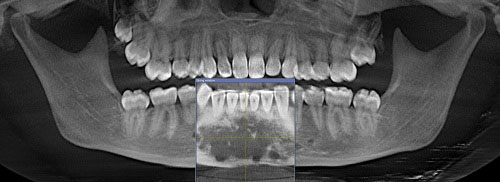
What causes Radiolucency in teeth? Description. Most of periapical radiolucencies are the result of inflammation such as pulpal disease due to infection or trauma. Not all radiolucencies near the tooth root are due to infection.
Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal air sinuses. Odontogenic sinusitis is an inflammatory condition of the paranasal sinuses that is the result of dental pathology, most often resulting from prior dentoalveolar procedures, infections of maxillary dentition, or maxillary dental trauma.
What does Radiolucency in a tooth mean?
Periapical radiolucency is the descriptive term for radiographic changes which are most often due to apical periodontitis and radicular cysts, that is, inflammatory bone lesions around the apex of the tooth which develop if bacteria are spread from the oral cavity through a caries-affected tooth with necrotic dental ...
What does increased Radiolucency mean?
(rā'dē-ō-lū'sen-sē), A region of a radiograph showing increased exposure, either because of greater transradiancy of the corresponding portion of the subject or because of inhomogeneity in the source of radiation, such as off-center positioning.
What does radiolucent lesion mean?
Radiolucent mandibular lesions seen on panoramic radiographs develop from both odontogenic and non-odontogenic structures. They represent a broad spectrum of lesions with a varying degree of malignant potential.
How long does it take for a periapical Radiolucency to resolve?
The average radiographic rate of repair was 3.2 mm2/mo. Less than 6 months after treatment, 17.6% of lesions demonstrated complete radiographic resolution, whereas 70.6% showed radiographic resolution at 12 months or longer.
What is an example of radiolucent?
For example, on typical radiographs, bones look white or light gray (radiopaque), whereas muscle and skin look black or dark gray, being mostly invisible (radiolucent).
What is radiolucent image?
Radiolucent – Refers to structures that are less dense and permit the x-ray beam to pass through them. Radiolucent structures appear dark or black in the radiographic image. Radiopaque – Refers to structures that are dense and resist the passage of x-rays.
Which of the following is a type of radiolucent lesion?
The radiolucent lesions most commonly seen in group 1 are osteomyelitis, eosinophilic granuloma, and metastatic Wilms' tumor. Nonossifying fibromas, unicameral bone cysts, and aneurysmal bone cysts do occur in this age group, but are more common in the slightly older patient.
What does radiolucent bone mean?
It is common to see dark areas, known as radiolucencies, on a dental x-ray. A radiolucency often represents a void or an area of tissue that is less dense. Some of these radiolucencies are normal, such as those that represent openings in the jaw bone that allow certain nerves to enter and exit the jaw.
What causes radiopaque?
Radiopaque lesions of the jawbones are frequently encountered in dental radiographs. A variety of conditions such as chronic inflammation, soft tissue calcifications, fibrosseous lesions, odontogenic tumors, and bone neoplasms can manifest as radiopaque lesions on the jawbones.
What is periapical disease?
Periapical periodontitis, also known as periapical lesion, is a common dental disease, along with periodontitis (gum disease). Periapical periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease, caused by endodontic infection, and its development is regulated by the host immune/inflammatory response.
How is periapical periodontitis treated?
The treatment will either be to extract the tooth or to open the pulp chamber and root canal system, debride away necrotic debris, irrigate with an antiseptic and dressing with a combined steroid and antibiotic paste. The use of antibiotics is ineffective and they should not be prescribed.
How is periapical periodontitis diagnosed?
If no other diagnosis may explain the pain consider a cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan. If an apical radiolucency is observed in the scan, then AP is diagnosed as present. If no bone destruction is seen in the CBCT scan, reconsider other diagnoses (Step 1 and 2) that may mimic the symptoms of AP.
Are lungs radiolucent?
The air-filled lungs are the easiest penetrated and absorb the least amount of the beam - they are considered radiolucent. Bone is dense and absorbs more of the beam - they are considered radiopaque. Radiolucent tissues appear dark or black, radiopaque tissue appear light or white.
What technique error would cause the image of the teeth on the radiograph to look too long?
Elongation or lengthening of the teeth and surrounding structures results from underangulation of the x-ray beam (not enough vertical angle). When elongation occurs using the paralleling technique, the angulation of the x-ray beam is less than the long axis plane of the teeth.
Is cyst radiolucent or radiopaque?
