Paramyxovirus. Transmission occurs primarily from direct contact with feces, respiratory secretions or through a contaminated environment. Poultry populations are especially susceptible to infections when in close contact with other birds commonly infected like cormorants, pigeons, and imported psittacine species.
Full Answer
What are the three types of Paramyxoviridae?
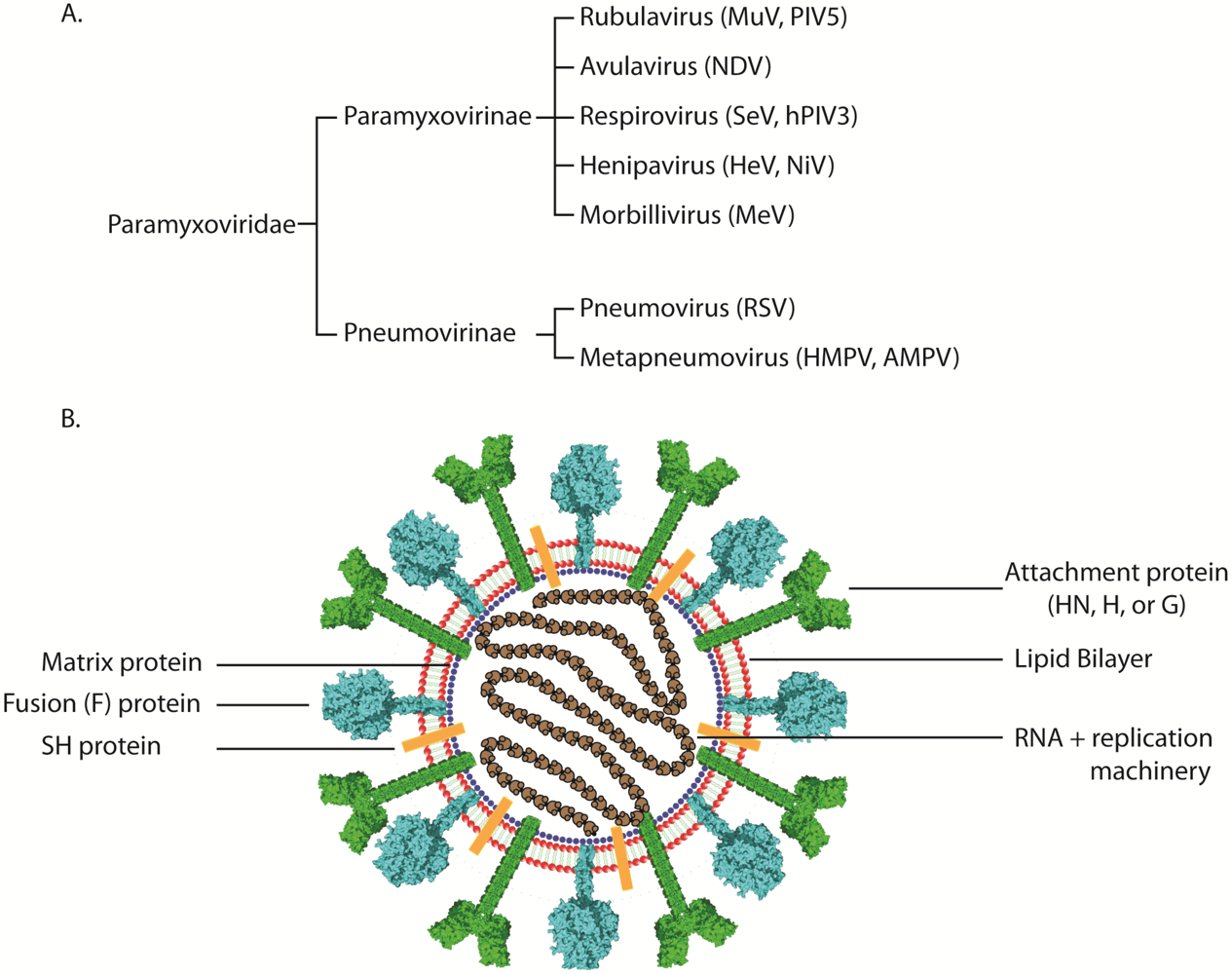
The family Paramyxoviridae consists of three genera: Paramyxovirus, Pneumovirus, and Morbillivirus (Table 59-1). All members of the genus Paramyxovirus share similar properties. Pneumoviruses lack hemagglutinin and neuraminidase activity. They also differ from other paramyxoviruses in morphology (diameter of nucleocapsid and surface projections). Morbillivirus is distinguished by the absence of neuraminidase in the virions and by the presence of common envelope and nucleocapsid antigens in the species listed in Table 59-1.
What is the Morbillivirus family?
The family Paramyxoviridae consists of three genera: Paramyxovirus, Pneumovirus, and Morbillivirus (Table 59-1).
What is a paramyxovirus?
Paramyxoviruses are enveloped, single-stranded negative-sense RNA viruses that replicate in the cytoplasm. Diseases caused by these viruses continue to produce high mortality and morbidity across the world.[1] . With the development and use of vaccinations and medications, the incidence of serious illness due to paramyxoviruses has tremendously ...
How does paramyxovirus spread?
The paramyxoviruses primarily spread via respiratory droplets. To avoid the spread of this virus, appropriate administration of vaccinations, appropriate hand washing, and appropriate hygiene and employment of face masks are highly encouraged.
What is the bacterial etiology of croup?
In the United States, 7% of pediatric populations under age 5 will be admitted for croup. Type 3 parainfluenza virus could also cause bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
What is the name of the family of single stranded RNA viruses that cause different types of infections in verte?
