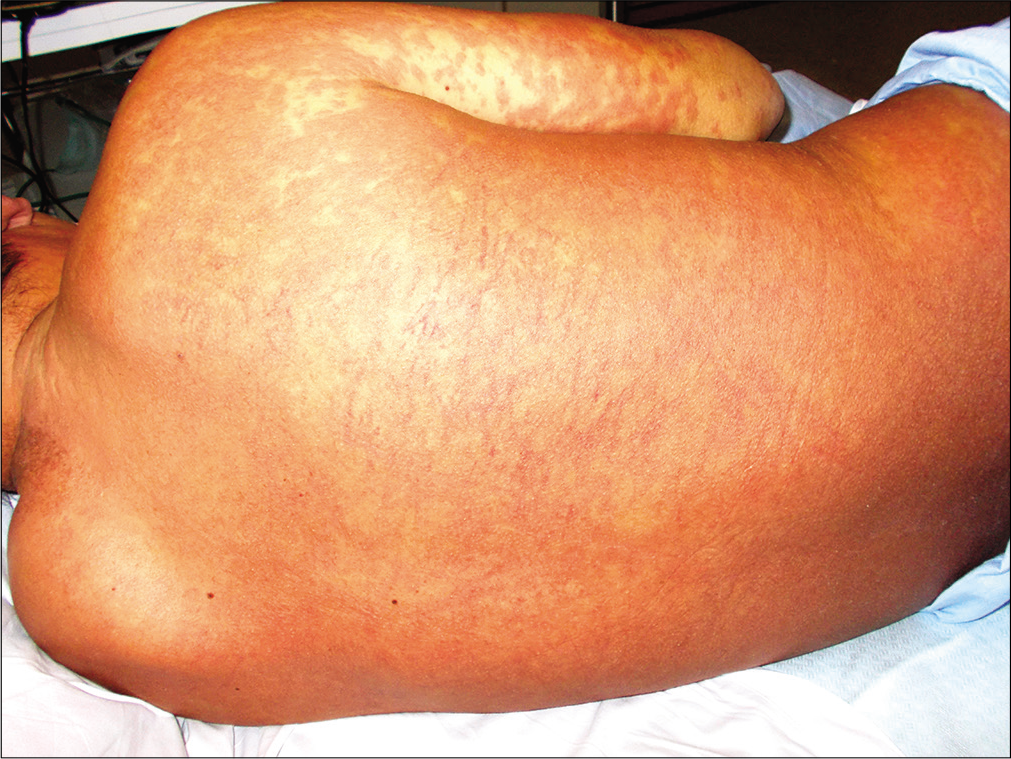
Common Causes
The main causes leading to eosinophilia. Eosinopenia - a decrease in the content of eosinophils (less than 0.05 × 10 9 / l) - in most cases is due to an increase in adrenocorticoid activity, which leads to a delay in eosinophils in the bone marrow. Eosinopenia is especially characteristic for the initial phase of the infectious-toxic process.
Related Conditions
The causes of high eosinophils can be: Allergies of all kinds, from acute hives to lactose intolerance. Autoimmune skin diseases such as pemphigus, psoriasis, among others. Bacterial infections of any kind.
What causes increased or decreased eosinophils?
What Causes High Absolute Eosinophils?
- Parasites and fungal diseases
- Allergies
- Adrenal conditions
- Skin disorders
- Toxins
- Autoimmune diseases
- Endocrine disorders
- Tumors. Certain medications can elevate your eosinophil count.
- Appetite suppressants
- Laxatives containing psyllium
What can cause elevated eosinophils?
The most common symptoms when high eosinophils or eosinophilia are:
- Difficulty breathing.
- Cough.
- Whistling when breathing.
- Abdominal pain.
- Diarrhea.
What causes elevated eosinophils levels?
What are the symptoms of high eosinophils?
