Causes
Some known risk factors for Secondary Peritonitis include:
- Appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix)
- Stomach or duodenal ulcers
- Torn or twisted intestine (volvulus)
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- Inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis
- Diverticulitis
- Abdominal injury caused by a surgery
- Peritoneal dialysis
- Trauma (such as stab wounds and motor vehicle accidents)
Symptoms
The most common causes are alcoholism, vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency, and medication. Medical history and physical examination, vitamin B12 levels, reticulocyte counts, and peripheral blood films can help delineate the root cause of macrocytosis. Why is macrocytosis bad?
Prevention
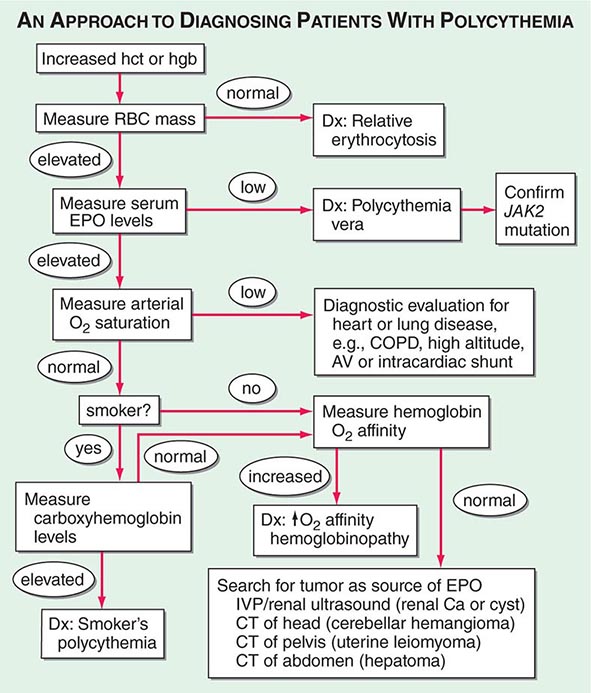
Secondary hypersplenism results from another disease such as chronic malaria, rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, or polycythemia vera, a blood disorder. Spleen disorders in general are almost always secondary in nature.
Complications
This can help suggest and identify what causes a high platelet count in a patient who is experiencing either a viral or bacterial infection. Bacterial infections may be pneumonia, pyelonephritis, purulent arthritis, osteomyelitis, chronic wound infections, tuberculosis, among others.
What are common causes of secondary peritonitis?
What can be the cause of prolonged macrocytosis?
What causes secondary hypersplenism?
What can cause increased platelets?

How is secondary thrombocytosis treated?
How is thrombocytosis treated?Taking a daily low-dose aspirin: You can take aspirin to prevent blood clots. ... Taking medicines that lower platelet levels: Medications such as hydroxyurea (Droxia®, Hydrea®, Siklos®, Mylocel®) and anagrelide (Agrilyn®) suppress platelet production in your bone marrow.More items...•
Is secondary thrombocytosis curable?
Treatment for this condition depends on the cause. If you've had significant blood loss from a recent surgery or an injury, your elevated platelet count might resolve on its own. If you have a chronic infection or an inflammatory disease, your platelet count likely will remain high until the condition is under control.
What is the most common cause of thrombocytosis?
The cause of this disorder is unclear but it often appears to be connected to mutations in a variety of genes. Your bone marrow produces too many of the cells that form platelets and these platelets are often abnormal.
What's the difference between primary and secondary thrombocytosis?
Primary thrombocytosis is caused by a clonal disorder of hematopoietic stem cells or by inherited mutations (familial or congenital thrombocytosis). Secondary or reactive thrombocytosis occurs when signals (often cytokines like IL-11) promote proliferation and differentiation of normal megakaryocytes.
Is secondary thrombocytosis serious?
[6] Even though secondary thrombocytosis is benign, the underlying etiology of thrombocytosis (e.g., malignancy, connective tissue disorders, chronic infections) can be associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes.
What cancers cause thrombocytosis?
Thrombocytosis is an adverse prognostic factor in many types of cancer. These include breast cancer, ovarian and other gynecologic cancers, renal cell carcinoma and lung cancers.
What autoimmune diseases cause thrombocytosis?
Objective: Thrombocytosis can be due to a myeloproliferative disorder or to a reactive or secondary process; among these are connective tissue disorders, in particular systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
What kind of infection can cause high platelets?
Inflammation or infections: Conditions such as connective tissue disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, and tuberculosis can raise your platelet count.
What autoimmune disease causes high platelets?
