Ghrelin is your hunger-causing hormone and is produced or released in the stomach when it becomes empty. It basically tells your brain that you are hungry and to seek out food. The emptier your stomach, the more ghrelin hormone is produced and hence more hunger.
How to increase ghrelin to gain weight?
Strategies to increase PYY:
- Lower-carb diet: You should eat a lower-carb diet based on unprocessed foods in order to keep blood sugar levels stable. ...
- Protein: Eat plenty of protein from either animal or plant sources ( 58, 109 ).
- Fiber: Eat plenty of fiber ( 89, 110, 111 ).
How to control ghrelin?
Ghrelin is one of the hardest hormones to control because basically there is no stopping it once it starts. Your best control measure is to not allow its levels to rise in the first place by eating healthy portions and exercising to supplement your diet efforts.
What hormone makes you hungry?
The first hormone is called ghrelin, otherwise known as the "I'm hungry" hormone. When your stomach is empty—or thinks it is—it secretes ghrelin. This causes hunger by sending signals to the brain, urging it on to a search-and-destroy mission aimed at any nearby bag of Doritos. Leptin is the second hormone.
How to reduce ghrelin production?
Tips to manage ghrelin levels
- Maintain a moderate body weight. Obesity may increase your sensitivity to ghrelin, ultimately increasing your appetite ( 25, 26, 27 ).
- Try to get good quality sleep. Poor sleep may lead to increases in ghrelin, overeating, and weight gain ( 32, 33 ).
- Eat regularly. ...
What stimulates ghrelin secretion?
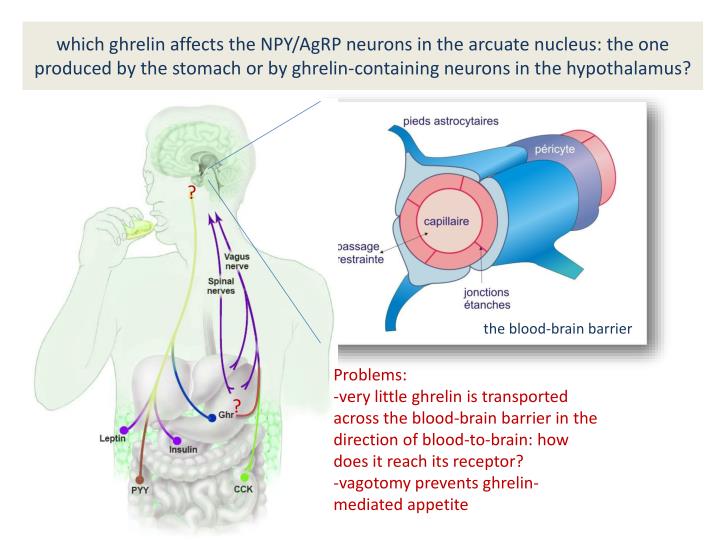
Autonomic Nervous System. The autonomic nervous system plays an important role in the regulation of ghrelin. Excitation of the vagus nerve can stimulate ghrelin secretion.
Why does ghrelin get released?
This hormone is produced in your stomach and secreted when your stomach is empty. It enters your bloodstream and affects a part of your brain called the hypothalamus, which helps regulate your hormones and appetite ( 4 , 7 ). The higher your levels of ghrelin, the hungrier you get.
How do you stop ghrelin release?
A person who wishes to naturally reduce ghrelin levels in the body may consider eating a healthy, fiber-rich diet, consuming adequate protein, exercising, getting enough sleep, and minimizing stress.
What suppresses ghrelin secretion?
H2S suppresses ghrelin secretion in gastric primary culture.
Why is ghrelin called hunger hormone?
It is termed the ‘hunger hormone’ because it stimulates appetite, increases food intake and promotes fat storage. When administered to humans, ghrelin increases food intake by up to 30%; it circulates in the bloodstream and acts at the hypothalamus, an area of the brain crucial in the control of appetite. Ghrelin has also been shown ...
Does eating reduce ghrelin?
Eating reduces concentrations of ghrelin. Different nutrients slow down ghrelin release to varying degrees; carbohydrates and proteins restrict the production and release of ghrelin to a greater extent than fats. Somatostatin also restricts ghrelin release, as well as many other hormones released from the digestive tract.
Does ghrelin increase when fasting?
Ghrelin levels are primarily regulated by food intake. Levels of ghrelin in the blood rise just before eating and when fasting, with the timing of these rises being affected by our normal meal routine. Hence, ghrelin is thought to play a role in mealtime ‘hunger pangs’ and the need to begin meals. Levels of ghrelin increase when fasting (in line ...
Does ghrelin cause muscle growth?
Ghrelin also stimulates the release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland, which, unlike ghrelin itself, breaks down fat tissue and causes the build-up of muscle. Ghrelin also has protective effects on the cardiovascular system and plays a role in the control of insulin release.
Is ghrelin a cause of obesity?
However, ghrelin levels are usually lower in people with higher body weight compared with lean people, which suggests ghrelin is not a cause of obesity; although there is a suggestion that obese people are actually more sensitive to the hormone. However, more research is needed to confirm this.
Does ghrelin cause weight gain?
This suggests that ghrelin may contribute to their increased appetite and body weight. Ghrelin levels are also high in cachexia and the eating disorder, anorexia nervosa. This may be the body’s way of making up for weight loss by stimulating food intake and fat storage.
How does ghrelin affect animal behavior?
Ghrelin injections also increase an animal's motivation to seek out food, behaviors including increased sniffing, foraging for food, and hoarding food. Body weight is regulated through energy balance, the amount of energy taken in versus the amount of energy expended over an extended period of time.
Where is ghrelin found?
