What causes an elevated RBC?
There are several potential causes of RBC in the urine, including:
- urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- kidney or bladder infections
- kidney stones
- vigorous exercise, which requires the body to send lots of blood to the muscles
- rhabdomyolysis, wherein severely damaged muscles cause substances from within the muscles to leak into the blood
- sexual intercourse that causes irritated tissue
What causes low RBC and hemoglobin levels?
What causes low red blood cell count hemoglobin and hematocrit? Low RBC counts, hemoglobin and hematocrit levels can be caused by other things too, such as a lot of bleeding or malnutrition (not enough nutrients in the food eaten). Kidney disease, liver disease (cirrhosis), cancer, and medications used to treat cancer can also cause low levels. ...
Is agglutination always bad?
There are numerous causes that can provoke male infertility; one of the most common problems is the spermatic agglutination. The agglutination consists on the formation of heaps, or groups of spermatozoa that are linked to each other.
What causes presence of WBC and RBC in urine?
These include the following:
- Holding your urine. If you do not urinate frequently, this can cause the bladder to stretch and weaken so that white blood cells leak into the urine. ...
- Obstruction of the urinary tract. ...
- Pregnancy. ...
- Sexual intercourse. ...
- Excessive amount of exercise. ...
- Blood disorders. ...
- Cancers. ...

What happens when a red blood cell Agglutinate?
The agglutinated red cells can clog blood vessels and stop the circulation of the blood to various parts of the body. The agglutinated red blood cells also crack and its contents leak out in the body. The red blood cells contain hemoglobin which becomes toxic when outside the cell.
What is the agglutination of red blood cells called?
Hemagglutination is the process by which red blood cells agglutinate, meaning clump or clog. The agglutin involved in hemagglutination is called hemagglutinin. In cross-matching, donor red blood cells and the recipient's serum or plasma are incubated together.
What happens when your red blood cells clump together?
These damaged red blood cells (sickle cells) clump together. They can't move easily through the blood vessels. They get stuck in small blood vessels and block blood flow. This blockage stops the movement of healthy oxygen-rich blood.
Is blood agglutination good or bad?
The agglutinated red cells can clog blood vessels and stop the circulation of the blood to various parts of the body. The agglutinated red blood cells can also crack open, leaking toxic contents out in the body, which can have fatal consequences for the patient.
What does it mean when blood Agglutinates?
The agglutination indicates that the blood has reacted with a certain antibody and is therefore not compatible with blood containing that kind of antibody. If the blood does not agglutinate, it indicates that the blood does not have the antigens binding the special antibody in the reagent.
Does cold agglutinin disease go away?
Most cold agglutinins that are associated with infections or autoimmune disorders are likely to be polyclonal and to resolve spontaneously with resolution of the infection (which may include antibiotic therapy) or treatment of the autoimmune disorder.
Is Cold agglutinin disease serious?
CAD can lead to severe and even life-threatening heart conditions in emergency scenarios. Related to its name — “cold” agglutinin disease — CAD causes most intense symptoms in cold climates or chilly weather.
What type of doctor treats cold agglutinin disease?
Hematologists. Hematologists specialize in the treatment of blood disorders and are familiar with CAD. They can guide the diagnostic process and treat affected patients to maintain their red blood cells at optimal levels.
What is the common name for agglutination?
What is another word for agglutination?accretionadhesionclumpingcohesionjoining
What are the types of agglutination?
There are two forms of agglutination. They are the active agglutination and the passive agglutination. With active agglutination, the antigen occurs naturally on particle. With passive agglutination, the antigen must first be bound to an inert particle to detect an antibody.
What Polychromasia means?
A peripheral blood smear tells how many red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are in your blood. Polychromasia shows up when your red blood cells appear blue or gray when treated with the dye. This indicates they have more of a substance called ribonucleic acid (RNA) than normal red blood cells.
Does agglutination result in red blood cell lysis?
Cold agglutination disease (CAD) is characterized by an auto-antibody which is able to agglutinate red blood cells (RBCs) at temperatures lower than that of the body, and subsequently to activate the complement system responsible for lysis of RBCs.
