See more

What does it mean to have nodules on your liver?
Liver lesions are groups of abnormal cells in your liver. Your doctor may call them a mass or a tumor. Noncancerous, or benign, liver lesions are common. They don't spread to other areas of your body and don't usually cause any health issues. But some liver lesions form as a result of cancer.
Should I worry about liver nodules?
Liver lesions are abnormal growths that may be noncancerous (benign) or cancerous. Benign lesions occur for a variety of reasons and are typically not cause for concern. Liver cancer is less common but more serious.
Can a liver nodule go away?
No, liver hemangioma doesn't go away without treatment. People who have liver hemangioma rarely experience signs and symptoms and typically don't need treatment. They are generally small and even if they become large they may not carry significant risk.
What percent of liver nodules are cancerous?
Caturelli showed that 69% of new nodules in a cirrhotic liver are malignant.
How do you know if a liver cyst is cancerous?
If you have a cystic liver tumor, the only way to know whether it is benign or cancerous is to surgically remove the entire growth and examine it carefully. People do very well when the surgeon is able to remove the entire tumor during surgery.
How do you know if a liver lesion is cancerous?
Malignant liver lesions are diagnosed using several types of tests. If your healthcare provider suspects you have liver cancer, any of these may be ordered: Blood tests like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) tumor marker and liver function tests (LFTs) Imaging tests like ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) scan, and MRI.
How do you get rid of liver nodules?
Treatment may include:Surgery. In some cases, surgery may be used to remove cancerous tissue from the liver. However, the tumor must be small and confined.Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill or shrink cancer cells.Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses anticancer drugs to kill cancer cells.
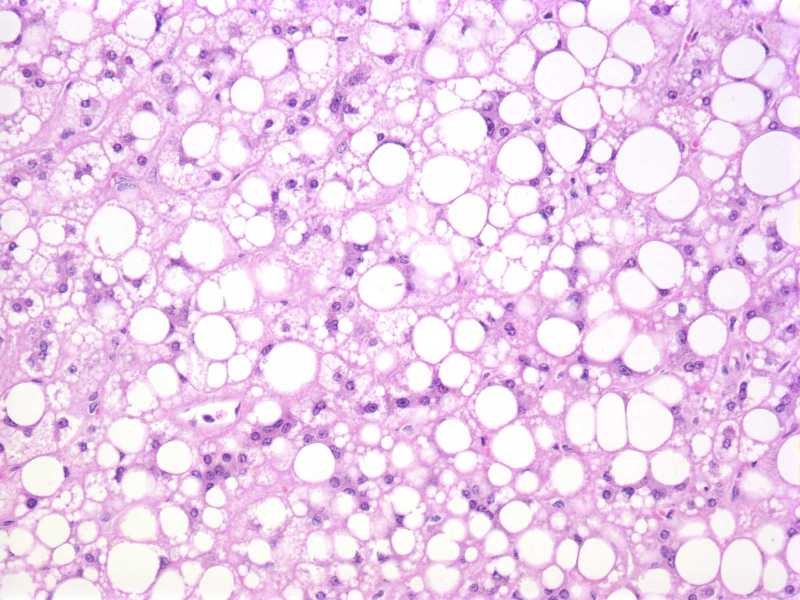
Can fatty liver cause nodules?
Fatty infiltration of the liver usually has a diffuse pattern in the parenchyma. Occasionally, fatty infiltration may appear as multiple nodular areas separated by normal liver tissue producing a pseudotumor appearance, which has been described as multifocal nodular fatty infiltration of the liver (MNFIL).
Are most liver nodules benign?
Liver masses are very common and most are benign. It is therefore important to avoid unnecessary interventions for benign lesions, while at the same time ensuring accurate diagnosis of hepatic malignancies. Many cancer patients, like the general population, have incidental benign liver lesions.
Is nodule same as tumor?
Tumors that are generally larger than three centimeters (1.2 inches) are called masses. If your tumor is three centimeters or less in diameter, it's commonly called a nodule. If the nodule forms in your lungs, it's called a pulmonary nodule. Hamartomas are the most common type of benign lung nodule.
Are nodules cancerous?
Yes, a lung nodule can be cancerous. But most lung nodules aren't cancerous. Lung nodules are small clumps of cells in the lungs. They're very common.
Can alcohol cause liver lesions?
The liver sustains the greatest degree of tissue injury by heavy drinking because it is the primary site of ethanol metabolism. Chronic and excessive alcohol consumption produces a wide spectrum of hepatic lesions, the most characteristic of which are steatosis, hepatitis, and fibrosis/cirrhosis.
What size liver lesions are concerning?
Recent work indicates that with colorectal liver metastases, careful MRI or CT should detect 95% or more of lesions larger than about 15 mm. The real issue now is the accuracy of detection for lesions smaller than this.
