
What causes prothrombin gene mutation? It is caused by a change or mutation in the gene for the blood clotting protein called prothrombin (which is also called Factor II). People with the prothrombin gene mutation have higher than normal levels of prothrombin in their blood, making them prone to blood clots, most common in the veins.
Which type of gene mutation is more damaging?
What causes prothrombin gene mutation? It is a genetic mutation in your Factor II gene that makes it create too much prothrombin (coagulation factor II), and you end up with a higher risk of developing blood clots than someone with a normal prothrombin gene. Other things can add to your blood clot risk, including: Smoking. Having surgery.
What causes thrombin gene mutation?
It can be caused by: Lack of vitamin K (some babies are born with vitamin K deficiency) Severe liver disease. Use of medicines that prevent clotting (anticoagulants such as warfarin)
What diseases are caused by gene mutations?
· The Risks of Prothrombin Gene Mutation in Pregnancy. pregnancy loss (miscarriage or stillbirth) preeclampsia (increased blood pressure and protein in the urine during pregnancy) slow fetal growth. placental abruption (early separation of …
What do high prothrombin levels mean?
· The presence of the mutated gene is associated with increased levels of prothrombin in the blood plasma by 30% in heterozygotes. Prothrombin is a protein present in blood, which is essential for blood clotting. Also called factor II. The clot is formed by the combination of platelets and clotting protein mesh of fibrin.

How common is prothrombin gene mutation?
How common is prothrombin gene mutation? About 1 in every 50 white people in Europe and North America has the heterozygous prothrombin gene mutation, making it the second most common inherited clotting disorder.
What do you do if you have a prothrombin mutation?
No treatment can prevent the prothrombin gene mutation or make it go away. The goal of treatment is to prevent blood clots (see next question and page 7). If you have had a blood clot, you may be treated with medications called anticoagulants. Anticoagulants are used to help to prevent blood clots.
Can you have a baby with prothrombin gene mutation?
The second most common genetic type is prothrombin thrombophilia, which mainly affects people of European ancestry. It involves a mutation in the F2 gene. Genetic types of thrombophilia may raise the risk of multiple miscarriages, but most women with these genetic mutations have normal pregnancies.
How serious is prothrombin gene mutation?
Having the prothrombin mutation increases the risk of developing a DVT (a blood clot in the deep veins, typically the legs) and/or PE (blood clot that travels to the lungs). DVTs are dangerous because they can damage the veins, leading to pain and swelling, and sometimes to disability.
How is prothrombin gene mutation inherited?
The Prothrombin Gene Mutation is an inherited condition (i.e. from your parents). We inherited one copy of each gene from each of our parents. One (or both) of your parents will have passed the Prothrombin Gene Mutation on to you and you may pass the condition onto your children.
Is prothrombin gene mutation recessive?
Prothrombin-related thrombophilia is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. All individuals inherit two copies of each gene .
How do you test for prothrombin gene mutation?
Prothrombin testing is done by taking a blood sample, and using a genetic test to look at the prothrombin gene. The DNA is isolated from blood cells and the prothrombin gene is examined to see if there is a mutation in the DNA code.
Does prothrombin increase in pregnancy?
It has been demonstrated that thrombin (resulting from prothrombin) generation increased during pregnancy, starting with the very early stages of the first trimester of normal pregnancy. We did not determine thrombin values, but prothrombin time was within normal limits in healthy pregnant patients.
What is the gene for prothrombin?
The prothrombin gene G20210A mutation differs from the gene for normal prothrombin or factor II by a single nucleotide (nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA). This mutation causes the body to produce excess amounts of prothrombin. Consequently, in individuals with the prothrombin gene mutation, prothrombin levels are higher, ...
Does prothrombin cause blood clots?
Consequently, in individuals with the prothrombin gene mutation, prothrombin levels are higher, which in turn contributes to the formation of blood clots. Individuals who have inherited one copy of the gene (heterozygotes) have a risk of DVT or PE similar to the risk of individuals who have inherited one copy of the factor V Leiden gene.
How common is the prothrombin gene mutation?
The Prothrombin Gene Mutation is relatively common – it occurs in about 1 in every 50 people in Australia. This mutation is more common than many other gene changes (mutations). Because the mutation is very common, it has been suggested that there is some “benefit” in having the Prothrombin Gene Mutation.