What is red cell agglutination?
For the use of red cell agglutination as a testing method, see hemagglutination. Red cell agglutination in a patient with cold agglutinin disease . In hematology, red cell agglutination or autoagglutination is a phenomenon in which red blood cells clump together, ...
What is cold agglutinin disease?
This often occurs in cold agglutinin disease, a type of autoimmune hemolytic anemia in which people produce antibodies (termed cold agglutinins) that bind to their red blood cells at cold temperatures and destroy them.
What is the term for the clumping of red blood cells?
Red cell agglutination in a patient with cold agglutinin disease. In hematology, red cell agglutination or autoagglutination is a phenomenon in which red blood cells clump together, forming aggregates. It is caused by the surface of the red cells being coated with antibodies.
Can agglutination be reversed?
People with red cell agglutination may exhibit spontaneous agglutination reactions during testing, leading to a false positive result. If the causative antibodies are only active at room temperature, the agglutination can be reversed by heating the blood sample to 37 °C (99 °F).
Does agglutination affect blood typing?
This leads to a markedly decreased red blood cell count and hematocrit and markedly elevated mean cell volume and mean cell hemoglobin concentration. Red cell agglutination also interferes with routine methods for blood typing and blood compatibility testing, which rely on agglutination reactions.
Can red cell agglutination occur in paroxysmal hemoglobinuria?
Red cell agglutination can also occur in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia.:88 . In cases of red cell agglutination, the direct antiglobulin test can be used to demonstrate the presence of antibodies bound to the red cells.
What Causes Agglutination?
The red blood cell or bacteria in presence of an antibody clump together and form a large complex or the agglutinated material.
Why is agglutination important?
Hematological importance of agglutination: Before blood transfusion, hemagglutination reaction is used in laboratory to cross match the donor blood and recipient blood. If the donor red blood cells and the recipient’s serum agglutinate, than the donor blood is said to be incompatible for the recipient. In this way it helps to find out the ...
What is the agglutination method?
The complication is fatal. Agglutination method is also used to find out specific bacterial antigen in the blood, it is a laboratory procedure. It also reveals the identity of the bacteria and helps in diagnosis of the disease.
What happens when blood cells clog together?
Agglutination in blood occurs when the red blood cells clog together in the blood vessels; it stops the circulation of blood to various organs of the body resulting to their failure. Death occurs due to organ failure.
What causes agglutination of red blood cells?
Red cell agglutination. •Clumping (agglutination) of red blood cells is frequently caused by cold agglutinins. Cold agglutinins are IgM antibodies that may arise following viral or Mycoplasma infections, or in the setting of plasma cell or lymphoid neoplasms.
Can agglutination affect blood count?
Agglutination of red cells can interfere with red blood cell indices. The red blood cell count may be falsely decreased, and the MCV falsely increased, as clumps of red cells are measured as single cells.
What causes agglutination in red blood cells?
