.g., oxidative phosphorylation or protein synthesis) Deficiency of oxygen and/or essential nutrients and metabolites.
What factors determine whether cell injury is reversible or irreversible?
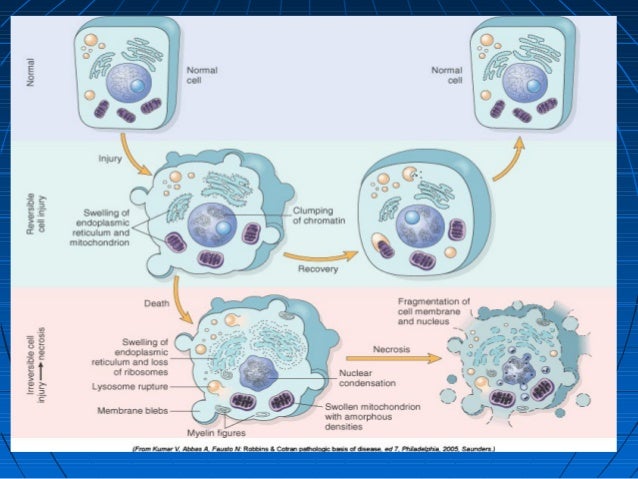
Cell injury is classified as reversible if the injured cell can regain homeostasis and return to a morphologically (and functionally) normal state. Acute cell swelling is the classic morphologic change in reversible injury; however, it is also the typical early change of irreversible cell injury.
When does a cell become irreversibly injured?
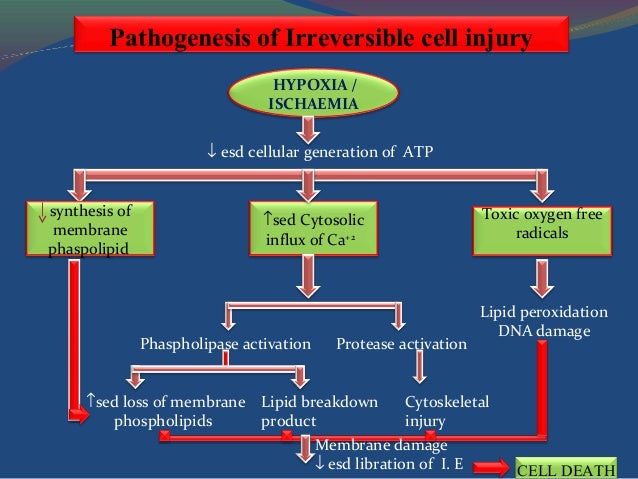
Two phenomena consistently characterize irreversible injury. The first is the inability to reverse mitochondrial dysfunction (lack of oxidative phosphorylation and ATP generation) even upon restoration of oxygen; the second is the development of profound disturbances in membrane function.
What are 7 main causes of cell injury?
Generally, stimuli that cause cellular injury include immunological reactions (hypersensitivity reaction to foreign agents, autoimmune reactions, immune deficiency), nutritional imbalances (protein calorie malnutrition, excessive intake of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins), genetic defects (inborn errors in metabolism ...
What is the difference between reversible and irreversible cell injury?
When cells are injured, one of two patterns will generally result: reversible cell injury leading to adaptation of the cells and tissue, or irreversible cell injury leading to cell death and tissue damage.
Can cell damage be reversed?
Cell damage can be reversible or irreversible. Depending on the extent of injury, the cellular response may be adaptive and where possible, homeostasis is restored. Cell death occurs when the severity of the injury exceeds the cell's ability to repair itself.
What are the three mechanisms of cell injury?
Cellular swelling due to water influx (earliest manifestation of cell injury) Hydropic change or vacuolar degeneration: small, clear vacuoles within the cytoplasm (from distended ER) Plasma. Transfusion Products membrane alterations (blebbing, blunting, loss of microvilli)
What are the hallmarks of irreversible cell injury?
Irreversible cell injury: mitochondria swell, lysosomes swell, damage to plasma membrane and lysosomal membranes leads to enzyme leakage; acidosis somewhat protective by inhibiting enzymatic reactions.
What is an example of reversible cell injury?
Morphological changes of reversible cell injury occur earlier than those of irreversible injury. Example:Myocardial infarction due to blockade of a coronary artery.
What is irreversible cell?
Irreversible cells are those which necessitate alternate of chemicals when they give out electricity these cannot be recharged. Irreversible cells are not amenable to exact theoretical treatment. For reversible cells, thermodynamic principles may be applied.
What are two causes of cellular injury quizlet?
Hypoxia is the most common cause of cellular injury and can be initiated by decreased oxygen in the environment, decreased hemoglobin, decreased red blood cells, or cardiovascular collapse. A free radical-induced injury, chemical injury, and mechanical factors are other types of cell injury but are not the most common.
How many types of cell injury are there?
Types of cell injury: Reversible injury Reversible Injury Ischemic Cell Damage Irreversible injury Irreversible Injury Ischemic Cell Damage (leads to cell death)
How do infectious agents cause cell injury?
Intracellular infectious agents frequently cause disease by damaging the cells that house them. The specific killing of virus-infected cells by cytotoxic T cells thus not only prevents virus spread but removes damaged cells.
How does aging cause cell injury?
Aging is characterized by increased oxidative stress, heightened inflammatory response, accelerated cellular senescence and progressive organ dysfunction. The homeostatic imbalance with aging significantly alters cellular responses to injury.