Location. Ghrelin cells are found mainly in the stomach and duodenum, but also in the jejunum, lungs, pancreatic islets, gonads, adrenal cortex, placenta, and kidney. It has also been shown that ghrelin is produced locally in the brain.
What is the gastric brain communication pathway?
Gastric-brain communication is an essential part of energy homeostasis, and several communication pathways are probable, including the gastric intracellular mTOR / S6K1 pathway mediating the interaction among ghrelin, nesfatin and endocannabinoid gastric systems, and both afferent and efferent vagal signals.
How does ghrelin affect energy?
Ghrelin is a participant in regulating the complex process of energy homeostasis which adjusts both energy input – by adjusting hunger signals – and energy output – by adjusting the proportion of energy going to ATP production, fat storage, glycogen storage, and short-term heat loss. The net result of these processes is reflected in body weight, and is under continuous monitoring and adjustment based on metabolic signals and needs. At any given moment in time, it may be in equilibrium or disequilibrium. Gastric-brain communication is an essential part of energy homeostasis, and several communication pathways are probable, including the gastric intracellular mTOR / S6K1 pathway mediating the interaction among ghrelin, nesfatin and endocannabinoid gastric systems, and both afferent and efferent vagal signals.
What is the function of ghrelin?
Ghrelin stimulates brain structures having a specific receptor – the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1A ( GHSR -1A). Ghrelin also participates in regulation of reward cognition, learning and memory, the sleep-wake cycle, taste sensation, reward behavior, and glucose metabolism.
How many exons does GHRL have?
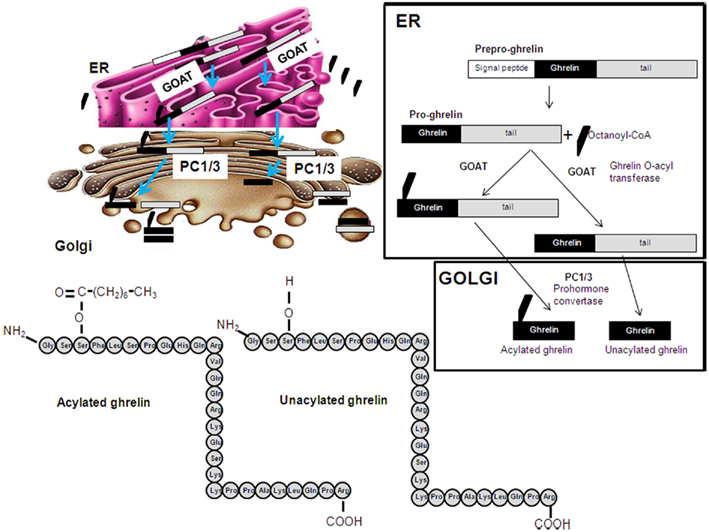
The GHRL gene produces mRNA which has four exons. Five products arise: the first is the 117-amino acid preproghrelin. It is homologous to promotilin; both are members of the motilin family. It is cleaved to produce proghrelin which is cleaved to produce an unacylated 28-amino acid ghrelin and an acyated C-ghrelin.
What is the hormone that increases food intake called?
Ghrelin . Ghrelin / ˈɡrɛlɪn / (or lenomorelin, INN) is a hormone produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases food intake.

Overview
Ghrelin receptor
The ghrelin receptor GHS-R1a (a splice-variant of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor, with the GHS-R1b splice being inactive) is involved in mediating a wide variety of biological effects of ghrelin, including: stimulation of growth hormone release, increase in hunger, modulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, regulation of gastrointestinal motility and secretion, protection of neuronal and cardiovascular cells, and regulation of immune function. They are present in high d…
History and name
Ghrelin was discovered after the ghrelin receptor (called growth hormone secretagogue type 1A receptor or GHS-R) was determined in 1999. The hormone name is based on its role as a growth hormone-releasing peptide, with reference to the Proto-Indo-European root gʰre-, meaning "to grow".
Gene, transcription products, and structure
The GHRL gene produces mRNA which has four exons. Five products arise: the first is the 117-amino acid preproghrelin. It is homologous to promotilin; both are members of the motilin family. It is cleaved to produce proghrelin which is cleaved to produce an unacylated 28-amino acid ghrelin and an acyated C-ghrelin. Obestatin is presumed to be cleaved from C-ghrelin.
Ghrelin cells
The ghrelin cell is also known as an A-like cell (pancreas), X-cell (for unknown function), X/A-like cell (rats), Epsilon cell (pancreas), P/D sub 1 cell (humans) and Gr cell (abbreviation for ghrelin cell).
Ghrelin cells are found mainly in the stomach and duodenum, but also in the jejunum, lungs, pancreatic islets, gonads, adrenal cortex, placenta, and kidney. It has also been shown that ghrel…
Function and mechanism of action
Ghrelin is a participant in regulating the complex process of energy homeostasis which adjusts both energy input – by adjusting hunger signals – and energy output – by adjusting the proportion of energy going to ATP production, fat storage, glycogen storage, and short-term heat loss. The net result of these processes is reflected in body weight, and is under continuous monitoring and adjustment based on metabolic signals and needs. At any given moment in time, it may be in eq…
Blood levels
Blood levels are in the pmol/l range. Both active and total ghrelin can be measured. Circulating ghrelin concentrations rise before eating and fall afterward, more strongly in response to protein and carbohydrate than to lipids.
Locations of action
The entire ghrelin system (dAG, AG, GHS-R and GOAT) has a gluco-regulatory action.
Preliminary research indicates that ghrelin participates in the regulation of circadian rhythms. A review reported finding strong evidence that sleep restriction affected ghrelin or leptin levels, or energy expenditure.
Ghrelin has inhibitory effects on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion. It may caus…