What are the causes of pompholyx eczema?
The exact causes of pompholyx eczema are not known, although it is thought that factors such as stress, sensitivity to metal compounds (such as nickel, cobalt or chromate), heat and sweating can aggravate this condition. Fifty percent (50%) of people with pompholyx have atopic eczema as well, or a family history of atopic eczema.
What can aggravate pompholyx?
Pompholyx may be aggravated by anything which is irritant to the skin, such as detergents, various solvent-type chemicals and water (if there is frequent or prolonged contact with water). Suffer from dermatitis? Who develops pompholyx?
Can pompholyx eczema cause paronychia?
Pompholyx eczema can also affect the nail folds and skin around the nails, causing swelling (paronychia). What causes pompholyx eczema?
What are other conditions that look like pompholyx?
Conditions that can look similar to pompholyx include: bullous impetigo – a contagious skin infection that mainly affects children and causes sores and blisters. bullous pemphigoid – a blistering skin condition that tends to affect the elderly.
See more
How do you prevent pompholyx?
Here's what dermatologists recommend does just that:Remove your rings BEFORE you: ... Wash skin with dyshidrotic eczema gently. ... Ask your dermatologist to recommend a hand sanitizer. ... Apply moisturizer (or barrier repair cream) frequently throughout your day. ... Learn to manage stress really well. ... Try to avoid scratching.More items...•
Can pompholyx be cured?
Your doctor might call it by another name, including dyshidrosis, foot-and-hand eczema, pompholyx, vesicular eczema, or palmoplantar eczema. There's no cure, so these blisters will come and go over time. But you can manage them with medicine, moisturizers, and good hygiene.
What is the fluid in pompholyx?
Botulinum toxin is a substance that affects the nerves in the skin. Exactly why this works for pompholyx is not known. Possibly, it works by affecting the sweat glands, reducing sweat and moisture in the skin. Testing and treating for possible trigger factors.
Does Pompholyx eczema go away?
Pompholyx eczema usually goes away without problems, but symptoms may come back. Severe scratching may lead to thick, irritated skin.
Can you spread pompholyx?
Dyshidrotic eczema isn't contagious, so you can't pass it on to someone or get it from another person. However, an eczema rash can become infected. To lower your risk for infection, take care of your skin and avoid triggers that worsen your condition.
Is pompholyx contagious?
Dyshidrotic eczema isn't contagious. You can't spread it to another person. If you scratch your blisters, you may break your skin, which can lead to infections. If your blisters become infected, contact your healthcare provider.
Is pompholyx stress related?
The exact causes of pompholyx eczema are not known, although it is thought that factors such as stress, sensitivity to metal compounds (such as nickel, cobalt or chromate), heat and sweating can aggravate this condition.
Is pompholyx genetic?
Pompholyx often occurs sporadically, but a genetic predisposition for pompholyx formation has been considered. The first familial aggregation of pompholyx was noted as early as 1969 and the results showed an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern (Curth, 1969).
Should I pop pompholyx?
Is it OK to pop eczema blisters? Though it might be tempting to pop the blisters, especially if they itch or hurt, try to resist the urge. Popping blisters can actually cause more pain and give bacteria a chance to get under your skin and cause an infection. It's also important not to scratch or pick at the blisters.
Can pompholyx spread to other parts of body?
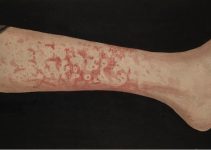
Signs and symptoms of pompholyx In severe cases, the blisters may be quite large and may spread to the backs of the hands, feet and limbs. The skin can sometimes become infected. Signs of an infection can include the blisters becoming very painful and oozing pus or becoming covered in a golden crust.
Is dyshidrotic eczema an autoimmune disease?
Few studies have looked at the immune response in people with dyshidrotic eczema, so it is unclear if it has an autoimmune component.
Is it OK to pop dyshidrotic eczema?
Do not pop the blisters of dyshidrotic eczema because of the risk of infection. A doctor may prescribe a cream to help the rash heal.
Is Pompholyx genetic?