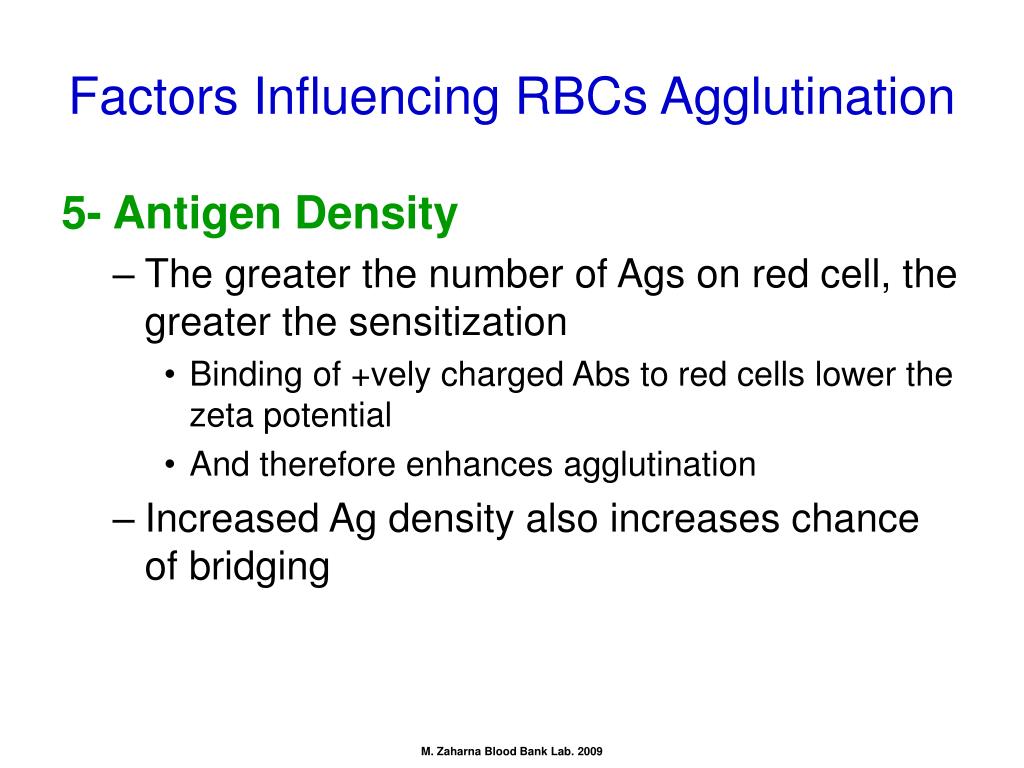
Agglutination of red blood cells is caused by antigens present on cell wall membrane in presence of suitable agglutinins (antibodies). The classical ABO grouping system is based on the presence or absence of the type of agglutinogens on the cell membrane of red blood cells.
What causes abnormal agglutination?
Causes for Abnormal Red Blood Cell Agglutination. Cold Agglutinin Disease – Antibodies, usually IgM bind to red blood cells at low temperatures and cause them to agglutinate. Cold ag glutinin disease can be acute or chronic depending upon the nature of the antibody. Infectious Organisms – In association with infectious organisms like Epstein Barr ...
What Happens to Red Blood Cells that are Agglutinated?
IgM antibodies bind to red blood cell surface which causes red blood cells to agglutinate at temperatures lower than the normal body temperature.
What is the difference between agglutinogens and agglutinogens?
Some Basic Terminologies. Agglutinogens are antigens present on cell membranes of red blood cells. Agglutinins are antibodies against agglutinogens, present in the plasma. Agglutination comes from the Latin word “Agglutinare” which means “Clumping’ or “To Glue”.
What is cold agglutinin?
B Cell Lymphoma – Chronic cold agglutinin disease can affect elderly in association with an underlying low grade B-cell lymphoma. Cryoglobulinemia – A condition in which the blood contains large amounts of the protein cryoglobulin. Blood Transfusion – During blood transfusion when there is a mismatch between cells of donor and recipient.
Why does the liver get enlarged?
The workload of the liver also increases sharply as it has to metabolize all the bilirubin released from destroyed red blood cells. This may result in an enlarged liver (hepatomegaly). In case of infections, agglutinated red blood cells are destroyed rapidly. It usually stops once the disease period is over.
What is the process of destroying red blood cells?
This results in both intra vascular and extra vascular hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells). The process is called Complement Mediated Hemolysis.
What happens if red cells are agglutinated?
If there is red cell agglutination, then red cell clumps will be counted as single red cells, but the volume of the estimated cell will be much higher. This may result in falsely high MCV values. If large platelets are counted as red cells, then these platelets typically have less volume than a normal red cell. This may also result in falsely low MCV values.
Why do RBCs clump together?
In the presence of virus particles, RBCs clump together as a result of interaction between HA proteins of virus particles and RBC, leading to a lattice formation. In this case, as RBCs are dispersed as a clump, a red dot is not formed. In a given sample, a red dot will appear beyond a certain dilution fold.
What is a sheep hemagglutination assay?
