
What causes the P wave to be peaked?
Anything that causes the right atrium to become hypertrophied (such as tricuspid valve stenosis or pulmonary hypertension) causes the P wave to become peaked ( Fig. 4.1 ). 2. Left atrial hypertrophy (usually due to mitral stenosis) causes a broad and bifid P wave ( Fig. 4.2 ).
What are the causes of absence of P waves?
1 Causes of Absence of P Waves 2 Lack of sinus beats - sinus arrest, sinoatrial axit block 3 P wave hidden in the QRS complex - AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, AV reentrant tachycardia 4 Fibrillation or flutter waves - atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter
What does it mean when P waves are high in lead II?
The presence of tall, peaked P waves in lead II is a sign of right atrial enlargement, usually due to pulmonary hypertension (e.g. cor pulmonale from chronic respiratory disease).
What are the different types of P waves?
Common P wave abnormalities include: P mitrale (bifid P waves), seen with left atrial enlargement. P pulmonale (peaked P waves), seen with right atrial enlargement. P wave inversion, seen with ectopic atrial and junctional rhythms. Variable P wave morphology, seen in multifocal atrial rhythms.
What causes P waves peaked or enlarged?
P Pulmonale The presence of tall, peaked P waves in lead II is a sign of right atrial enlargement, usually due to pulmonary hypertension (e.g. cor pulmonale from chronic respiratory disease).
Why do ECG waves start with P?
His labeling of the primitive tracing was then mixed: A and B, the first letters of the alphabet, were used to indicate ventricular events, and P, from near the middle of the alphabet, was used to indicate atrial events.
What do P waves indicate?
The P wave represents the electrical depolarization of the atria. In a healthy person, this originates at the sinoatrial node (SA node) and disperses into both left and right atria.
What do abnormal P waves indicate?
P Waves. Tall (>2.5 mm), narrow, and spiked P waves are indicative ofright atrial enlargement and are seen in congenital pulmonary stenosis, Ebstein anomaly of the tricuspid valve, tricuspid atresia, and sometimes cor pulmonale. These abnormal waves are most obvious in leads II, V3R, and V1 (Fig. 450.8A).
How are P waves different from T waves?
In a normal ECG different waves like P-wave, the QRS complex, and the T-wave are seen....Complete answer:P-WaveT-WaveThe normal duration of the P-wave is 0.1 seconds.The normal duration of the T-wave is 0.2 seconds.The normal amplitude of P-wave is 0.1 to 0.12 mV.The normal amplitude of T-wave is 0.3 mV3 more rows
What do the P QRS and T waves represent?
The P wave in an ECG complex indicates atrial depolarization. The QRS is responsible for ventricular depolarization and the T wave is ventricular repolarization.
What does P axis mean on an ECG?
P-wave axis is a measure of the net direction of atrial depolarization. It is determined by measuring net positive or negative P-wave deflections on all six limb leads and calculating the net direction of electrical activity using the hexaxial reference system.
When do you see P waves before QRS?
The presence of P waves immediately before every QRS complex indicates sinus rhythm. If there are no P waves, note whether the QRS complexes are wide or narrow, regular or irregular.
What does it mean when there are no P waves?
A lack of visible P waves preceding QRS complexes suggests a lack of sinus beats; this may occur with sinus dysfunction or in the presence of fibrillation or flutter waves. The P wave may also be hidden within the QRS complex.
What is bifid P wave?
Bifid P waves are also referred to as P mitrale. Their presence indicates dyssynchrony between right and left atrial depolarisation; this may be normal, or suggestive of left atrial enlargement.
What does it mean when there are multiple P wave morphologies?
The presence of multiple P wave morphologies indicates multiple ectopic pacemakers within the atria and/or AV junction . If ≥ 3 different P wave morphologies are seen, then multifocal atrial rhythm is diagnosed:
What does it mean when you have a P wave in lead II?
The presence of tall, peaked P waves in lead II is a sign of right atrial enlargement, usually due to pulmonary hypertension (e.g. cor pulmonale from chronic respiratory disease).
