What forces drive sea floor spreading?
What force causes seafloor spreading? Convection Currents Convection forms into currents that drive the tectonic plates either together or apart. The seafloor spreads along diverging boundaries, but it also contracts along the converging boundaries as seafloor is pushed below the surface by two plates in collision with each other.
What is the primary force that causes sea floor spreading?
The primary force that causes sea floor to spread and continents to drift is the convection in the mantle. Convection is a form of heat transfer that produces convection cells in the mantle. The earth is broken up into about 13 lithospheric plates. The lithosphere are located on top of the weak and plastic asthenosphere below.
What are the three pieces of evidence for seafloor spreading?
What three types of evidence provided support for the theory of sea floor spreading? eruptions of molten material, magnetic stripes in the rock of the ocean floor, and the ages of the rocks themselves. What is the evidence of the seafloor spreading? Abundant evidence supports the major contentions of the seafloor-spreading theory.
What is the major evidence that seafloor spreading?
What are three kinds of evidence scientists have found to support this idea?
- Molten Material (magma/lava) – scientists have found strange rocks shaped like pillows in the central valley of the ocean ridge. …
- Magnetic Stripes – The molten rock contains iron – it is magnetic. …
- Drilling Samples – the Glomar challenger drilled holes in the ocean 6km deep.
Where can you find fault lines?
Reverse faults, also called thrust faults, slide one block of crust on top of another. These faults are commonly found in collisions zones, where tectonic plates push up mountain ranges such as the Himalayas and the Rocky Mountains. All faults are related to the movement of Earth’s tectonic plates.
When did Pangaea begin to break apart?
Pangaea (sometimes spelled Pangea), the most recent of a series of supercontinents on Earth, formed about 270 million years ago and broke apart about 200 million years ago. At this time most of the dry land on Earth was joined into one huge landmass that covered nearly a third of the planet’s surface.
Where are the youngest rocks found in the ocean?
The youngest ocean floor is located on the mid-ocean ridge. The oldest ocean floor is located near the continents, next to a subduction zone. There are rocks on every continent that are 3 to 4 billion years old.
How do the plates move at a divergent boundary?
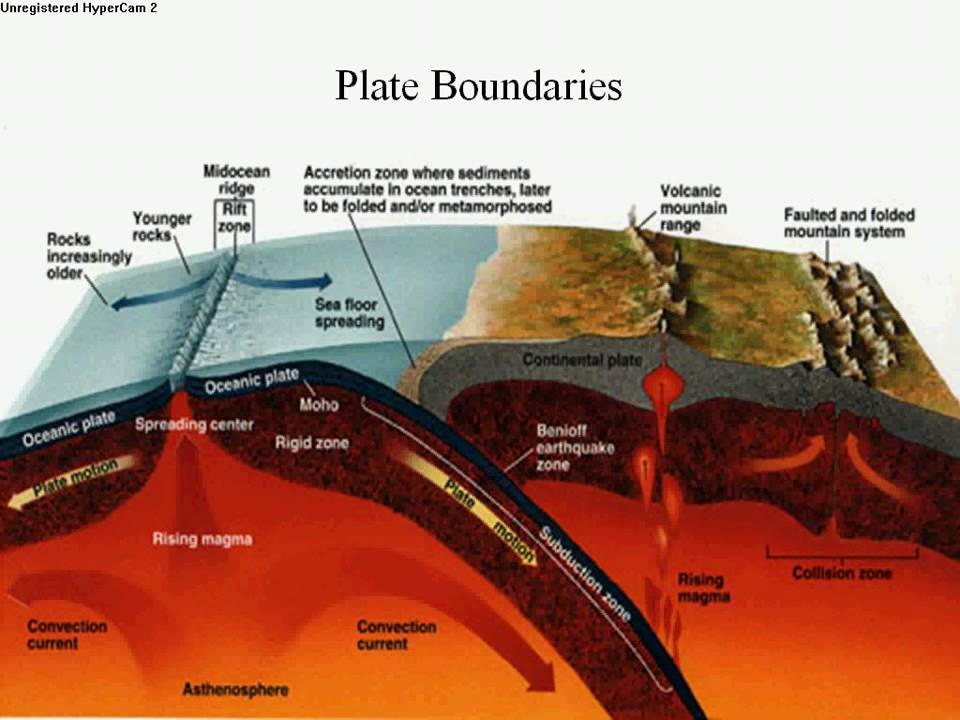
Divergent boundaries occur along spreading centers where plates are moving apart and new crust is created by magma pushing up from the mantle. Picture two giant conveyor belts, facing each other but slowly moving in opposite directions as they transport newly formed oceanic crust away from the ridge crest.