Are nodules cancerous?
Yes, a lung nodule can be cancerous. But most lung nodules aren't cancerous. Lung nodules are small clumps of cells in the lungs. They're very common.
Can fatty liver cause nodules?
Fatty infiltration of the liver usually has a diffuse pattern in the parenchyma. Occasionally, fatty infiltration may appear as multiple nodular areas separated by normal liver tissue producing a pseudotumor appearance, which has been described as multifocal nodular fatty infiltration of the liver (MNFIL).
Do benign liver tumors need to be removed?
Benign (Non-Cancerous) Liver Tumors The tumors are abnormal blood vessels that grow by dilating. Most of these tumors do not cause symptoms and need no treatment. Some may bleed or cause pain and need to be removed.
What are the nodules of cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is a chronic, diffuse process characterized by extensive interstitial fibrosis and the conversion of normal liver architecture into structurally abnormal nodules. Grossly, the nodular pattern may be micronodular or macronodular. In the micronodular category, the nodules of a cirrhotic liver are of the same size, no larger than 0.3mm in their greatest dimension. In the macronodular category, the nodules are much more variable in size and many exceed 1cm in the greatest dimension. A macronodular, heavily fibrotic liver is typical of the late stage of cirrhosis, whatever its etiology. Microscopically, rounded nodules are well demarcated and separated by dense fibrous septa. The regenerative nodules are composed of hepatocytes exhibiting marked variations in size and shape. Binucleation is a common finding. Focal areas of necrosis may be seen. Bile ductular proliferation and a mixed inflammatory infiltrate occur in some nodules. However, in inactive cirrhosis, inflammatory infiltration is mild, ductular proliferation is inconspicuous, and hepatocytes show little or no necrosis. Variation in activity from one part of a cirrhotic liver to another is common.
How big are cirrhotic nodules?
In the micronodular category, the nodules of a cirrhotic liver are of the same size, no larger than 0.3mm in their greatest dimension. In the macronodular category, the nodules are much more variable in size and many exceed 1cm in the greatest dimension.
What is differential diagnosis of liver nodules?
The main differential diagnosis in liver nodules is benign liver tumors (fo cal nodular hyperplasia, liver cell adenoma, dysplastic no dules) and primary and secondary liver cancer. The histologic appearance of tumorlike nodules is, at least in most cases, typical, and the differential diagnosis is relatively easy in everyday practice. However, the differential diagnosis of liver cell adenoma (LCA) versus well-differentiated HCC may cause problems, at least in fine-needle biopsies. Molecular markers are of limited value in this setting because there are no clear “cutoff” data to differentiate between LCA and HCC. In LCA, genetic alterations are also present, e.g., hypermethylation of p16 INK4a ( Tannapfel et al., 2002). β-catenin and p53 mutations may occur in a subset of LCA, making these markers unsuitable for differential diagnosis (Chen et al., 2002). It may be difficult to exclude metastases from primary liver tumors in some cases. When there is doubt about the hepatocyte origin of the tumor, further evidence can be gained by immunohistochemical analysis of (polyclonal) carcinoembryonic antigen, liver cell cytokeratins 8 and 18, albumin, or fibrinogen. In situ hybridization may show albumin messenger ribonucleic acid in the tumor cells as evidence for hepatocellular origin. To exclude primary cholangiocarcinoma of the liver, immunohistochemical analysis of biliary cytokeratins 7 and 19, and epithelial membrane antigen may be useful because these markers are negative in HCC. The specificity of alpha feto protein (AFP) is high, but, unfortunately, the sensitivity of AFP staining in HCC tumor tissue is low. The expression pattern may be weak, and a specific staining may be detected only in ∼30% of all HCCs. The proliferative activity of HCC is not of special value in the differential diagnosis of HCC. The expression of Ki-67 (MIB1) or proliferating cell nuclear antigen correlates with histologic grade of differentiation. In general, the proliferation rate in liver cirrhosis and LCA may be as high as in well-differentiated HCC (Tannapfel et al., 1999a; Tannapfel et al., 1999b ).
What is a macronodular liver?
A macronodular, heavily fibrotic liver is typical of the late stage of cirrhosis, whatever its etiology. Microscopically, rounded nodules are well demarcated and separated by dense fibrous septa. The regenerative nodules are composed of hepatocytes exhibiting marked variations in size and shape.
What are the three clinical settings for a liver nodule?
In clinical practice, pathologists are faced with diagnosis and classification of dysplastic liver nodules and small HCC in three clinical settings: 1. Grossly distinct nodules, in surgically resected specimens for HCC. 2. Grossly distinct nodules, in explanted liver for end-stage cirrhosis with or without HCC. 3.