Last Update: January 10, 2021. Continuing Education Activity. The Paramyxoviridae is a family of single-stranded RNA viruses known to cause different types of infections in vertebrates. Examples of these infections in humans include the measles virus, mumps virus, parainfluenza virus, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Which family of Paramyxoviridae gives rise to the genus Pneumovirus?
The family Paramyxoviridae contains two subfamilies that are relevant to humans: Pneumovirinae and Paramyxovirinae. The subfamily Pneumovirinae gives rise to the genus Pneumovirus (respiratory syncytial virus). The subfamily Paramyxovirinae gives rise to the genus Morbillivirus (measles virus/ rubeola), to the genus Respirovirus (para-influenza viruses 1 and 3), and to the genus Rubulavirus (mumps virus and para-influenza viruses 2 and 4).[3] The transmission occurs via respiratory droplets or direct contact. [3]
What are the symptoms of parotitis?
Prodrome symptoms may include fever, headache, myalgias, weakness, malaise, and anorexia. Parotitis is present in 70% of Mumps infection, as it is the most common manifestation.
How is RSV transmitted?
RSV is transmitted via respiratory droplets. Patients with a history of prematurity, immunosuppression, and the elderly are at higher risk of morbidity and mortality from RSV infections. [8] History and Physical.
How to report pigeon paramyxovirus?
If you suspect it you must report it immediately by calling the Defra Rural Services Helpline on 03000 200 301. In Wales, contact 0300 303 8268. In Scotland, contact your local Field Services Office. Failure to do so is an offence.
What to do if you report paramyxovirus in a pigeon?
If you report suspicion of paramyxovirus infection in a racing or other captive pigeon, the Animal and Plant Health Agency ( APHA) vets will investigate.
Is pigeon disease contagious?
The disease is very contagious so it is common for most of the pigeons sharing a loft to display clinical signs at the same time.
Can pigeons get paramyxovirus?
pigeon fanciers carrying infection on their clothes, hands and feet. The disease can be introduced to a loft of kept pigeons through contact with wild pigeons. The disease can be spread to chickens if, for example, their feed is infected with the faeces of infected pigeons. In chickens paramyxovirus can cause Newcastle disease.
Which family of viruses are closely related to the avulavirus?
Rubulavirus - The viruses in this family are closely related to the avulavirus, but utilize humans, apes, pigs, and dogs as their natural hosts rather than birds
What is the name of the virus that attacks snakes?
The paramyxovirus that attacks snakes is the Fer-de-Lance paramyxovirus, previously known as ophidian paramyxovirus. It's currently the only virus in the Ferlavirus genus. This virus attacks the respiratory system of the snake and can cause severe congestion and neurological disturbances.
How to determine if a snake has a virus?
The examining doctor will then determine the animal’s rate of breathing and will use an ultrasonic device known as a doppler to record the snake’s heart rate. A haemagglutination inhibition test may help to reveal exposure to this virus in living animals, but the definitive diagnosis is frequently made during the necropsy by virus isolation using tissues from the vital organs such as the lungs, liver, kidneys, or heart.
Can you quarantine a snake with paramyxovirus?
Any reptile suspected of paramyxovirus should be quarantined from other reptiles as soon as possible to prevent the spread of this virus. As this virus can easily spread through a population of snakes, proper hygiene should observed when working with infected animals to ensure no cross infection takes place. Although there is no specific medication to fight the virus itself, supportive measures that are provided to the patient may improve their chances of surviving the illness on their own.
Symptoms of Paramyxovirus
Anytime you have a sick pigeon, it pays to call the vet and have them examined. If your vet doesn’t deal with pigeons, try your local/nearest pigeon-friendly rescue center.
Tr ansmission of Paramyxovirus
This viral disease is very transmissible and once established, spreads very rapidly.
What are the most common diseases caused by paramyxovirus?
Pathogenic paramyxoviruses. A number of important human diseases are caused by paramyxoviruses. These include mumps, as well as measles, which caused around 733,000 deaths in 2000. The human parainfluenza viruses (HPIV) are the second most common causes of respiratory tract disease in infants and children.
What happens when a paramyxovirus is exposed to UV light?
When paramyxovirus genome was exposed to UV light, the level of inhibition of transcription was proportional to the distance from the leader sequence. That is, the further the gene is from the leader sequence, the greater the chance of RNA dimerization inhibiting RNA polymerase.
How many species are in the Avulavirinae family?
Subfamily: Avulavirinae, which contains three genera and 22 species. Subfamily: Metaparamyxovirinae, which contains one genus and one species. Subfamily: Orthoparamyxovirinae, which contains eight genera and 34 species. Subfamily: Rubulavirinae, which contains two genera and 18 species. Unassigned genera:
How does a virus take advantage of the single promoter model?
The virus takes advantage of the single promoter model by having its genes arranged in relative order of protein needed for successful infection. For example, nucleocapsid protein, N, is needed in greater amounts than RNA polymerase, L.
Why is the genome of paramyxovirus always multiple of six?
The total length of the genome is almost always a multiple of six. This is probably due to the advantage of having all RNA bound by N protein (since N binds hexamers of RNA). If RNA is left exposed, the virus does not replicate efficiently. The gene sequence is:
What are the subfamilies of RNA viruses?
Subfamilies. Avulavirinae. Metaparamy xovirinae. Orthoparamyxovirinae. Rubulavirinae. Paramyxoviridae (from Greek para- “by the side of” and myxa “ mucus ”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts.
Why are viruses antigenically stable?
Viruses in the Paramyxoviridae family are also antigenically stable, meaning that the glycoproteins on the viruses are consistent between different strains of the same type. Two reasons for this phenomenon are posited: The first is that the genome is nonsegmented, thus cannot undergo genetic reassortment.