Radiographically, residual cyst appears as well-defined radiolucency, with a distinct sclerotic margin in edentulous area. The sclerotic margin may be fine, thin and it may be thicker and diffusely sclerotic.
What is radiolucent material?
The broadest definition of a radiolucent composite includes the entire family of plastics that contain a fiber reinforcement to increase structural properties yet still maintain transparency to x-rays.
What causes radiolucency of inflammatory origin?
Radiolucency of Inflammatory Origin. Radiolucencies of inflammatory origin arise from a dental infection. This most frequently arises from a necrotic pulp secondary to dental caries or trauma. The radiolucencies that result are most frequently sited at the apex of the affected tooth and are unilocular.
What is radiolucency on a radiograph?
A radiolucency is the black or darker area on a conventional radiograph. It suggests an osteolytic process, particularly when it presents in bone. Most lesions associated with this process remain radiolucent, whereas some subsequently acquire a central opacity or opacities or eventually become completely radiopaque.
What is the effect of radiolucency on teeth?
This effect is manifested by either displacement or erosion. The latter when applied to teeth, particularly their roots, is termed root resorption. Although all lesions presenting as radiolucencies may in due course cause root resorption, this would appear to be a particular feature of certain odontogenic neoplasms.
What is radiolucency in tooth crown?
If the radiolucency is associated with the crown of an unerupted tooth, a dentigerous cyst or an odontogenic neoplasm (assuming a secondary relationship to it) should be considered. Lesions that commonly present as well-defined radiolucencies are cysts and neoplasms. Cysts are common and the majority are inflammatory.
Is a multilocular radiolucency a neoplasm?
Although unilocular radiolucencies are more likely to be odontogenic or simple bone cysts, multilocular radiolucencies almost always are odontogenic neoplasms. Nevertheless, the early, and therefore the dimensionally small, stage of some odontogenic neoplasms may present as a unilocular radiolucency.
Is radiolucency benign or malignant?
If it is well defined, the radiolucency is more likely to be benign; it is likely to be a benign neoplasm or a cyst. A poorly defined radiolucency on the other hand could represent a malignancy or infection. Locularity is essentially a feature of radiolucencies; most are either unilocular or multilocular.
Is radiolucency odontogenic?
If the radiolucency is above the mandibular canal or below the image of the hard palate, it is within the dental alveolus and therefore likely to be of odontogenic origin. If the radiolucency is sited within the alveolus, its relationship to teeth is important to further refine the differential diagnosis.
What is the region of a radiograph showing increased exposure?
A region of a radiograph showing increased exposure, either because of greater transradiancy of the corresponding portion of the subject or because of inhomogeneity in the source of radiation , such as off-center positioning.
What is the quality of permitting the passage of radiant energy, such as x-rays, yet offering some resistance?
the quality of permitting the passage of radiant energy, such as x-rays, yet offering some resistance to it, the representative areas appearing dark on the exposed film. adj., adj radiolu´cent.
Introduction
A healthy 53-year-old male presented to our office on May 9, 2011, after being referred by a friend who was treated at our office. He was advised that he needed to have tooth No. 19 removed, and the extraction site grafted with bone and soft tissue.
Clinical and Radiographic Examination
patient had a 3-unit FPD on the left mandibular molar area extending from the second premolar, mesially, to the second molar (18-20) distally. A slight swelling was present, buccal to tooth No. 18, and the probing depths were surprisingly within normal limits, even when probed under anesthesia.
Medical history
Non-contributory. Patient was prescribed amoxicillin 500 mg TID for 2 days by his general dentist.
Treatment
Treatment was initiated with an I and D of the buccal swelling. The patient’s antibiotic regimen was changed to clindamycin 300 mg, sig 1 tab TID for 5 days. Retreatment followed by accessing the distal abutment of the 3-unit FPD. The cast post and existing gutta percha were removed.
Discussion
Management of teeth with previous root canal treatment that is failing requires more than just performing endodontic retreatment or surgery. The treating clinician must evaluate the cause of failure. These causes can range from being endodontic, restorative, periodontic, occlusion, patient’s habit (i.e. tongue ring), trauma, etc.
What causes bone lucencies?
According to the University of Washington School of Medicine, bone lucencies can be caused by a variety of factors, such as cysts, cancer, benign tumors or infection. Healio goes on to point out that fractures also cause bone lucencies.
What vitamin deficiency causes bone lucencies?
When bone lucencies are caused by fractures, Healio makes the correlation between these bone breaks and a Vitamin D deficiency.
What does lucency in a tumor mean?
