
Some of the common liver diseases that affect children include:
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, a genetic disorder that damages the liver
- Autoimmune hepatitis, liver inflammation caused by an overactive immune system
- Biliary atresia, inflammation in the bile ducts that carry digestive juices
- Glycogen storage disease, a buildup of glycogen, or sugar, in the liver
- Pediatric liver cancer
What causes liver problems in children?
What Causes Liver Problems?
- Viral Infections. Viral infections can also cause liver problems in children. ...
- Genetic Disorders. Sometimes liver problems are caused by disorders that are passed down the family line; hemochromatosis, for example, a disorder that is genetic and that causes the body ...
- Cholestasis. ...
- Cancer. ...
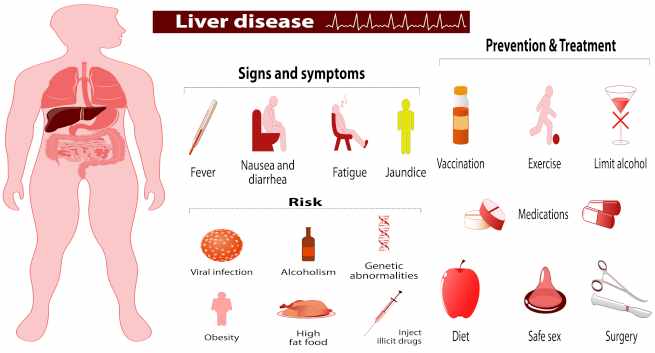
What are the symptoms of liver disease in children?
Other later symptoms, some due to complications, include:
- Reddened palms
- Loss of body hair
- Enlarged liver
- Enlarged spleen
- Appearance of thin, purplish-red, spidery looking blood vessels on the skin, especially around the navel
- Water retention and swelling in the legs and abdomen
- Vomiting blood
- Itching
- Abdominal infections
- Forgetfulness or confusion
What are the signs of a liver problem?
- Strange Colored Elimination – Pale, bloody or tar-colored stool and/or dark colored urine.
- Fatigue and General Malaise
- Nausea and Low Appetite
- Liver Area Pain (upper right hand side of the abdomen) – likely caused by inflammation in the liver.
What are treatment options for liver disease?
Treatment and management include very diligent and judicious use of:
- Diuretics
- Non-selective beta blockers
- Diagnostic and therapeutic paracentesis (often recurrent)
- Antibiotic prophylaxis
- Endoscopic screening
- Surveillance and treatment of varicose veins
- Gastropathy and gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE)
- Identification and treatment of iron deficiency anemia
- ECHO of heart
- Right heart catheterization
What is the best treatment for chronic liver failure?
Chronic liver failure always requires long-term care by a liver specialist who may prescribe various medications to treat or prevent complications – vitamins, antibiotics, diuretics (water pills), drugs to lower blood pressure or medicines to help against sleepiness or confusion (encephalopathy).
What happens when the liver stops working?
Liver failure happens when the liver becomes so sick that it stops working. Liver failure can be due to many different types of injury or disease. Liver failure may come on suddenly (acute) or be a long-lasting disease (chronic). Some cases of liver failure get better without treatment.
What are the two types of liver failure in children?
There are two main types of liver failure in children: Acute liver failure. This type comes on suddenly. It occurs in children with no known prior liver disease. Chronic liver failure. This type occurs when a long-lasting liver disease becomes much worse, either slowly or suddenly.
What is the largest organ in the body?
The liver is the largest organ inside the abdomen (belly). It has many important jobs. Some of them have to do with filtering toxic or harmful chemicals out of the blood, with using medicines and with processing other foreign substances. The liver also helps to digest food.
Why does my liver fail?
The liver can fail due to many different types of injury or disease. Often, a cause cannot even be found. Some known causes of acute (sudden) liver failure include: Viruses, such as herpes (HSV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV) or hepatitis A, B and E.
What are the causes of a backup of blood flow in the liver?
Inherited conditions, such as hemochromatosis (too much iron in the body), alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency or cystic fibrosis ( inherited diseases that also affect the lungs) Heart problems that reduce blood supply to the liver or lead to a backup of blood flow in the liver.
What are some medicines that cause hepatitis?
Certain medicines, such as erythromycin, valproic acid or too much acetaminophen. Immune system problems, such as [autoimmune hepatitis] Low blood flow to the liver, such as in heart failure, shock or a blocked blood vessel.
Why do newborns have jaundice?
Newborns may develop jaundice as part of inflammation of the liver associated with A1AT deficiency. Older children and teens can present with a liver that has been inflamed for a long time, causing scarring (cirrhosis) to develop. Lung disease usually develops only in adulthood.
What is the A1AT?
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT) deficiency is an inherited disease in which a protein known as A1AT is unable to be released from the liver into the blood in adequate amounts. This causes a deficiency of the A1AT protein in the circulation. A1AT is a specialized protein that blocks the action of other proteins important in inflammation (swelling) ...
What is A1AT in the body?
A1AT is a specialized protein that blocks the action of other proteins important in inflammation (swelling) and breakdown of tissues in the body. When the A1AT protein is deficient in the circulation, tissue inflammation and tissue damage is more severe, especially in the lungs. The defective A1AT protein that remains in ...