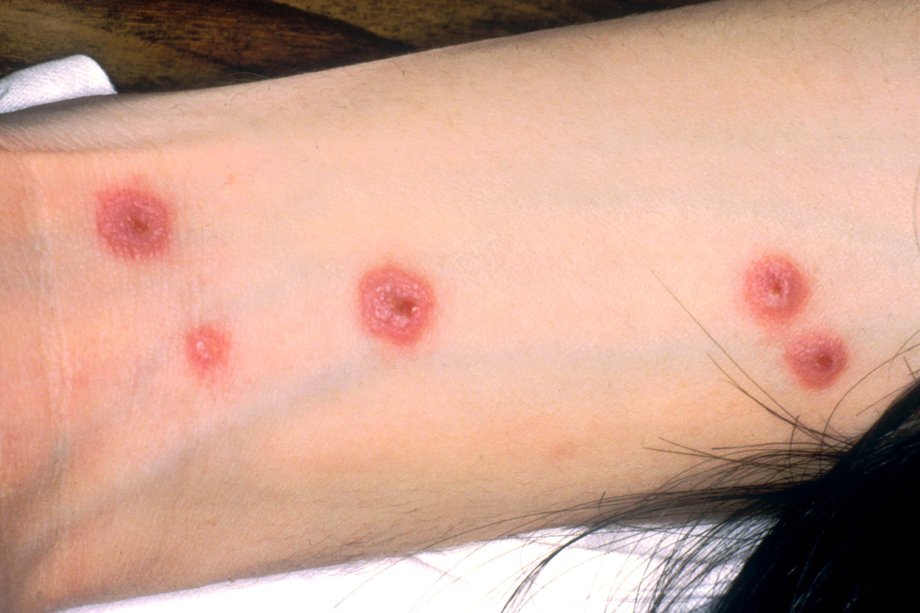
What is eosinophilia in blood?
What is eosinophilia? Eosinophilia refers to a condition of having an increased numbers of eosinophils in the peripheral blood. White blood cells are an essential component of the cellular immune system.
What is eosinophilic fasciitis?
Eosinophilic fasciitis, a disorder of the fascia, or the connective tissue throughout the body
What is the hematologic name for eosinophilic granulomatosis?
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis involves the lungs, heart, sinuses, and other organs. It is also known as Churg-Strauss syndrome . Another condition is hypereosinophilic syndrome, which is a primary hematologic disorder involving the blood and other organs.
How many eosinophils are there in a microliter?
Eosinophilia is said to occur when there are greater than 500 eosinophils per microliter, though the exact cutoff varies by laboratory. Eosinophilia can be considered mild, moderate or severe. Usually, less than 5% of the circulating white blood cells in a person are eosinophils.
How to treat eosinophils in asthma?
Treatments might include stopping certain medications (in the case of drug reactions), avoiding certain foods (in the case of esophagitis), or taking an anti-infective or anti-inflammatory medication. Treatment s that target eosinophils in asthma specifically have been approved by the Food & Drug Administration (FDA) and are being used in the clinic, while treatments for other eosinophil-mediated conditions are under further investigation.
What is the role of eosinophils in the immune system?
Eosinophils are specific white blood cells that are a normal part of the cellular immune system, play a role in normal physiologic processes and host defense, and participate in allergic reactions and the defense against parasitic infections.
What are the different types of eosinophils?
Eosinophilic disorders are often called by names that reflect where the problem is located. These include: 1 Eosinophilic cystitis, a disorder of the bladder 2 Eosinophilic fasciitis, a disorder of the fascia, or the connective tissue throughout the body 3 Eosinophilic pneumonia, a disorder of the lungs 4 Eosinophilic colitis, a disorder of the colon (large intestine) 5 Eosinophilic esophagitis, a disorder of the esophagus 6 Eosinophilic gastritis, a disorder of the stomach 7 Eosinophilic gastroenteritis, a disorder of both the stomach and the small intestine
What is the most common cause of eosinophilia?
Parasite infections: Worldwide the most common cause of eosinophilia is a parasite infection. 2 Names of these infections include schistosomiasis, trichinosis, strongyloidiasis, and ascariasis. These parasites can be found worldwide including the United States.
