What is marbling in postmortem?
Putrefaction of erythrocytes within the superficial blood vessels leads to the formation of greenish-blue discoloration, which is observable through the skin. This outlining of the superficial blood vessels is known as 'marbling' of the skin.[20]
How long after death does marbling occur?
about 24 to 48 hoursMoreover, the phenomenon of marbling is also present during this stage, where blood vessels are visible on the skin as greenish-black streaks and eventually results in skin discoloration ranging from green to black. [4] These postmortem changes are apparent in about 24 to 48 hours after death.
What is blanching after death?
Blanching, or a whitish discoloration that results when pressure is applied to the skin, can occur up to 8–12 hours after death. After this time period, however, the blood becomes fixed (or non-blanchable).
Why does the body turn blue after death?
Livor mortis is the gravitational settling of blood which is no longer being pumped through the body after death, causing a bluish-purple discoloration of the skin. It is one of the post-mortem signs of death, along with pallor mortis, algor mortis, and rigor mortis.
What happens in the last minutes before death?
Facial muscles may relax and the jaw can drop. Skin can become very pale. Breathing can alternate between loud rasping breaths and quiet breathing. Towards the end, dying people will often only breathe periodically, with an intake of breath followed by no breath for several seconds.
What happens immediately after death?
Decomposition begins several minutes after death with a process called autolysis, or self-digestion. Soon after the heart stops beating, cells become deprived of oxygen, and their acidity increases as the toxic by-products of chemical reactions begin to accumulate inside them.
What are the 4 post mortem stages of death?
Of these, with obvious mortal damage to the body, the textbook conclusive signs of death clear to a lay person are: algor mortis, rigor mortis, livor mortis, and putrefaction.
Why does a body turn purple after death?
Postmortem lividity (hypostasis, livor mortis) is a plurifocal staining of the skin, usually in the form of a more or less intense purple discoloration, due to the gravitational settling of blood in vessels after the circulation has ceased.
What is the color of the blood after 6 hours after death?
This stagnation and settling of blood corpuscles leads to the development of livor mortis, but livor mortis would not develop without another physiological change. Lividity can be seen as red areas. This occurs in the first 2 to 6 hours after death.
When someone is dying what do they see?
Visual or auditory hallucinations are often part of the dying experience. The appearance of family members or loved ones who have died is common. These visions are considered normal. The dying may turn their focus to “another world” and talk to people or see things that others do not see.
What does death smell like?
Some people compare the putrid stench of a decomposing body to that of rotting meat with rotting fruit undertones. When someone dies, the body immediately begins the decomposition process and the smell of death can begin.
What happens to the eyes after death?
About two hours after death, the cornea becomes hazy or cloudy, turning progressively more opaque over the next day or two. This obstructs the view of the lens and back of the eye. (See A New Look at a Dead Retina, on page 80.) But this clouding may provide a rough estimate in helping to determine time of death.
How long after death does skin slippage occur?
Surrounding temperature: The warmer and more humid an environment is around the body, the faster the skin will detach from the rest of the body. In high humidity, this can take place in 2-3 days. If it is cold, the whole decomposition process takes much longer, and skin will stay connected for a longer period of time.
How long after someone dies is the will read?
While there is no legal timescale, a Will should be read as soon as possible. This ensures that: Funeral instructions are followed. The deceased may ask to be buried or cremated and may also leave instructions on how the funeral should be paid for.
Why are funerals 3 days after death?
Historically, funerals had to take place after just a matter of days, because of decomposition. With today's preservation methods, families have a bit more time to prepare and get affairs in order. This helps families make arrangements, and to pick a day to hold the funeral.
How long does it take for rigor mortis to pass?
Rigor mortis appears approximately 2 hours after death in the muscles of the face, progresses to the limbs over the next few hours, completing between 6 to 8 hours after death. [10] Rigor mortis then stays for another 12 hours (till 24 hours after death) and then disappears.
What happens to a body after death?
Decomposition is what naturally occurs to bodies after death. What is there to know about it?
What happens when a body is left out in a shallow grave?
