According to the Nationwide Children's Hospital, ranulas occur when:
- The saliva from these glands doesn't drain properly into your mouth as it should
- That's due to a damaged, diseased, or ruptured salivary gland
- The injury from the gland creates swelling and for saliva to accumulate
- The saliva then overflows onto tissues next to the gland producing a cyst — a ranula
What causes a ranula in the mouth?
In other cases, ranulas occur after trauma to the floor of the mouth (like an oral surgery). An injury can damage the ducts that move saliva from the salivary gland into the mouth, causing a blockage. When saliva can’t properly drain, it accumulates in the gland and forms a dome-shaped cyst.
What is a ranula?
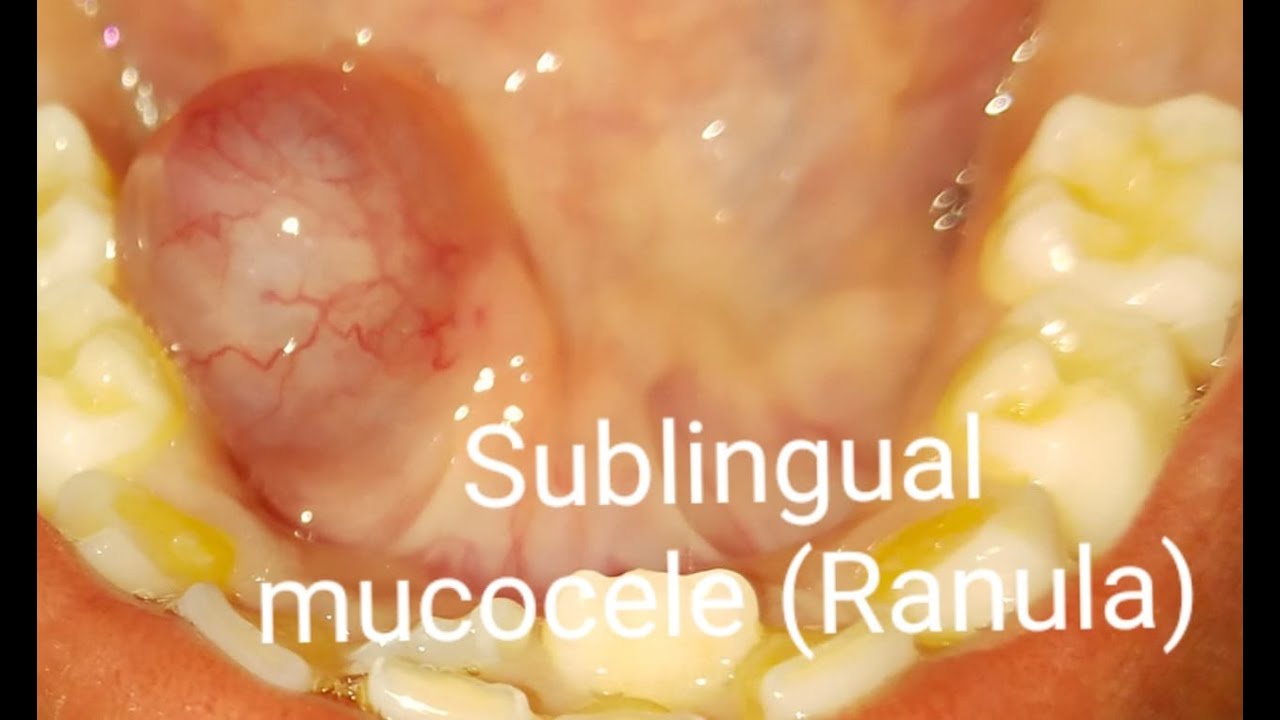
A ranula is a cyst that can form on the floor of your mouth, under your tongue. It’s filled with saliva (spit), and it’s the result of a blocked or damaged salivary gland. A healthy salivary gland empties saliva directly into your mouth. A blocked or damaged salivary gland may cause saliva to drain into surrounding tissues instead.
Which salivary glands are affected by a simple ranula?
If you have a simple ranula, swelling is confined to the sublingual gland. This is the smallest of the three paired salivary glands around the throat and mouth.