Pompholyx often occurs sporadically, but a genetic predisposition for pompholyx formation has been considered. The first familial aggregation of pompholyx was noted as early as 1969 and the results showed an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern (Curth, 1969).
Why is Pompholyx so itchy?
The exact causes of pompholyx eczema are not known, although it is thought that factors such as stress, sensitivity to metal compounds (such as nickel, cobalt or chromate), heat and sweating can aggravate this condition.
Is Dyshidrotic eczema an autoimmune disease?
Few studies have looked at the immune response in people with dyshidrotic eczema, so it is unclear if it has an autoimmune component.
How long does it take for Dyshidrosis to go away?
Dyshidrotic eczema blisters tend to go away within 3–4 weeks. The skin generally becomes dry and cracks or peels as it starts to heal. In severe cases, the blisters may be quite large and spread to the backs of the hands, feet, and limbs. The condition is not contagious to others.
What is pompholyx?
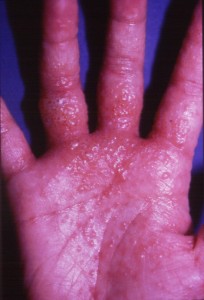
Pompholyx is a type of eczema which affects the hands and feet, causing tiny blisters and irritation. Eczema is a condition causing skin inflammation. See separate leaflet called Atopic Eczema for more details. Pompholyx is also known as dyshidrotic eczema or vesicular eczema of the hands and feet. Other names are cheiropompholyx if it affects the hands, or pedopompholyx if it affects the feet.
Who develops pompholyx?
Pompholyx probably affects about 1 in 20 people who have hands eczema. It is less common after middle age and in older people. It is slightly more common in women than in men. It happens more often in the spring and summer and is more common in warmer countries.
What are the symptoms of pompholyx?
They are located on the palms or fingers of the hands (often on the sides of the fingers) and on the toes or soles of the feet. The blisters may feel itchy or burning sensation. Sometimes the small blisters can merge to form larger ones. As the blisters start to heal, the skin goes through a dry stage where there are cracks or peeling skin.
How is pompholyx diagnosed?
It is diagnosed by the medical history and the appearance of the skin. Samples (swabs) are sometimes taken to rule out infection and you may be asked to have a blood test if the diagnosis is not obvious. A small piece of skin (a biopsy) may also need to be taken for examination under the microscope.
What is the treatment for pompholyx?
As with eczema, there is no absolute cure for pompholyx but it does respond to treatments. Possible treatments are:
What is the name of the condition where you get itchy blisters on your hands and feet?
Pompholyx is a type of eczema where there are itchy blisters on the hands and feet, followed by inflamed and dry skin. It can be a temporary condition, or in some cases, is more persistent. There are various treatments that can help. Pompholyx.
How long does it take for pompholyx to clear up?
The time course of pompholyx varies for each individual. In some people it clears up in about 3-4 weeks and does not return. In others, it can be more persistent (doctors call this the chronic form). Some people have repeated bouts - each lasting a few weeks - and so the condition may seem to wax and wane.
What causes pompholyx?
It's not clear exactly what causes pompholyx, but it may be triggered or made worse by:
What is pompholyx in the summer?
stress. sweating – pompholyx is more common in spring and summer, in warmer climates, and in people with excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis)
What to do if your pompholyx keeps returning?
If your pompholyx keeps returning or is severe and does not get better with the above treatments, your GP may refer you to a specialist in treating skin conditions (dermatologist). A dermatologist may recommend 1 of the following treatments: phototherapy – controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light.
What to do for pompholyx?
The main treatments your GP may recommend to treat the symptoms of pompholyx are similar to those used when treating atopic eczema, including: emollients (moisturisers) – use these all the time and instead of soap to stop your skin becoming dry.
What is the name of the blister on the palm of the hand?
Pompholyx (dyshidrotic eczema) Pompholyx (dyshidrotic eczema) is a type of eczema that causes tiny blisters to develop across the fingers, palms of the hands and sometimes the soles of the feet. It can affect people of any age, but it's most often seen in adults under 40. Pompholyx can sometimes be confused with similar-looking conditions.
How do you know if you have pompholyx?