Irreversible Cell Injury and Necrosis Flashcards
phospholipase activation (via Ca2+) and lack of synthesis of new membrane lipids. Also, breakdown products of membrane phospholipids, like fatty acids and lysophospholipids may accumulate, having a detergent effect on remaining membranes
Irreversible Injury - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
C. Gandhimathi, ... D.K. Srinivasan, in Nanofiber Composites for Biomedical Applications, 2017 17.3.1 Cardiomyocytes remodeling in ischemic heart disease. The cardiomyocytes are the major cells involved in the cardiac remodeling. Immediately following an ischemic insult, irreversible injury and subsequent cell death occurs to the cardiomyocytes. Although cell death occurs through both ...
What is Irreversible Cell Injury?
Irreversible cell injury takes place when a cell is subjected to intense stress. Irreversible cell injury results in cell death. This is either caused by apoptosis or necrosis. Apoptosis is the controlled cell death which takes place in response to cell aging. Necrosis is the process of cell death taking place due to a physical, chemical or a biological agent that causes irreversible cell injury.
How can reversible cell injury be brought back to normal?
The above three outcomes of reversible cell injury can be brought back to the normal by providing the necessary homeostatic mechanisms which will remove the respective stresses on the cells.
What happens when a cell is injured?
Irreversible cell injury results in complete cell death. Ability to Return to Normal State. Cells can return to the normal cellular state when the stress is taken off. Cells cannot return to the normal state even if the stress is taken off. Cause.
What are the two types of cell injury?
Cell injury can be mainly divided into two types: reversible and irreversible cell injury. Reversible cell injury results in morphological and cellular changes that could be reversed if the stress is taken off. Irreversible cell injury results in complete cell death and normal cellular conditions cannot be achieved even if the stress is relieved .
What is the process of cell death that takes place in response to aging?
Apoptosis is the controlled cell death which takes place in response to cell aging. Necrosis is the process of cell death taking place due to a physical, chemical or a biological agent that causes irreversible cell injury. DNA damage.
What is the cause of depleted ATP?
Depleted resources of ATP in the cell which is due to decreased rate of oxidative phosphorylation resulting from oxidative stress.
Can cellular injury be reversed?
This result in abnormal outcomes leading to cellular injury which can either be reversed or complete cell death. Reversible cell injuries can be reversed back to normal while irreversible cell injuries cannot reverse back to normal. This is the difference between reversible and irreversible cell injury.
What is Irreversible Cell Injury?
Irreversible cell injury is injury to a cell that also causes morphological changes to the cell, albeit more permanent and often, more internal to the inner machinery of the cell. If the injurious stimulus is not removed after a long period of time, for example in chronic viral infections, chemical exposures, or an internal response that is intentional (i.e., an immunological response), irreversible injury and ultimately cell death can occur.
What causes cell injury?
However, there are established causes of cell injury including: hypoxia (oxygen deficiency), ischemia (lack of blood flow), physical and mechanical injury, chemical injury, radiation, ...
What is the difference between irreversible and reversible cell injury?
Reversible cell injury is usually the result of the beginning stages of lack of oxygen, also known as hypoxia, or ischemia, the lack of blood flow to cells, while irreversible cell injury involves more insidious agents such as viruses, immunological responses, or genetic disadvantages.
What are the characteristics of a cell undergoing reversible cell injury?
Identifiable characteristics of a cell undergoing reversible cell injury are reduced oxidative phosphorylation, downregulation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, and swelling of the cell caused by changes in ion concentrations within the cell. Other global responses can be see as well. One global response, cellular swelling, is common ...
How can a reversible cell injury be stopped?
Reversible cell injury can usually be stopped by removing or destroying the injurious stimulus, while irreversible cell injury has progressed past a point of “no return.”. 2. Type of Injury involved in Reversible and Irreversible Cell Injury. Reversible cell injury is usually the result of the beginning stages of lack of oxygen, ...
What causes cellular swelling?
Increase in cellular glycolysis to increase ATP stores. Decrease in cellular glycogen; decrease in intracellular pH. Decrease in AT P leads to accumulation of sodium and diffusion of potassium, leading to cellular swelling.
What causes enzyme leakage?
Damage to plasma membrane and lysosomal membranes that cause enzyme leakage
What are some examples of irreversible cell injury?
One such example is radiation that causes lipid peroxidation, or the breakdown of lipid-based cellular structures due to oxidation.
What causes cell and tissue injury?
Other lessons mentioned the wide variety of injuries that can cause a cell to die, such as radiation that may cause lipid peroxidation, or the breakdown of lipid-based cellular structures due to oxidation.
What is caseous necrosis?
Caseous necrosis can be thought of as a middle ground between the more structured coagulation necrosis and the utterly destroyed mess of liquefactive necrosis. If you were to take a piece of tissue undergoing caseous necrosis, it would crumble in your hands like cottage cheese and in longstanding cases may feel a bit gritty as well as a result of tissue calcification. Longstanding bacterial infection such as by tuberculosis or fungal infections are common causes for this type of necrosis.
Why does coagulation necrosis occur?
The major reason that coagulation necrosis occurs is due to a lack of blood or oxygen supply to a part of the body.
What is the term for cell death caused by irreversible injury?
Liquefactive Necrosis. Another form of cell death as a result of irreversible injury is known as liquefactive necrosis. This type of cell death is characterized by rapid enzymatic degradation of cells into a liquid form.
What happens when a cell is injured?
Once an irreversible injury to a cell occurs, then necrosis will result. However, there are different types of necrosis that may occur, and that's what we'll focus in on from now on.
What causes a yellow-white mixture of dead debris to accumulate?
In the case of the latter, the inflammatory response initiated by the bacteria causes a lot of destructive enzymes to be released by cells called neutrophils, resulting in the death of bacteria, cells, and tissues. This causes a yellow-white mixture of dead debris to accumulate.