Do Ranulas go away on their own?
A ranula is a spit-filled cyst that forms under your tongue. It can result from a blocked salivary gland. Instead of saliva draining from the gland into your mouth, it leaks into nearby tissues, forming a cyst or “bubble.” Ranulas aren’t serious, and they typically aren’t painful. Sometimes ranulas go away on their own, but some require surgery.
What is the reason for ranula?
If one of the salivary glands, usually the sublingual gland, is injured or diseased the saliva will no longer reach the mouth where it can be swallowed. The saliva leaks out of the injured gland and forms a bubble of fluid in the tissue around the gland which is called a ranula.
How do I get rid of ranulas?
There are a few ways the ranula can be treated:Incision or needle aspiration: Depending on its size, your doctor can make an incision and drain the cyst to decrease swelling or use a needle to withdraw the fluid. ... Marsupialization: The surgeon makes a slit in the cyst and sutures the edges to maintain an opening.More items...
Will a ranula go away?
A simple, small ranula is usually minor and resolves itself without treatment. Larger ranulas can be more complicated, but with treatment the outlook is generally positive. Surgery to remove the cyst and the sublingual gland may produce the best outcome.
What happens if a ranula is left untreated?
Patients with an untreated ranula will continue to experience the pain and swelling of the ranula, and if infected, can result in serious neck abscesses requiring hospitalization and abscess drainage procedures.
Can ranula be cancerous?
Or, depending on the size of the ranula, they may recommend treatment. A ranula is a clear or bluish cyst that can form under your tongue. It can happen spontaneously, or as a result of trauma or injury to your mouth. Ranulas aren't cancerous or dangerous.
Should you pop a ranula?
Although some mucoceles resolve themselves, most remain large, continue to grow, and cause continuous problems. Unfortunately, simply popping or removing the fluid from the gland does not resolve the problem because the duct will continue to stay blocked.
What kind of doctor treats ranula?
At the initial visit to her dentist, the patient was referred to an oral surgeon. The patient was examined then by two oral surgeons. The first oral surgeon recommended a laser procedure. The second surgeon referred the patient to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist on the basis of the clinical examination.
What does a ranula look like?
A ranula usually presents as a translucent, blue, dome-shaped, fluctuant swelling in the tissues of the floor of the mouth. If the lesion is deeper, then there is a greater thickness of tissue separating from the oral cavity and the blue translucent appearance may not be a feature.
Is ranula true cyst?
Ranulas can be true cysts occurring due to ductal obstruction of the sublingual gland or a minor salivary gland or a pseudocyst as a result of ductal injury leading to extravasation and accumulation of saliva in the surrounding tissues. Clinically ranulas present as intraoral or plunging ranulas.
How do you get rid of a bubble under your tongue?
gargling with warm salt water and baking soda mouth rinses on a regular basis. applying topical remedies to reduce pain. Some products are available to purchase over the counter or online, such as canker sore medication or oral numbing gels. avoiding alcohol-based mouthwashes until the bumps disappear.
How common are ranulas?
Ranulas are less common (0.2 cases per 1000 persons) and tend to occur in children and young adults. The lateral aspect of the lower lip is the most common site for mucoceles, but other common sites include the floor of the mouth and ventrum of the tongue. Ranulas typically present in the floor of the mouth.
What does a ranula look like?
A ranula usually presents as a translucent, blue, dome-shaped, fluctuant swelling in the tissues of the floor of the mouth. If the lesion is deeper, then there is a greater thickness of tissue separating from the oral cavity and the blue translucent appearance may not be a feature.
What kind of doctor treats ranula?
At the initial visit to her dentist, the patient was referred to an oral surgeon. The patient was examined then by two oral surgeons. The first oral surgeon recommended a laser procedure. The second surgeon referred the patient to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist on the basis of the clinical examination.
Why do you get mucous cyst?
Common sites and causes of cysts include: Inner surface of the upper or lower lip, inside the cheeks, bottom surface of the tongue. These are called mucoceles. They are often caused by lip biting, lip sucking, or other trauma.