What is the gene that controls a blood clotting protein that circulates in the blood called?
The Prothrombin Gene Mutation is a change in the gene that controls a blood clotting protein that circulates in the blood called prothrombin. This particular gene change leads to an increase in the level of this protein in the blood.
Where do blood clots occur?
Blood clots can occur in blood vessels and can sometimes travel to different parts of the body including the lungs. Having the Prothrombin Gene Mutation increases your risk of having a blood clot.
What is the mutation of the prothrombin gene?
Mutation of the prothrombin gene can be also called a mutation of factor II (FII), prothrombin mutation 20210 or is referred to as prothrombin G20210A. This is the second most common inherited thrombophilia.
How to diagnose prothrombin mutation?
Diagnosis of prothrombin gene mutation is carried out by a blood test. The blood is sent to a laboratory for analysis of DNA (genetic code), and it detects, if the patient is homozygote or heterozygote for this mutation.
Can prothrombin cause heart attacks?
However, most studies indicated that the prothrombin mutation is not a risk factor for heart attack and stroke in middle and older age. Several studies have demonstrated that prothrombin mutation may increase the risk of heart attack in young women, especially among the smokers.
What is the protein that forms blood clots?
Prothrombin is a blood clotting protein that is needed to form fibrin. If somebody has too little prothrombin , he or she has a bleeding tendency.
What is the mutated gene?
The presence of the mutated gene is associated with increased levels of prothrombin in the blood plasma by 30% in heterozygotes. Prothrombin is a protein present in blood, which is essential for blood clotting. Also called factor II. The clot is formed by the combination of platelets and clotting protein mesh of fibrin.
What is the role of thrombin in blood coagulation?
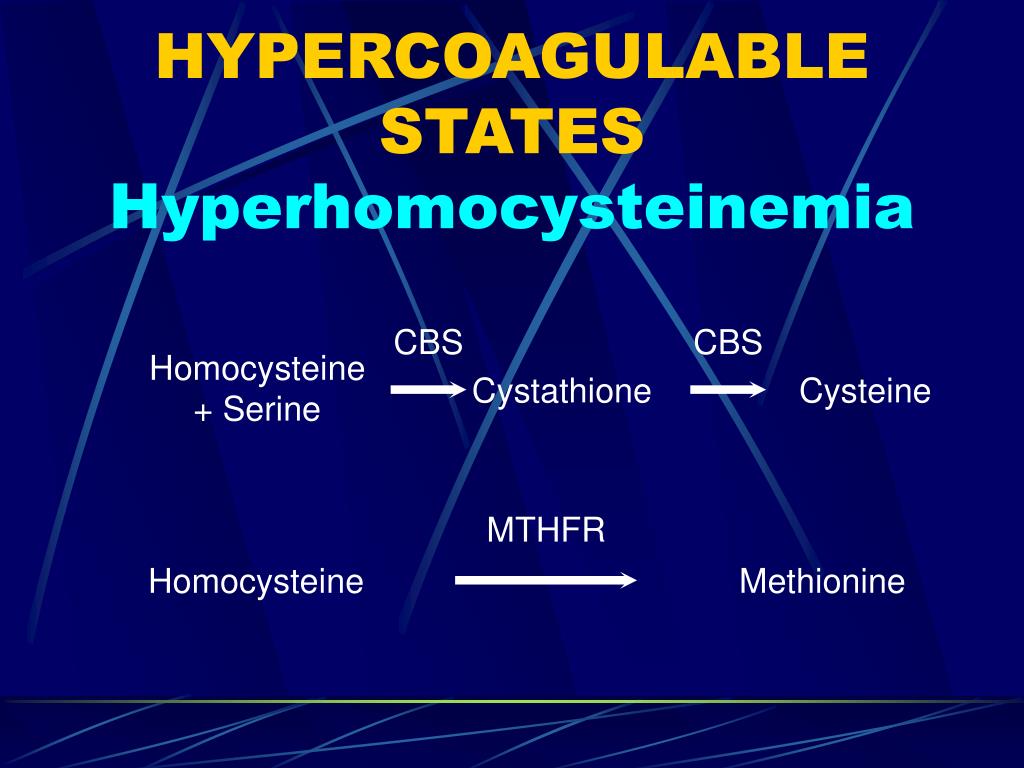
Thrombin plays a key role in the initiation of blood coagulation. If therefore G20210A mutation increases the level of thrombin in blood plasma it increases the risk of excessive blood coagulation and thrombosis.