In hemagglutination (or hemagglutination inhibition assay, HIA, or passive hemagglutination assay, PHA), RBCs (generally sheep), which have been coated or coupled with antigen (thus called sensitized RBCs), are incubated with antibody and sample. After incubation, the degree of agglutination is determined. In this assay, antigen in the sample competes with the antigen coated on the RBCs for their interaction with antibody. Another variation of the HIA is reverse passive hemagglutination assay, in which the purified antibody is coupled to the RBCs. Agglutination is observed when antigen or sample extract is added to the system. Although HIA is relatively simple, food extracts often interfere with the assay and a large amount of antiserum is needed. Only semiquantitative information can be obtained.
What is hemagglutination in blood?
Immune hemagglutination, used for cross-matching donor red blood cells (RBCs), refers to coagulation of RBCs, with antibodies either directed to the RBC themselves or specific carbohydrates coating the cells ( Gyenes & Sehon, 1962 ). The method is highly sensitive, and the degree of agglutination is directly proportional to the concentration of free antibody against RBC antigenic determinants and inversely proportional to the amount of antigen. A modification of this technique, for the purpose of detecting an infection, is the indirect or passive hemagglutination assay. Examples of this type of test procedure, that has been used for many years by clinical diagnostic laboratories, are well described in one of the other chapters ( Pavia, 2020) included in this volume.
How long does it take for a virus to respond to hemagglutination?
Hemagglutination-inhibiting and virus-neutralizing antibodies can be detected within 6–10 days of infection, and the response peaks at 3–4 weeks, and persists for over a year. While the level of hemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies is an indirect correlate of immunity, neutralizing antibody titers directed against both the HN and F proteins provide a functional measure of protection. Maternal antibodies transferred via the egg yolk protect chicks for 3–4 weeks after hatching as they have a half-life of approximately 4.5 days. Immunoglobulin Y (IgY) is confined to the circulation and does not prevent respiratory infection, but it does block viremia; locally produced IgA antibodies play an important role in protection in both the respiratory tract and the intestine, although IgY secreted in the respiratory tract contributes as well.
What happens to RBC in a positive reaction?
In a positive reaction, RBC becomes agglutinated by virus particles, showing a lattice formation. In a negative reaction, RBC precipitates to the bottom of the well, forming a distinct red dot in a cone-shaped bottom. (B) Titration of virus stocks by hemagglutination assay. The wells denoted by arrows represent the highest dilution ...
When were monoclonal antibodies first used?
In 1975 , George Kohler and Cesar Milstein isolated the first monoclonal antibodies from clones of cells selected in vitro to produce an antibody of a single specificity directed against a particular antigen. This enabled virologists to look not only at the whole virus, but at specific regions—epitopes—of individual virus antigens ( Figure 1.3 ). This ability has greatly increased our understanding of the function of individual virus proteins. Monoclonal antibodies found increasingly widespread application in other types of serological assays (e.g., ELISAs) to increase their reproducibility, sensitivity, and specificity.
What is the blood type of agglutination?
If agglutination is seen only with Anti-B, the blood type is B. If agglutination is seen with both Anti-A and Anti-B , the blood type is AB. If agglutination is seen neither with Anti-A nor with Anti-B , the blood type is O. If agglutination is seen with Anti-D, the blood subtype is Rh positive.
What type of serum reacts with antigens?
The Anti-A, Anti-B and Anti-D serums react with the respective antigens on the blood cells to cause agglutination, unless the antigens are absent (as in O negative blood type).
What are the three antigens used in blood typing?
The three dominant antigens (surface protein molecules) tested for blood typing are A, B and D. The presence, combination, or absence of the first two determine whether a person is A, B, AB or O, while the presence or absence of the third determines whether a person is Rh positive or Rh negative. See the link for details:
What is agglutination in RBC?
This alteration of RBC distribution presents as irregular and random grape-like clusters or clumps. Agglutination is differentiated from Rouleaux by the lack of linear chains or “coin staking”. 1-4
What is auto-agglutination?
Auto-agglutination is produced as a result of a complex formed between the patient’s own RBC antigens and antibodies, mediated by cold-reacting antibodies. Agglutination can be reversed when the blood sample is warmed to 37°C.1,2,5. Associated Disease/Clinical States: 2-4. Cold Hemagglutinin Disease.