What Causes a Ranula?
The saliva leaks out of the injured gland and forms a bubble of fluid in the tissue around the gland which is called a ranula.
What is a Ranula?
A ranula is a fluid collection or cyst that forms in the mouth under the tongue. It is filled with saliva (spit) that has leaked out of a damaged salivary gland. Salivary glands are small structures around the mouth which make saliva. Saliva should drain from these glands directly into the mouth. If one of these glands is damaged then the saliva leaks out into the tissues next to the gland forming a cyst or bubble near the gland. This cyst is called a ranula.
What are the Symptoms of a Ranula?
It usually is a 2-3 inch diameter painless soft swelling under the tongue or chin that is easy to identify. Occasionally, the fluid collection can hurt a little and sometimes is can spontaneously empty into the mouth only to slowly fill back up in the weeks after it empties. Usually, it just slowly grows in size until it is discovered.
What is the Outlook for Patients With a Ranula?
Ranulas are benign fluid collections near the mouth which can be effectively treated with our percutanous treatment but also with traditional surgical approaches. Both appraches offer permanent removal of the ranula and resolution of symptoms. We feel our percutanous approach offers a less invasive treatment for this benign condition.
How are Ranulas Diagnosed?
The diagnosis is usually easy for an experienced physician to make based primarily on physical examination but often specialized radiology studies such as Ultrasound, Computed Tomography (CT Scan), or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are needed to define the full extent of the problem and exclude other causes for swelling. No other laboratory tests are usually needed to make the diagnosis.
How are Ranulas Treated at Nationwide Children's?
Rarely, a ranula can spontaneously go away without any treatment but usually a procedure will be needed to treat the problem. Simple drainage of the fluid collection rarely permanently fixes the problem as the diseased gland continues to leak saliva.
How to remove ranula?
Traditionally, open surgical procedures drain the ranula and remove the diseased gland through an incision in the mouth or under the chin. A percutaneous treatment was developed in Interventional Radiology at Nationwide Children’s Hospital around 2004 and has been used successfully since then to treat ranulas without open surgery or incisions.
What does it mean when you have a ranula?
A clear or bluish translucent growth on the floor of the mouth is the main symptom of a ranula. They don’t typically cause pain, so you may not notice it until the cyst increases in size. If you have a simple ranula, swelling is confined to the sublingual gland. This is the smallest of the three paired salivary glands around the throat and mouth.
Why does my ranula swell?
Sometimes, the cause of a ranula is unknown and the swelling occurs spontaneously. In other cases, ranulas occur after trauma to the floor of the mouth (like an oral surgery).
How to treat ranula cyst?
Another treatment option for a ranula is marsupialization. This is when your doctor cuts a slit in the cyst and sutures the edges. This procedure allows the cysts to drain freely.
What happens if you plunge your ranula?
A plunging ranula can produce additional symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, difficulty speaking, and tracheal compression.
Can ranula cysts disappear on their own?
Some cysts disappear on their own. But treatment is necessary for enlarged ranulas, especially when swelling interferes with swallowing or speaking. Depending on its size, your doctor can make an incision and drain the cyst to decrease swelling. Even if this treatment works, fluid may accumulate again.
Do you need to see a doctor for ranula?
A small ranula that causes no symptoms may not require a visit to your doctor. But you should see a doctor for an enlarged ranula since there’s the risk of the lesion rupturing. You’ll know the ranula is enlarged if it impairs eating, swallowing, speech, or breathing.
Can a doctor diagnose a ranula cyst?
Some doctors can make a diagnosis based on the appearance and location of the cyst. Your doctor may order image tests to examine the extent of the swelling or to confirm that your symptoms are caused by a ranula.
What is a ranula?
A ranula is a fluid collection, or cyst, that forms in the mouth under the tongue. It is filled with saliva (spit) that has leaked out of a damaged salivary gland. Instead of the saliva draining from the glands directly into the mouth, one of these glands is damaged, so the saliva leaks into the tissues next to the gland and forms a bubble.
What is a plunging ranula?