What are the risks of thrombophilia?
A healthy lifestyle and avoiding risk factors such as obesity, smoking. Avoid long immobility (e.g. when traveling) and dehydration.
What is the cause of prothrombin thrombophilia?
Prothrombin thrombophilia is caused by a particular mutation in the F2 gene. The F2 gene plays a critical role in the formation of blood clots in response to injury. The protein produced from the F2 gene, prothrombin (also called coagulation factor II), is the precursor to a protein called thrombin that initiates a series ...
What is the inherited disorder of blood clotting?
Prothrombin thrombophilia is an inherited disorder of blood clotting. Thrombophilia is an increased tendency to form abnormal blood clots in blood vessels. People who have prothrombin thrombophilia are at somewhat higher than average risk for a type of clot called a deep venous thrombosis, which typically occurs in the deep veins of the legs. Affected people also have an increased risk of developing a pulmonary embolism, which is a clot that travels through the bloodstream and lodges in the lungs. Most people with prothrombin thrombophilia never develop abnormal blood clots, however.
What is thromophilia in blood?
Thrombophilia is an increased tendency to form abnormal blood clots in blood vessels. People who have prothrombin thrombophilia are at somewhat higher than average risk for a type of clot called a deep venous thrombosis, which typically occurs in the deep veins of the legs. Affected people also have an increased risk of developing ...
How is prothrombin related thrombophilia inherited?
Prothrombin-related thrombophilia is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern . [1] All individuals inherit two copies of each gene. Autosomal means the gene is found on one of the numbered chromosomes found in both sexes. Dominant means that only one pathogenic variant on one copy of a gene is necessary to have the condition. The variant can be inherited from either parent. Sometimes an autosomal dominant condition occurs because of a new genetic variant ( de novo ), and there is no history of this condition in the family.#N#Each child of an individual with an autosomal dominant condition has a 50% or 1 in 2 chance of inheriting the variant and the condition. Typically, children who inherit a dominant variant will have the condition, but they may be more or less severely affected than their parent. Sometimes a person may have a gene variant for an autosomal dominant condition and show no signs or symptoms of the condition. Individuals with prothrombin-related thrombophilia may inherited one or two copies of the gene variant.
Can you get a blood clot while pregnant?
Blood clot during pregnancy. Many people with prothrombin-related thrombophilia have no symptoms and never have a blood clot. Factors that may increase the risk for getting blood clots in people with this condition include underlying medical conditions, use of oral contraceptives, and having a family history of blood clots. [1] [2]
What does it mean to be dominant?
Dominant means that only one pathogenic variant on one copy of a gene is necessary to have the condition. The variant can be inherited from either parent. Sometimes an autosomal dominant condition occurs because of a new genetic variant ( de novo ), and there is no history of this condition in the family.
Clinical significance
- The prothrombin gene G20210A mutation differs from the gene for normal prothrombin or factor II by a single nucleotide (nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA). This mutation causes the body to produce excess amounts of prothrombin. Consequently, in individuals with the prothrombin gene mutation, prothrombin levels are higher, which in turn con...
Causes
Epidemiology
Risks
Adverse effects
Uses
Treatment
- The Prothrombin Gene Mutation is an inherited condition (i.e. from your parents). We inherited one copy of each gene from each of our parents. One (or both) of your parents will have passed the Prothrombin Gene Mutation on to you and you may pass the condition onto your children. Blood clots usually only develop when there are other risk factors fo...
Prevention
- The Prothrombin Gene Mutation is relatively common it occurs in about 1 in every 50 people in Australia. This mutation is more common than many other gene changes (mutations). Because the mutation is very common, it has been suggested that there is some benefit in having the Prothrombin Gene Mutation.
Diagnosis
- The main problem with having the Prothrombin Gene Mutation is having an increased risk of developing blood clots. Blood clots can occur in blood vessels and can sometimes travel to different parts of the body including the lungs. Having the Prothrombin Gene Mutation increases your risk of having a blood clot. If you have one copy of the Prothrombin Gene Mutation (also cal…