Lucencies in general may indicate things like a cyst, a benign tumor, an infection or cancer. Previous radiographs, the history of the patient, the symptoms and why the exam was prescribed combined with the exact location and details about the lucency such as the type of tissue and what portion of the tissue was it found in, how the margins are, what other changes can be noted in the area, are some of the further details needed for narrowing down the diagnosis. In many cases, for a proper diagnoses further tests will be prescribed such as other medical imaging studies or a biopsy.
What does lucency mean in a mammogram?
In a mammogram it may indicate a lipid cyst, a harmless lump of fatty tissue. In a bone radiograph, it may indicate an area of demineralization due to a trauma.
What are lucencies?
Radiographs, commonly known as X Rays, are images obtained for diagnostic purposes; in medical radiography, an X-ray generator produces a beam of energy (x-rays) that travels towards the body of the patient: part of these X rays will be absorbed by body structures while some of them will make it through the body and will be captured on a film placed behind the patient. CT Scans employ the same principle but can produce three dimensional images.
What does it mean when a radiograph is white?
A radiopaque structure has high density and will result in a white color on the radiograph. This means that X-rays were absorbed and didn’t make it through. A lucency is an area of low density, hence appearing black in color, often highlighted in the report because unexpected such as in a tissue that is supposed to be radiopaque (white in color).
What does CT scan show on a radiograph?
The obtained image on film will show radiolucent and radiopaque structures: A radiolucent structure has low density and will result in a black color on the radiograph. This means that X-rays made it through the body.
What is X-rays in medical terms?
Radiographs, commonly known as X Rays, are images obtained for diagnostic purposes; in medical radiography, an X-ray generator produces a beam of energy (x-rays) that travels towards the body of the patient: part of these X rays will be absorbed by body structures while some of them will make it through the body and will be captured on ...
What is a radiology doctor?
Radiologists are physicians specialized in performing medical imaging procedures and diagnosing patients by interpreting the images obtained. You should bring the report of your exam to your referring specialist or to your GP to discuss the results and better understand the findings.
What is radiodensity in physics?
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material.
What is the difference between radiopaque and radiolucent?
Radiopaque volumes of material have white appearance on radiographs, compared with the relatively darker appearance of radiolucent volumes. For example, on typical radiographs, bones look white or light gray (radiopaque), whereas muscle and skin look black or dark gray, being mostly invisible (radiolucent).
What is radiodense contrast?
In modern medicine, radiodense substances are those that will not allow X-rays or similar radiation to pass. Radiographic imaging has been revolutionized by radiodense contrast media, which can be passed through the bloodstream, the gastrointestinal tract, or into the cerebral spinal fluid and utilized to highlight CT scan or X-ray images. Radiopacity is one of the key considerations in the design of various devices such as guidewires or stents that are used during radiological intervention. The radiopacity of a given endovascular device is important since it allows the device to be tracked during the interventional procedure. The two main factors contributing to a material's radiopacity are density and atomic number. Two common radiodense elements used in medical imagery are barium and iodine .
Why is radiopacity important?
The radiopacity of a given endovascular device is important since it allows the device to be tracked during the interventional procedure.
Why do medical devices have radiopacifiers?
Medical devices often contain a radiopacifier to enhance visualization during implantation for temporary implantation devices, such as catheters or guidewires, or for monitoring the position of permanently implanted medical devices, such as stents, hip and knee implants, and screws.
Is radiodensity a qualitative measure?
Though the term radiodensity is more commonly used in the context of qualitative comparison, radiodensity can also be quantified according to the Hounsfield scale, a principle which is central to X-ray computed tomography (CT scan) applications. On the Hounsfield scale, distilled water has a value of 0 Hounsfield units (HU), while air is specified as -1000 HU.
Where are lucent lesions located?
Location. Most expansile, lucent lesions are located in the medullary space of the bone. However, we can further define the location of the lesion by noting its relationship to the physis. Many lesions tend to occur in a “favorite” part of the bone. The favored locations are listed in the figure below.
Why is it important to know about a solitary, lucent, expansile bone?
Why is this? Because, this is the finding that will give you your best shot at determining the biological activity of the lesion ( how fast is it growing?). This is important, because in general, the faster a process grows, the more likely it is to be malignant.
Is a plain radiograph sensitive?
Plain films are not terribly sensitive, but they do have a decent specificity.