Under natural conditions — for example, if the body is left out in a natural environment, or placed in a shallow grave — a lifeless body begins to slowly disintegrate, until only the bones are left for future archeologists to dig up. In this Spotlight, we describe the process of decomposition and explain why it can be useful to understand ...
What are the signs that a body is decomposing?
Perhaps the three best-known ones, which are often cited in crime dramas, are livor mortis, rigor mortis, and algor mortis.
Why does my skin turn discolored?
This is due to the loss of blood circulation as the heart stops beating. Goff explains, “ [ T]he blood begins to settle, by gravity, to the lowest portions of the body,” causing the skin to become discolored.
What is the process of decomposition?
In the words of forensic scientist M. Lee Goff, it is “a continuous process, beginning at the point of death and ending when the body has been reduced to a skeleton.”.
Why do flies lay eggs on dead bodies?
The egg-laying flies that are attracted to dead bodies, she explains, “are mainly bluebottles from the Calliphora genus,” which will “lay eggs on orifices or wounds only, because the very young larvae need to eat decaying flesh but can’t break the skin to feed.”
How long does it take for a body to become unpliable after death?
This process may begin after about an hour following death and can continue to develop until the 9–12 hour mark postmortem. In rigor mortis, the body becomes stiff and completely unpliable, as all the muscles tense due to changes that occur in them at a cellular level.
What are unknown factors in assessing the time of death?
2 unknown factors in assessing the time of death: Actual body temperature at the time of death and Length of Plateau phase
What happens when you die with your eyes open?
Tache noir Sclerotique: If death occurs with eyes open, the open part dries up (non-functioning tear gland) and gives a brownish black horizontal band of discoloration (a film of cell debris and mucus on sclera on each side of iris from yellow → brown → black)
What is the term for darkening of death?
6. Livor mortis (Darkening of Death)/PM Hypostasis or Lividity:
How long does it take for rigor mortis to develop?
No relaxation: Membrane disruption and lack of ATP. Begins 1-2 hours after death and takes further 1-2 hours to develop. According to Shapiro, rigor mortis develops simultaneously in all muscles, although changes are visible earlier in smaller masses than larger.
When rigor mortis developing, can extremities be moved and rigor, temporarily overcome, develops in?
When rigor mortis developing: extremities can be moved and rigor, temporarily overcome, develops in new position (rigidity will be less in disturbed part)
What is immediate death?
Immediate (Somatic death): 1. Insensibility and loss of voluntary power. 2. Cessation of respiration. 3. Cessation of circulation.
What prevents formation of lividity?
Pressure prevents formation of lividity (Contact pallor or Vibices): area contact with another body part or surface, tight clothing, jewellery
Why is my skin mottled?
Causes of mottled skin. Many conditions can cause mottled skin. Blood circulation problems and blood vessel spasms are two common causes. Causes also include:
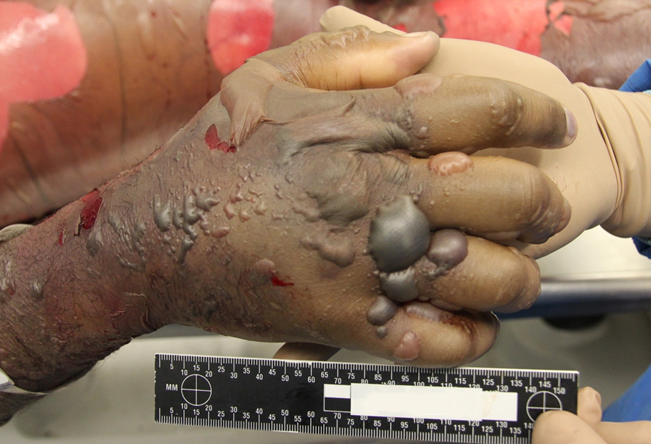
What is a marbled skin?
Mottled skin, also called livedo reticularis, is skin that has patchy and irregular colors. The skin may have red and purple marks, streaks, or spots. It may also have a marbled appearance with different colors.
Why does my newborn have mottled skin?
Some newborn babies have mottled skin. Usually, this benign condition goes away on its own. Exposure to cold temperatures frequently causes it. Treatment includes keeping the baby warm and avoiding the cold. There is usually no need to have additional medical treatment.
What medications cause mottled skin?