How long do solitary nodules last?
Solitary nodules in the liver, lung, abdominal cavity, or head can usually be safely resected with improved long-term survival Five-year survival rates for those with resected solitary liver nodules are about 25–30%. Recommendations for chemotherapy postoperatively in these cases need to be made on a case-by-case basis.
Is a cirrhotic liver nodule suspicious?
In this setting, the size of the nodule is important. A hepatocellular nodule of >2cm occurring in cirrhotic liver is highly suspicious of hepatocellular carcinoma unless proven otherwise. Smaller nodules may be borderline or macroregenerative in nature.
What is liver adenoma?
Liver adenoma, a rare liver tumor. It occurs in people who take steroids, like those found in birth control pills. Liver cysts, fluid-filled sacs that may be present at birth. They can also develop later in life.
What is the most common benign liver lesion?
Liver hemangioma, the most common benign liver lesion. It occurs in up to 5% of adults and consists of abnormal blood vessels. Focal nodular hyperplasia, which often develops in women and has a scar-like appearance. Liver adenoma, a rare liver tumor.
What is the most common form of liver cancer?
Cancerous liver lesions include: Hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common form. It develops in people with liver damage due to viral hepatitis and alcoholism. Metastatic liver cancer, which occurs when tumors from other parts of the body spread to the liver.
What are the most important tests for liver cancer?
The most important tests used are: Abdominal imaging such as ultrasound, CT scan and MRI. Tumor markers. These are blood tests that can diagnose certain types of liver lesions. Biopsy. This a procedure that allows the provider to obtain a tiny piece of the liver or liver lesion to examine under the microscope.
How to treat liver cancer?
Treatments for liver cancer include: Ablation: Ablation destroys the liver lesion with heat or chemicals. This works best in small lesions. Removal of the tumor: Surgery to remove the tumor usually works best if the liver is healthy.
How long does it take for liver cancer to get worse?
It will not have much, if any, impact on your daily life. Liver cancer can make you feel sick and run down in later stages. It also gets worse over time and can spread to other areas. Cancer treatment can take months to complete. During this time, you might not be able to work or take care of yourself.
What to do if you have a liver lesion?
They may recommend specialized testing or monitoring to check for changes that require additional care. And if imaging studies show signs of a liver lesion, remember that it might not be serious.
What are the most common types of liver infections?
The most common types of liver infection are hepatitis viruses, including: Hepatitis A. Hepatitis B.
How to prevent liver disease?
To prevent liver disease: Drink alcohol in moderation. For healthy adults, that means up to one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men. Heavy or high-risk drinking is defined as more than eight drinks a week for women and more than 15 drinks a week for men. Avoid risky behavior.
What are the problems that can occur in the liver?
Liver problems that can occur include fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. The liver and its cells — as seen through a microscope — change dramatically when a normal liver becomes fatty or cirrhotic.
Why is the liver important?
The liver is essential for digesting food and ridding your body of toxic substances. Liver disease can be inherited (genetic). Liver problems can also be caused by a variety of factors that damage the liver, such as viruses, alcohol use and obesity. Over time, conditions that damage the liver can lead to scarring (cirrhosis), ...
What to do when using insecticides?
When using insecticides and other toxic chemicals, wear gloves, long sleeves, a hat and a mask so that chemicals aren't absorbed through your skin. Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can cause nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Liver disease care at Mayo Clinic.
How to prevent hepatitis?
Avoid contact with other people's blood and body fluids. Hepatitis viruses can be spread by accidental needle sticks or improper cleanup of blood or body fluids. Keep your food safe. Wash your hands thoroughly before eating or preparing foods .
Where is the liver located?
About the size of a football, it's located mainly in the upper right portion of your abdomen, beneath the diaphragm and above your stomach.
Who Gets Them?
Anyone can have a liver lesion, but some things can make you more likely to have cancerous ones:
How to reduce the chance of liver cancer?
You can lower your chances of getting cancerous liver lesions if you exercise, stay at a healthy weight, and drink only in moderation (up to two drinks a day for men and one for women). And you can do a few things to keep from getting hepatitis B or C, which cause 80% of liver cancer cases.
What are liver lesions?
Liver Lesions. Hepatitis C Prevention. Liver lesions are groups of abnormal cells in your liver. Your doctor may call them a mass or a tumor. Noncancerous, or benign, liver lesions are common. They don’t spread to other areas of your body and don’t usually cause any health issues. But some liver lesions form as a result of cancer.
What tests are done to check for liver lesion?
Diagnosis. If your doctor thinks you might have a liver lesion, they’ll probably recommend one or more of these: Blood tests: They might use these to test for viral hepatitis or to see how well your liver is working. They also may want to check your level of a certain protein (alpha-fetoprotein, or AFP).