A plunging (or diving) ranula is when the cyst grows down under the mouth and into the neck. It is rarer than a simple ranula and may occur along with a simple ranula. Ranulas are one of the most common salivary gland disorders.
What is a ranula in the mouth?
There are two types of ranulas. A simple (or oral) ranula is when the cyst stays in the floor of the mouth, underneath the tongue. A plunging (or diving) ranula is when the cyst grows down under the mouth and into the neck.
How to tell if you have a ranula?
Symptoms of a ranula. A clear or bluish bubble-like growth on the floor of the mouth is the main symptom of a ranula. Since they don’t typically cause pain, they may go unnoticed until the cyst grows in size. Then it may cause problems with speech, swallowing and, occasionally, breathing if it grows large enough to press on the trachea (windpipe).
What doctor will examine a ranula?
Diagnosis of a ranula. A pediatric otolaryngologist, a physician who specializes in the ears, nose and throat (ENT), will examine the child. Depending on the location and type of problem, the doctor may press on (palpitate) the child’s neck or look inside their mouth, pushing on the floor of the oral cavity.
Who treats ranulas?
Children who require treatment for a ranula will see a pediatric otolaryngologist ( ENT). At Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, pediatric ENT surgeons on our Head and Neck Disorders team will care for children with ranulas.
Can ranulas disappear on their own?
Small, simple ranulas that don’t cause problems may not require treatment. Some cysts may disappear on their own. Treatment is necessary, however, for enlarged simple ranulas, especially when swelling interferes with swallowing or speaking, and for most plunging ranulas.
Which glands are at risk for ranula?
Anatomic variation of ductal system of the sublingual gland may increase the risk for the development of a ranula. In particular, this risk appears to be increased when the Bartholin duct is connected to and empties into the Wharton duct. [ 4]
What is a purple ranula?
Unilateral oral ranula in a young adult manifesting as a purple swelling. Ranula on the floor of the mouth with focal ulceration. Example of a cervical ranula with no oral involvement in an adult. The swelling developed after a car accident in which the individual had trauma to the face and neck.
What is the difference between a translucent papular lesion and a red lesion?
Example of 2 superficial mucoceles of the soft palate in a 50-year-old woman. The red lesion represents a recently ruptured mucocele , and the translucent papular lesion represents an intact mucocele.
Does HIV cause ranulas?
In addition, HIV infection may increase the risk of developing a ranula in children and adults. [ 5, 6]
What is a ranula in your mouth?
They say when you "have a frog in your throat," you have trouble speaking. Well, if a ranula, Latin for "little frog," goes untreated, it can be the source of that problem. A ranula is a cyst that forms under your tongue and a common salivary gland disorder, ...
Why do you need an ultrasound for a ranula?
According to the Western Journal of Emergency Medicine, an ultrasound is needed to differentiate a ranula from other cysts.
How long does it take for a ranula to pop up?
The stitches should dissolve, medication may be needed, and scarring will disappear within a few months. Swelling will be present for 1-2 weeks while numbness around the tongue lasts up to 4 weeks, according to the Nationwide Children's Hospital. Often, ranulas pop up on their own. That's the reality.
How big is a ranula?
Soft and bluish. Approximately 2-3 inches in diameter. Usually painless. Occasionally large ones affect swallowing, speech, and chewing. If infected, pain and fever are possible. Ranulas are pretty rare and found most often in children, adolescents, and young adults.
What is the procedure to remove ranula legion?
According to the NCBI, usually, the ranula legion and salivary gland are both removed. Marsupialization. This surgical procedure opens up, drains, and attempts to dry out the cyst , without removing the gland, according to the NCBI. Salivary gland ablation.
How to treat ranulae?
Treatment of ranulae usually involves removal of the sublingual gland. Surgery may not be required if the ranula is small and asymptomatic. Marsupialization may sometimes be used, where the intra-oral lesion is opened to the oral cavity with the aim of allowing the sublingual gland to re-establish connection with the oral cavity.
What is the consistency of a ranula?
The fluid within a ranula has the viscous, jellylike consistency of egg white .
What is the most common pathologic lesion associated with the sublingual glands?