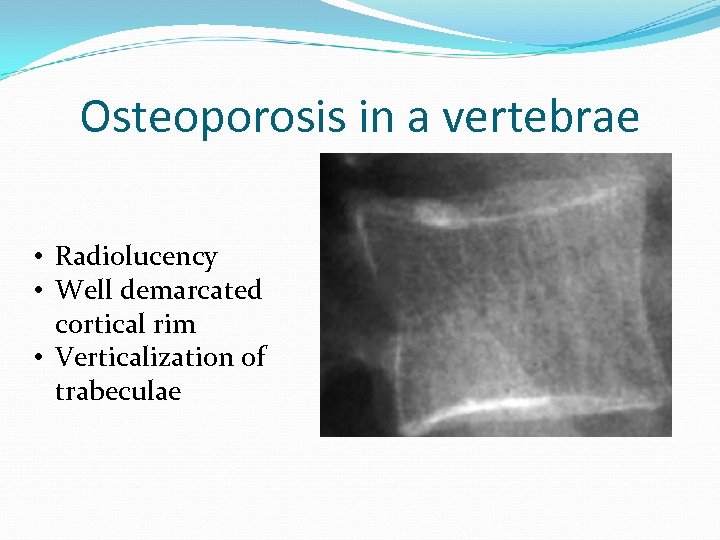
Cause
Significance
- The degree of marginal definition is crucially important to determine potentially serious disease. If it is well defined, the radiolucency is more likely to be benign; it is likely to be a benign neoplasm or a cyst. A poorly defined radiolucency on the other hand could represent a malignancy or infection. The radiolucencys relationship to mandibular canal or the image of the hard palate (o…
Pathophysiology
- Lesions that commonly present as well-defined radiolucencies are cysts and neoplasms. Cysts are common and the majority are inflammatory. Almost all true cysts and most benign neoplasms expand by hydrostatic pressure and are therefore frequently spherical or nearly spherical in shape. This shape is achieved in larger cysts and neoplasms by displacing the buccal and lingual cortic…
Diagnosis
- Giant cell lesions and hemangiomas each have an extensive range of presentations. As a result they appear in the differential diagnosis of several lesions. Thalassemia has not only a specific presentation upon diagnosis but also subsequently according to the mode of treatment. Hypertransfusions and chelating agents also affect changes in both the skeleton and the extras…
Appearance
- Some lesions that are generally understood to be radiopaque, may appear initially as radiolucencies in their earliest stage. This apparent inconsistency is analogous to the clearing of a building site and first excavating to establish the foundations of the new building to be erected.
Symptoms
- In younger patients, generally of Mediterreanean, Middle Eastern, and South Asian extraction, such a presentation may be indicative of thalassemia, the most common genetic disease. The classical features of thalassemia are hair-on-end appearance of the vault of the skull, obliteration of the air-sinuses and replacement of the normal trabecular pattern by fewer coarse straight trabeculae (F…
Clinical significance
- SICKLE CELL DISEASE The radiology of hyperparathyroidism affecting the jaws, in addition to generalized bone resorption, osteopenia, and osteosclerosis, may reveal localized lesions. These are brown tumors and are rarely reported. They may appear either as radiolucencies or leontiasis ossea (discussed further in Chapter 10). A brown tumor presenting as a radiolucency is displaye…
Epidemiology
- Although sickle cell disease is most frequently found among West Africans and their Afro-Caribbean and African-American descendants it is also found among Mediterranean and Middle Eastern communities. White et al.4 reported that its detection by fourier analysis is more effective than counting struts. Fourier analysis revealed increased trabecular spacing in sickle cell diseas…
Prognosis
- Observation of solitary osseous plasmacytoma (SOP) in a radiograph of the jaws may enhance the patients prognosis by earlier local treatment prior to it becoming widespread disease. Seventy percent of cases, if untreated, progress to multiple myeloma. Thirty percent progress to multiple osteolytic (radiolucent) lesions without marginal sclerosis; in other words they present the classi…
Types
- There are three types of hyperparathyroidism, and they all have their effects by disrupting normal calcium homeostasis.16,17 The most common type is primary hyperparathyroidism, which presents as a disease in middle- to old-aged patients, principally women. Its most common cause is a secreting adenoma arising in one of the 4 parathyroid glands. Occasionally, a secreting carci…
Classification
- Eversole et al. defined the primary intraosseous squamous cell carcinoma (PIOSCC) as a central jaw carcinoma derived from odontogenic epithelial remnants. Subcategories of PIOSCC include (1) a solid tumor that invades marrow spaces and induces osseous resorption, (2) squamous cancer arising from the lining of an odontogenic cyst and (3) a squamous cell carcinoma in ass…