What does the separation of right and left atrial electrical forces in lead V1 mean?
This separation of right and left atrial electrical forces in lead V1 means that abnormalities affecting each individual atrial waveform can be discerned in this lead. Elsewhere, the overall shape of the P wave is used to infer the atrial abnormality.
Which direction do the right and left atrial waveforms move?
However, in lead V1 the right and left atrial waveforms move in opposite directions. This produces a biphasic P wave with the initial positive deflection corresponding to right atrial activation and ...
What is the first positive deflection on the ECG?
The P wave is the first positive deflection on the ECG
How wide is the P wave?
The combined depolarisation wave, the P wave, is less than 120 ms wide and less than 2.5 mm high
Is the P wave biphasic?
The P wave is typically biphasic in V1, with similar sizes of the positive and negative deflections.
What is the P wave in ECG?
The P wave and PR segment is an integral part of an electrocardiogram (ECG). It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart. It is typically a small positive deflection from the isoelectric baseline that occurs just before the QRS complex. It can sometimes have abnormalities in morphology or timing that can be indicative of significant clinical pathology.[1] An understanding of the normal and abnormal P wave morphology is, therefore, a crucial part of ECG interpretation. This article will review the basics of P wave interpretation, including characteristics of both the normal P wave and its pathologic abnormalities.
Why is it important to alert clinicians of an abnormal rhythm or electrical conduction defect on ECG?
Early identification by nursing staff to alert clinicians of an abnormal rhythm or electrical conduction defect on ECG can lead to rapid management and decreased morbidity and mortality of patients. It is in the patients' best interest for all healthcare team members to have the ability and confidence to point out P wave abnormalities and PR segment prolongations or heart blocks.
What is the PR interval?
The PR interval represents the time between atrial depolarization and ventricular depolarization. Abnormalities in the timing of the PR segment can indicate pathology.
What causes the P wave to become peaked?
Apart from alterations of the shape of the P wave associated with rhythm changes, there are only two important abnormalities: 1. Anything that causes the right atrium to become hypertrophied (such as tricuspid valve stenosis or pulmonary hypertension) causes the P wave to become peaked ( Fig. 4.1 ).
What is Q wave in lead III?
Curiously, a ‘Q’ wave in lead III resembling an inferior infarction (see below). However, do not hesitate to treat the patient if the clinical picture suggests pulmonary embolism but the ECG does not show the classical pattern of right ventricular hypertrophy. If in doubt, treat the patient with an anticoagulant.
What are the three abnormalities of the QRS complex?
2. The QRS complex can only have three abnormalities – it can be too broad or too tall, and it may contain an abnormal Q wave. 3. The ST segment can only be normal, elevated or depressed. 4. The T wave can only be the right way up or the wrong way up.
Which leads have right ventricular hypertrophy?
Right ventricular hypertrophy is best seen in the right ventricular leads (especially V 1. Since the left ventricle does not have its usual dominant effect on the QRS shape, the complex in lead becomes upright (i.e. the height of the R wave exceeds the depth of the S wave) – this is nearly always abnormal ( Fig. 4.3 ). There will also be a deep S wave in lead V 6.
Is the P wave normal?
1. The P wave can only be normal, unusually tall or unusually broad .
What are the P waves?
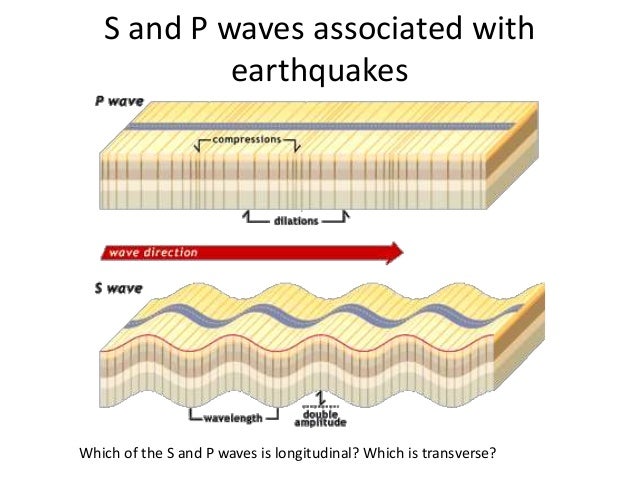
P waves. P waves, or Primary waves, are the first waves to arrive at a seismograph. P waves are the fastest seismic waves and can move through solid, liquid, or gas. They leave behind a trail of compressions and rarefactions on the medium they move through. P waves are also called pressure waves for this reason.