Drugs that are known to cause mottled skin include: amantadine. catecholamines. minocycline (Minocin) gemcitabine (Gemzar)
What are the changes after death?
A body undergoes complex and intricate changes after death.[1] These post mortem changes depend on a diverse range of variables. Factors such as the ambient temperature, season, and geographical location at which the body is found, the fat content of the body, sepsis/injuries, intoxication, presence of clothes/insulation over the body, etc. determine the rate at which post-mortem changes occur in a cadaver. Understanding the post mortem changes is imperative to estimate the time since death (TSD) or the post mortem interval (PMI). This chapter is written in with a view of explaining the various changes that occur in a human once they are dead, their time of onset, their rate, and the factors influencing them.
What are the immediate changes after death?
Immediate changes after death relate to the ‘somatic death’ or ‘systemic death.’ Somatic death deals with the irreversible cessation of the vital functions of the brain, heart, and lungs. Thus, immediate post-mortem changes are dubbed as the “signs or indications of death.” Immediate changes include insensibility, loss of voluntary movements, cessation of respiration, cessation of circulation, and cessation of nervous system functions. During this time, primary relaxation of muscles occurs. Though insensibility and loss of voluntary movement are considered as one of the earliest signs of death, these can also appear in cases of trance, fainting attacks, narcosis, catalepsy, and electrocution, etc.
What color is post mortem staining?
Post mortem staining can be of a distinct color in cases of poisoning. Cherry red staining presents in carbon monoxide poisoning, pink-colored staining is observable in cyanide poisoning, and brown colored staining occurs in nitrate poisoning. [28][29][30] Thus, postmortem staining, besides PMI, can provide useful information on the position of the body, or even the cause of death.
How to determine if postmortem lividity is fixed?
This phenomenon is termed as ‘fixation of postmortem staining.’ Whether or not lividity is fixed is determined by the blanching test. The pressure is applied to the livid area by the thumb of the observer for about a minute, then released. If the area underneath the thumb becomes pale on the removal of pressure, the lividity is said to be not fixed, while if the region stays stained even after removal of pressure, the lividity is said to be fixed.
What is post mortem change?
Early and late post mortem changes are a sure indication that death has occurred. The post mortem changes can be used to estimate the time since death (TSD) or post mortem interval (PMI). PMI is a crucial aspect of medicolegal investigation as it helps in determining when a crime has been committed. Based on this estimated time, alibis of suspected individuals may be verified, and conviction or acquittal of a suspect may be determined. The medicolegal expert needs to be extremely careful while opining about the PMI since a variety of factors affect the post mortem changes. An estimate of ‘time since death’ should always be given, rather than a specific ‘time of occurrence.’ Besides, PMI, specific postmortem changes can provide information on the cause and manner of death, position/ change in position of the body, identification, etc. Medicolegal experts can determine the existence and location of external injuries, if any, on a cadaver in advanced stages of putrefaction.
What causes rigidity in the body?
Rigor mortis is the post mortem stiffening/ rigidity of the body. It results from a decrease in levels of adenosinetriphosphate (ATP) beyond critical levels. When a person dies, calcium ions flood muscle fibers due to the loss of integrity of the muscle cells. These ions cause the binding of actin and myosin filaments, causing contraction. Relaxation of muscles is achieved by ATP driven pumping of the calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the muscle cells. As a result of the lack of ATP, the muscles fail to relax, and the actinomyosin complex created during the contraction stays intact; this causes the muscles to become hard and rigid. [20][21][22] Rigor mortis first appears in the involuntary muscles of the heart, and apparently follows proximal to distal progression. It is observed in eyelids, followed by the neck, lower jaw, chest, upper limbs, abdomen, lower limbs, and then finally in the fingers and toes. Rigor mortis appears in 1 to 2 hours after death, is completely formed 12 hours after death, is sustained for the next 12 hours, and vanishes over the next 12 hours, sometimes referred to as the ‘march of rigor.’
Why does lividity not appear on the body?
The lividity does not appear on the parts of the body which are in contact with the floor/ bed/ slab, etc., or those compressed due to tight clothing, bands, etc., because of the obstruction and compression effect of surface in the underlying vessels. The absence of discoloration in these areas is called ‘contact flattening,’ ‘contact pallor,’ or ‘contact blanching.’