How to treat eosinophilia?
Similar to what diagnostic tests may be needed, treatment is determined by the cause of eosinophilia. 1 Options include: 1 Observation: If your eosinophilia is mild, observation with repeat labs may be recommended. 2 If a medication is causing your elevated eosinophil count, it may be discontinued 3 Maximizing therapy for asthma, eczema, and allergies 4 Parasite infections are treated with anti-parasitic medications. 5 Steroids such as prednisone may be used to treat hypereosinophilic syndromes
What is the name of the disorder where eosinophils are not present?
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE): This is a disorder characterized by eosinophils spreading to the esophagus which normally does not contain eosinophils. About 50% of people with EoE will also have elevated eosinophil counts in the blood. 4
How many cells are in eosinophils?
Eosinophilia can be categorized by the number of eosinophils (absolute eosinophil count). 1 . Mild: 500 - 1500 cells/mL. Moderate: 1500 - 5000 cells/mL. Severe: > 5000 cells/mL. Determining the cause of your eosinophilia will be based on your symptoms.
What is the technical name for an increased eosinophil count?
Treatment. Eosinophilia is the technical name for an increased eosinophil count. Eosinophils are a type of white blood cells that destroy substances in the body like parasites and participate in allergic reactions. Verywell / Laura Porter.
Why is my eosinophil count elevated?
Causes. There are numerous reasons your eosinophil count may be elevated. Some of the causes are benign and require little treatment. It is not uncommon for the elevated count to be transient and resolve without treatment. Let's review some of the causes now. Parasite infections: Worldwide the most common cause of eosinophilia is ...
What are the symptoms of eosinophilia?
If your eosinophil count is mildly elevated you may not have any symptoms. 1 Common symptoms include: Rash. Itching.
What causes eosinophilia?
Of causes of eosinophilia, the most major ones are allergies or infections of a parasitic nature. Check out everything you need to know about it.
Why is eosinophilia so common?
According to medical sources, helminth parasite infections are the most widespread cause of eosinophilia worldwide. This is because helminthiases are very common in tropical countries, where food conditions and sanitary structures are poor.
How many eosinophils are in a cubic millimeter of blood?
In general, it can be concluded that more than 500 eosinophils per cubic millimeter of blood lead to eosinophilia.
What causes eosinophilia in Western countries?
Atopic disease (allergy) is the most common cause of eosinophilia in Western countries. It appears in cases of dermatitis, asthma, and rhinitis, but they are always low blood cell counts.
What is the importance of eosinophilia?
The importance of this event lies on two fronts: diagnostic and pathogenic. On the one hand, eosinophilia suggests the presence of an infection in the patient , but on the other hand, the release of products from these white blood cells can be associated with tissue damage.
What is the most common disease associated with eosinophilia?
Neoplasms, that is, the growth of abnormal masses, both cancerous and non-cancerous, are associated with eosinophilia. The most common diseases are Hodgkin’s lymphoma (up to 15% of those affected have it), other non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, and various types of leukemia.
Is eosinophilia a parasite?
Thus, it is not surprising to learn that eosinophilia is widely associated with allergi es, neoplasms, or the presence of parasites in the host. In industrialized countries, the most common cause of eosinophilia is allergic processes, while in other places it is infections by parasites.
Where are eosinophils found?
In healthy individuals, eosinophils can be found in the spleen, lymph nodes, thymus, and digestive tract (although not the esophagus) [ 7 ].
What is the function of eosinophils?
The physiologic functions of eosinophils are incompletely understood, but they are involved in host immune response to infection, tissue remodeling, tumor surveillance, and maintenance of other immune cells ...
What is the role of eosinophils in the peripheral blood?
Eosinophils in the peripheral blood or tissues can increase in a wide array of disease states, ranging in severity from mild to life-threatening, and as a result of several mechanisms. When activated, eosinophils are capable of releasing mediators and substances that can damage tissues and contribute to disease pathology.