What is the difference between a PET scan and a biopsy?
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan uses a special dye that makes your liver show up more clearly. And an ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make live images of your liver. Biopsy: To rule out cancer, your doctor may want to take a small sample of the lesion to look for problem cells.
What is the best way to see if a lesion is on your liver?
Imaging tests: These can show where a lesion is on your liver and how big it is. A magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) scan uses powerful magnets and radio waves to make detailed images of your liver. A computed tomography (CT) scan is a series of X-rays put together to make a more complete picture. A positron emission tomography (PET) scan uses a special dye that makes your liver show up more clearly. And an ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make live images of your liver.
What is the most common type of liver cancer?
About 80% of people who are diagnosed with the most common type of liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, have cirrhosis. Iron storage disease ( hemochromatosis ): This is one of the most common genetic disorders in the U.S. It makes your body take in too much iron from food.
What causes cirrhosis of the liver?
The most common causes of cirrhosis of the liver are: Alcohol abuse (alcohol-related liver disease caused by long-term [chronic] use of alcohol). Chronic viral infections of the liver ( hepatitis B and hepatitis C ). Fatty liver associated with obesity and diabetes and not alcohol.
What is the term for the abnormal deposits in the liver of an abnormal protein called?
Rare diseases, such as amyloidosis, in which abnormal deposits in the liver of an abnormal protein called amyloid disrupts normal liver function. Changes from liver diseases that lead to cirrhosis are gradual. Liver cells are injured and if injury – from whatever cause – continues, liver cells start to die.
How does scar tissue affect the liver?
The scar tissue blocks the flow of blood through the liver and slows the liver’s ability to process nutrients, hormones, drugs and natural toxins (poisons). It also reduces the production of proteins and other substances made by the liver. Cirrhosis eventually keeps the liver from working properly.
How long does cirrhosis last?
Median survival in patients with compensated cirrhosis is approximately nine to 12 years. (Median is the middle point in set of numbers, so an equal number of individuals survived less than 9 to 12 years as the number of individuals who survived over this time range.)
What causes scaring and nodules in the liver?
Cirrhosis causes scaring and nodules to form throughout the liver.
How to tell if you have cirrhosis?
Physical exam : Your doctor will examine you, looking for the signs and symptoms of cirrhosis including: the red, spider-like blood vessels on your skin; yellowing of your skin or whites of your eyes; bruises on your skin; redness on your palms; swelling, tenderness or pain in your abdomen; enlarged firmer-feeling, bumpy texture to the lower edge of your liver (the part of your liver below the rib cage that can be felt).
What does it feel like to have a liver problem?
Pain in your liver itself can feel like a dull throbbing pain or a stabbing sensation in your right upper abdomen just under your ribs. General abdominal pain and discomfort can also be related to swelling from fluid retention and enlargement of your spleen and liver caused by cirrhosis.
What causes thyroid nodules?
Thyroid nodules have a variety of causes. The following are common types of thyroid nodules: 1 Colloid nodules develop from a lack of iodine, which is a mineral essential to the production of thyroid hormones. These growths are noncancerous, but they may be large. 2 Hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules produce thyroid hormone, which may cause hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). 3 Multinodular goiter occurs when the thyroid gland forms multiple nodules, which grow over time. It can occur due to a lack of iodine in your diet, but most people with goiters have a thyroid gland that functions normally. 4 Thyroid cancer is another cause of thyroid nodules, but most thyroid nodules aren’t cancerous. Research estimates 5 percent of biopsied thyroid nodules are cancerous.
What gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism and growth?
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate your metabolism and growth. Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which your thyroid produces too much thyroid hormone. Sometimes, nodules form that produce excess thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism.
Why do thyroid nodules grow?
Thyroid nodules. Thyroid nodules have a variety of causes. The following are common types of thyroid nodules: Colloid nodules develop from a lack of iodine, which is a mineral essential to the production of thyroid hormones. These growths are noncancerous, but they may be large.
What is the size of a lung nodule?
Lung nodules typically range from 0.2 to 1.2 inches in size, but they can be larger. They may represent swollen lymph nodes in some instances. There are several reasons why a nodule forms in the lungs, such as infection.
What is a lymph node?
Lymph nodes are small, oval-shaped organs located throughout the body. They play an important role in your body’s immune system and may temporarily swell when you’re sick.
What is a nodule in the body?
A nodule is a growth of abnormal tissue. Nodules can develop just below the skin. They can also develop in deeper skin tissues or internal organs.
How big is a noncancerous nodule?
Noncancerous nodules usually don’t require treatment. Nodules bigger than 1.2 inches may be more likely to be cancerous. Your doctor will come up with a plan with you to monitor these nodules and determine when a biopsy is necessary.