What is the term for the postmortem stiffening of the body due to depletion of ATP and?
Rigor mortis . Definition: Postmortem stiffening or rigidity of the body due to depletion of ATP and accumulation of lactic acid; in a dead body, the glycogen stores are rapidly depleted, preventing the energy dependent breakage of sarcomere contraction ( J Physiol 1947;106:177 ) Process:
How long does it take for a livor mortis to become blanchable?
Livor mortis will eventually become fixed in several hours (approximately 8 - 12 hours or so) and lose its ability to become blanchable; this is due to breakdown of red blood cells and vessels ( Z Rechtsmed 1984;93:283 )
What does rigor mortis mean?
Rigor mortis can indicate the position of the body at the scene; inappropriate or antigravitational rigor mortis can indicate that a body has been moved once rigor mortis has been fully fixed and the body is discovered prior to full dissipation of rigor mortis ( Int J Appl Basic Med Res 2011;1:120 )
How long does it take for rigor mortis to occur?
Typically, rigor mortis may begin within a couple of hours after death and occurs in all muscle groups but is initially notable in the small muscles (i.e. jaw) followed by larger muscle groups (i.e. legs) ( Forensic Sci Int 1978;12:97 )
What is postmortem change?
Definition / general. Postmortem changes refers to a continuum of changes that occur in a dead body following death; these changes include livor mortis, rigor mortis, decomposition and taphonomy ( StatPearls: Evaluation of Postmortem Changes [Accessed 1 July 2020] ) Given the postmortem changes and the rate of change are influenced by many ...
What is an artifact in autopsy?
Artifact is any change produced in the body after death or during resuscitation that may lead to misinterpretation of relevant antemortem findings ; postmortem changes may mimic injuries, obscure and hinder interpretation of antemortem findings ( Rutty: Essentials of Autopsy Practice - Advances, Updates and Emerging Technologies, 2014 )
Where does blanching occur?
Blanching occurs in gravity dependent areas of the body that come into contact with firm surfaces (i.e. floor, tight clothing); livor mortis is spared in these areas due to localized pressure preventing blood from entering the skin ( StatPearls: Postmortem Changes [Accessed 1 July 2020] )
What are the three changes that occur during a postmortem?
Three early postmortem changes occur while the body is still in the fresh stage before the breakdown of soft tissues, namely algor mortis, livor mortis, and rigor mortis , which are of forensic significance. [5]
What changes occur during the early postmortem period?
The eye changes during the early postmortem period include corneal turbidity/opacity and tache noire formation . The intraocular tension progressively falls to nil about 2 hours after death, although this is disputable.
What is rigor mortis?
Rigor mortis (postmortem rigidity) is the stiffening of the muscles of the corpse due to the depletion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) after death with the subsequent build-up of lactate in muscle tissue resulting in an inability to release the actin-myosin bond . This postmortem muscle change appreciated grossly follows the initial phase of primary flaccidity of muscles and is itself followed by the secondary flaccidity of muscles that coincides with the beginning of putrefactive changes. The process of rigor mortis uniformly involves all muscles of the body. However, it is first apparent generally in smaller muscles such as the jaw and the eyelids due to quicker depletion of ATP relative to larger muscles in the trunk and limbs. Rigor mortis occurs in both voluntary and involuntary muscles, including the cardiac muscle. It is first evident in the facial muscles at 1 to 4 hours after death. The gelling of the muscle proteins is apparent as muscle stiffening in about 6 hours after death in the rest of the muscles and is complete about 12 hours after death. This rigidity of the muscles lasts for about another 12 hours or so. The body then returns to a flaccid state after the enzymatic breakdown of actin and myosin binding sites. The rate at which rigor mortis passes off will be rapid in a hot environment as the onset of putrefaction is hastened in such an environment. Cold temperatures lengthen the duration of rigor.
How does algor mortis affect postmortem cooling?