What is the normal eosinophil count?
Normal levels — In peripheral blood, an absolute eosinophil count (determined by multiplying the total WBC count by the percentage of eosinophils) of 0 to 500 cells/microL (<0.5 x 10 9 /L) is typically considered normal. Defining the normal range by percentage of WBC can be problematic because differences in absolute neutrophil counts between ethnic groups can dramatically impact the percent of eosinophilia [ 3 ]. In addition, blood eosinophil counts have been reported to vary within the same person at different times of day and on different days, both in individuals with eosinophilic disorders and in healthy volunteers [ 4-6 ]. However, results are inconsistent among studies, and the variability in counts is rarely large enough to impact care.
Why is eosinophilic esophagitis increasing?
At first, researchers thought this was due to an increase in awareness among doctors and greater availability of tests.
What is the reaction of eosinophils?
Eosinophils are a normal type of white blood cells present in your digestive tract. However, in eosinophilic esophagitis, you have an allergic reaction to an outside substance. The reaction may occur as follows: Reaction of the esophagus. The lining of your esophagus reacts to allergens, such as food or pollen.
What is the name of the disease where white blood cells build up in the lining of the mouth?
Eosinophilic esophagitis (e-o-sin-o-FILL-ik uh-sof-uh-JIE-tis) is a chronic immune system disease in which a type of white blood cell (eosinophil) builds up in the lining of the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach (esophagus). This buildup, which is a reaction to foods, allergens or acid reflux, can inflame or injure the esophageal tissue. Damaged esophageal tissue can lead to difficulty swallowing or cause food to get stuck when you swallow.
What is the term for inflammation of the lining of the esophagus?
Esophagitis is inflammation that damages the lining of the esophagus. An endoscope — a long, flexible tube equipped with a camera — may be used to see inside your esophagus. This endoscopic image of eosinophilic esophagitis shows rings of abnormal tissue (esophageal rings) resulting from chronic inflammation.
What are the symptoms of a swollen esophagus?
Symptoms. Signs and symptoms include: Adults: Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) Food getting stuck in the esophagus after swallowing (impaction) Chest pain that is often centrally located and does not respond to antacids. Backflow of undigested food (regurgitation) Children: Difficulty feeding, in infants.
What happens to the lining of the esophagus?
The lining of your esophagus reacts to allergens, such as food or pollen. Multiplication of eosinophils. The eosinophils multiply in your esophagus and produce a protein that causes inflammation. Damage to the esophagus.
Is eosinophilic esophagitis more common in males than females?
Eosinophilic esophagitis is more common in males than in females. Family history. Doctors think that eosinophilic esophagitis may run in the family (have a genetic component). If your family members have eosinophilic esophagitis, you have a greater chance of being diagnosed. Allergies and asthma.
What causes eosinophilia in industrialized countries?
Respiratory, food allergies and dermatitis account for up to 80% of eosinophilia cases in industrialized countries: allergic rhinitis ( mild eosinophilia), asthma, eczema
What are eosinophils?
Eosinophils are white blood cells (leukocytes). There are three main types of white blood cells: neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils.
What is absolute eosinophils count (aec)?
The absolute eosinophil count is simply the absolute count of eosinophils in the white blood cells. Instead of being expressed in percentage we usually count them by absolute number per mm3.
What does high eosinophils mean?
High eosinophils often referred as eosinophilia is defined as an excessive number of eosinophilic cells in the circulation.
What is the eosinophil count in blood?
Moderate: the eosinophil count is between 1,500 and 5,000 per mm3 of blood. This is called hypereosinophilia;
What is the role of eosinophils in the immune system?
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell that play an important role in the body’s response to allergic reactions, asthma and parasitic infections. These cells play a defensive role against certain parasites, but also contribute to the inflammatory response in allergic diseases.
Why is low eosinophil count not a problem?
However, low eosinophil counts usually do not cause problems because other parts of the immune system compensate adequately.