What causes cold agglutinin?
Doctors call that the primary, or idiopathic, form of the condition, and they don’t know why it happens. In other cases, another illness can bring on cold agglutinin disease. One of the most common conditions that triggers it is lymphoma, especially in people over 60. That's a type of cancer that affects your lymph nodes.
What is cold agglutinin disease?
Treatment. Taking Care of Yourself. Cold agglutinin disease (CAD) is a condition that makes your body’s immune system attack your red blood cells and destroy them. It’s triggered by cold temperatures, and it can cause problems that range from dizziness to heart failure. It’s also called cold antibody hemolytic anemia.
How to avoid red blood cell count?
You may be able to avoid problems by keeping warm and staying out of cold weather. If your red blood cell count is very low, your doctor may need to filter your blood to get rid of the antibodies that are causing your condition (a procedure called plasmapheresis) or give you a blood transfusion.
Why are cold agglutinins called cold agglutinins?
Some of these antibodies are called cold agglutinins because they’re triggered when your body’s temperature is below normal.
What causes the immune system to turn on?
A parasitic infection like malaria. Other conditions that cause your immune system to turn on your body. Other kinds of cancer that affect your blood cells, like multiple myeloma or leukemia. Diagnosis. If your doctor thinks you have cold agglutinin disease, blood tests can tell.
Can cold agglutinin cause a period?
In women, cold agglutinin disease sometimes keeps them from having periods. Some people who have cold agglutinin disease also may get a cold, numb feeling and loss of color in their fingers or toes, known as Raynaud’s phenomenon. Symptoms are typically worse in the winter, when temperature are lower.
How to differentiate agglutination from rouleaux formation?
If necessary, agglutination may be differentiated from rouleaux formation by performing a saline dilution (dispersion) test. The presence of RBC agglutination warrants careful assessment of the blood film for other supportive evidence of IMHA such as spherocytes, and also for underlying causes of IMHA such as neoplastic cells and hemoparasites.
How to determine agglutination?
1. Agglutination is determined by visual inspection. This is easier with a black sheet under the microplate or with a test reading mirror. 2. The results are scored as +++ (complete agglutination), ++, +, +/− or – (absence of agglutination) ( Figure 1 ). Sign in to download full-size image.
What is the purpose of latex agglutination?
Latex agglutination assays are among the simplest to perform and are widely used in the diagnosis of acute infectious mononucleosis. In latex agglutination, latex particles are coated with target antigens, and, when incubated in the presence of patient serum containing specific antibodies, the latex particles form clumps that become visible to the naked eye. Latex agglutination tests using Paul–Bunnell antigen have largely supplanted the original monospot test for heterophile antibodies that used bovine or horse red blood cells following adsorption with guinea pig kidney (Bruu et al., 2000). Latex agglutination tests are subject to a “prozone effect” wherein high levels of antibody generate a falsely negative result due to saturation of all antibody-binding sites and minimal agglutination.
What is agglutination inhibition?
Agglutination inhibition or hemagglutination inhibition refers to the inhibition of these reactions by soluble antigen which reacts with the combining sites of the antibodies and thereby prevents their binding to and agglutination of the particles. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What is the term for the formation of clumps of cells or inert particles by specific antibodies to surface?
Agglutination is defined as the formation of clumps of cells or inert particles by specific antibodies to surface antigenic components (direct agglutination ) or to antigenic components adsorbed or chemically coupled to red cells or inert particles (passive hemagglutination and passive agglutination , respectively).
What is passive agglutination?
Passive Agglutination. Whereas agglutination allows the use of particulate antigens to determine concentrations of antibodies in sera, passive Agglutination allows the determination of the presence and concentration of soluble antigens.
How to determine the concentration of a soluble antigen?
Alternatively, to determine the concentration of a soluble antigen, particles can be coated with antibody specific to the soluble antigen and added to dilutions of sample containing the soluble antigen. Agglutination of the antibody-coated particles indicates the presence of the soluble antigen.