Algor mortis is the postmortem cooling of body temperature until it equalizes the temperature of the surrounding environment. The rate of cooling lags initially, then becomes linear before slowing down again as it approaches the ambient temperature, giving a sigmoid-shaped curve when graphically represented. The ambient temperature is a critical factor that affects the rate of postmortem cooling of the body. Postmortem cooling of the body continues for about 6 hours after death, and the rate of cooling is primarily dependent on the difference in body temperature at the time of death and the temperature of its surroundings. The rate of cooling will hasten in a body immersed in water, a naked body, and a thin body. The rate of cooling will be slower in a well-clothed body and an obese body. A prudent forensic pathologist will not estimate the time since death based on the single criterion of algor mortis. The rate of postmortem cooling of the body is affected by multiple variables.
Why should a doctor be aware of postmortem changes?
Secondly, a doctor should also be aware of the postmortem changes to avoid misinterpretation of these findings as signs of physical violence or unnatural death. It is not uncommon for the emotionally charged legal heirs of the deceased or members of the lay public to wrongly interpret postmortem lividity for a contusion, especially in instances where death is not witnessed by them, despite assertions from a forensic pathologist.
What are postmortem changes?
Postmortem changes constitute the natural progression of the body’s decomposition after death, beginning at the cellular level. The process involves complex cellular and biological phenomena. The changes that commence immediately after death continue to occur over a prolonged period at different rates for different organs. The onset and extent of these changes are affected by multiple intrinsic and extrinsic factors. The rates are not precise and differ from one geographical region to another and also differ in the same geographic region from one season to another. Understanding postmortem changes is essential for estimating the postmortem interval (PMI) or time since death, one of the primary objectives of the forensic autopsy. The timings of the appearance of the various postmortem changes mentioned in this brief overview of postmortem changes are only guidelines pertaining to tropical climates unless otherwise specified and should never be considered as absolute.
How to tell if you are dying from respiratory failure?
However, these tests are quite unreliable. Circulatory stoppage results in a loss of pulse, which can also be confirmed by a flat electrocardiogram (ECG) in a hospital setting. The absence of respiratory and cardiac sounds on auscultation over 5 minutes indicates a sign of death as advocated by expert clinicians. The finding of the break-up of the columns of blood in the retinal blood vessels (retinal vascular segmentation) on ophthalmoscopy confirms the stoppage of circulation and is one of the earliest indications of death. Cessation of nervous system functions results in the loss of sensory and motor functions and reflexes. The muscles begin to become flaccid with a loss of tone. Pupils also dilate as a result of this. A flat electroencephalogram (EEG) confirms the loss of electrical activity in the brain in a hospital setting.
How long does it take for a body to stiffen after death?
Rigor mortis, or a stiffening of the body, sets in about two to six hours after death [source: Marchant, Middleton ]. While the body as a whole may be dead, little things within the body are still alive. Skin cells, for example, can be viably harvested for up to 24 hours after death [source: Mims ]. But some things that are still alive lead ...
What is the meaning of burying the dead?
Sometimes, warriors or servants were buried standing up, eternally ready for action.
Why don't we see the process of ashes?
Now, most of us don't see that process because the law requires that we do something with the body. There are endless possibilities: We can choose a coffin for our body or an urn for our ashes. We can be embalmed, mummified or frozen.
What happens to the body after the heart stops beating?
After the heart stops beating, the body immediately starts turning cold. This phase is known as algor mortis, or the death chill. Each hour, the body temperature falls about 1.5 degrees Fahrenheit (0.83 degrees Celsius) until it reaches room temperature.
What happens to the pancreas after death?
A few days after death, these bacteria and enzymes start the process of breaking down their host. The pancreas is full of so many bacteria that it essentially digests itself [source: Macnair ]. As these organisms work their way to other organs, the body becomes discolored, first turning green, then purple, then black.
Why do Hindus burn their bodies?
Hindus are cremated, because it's believed that burning releases the soul from the body, while Roman Catholics frown on cremation out of respect for the body as a symbol of human life [sources: Mims; Cassell et al ].
Do hair and nails grow after death?
The hair and nails, by the way, while long rumored to keep growing after death, don't have any magical growth properties. They merely look bigger as the skin dries out. Internal organs and tissues have liquefied, which will swell the body until it bursts open. At that point, a skeleton remains.