The lesion is usually present in children. Ranulae are the most common pathologic lesion associated with the sublingual glands.
What is a cervical ranula?
A cervical ranula occurs when the spilled mucin dissects its way through the mylohyoid muscle, which separates the sublingual space from the submandibular space, and creates a swelling in the neck. It may occur following rupture of a simple ranula. Rarely, ranulae may extend backwards into the parapharyngeal space.
What is a ranula cyst?
Oral and maxillofacial surgery. A ranula is a mucus extravasation cyst involving a sublingual gland and is a type of mucocele found on the floor of the mouth. Ranulae present as a swelling of connective tissue consisting of collected mucin from a ruptured salivary gland caused by local trauma. If small and asymptomatic further treatment may not be ...
Where is the ranula in the neck?
An unusual variant is the cervical ranula (also called a plunging or diving ranula), where the swelling is in the neck rather than the floor of the mouth. The term ranula is also sometimes used to refer to other similar swellings of the floor of mouth such as true salivary duct cysts, dermoid cysts and cystic hygromas.
What imaging is used to identify a ranula?
Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging may be useful to image the lesion. A small squamous cell carcinoma obstructing the Wharton duct may require clinical examination to be distinguished from a ranula.
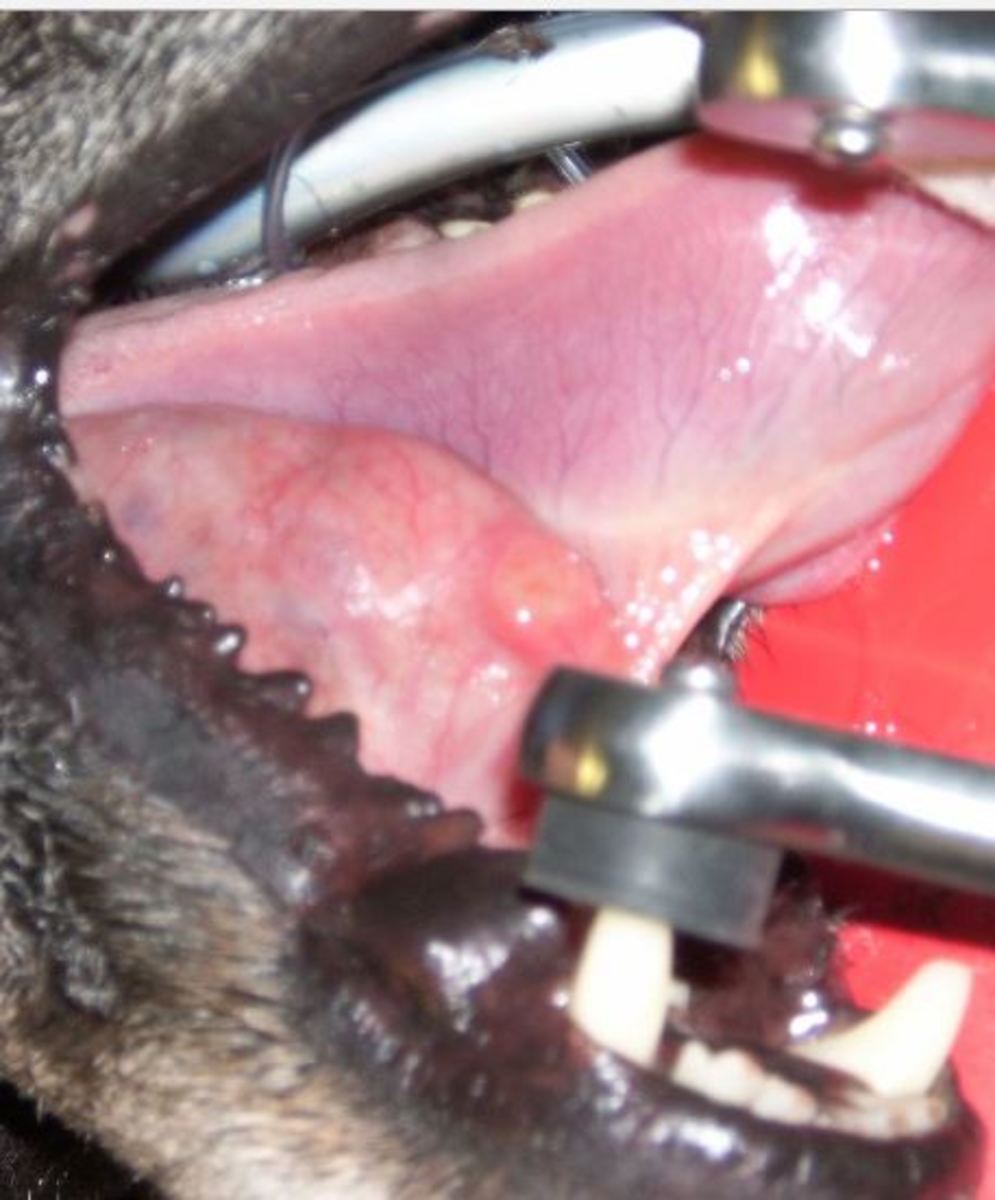
What is the cause of mucocoele in dogs?