How to understand P waves?
To understand P waves, we have to first look into the basics of seismology and seismic waves. The waves of energy that travel through the earth and cause earthquakes and related phenomena are seismic waves. There are two types of seismic waves : 1 Body waves 2 Surface waves
What are the two types of seismic waves?
There are two types of seismic waves : Body waves. Surface waves. Body waves are the waves that can travel through the layers of the earth. They are the fastest waves and as a result, the first waves that seismographs can record. Body waves can move through all states of matter including rocks and molten lava.
Can shear waves move through solids?
They are compression waves. They are shear waves. Can move through solids and liquids. Can only move through solids. Shake the medium in the direction in which they are propagating. Shake the medium in the direction perpendicular to which they are moving.
Why are R waves high?
It is important to assess the amplitude of the R-waves. High amplitudes may be due to ventricular enlargement or hypertrophy. To determine whether the amplitudes are enlarged, the following references are at hand:
Which wave progression follows the same rules as R wave progression?
T-wave progression follows the same rules as R-wave progression (see earlier discussion).
How many vectors are generated by depolarization of the ventricles?
Depolarization of the ventricles generates three large vectors, which explains why the QRS complex is composed of three waves. It is fundamental to understand the genesis of these waves and although it has been discussed previously a brief rehearsal is warranted. Figure 7 illustrates the vectors in the horizontal plane. Study Figure 7 carefully, as it illustrates how the P-wave and QRS complex are generated by the electrical vectors.
Why is Q wave important?
The Q-wave. It is crucial to differentiate normal from pathological Q-waves, particularly because pathological Q-waves are rather firm evidence of previous myocardial infarction. However, there are numerous other causes of Q-waves, both normal and pathological and it is important to differentiate these.
Why is the atria small?
It is small because the atria make a relatively small muscle mass. If the rhythm is sinus rhythm (i.e under normal circumstances) the P-wave vector is directed downwards and to the left in the frontal plane and this yields a positive P-wave in lead II ( Figure 2, right-hand side).
Which direction do vectors resulting from activation of the ventricular free walls go?
The vectors resulting from activation of the ventricular free walls are directed to the left and downwards ( Figure 7 ). The explanation for this is as follows:
Where is the T wave vector?
The T-wave vector is directed to the left, downwards and to the back in children and adolescents . This explains why these individuals display T-wave inversions in the chest leads. T-wave inversions may be present in all chest leads. However, these inversions are normalized gradually during puberty. Some individuals may display persisting T-wave inversion in V1–V4, which is called persisting juvenile T-wave pattern. If all T-waves persist inverted into adulthood, the condition is referred to as idiopathic global T-wave inversion.
What does it mean when the P wave is inverted?
If the p-wave is enlarged, the atria are enlarged . If the P wave is inverted, it is most likely an ectopic atrial rhythm not originating from the sinus node. Altered P wave morphology is seen in left or right atrial enlargement. The PTa segment can be used to diagnose pericarditis or atrial infarction.
What is the maximum height of the P wave?
The maximal height of the P wave is 2.5 mm in leads II and / or III. An example of normal sinus rhythm. center}Another example of normal sinus rhythm.
Is the p wave biphasic or positive?
The p wave is positive in II and AVF, and biphasic in V1. The p wave duration is shorter than 0.12 seconds. An example of normal sinus rhythm. center}Another example of normal sinus rhythm.