Symptoms of pompholyx. Pompholyx usually starts as intense itching and burning of the skin on the hands and fingers. The palms and sides of the fingers (and sometimes the soles of the feet) then erupt into tiny itchy blisters that may weep fluid. Credit:
How long does it take for pompholyx to clear up?
In many cases, pompholyx will clear up on its own within a few weeks. The treatments below may help relieve your symptoms in the meantime.
What is the best treatment for pompholyx?
Treatment may include a short course of oral immunosuppressant drugs. Alitretinoin (known as Toctino) is an oral treatment licensed for use in adults with severe chronic hand eczema (including pompholyx) that has not responded to treatment with potent topical steroids. Alitretinoin works by reducing the inflammation associated with eczema as well as damping down the response of the immune system. It is a capsule that is taken by mouth once a day with a meal for 12-24 weeks, depending on how the condition responds to the treatment.
What is the name of the rash on the side of the hand?
Pompholyx eczema (also known as dyshidrotic eczema/dermatitis) is a type of eczema that usually affects the hands and feet. In most cases, pompholyx eczema involves the development of intensely itchy, watery blisters, mostly affecting the sides of the fingers, the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Some people have pompholyx eczema on their hands and/or feet with other types of eczema elsewhere on the body. This condition can occur at any age but is usually seen in adults under 40, and is more common in women.
Can you get pompholyx from your hands?
First, any obvious trigger for the pompholyx flare should be avoided as far as possible, especially in the case of a The hands and feet, where pompholyx commonly occurs, contact allergy. are areas of the body that are also prone to contact dermatitis. This can take one of two forms – irritant contact dermatitis or allergic contact dermatitis.
What is the name of the blisters on the palm of your hand?
Treatment. Prevention. Dyshidrotic dermatitis is a skin condition characterized by small, itchy blisters over the palms, fingers, or feet. These progress to scaly spots over the course of several weeks. Also known as dyshidrotic eczema, foot-and-hand eczema, and pompholyx, it can be associated with atopic dermatitis and seasonal allergies.
How to diagnose dyshidrotic eczema?
There is no specific test that can definitively diagnose dyshidrotic eczema. It's generally diagnosed by a physical exam coupled with a detailed medical history.
When is dyshidrotic eczema most common?
Dyshidrotic eczema is most common between the ages of 20 and 40, although it may appear at any age. Women are twice as likely to develop the condition than men. There is a strong link between this condition and atopic dermatitis. Almost 50% of those with dyshidrotic dermatitis also have atopic dermatitis.
Why do blisters need to be drained?
Large blisters can be drained by a healthcare provider to help reduce pain and prevent infections.
Is dyshidrotic dermatitis atopic?
Almost 50% of those with dyshidrotic dermatitis also have atopic dermatitis. This leads some to believe that dyshidrotic dermatitis is a form of atopic dermatitis on the hands and feet. It's also more common in those with seasonal allergies and those with a history of contact dermatitis.
What causes atopic dermatitis?
It can be associated with a similar skin disorder called atopic dermatitis (eczema), as well as with allergic conditions, such as hay fever. Eruptions may be seasonal in people with nasal allergies.
What causes blisters on the bottom of the feet?
Dyshidrosis. Dyshidrosis causes very small, fluid-filled blisters to occur on the soles of the feet, the palms of the hands or sides of the fingers. Dyshidrosis is a skin condition that causes small, fluid-filled blisters to form on the palms of the hands and sides of the fingers. Sometimes the bottoms of the feet are affected too.
Why is dyshidrosis more common?
Stress. Dyshidrosis appears to be more common during times of emotional or physical stress.
Where do blisters occur?
The blisters associated with dyshidrosis occur most commonly on the sides of the fingers and the palms. Sometimes the soles of the feet also can be affected. The blisters are usually small — about the width of a standard pencil lead — and grouped in clusters, with an appearance similar to tapioca. In more-severe cases, the small blisters may merge ...
Can dyshidrosis cause itching?
Complications. For most people with dyshidrosis, it's just an itchy inconvenience. For others, the pain and itching may limit the use of their hands or feet. Intense scratching can increase the risk of a bacterial infection developing in the affected skin.