Overview. Essential thrombocythemia (throm-boe-sie-THEE-me-uh) is an uncommon disorder in which your body produces too many platelets. Platelets are the part of your blood that sticks together to form clots. This condition may cause you to feel fatigued and lightheaded and to experience headaches and vision changes.
Can you live a normal life with thrombocytosis?
Essential thrombocythemia, also known as ET, is a rare disease. The most important first fact about ET: on average, people with ET have a normal life expectancy.
What foods to avoid if you have thrombocytosis?
Eat Less...Canned and frozen foods and leftovers. The nutritional value of food deteriorates with time.White flour, white rice and processed foods. ... Hydrogenated, partially hydrogenated or trans-fats. ... Sugar. ... Dairy products. ... Meat. ... Alcoholic beverages. ... Foods that can interfere with blood clotting.More items...
Can vitamin D deficiency cause high platelet count?
According to the results of this study, lower vitamin D levels will cause higher platelet counts in people with normal calcium and magnesium levels.
Can you live a normal life with thrombocytosis?
Essential thrombocythemia, also known as ET, is a rare disease. The most important first fact about ET: on average, people with ET have a normal life expectancy.
How long does thrombocytosis last?
Reactive thrombocytosis is a predictable finding after splenectomy, with the platelet count peaking at 1 to 3 weeks and returning to normal levels in weeks, months, and, rarely, years (3).
Can thrombocytosis cause death?
The life expectancy of patients with essential thrombocytosis (primary thrombocythemia) is nearly that of the healthy population. Median survival is approximately 20 years. For patients younger than age 60 years, median survival is 33 years.
Can you live a long life with essential thrombocytosis?
In general, ET is a chronic disease that does not shorten life expectancy in the first decade following diagnosis; however, over longer periods of time, survival may be shortened. Median survival of patients with ET is about 20 years.
What is reactive thrombocytosis?
It's called reactive thrombocytosis or secondary thrombocytosis when the cause is an underlying condition, such as an infection. Less commonly, when thrombocytosis has no apparent underlying condition as a cause, the disorder is called primary thrombocythemia or essential thrombocythemia. This is a blood and bone marrow disease.
How to detect thrombocytosis?
Your doctor might detect thrombocytosis in a routine blood test result that shows a high platelet level. If your blood test indicates thrombocytosis, it's important to determine whether it's reactive thrombocytosis or essential thrombocythemia to know how to manage the condition.
What is the role of platelets in blood clots?
Platelets are blood particles produced in the bone marrow that play an important role in the process of forming blood clots. Thrombocytosis (throm-boe-sie-TOE-sis) is a disorder in which your body produces too many platelets.
Why is my bone marrow abnormal?
The cause of this disorder is unclear but it often appears to be connected to mutations in a variety of genes. Your bone marrow produces too many of the cells that form platelets and these platelets are often abnormal. This poses a much higher risk of clotting or bleeding complications than does reactive thrombocytosis.
What causes a person to lose blood faster than it produces?
Iron deficiency. Removal of your spleen. Hemolytic anemia — a type of anemia in which your body destroys red blood cells faster than it produces them, often due to certain blood diseases or autoimmune disorders. Inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis or inflammatory bowel disease.
Do people with thrombocytosis have symptoms?
People with thrombocytosis often don't have signs or symptoms. Signs and symptoms of reactive thrombocytosis, if they do occur, relate to the underlying condition.
Can thrombocytosis cause platelets to be higher than normal?
Because thrombocytosis isn't likely to cause symptoms, you probably won't know you have it unless a routine blood test reveals a higher than normal number of platelets. If that occurs, your doctor will try to determine the reason.
What causes secondary thrombocytosis?
Secondary, or reactive, thrombocytosis is caused by another condition the patient may be suffering from, such as: ++Anemia++ due to iron deficiency. Cancer. Inflammation or infection, Surgery, especially splenectomy (removal of the spleen).
What is thrombocytosis in blood?
What is thrombocytosis? Thrombocytosis refers to having too many platelets in your blood. Platelets are blood cells in plasma that stop bleeding by sticking together to form a clot. Too many platelets can lead to certain conditions, including stroke, heart attack or a clot in the blood vessels.
What causes a swollen hand and foot?
Some patients with essential thrombocythemia develop erythromelalgia, a condition that causes pain, swelling and redness of your hands and feet.
What happens if you have blood clots in your abdomen?
Abnormal blood clotting can also occur, leading to stroke, heart attack and unusual clots in the blood vessels of the abdomen.