A salivary mucocoele develops when there is leakage of saliva from the duct into surrounding tissue. Mucocoeles can develop from any of the salivary glands, but the sublingual gland is most commonly affected. The parotid and zygomatic glands are only infrequently affected. There may be a breed predilection (toy dogs, German shepherd dogs) and usually young dogs (1-4 years) are involved.
What causes salivary gland injury?
The cause of the injury to the salivary duct is rarely established. Blunt trauma to the head or neck, oral injuries, or sialoliths (salivary stones) have all been suggested as possible causes. However, establishing the cause of the injury is not always important in management of the condition.
What is the term for a fluid swelling in the tissues adjacent to the tongue?
Cervical, pharyngeal, and sublingual mucocoeles may be seen. A ranula is another term for a mucocoele, where saliva causes a fluid swelling in the tissues adjacent to the tongue. Pharyngeal mucocoeles may extend some distance into the back of the mouth causing respiratory obstruction.
What is sublingual mucocoele?
The most common presentation of sublingual/mandibular mucocoeles is a fluctuant (fluid-filled) swelling at the top of the neck. Often the swelling may intermittently become firm and painful or subside and even regress. In longer standing cases the swelling may migrate towards the midline in which case its origin may become difficult to determine. Less commonly, the mucocoele may develop under the tongue as a ranula and can cause interference with the function of the tongue provoking salivation.
Can mucocoele cause salivation?
Less commonly, the mucocoele may develop under the tongue as a ranula and can cause interference with the function of the tongue provoking salivation.
Is mucocoeles drainage a definitive management?
Drainage of mucocoeles is not a definitive means of management and may even result in the formation of a permanent cervical fistula. It is, however, a very useful means of temporarily relieving the respiratory obstruction caused by pharyngeal mucocoeles. It may also be an informative diagnostic step.
Is a tenacious mucoid blood tinged fluid uncommon?
Aspiration and identification of the tenacious mucoid blood-tinged fluid is often useful. Parotid mucocoeles are uncommon and present with discrete swelling of the duct or mucocoele over the side of the face. Zygomatic mucocoeles are rare.
Oral Mucous Cyst Symptoms
There are two types. Mucoceles show up on the inside of your lower lips, your gums, the roof of your mouth, or under your tongue. Those on the floor of the mouth are called ranulas. These are rare, but because they’re larger, they can cause more problems with speech, chewing, and swallowing.
Oral Mucous Cyst Causes
Where does an oral cyst come from? It centers on a small salivary gland, which makes saliva in your mouth.
Oral Mucous Cyst Diagnosis
Your doctor might be able to tell that you have a mucocele just by looking at it. If not, they may recommend one of these:
Oral Mucous Cyst Treatment
Mucoceles often go away without treatment. But sometimes they enlarge. Don't try to open them or treat them yourself. See your doctor, your child's pediatrician, or your dentist for expert advice.
Oral Mucous Cyst Outlook
Mucocele cysts are more unpleasant than harmful, but you still should see a specialist to take care of them. They can return after removal, and there may be pain in areas where they’re removed.