Where does the seafloor take place?
This rock (basalt) becomes a new part of Earth’s crust. Seafloor spreading occurs along mid-ocean ridges—large mountain ranges rising from the ocean floor. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, for instance, separates the North American plate from the Eurasian plate, and the South American plate from the African plate.
How do plate tectonics cause ocean trenches?
Trenches are formed by subduction, a geophysical process in which two or more of Earth’s tectonic plates converge and the older, denser plate is pushed beneath the lighter plate and deep into the mantle, causing the seafloor and outermost crust (the lithosphere) to bend and form a steep, V-shaped depression.
Why would deep trenches be found in or around the plate boundaries?
Some of the most familiar ocean trenches are the result of this type of convergent plate boundary. In a subduction zone, some of the molten material—the former seafloor—can rise through volcanoes located near the trench.
The Process of Sea Floor Spreading
The mid-ocean ridge is the region where new oceanic crust is created. The oceanic crust is composed of rocks that move away from the ridge as new crust is being formed. The formation of the new crust is due to the rising of the molten material (magma) from the mantle by convection current.
The Subduction Process
The highly dense oceanic crust that is formed after a progressive spreading is destined to two possible occurrences. It can either be subducted into the ocean deep trench or continue to spread across the ocean until it reaches a coast.
Evidence of Sea Floor Spreading
Harry Hess’s hypothesis about seafloor spreading had collected several pieces of evidence to support the theory. This evidence was from the investigations of the molten material, seafloor drilling, radiometric age dating and fossil ages, and the magnetic stripes. This evidence however was also used to support the Theory of Continental drift.
Why does the sea floor spread?
Sea floor spreading is caused by a ridge opening in the earths crust where new magma (lava) rises up and adds to the sea floor. As each new centimeter is added and cools, another takes its place. It happens on both sides of the ridge, so the sea floor is spreading in both directions. This is how new oceanic crust is created.
Where does seafloor spreading occur?
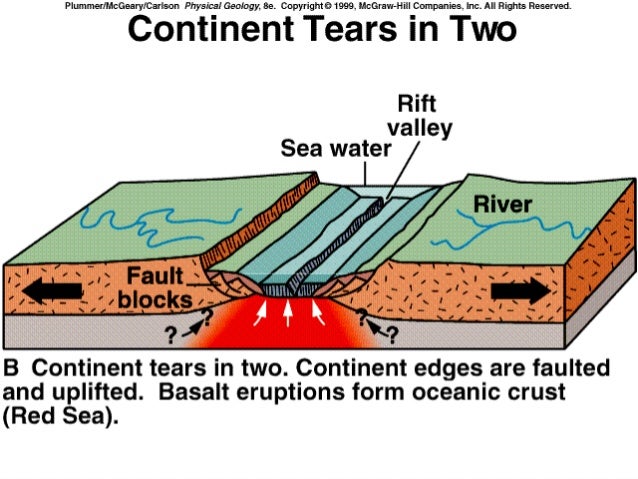
Seafloor spreading occurs at these rift valleys and ocean ridges where different plates of the Earth’s crust meet each other.
Why is seafloor spreading important?
Seafloor spreading is important as it is creating rifts and the oceanic crust below most of the Ocean. It is leaving a pattern of older crust moving away from the central mid-ocean ridges. Where the ocean floor meets the continental slope, the passive margins of large sedimentations are found, and where the floor meets destructive margins, vulcanic activity mingles with orogenic activity forming mountains and amalgamating more crust on the continental crusts.
What were the driving forces of subduction zones?
Those subduction zones were pulling the distant spreading centres open. They were the driving force.
Where does subduction occur?
Subduction occur when two plates converge towards each other and the denser plate being heavier slide below the lighter plate and Sea floor spreading occur at the Mid oceanic ridges where Diverging limbs of Convection cells tend to pull apart the plate and create a Rift Valley like the East African rift valley
How much does the spreading rate of the ocean floor change per year?
By calculating the age of the oldest rocks of the ocean floor and knowing the distance involved it was possible to calculate the spreading rate - in the Atlantic it is about 2.54 cm per year. Variations occur at other spreading centres.
How old is the ocean floor?
Before you do you need to consider: the age of the floor of the oceans is about 200 million years and that is against the continental masses. By comparison the youngest rocks of the ocean floor is associated with spreading centres - like the Mid Atlantic Ridge, East Pacific Rise etc!