Why does jaundice occur?
This alarming syndrome usually occurs in a previously well infant, child or adolescent and can be caused by a number of infectious or metabolic causes and reactions to medication. Jaundice occurs rapidly, often in concert with gastrointestinal symptoms like vomiting and fever.
Is there a cure for A1AT deficiency?
There is no cure for A1AT deficiency. Therapy involves controlling symptoms and attempting to prevent the development of complications. To protect their lungs, it is very important that the affected person and those around them not smoke. Vaccinations to protect against viruses, such as hepatitis A and hepatitis B, that can further damage the liver should be given. It is difficult to predict how severely a liver will be affected. Liver function tests are followed over time. Some patients may have minimal liver disease during their entire lifetime; however, a small number will eventually require liver transplant.
Can cirrhosis be caused by biliary disease?
Cirrhosis or chronic liver failure can be caused by a number of the liver and biliary diseases listed in Clinical Services or sometimes appear without known cause. Our approach to pediatric patients with this problem is to start with a thorough history and physical examination and nutritional assessment.
Can a parent have A1AT?
Both parents must be carriers of the genetic defect to have a child with A1AT deficiency. Although carrier parents partially produce the abnormal A1AT protein, they usually have no — or very minimal — symptoms and they may not realize they are partially affected until their child is diagnosed with the condition.
What is ascites in the liver?
What is ascites? Ascites is fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity caused by fluid leaks from the surface of the liver and intestine. Ascites due to liver disease usually accompanies other liver disease characteristics, such as portal hypertension. Symptoms of ascites may include a distended abdominal cavity.
What are the symptoms of portal hypertension?
Symptoms of portal hypertension may include: Ascites. Development of varicose veins. Varicose veins (esophageal varices) develop most commonly at the lower end of the esophagus and in the stomach lining, although they can develop anywhere from the mouth to the anus.
Why is my urine dark?
Urine is usually dark because of the bilirubin excreted through the kidneys. High levels of bilirubin may be attributed to inflammation, or other abnormalities of the liver cells, or blockage of the bile ducts. Sometimes, jaundice is caused by the breakdown of a large number of red blood cells.
What does it mean when bile is blocked?
Cholestasis means any condition in which bile flow is reduced or stopped. "Chole" refers to bile and "stasis" means "not moving.". Bile flow may be blocked inside the liver, outside the liver, or in both places. Symptoms may include: Pain from the biliary tract (the bile ducts and gallbladder) or pancreas.
What is liver encphalopathy?
Liver encephalopathy is also called portal-systemic encephalopathy, hepatic encephalopathy, or hepatic coma.
What is liver failure?
Liver failure is severe deterioration of liver function. Liver failure happens when a large portion of the liver is damaged due to any type of liver disorder. Symptoms may include: Jaundice. Tendency to bruise or bleed easily.
What does it mean when your liver is enlarged?
Liver enlargement is usually an indicator of liver disease, although there are usually no symptoms associated with a slightly enlarged liver (hepatomegaly). Symptoms of a grossly enlarged liver include abdominal discomfort or "feeling full.".
Why is bilirubin high in newborns?
High levels of bilirubin may be attributed to inflammation, or other abnormalities of the liver cells, or blockage of the bile ducts. Sometimes, jaundice is caused by the breakdown of a large number of red blood cells, which can occur in newborns. Jaundice is usually the first sign, and sometimes the only sign, of liver disease.
Why does bile back up in the liver?
The liver produces bile to help digest food. When a child has a choledochal cyst, a swelling of that duct, bile may back up in the liver. This can cause liver problems or inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) because it blocks the main duct from the pancreas gland to the intestine.
What does cholestasis mean?
Cholestasis means any condition in which bile flow is reduced or stopped. "Chole" refers to bile and "stasis" means "not moving." Bile flow may be blocked inside the liver, outside the liver or in both places. Learn more about cholestasis.
What happens when the liver breaks down harmful substances?
When the liver has broken down harmful substances, they are excreted into the bile or blood. Bile by-products enter the intestine and ultimately leave the body in the feces. Blood by-products are filtered out by the kidneys and leave the body in the form of urine.
Why is my urine yellow?
Jaundice is a yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes due to abnormally high levels of bilirubin (bile pigment) in the bloodstream. Urine is usually dark because of the bilirubin excreted through the kidneys. High levels of bilirubin may be attributed to inflammation, or other abnormalities of the liver cells, or blockage of the bile ducts. Sometimes, jaundice is caused by the breakdown of a large number of red blood cells, which can occur in newborns. Jaundice is usually the first sign, and sometimes the only sign, of liver disease. Learn more about jaundice.
What does it mean when your liver is enlarged?
Liver enlargement is usually an indicator of liver disease, although there are usually no symptoms associated with a slightly enlarged liver (hepatomegaly). Symptoms of a grossly enlarged liver include abdominal discomfort or "feeling full."
How many lobules are there in the hepatic duct?
The segments are made up of a thousand lobules. The lobules are connected to small ducts that connect with larger ducts to ultimately form the common hepatic duct. The common hepatic duct transports bile produced by the liver cells to the gallbladder and duodenum (the first part of the small intestine).