Is thrombocytosis an inherited disease?
It is also called essential thrombocythemia (or ET). The cause is unknown. It isn’t considered an inherited (genetic) condition even though certain gene mutations have been found in the blood or bone marrow.
Can you take aspirin for thrombocytosis?
Secondary forms of thrombocytosis rarely require treatment. For those with symptoms, a few treatment options are available. One is to treat the disease that is causing thrombocytosis. In some cases, you can take aspirin to help prevent blood clots.
Can thrombocytosis cause blood clotting?
Even though the platelet count is elevated for a short time (or even indefinitely after splenectomy), secondary thrombocytosis does not typically lead to abnormal blood clotting. Primary thrombocytosis, or essential thrombocythemia, can cause serious bleeding or clotting complications.
Drugs Mentioned In This Article
Thrombotic disorders can be caused by genetic defects, which increase the risk of venous thromboembolism, or acquired defects, which increase the risk of arterial and venous thrombosis. Of the acquired causes, which of the following is most likely to increase a patient’s risk of venous thrombosis?
Merck and the Merck Manuals
Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA is a global healthcare leader working to help the world be well. From developing new therapies that treat and prevent disease to helping people in need, we are committed to improving health and well-being around the world. The Merck Manual was first published in 1899 as a service to the community.
What is secondary thrombocythemia?
Click here for the Professional Version. Secondary thrombocythemia is excess platelets in the bloodstream that develops as a result of another disorder and rarely leads to excessive blood clotting or bleeding. Platelets (thrombocytes) are cell-like particles in the blood that help the body form blood clots. Platelets are normally produced in the ...
What is the cause of anemia?
Iron Deficiency Iron deficiency is a common cause of anemia, a condition in which the number of red blood cells is low. Iron deficiency usually results from loss of blood in adults (including bleeding from... read more
What are platelets in blood?
Platelets (thrombocytes) are cell-like particles in the blood that help the body form blood clots. Platelets are normally produced in the bone marrow by cells called megakaryocytes. In thrombocythemia, the body produces too many platelets. Thrombocythemia can be.
What tests are done to determine the cause of platelet elevation?
To identify possible causes, doctors do blood tests, sometimes including genetic testing, and occasionally a bone marrow biopsy. Other tests such as radiologic tests may be needed to ascertain the cause of the platelet elevation. Treatment is aimed at the cause of the platelet elevation.
Can platelets cause thrombocythemia?
Symptoms of the underlying condition usually dominate. Although an increased number of platelets might be thought to cause excessive blood clotting, this rarely happens in secondary thrombocythemia unless people also have severe arterial disease or prolonged immobility.
Can platelets cause blood clotting?
Although an increased number of platelets might be thought to cause excessive blood clotting, this rarely happens in secondary thrombocythemia unless people also have severe arterial disease or prolonged immobility. Although some people with essential thrombocythemia have an increased risk of bleeding, this is not a concern with secondary thrombocythemia.
Is thrombocythemia a myeloproliferative neoplasm?
When thrombocythemia is caused by such an underlying disorder, the thrombocythemia is called secondary thrombocythemia (or reactive thrombocytosis) and is not classified as a myeloproliferative neoplasm. Rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other inflammatory disorders.
What is secondary thrombocytosis?
In general, secondary thrombocytosis (reactive thrombocytosis) is a temporary laboratory anomaly that resolves when the primary causative condition is addressed. The overall prognosis in patients with secondary thrombocytosis reflects that of the underlying associated condition.
Why is platelet count elevated in secondary thrombocytosis?
Elevated platelet counts can be due to megakaryocyte proliferation; decreased platelet sequestration; or increased cytokine production, which stimulates platelet production.
What is the term for an abnormality of platelets?
[ 1, 2, 3] This phenomenon is called reactive or secondary thrombocytosis, which is a benign form of thrombocytosis. In contrast, clonal thrombocytosis (primary or essential thrombocytosis) is an unregulated abnormality of platelet production due to a clonal expansion of bone marrow progenitor cells. [ 4, 5]
What percentage of cases of thrombocytosis are multifactorial?
A retrospective chart review of 305 patients with extreme thrombocytosis (platelet count of 1,000 × 10 9 /L or greater) found that in appromixmately 80% of cases, the cause was multifactorial. Secondary thrombocytosis due to surgical complications accounted for 54.1% of cases. Among those cases, splenectomy (50.5%) and infections (44.9%) were the most common causes. [ 13]
What causes megakaryocytes to grow?
Overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, and IL-11, occurs in chronic inflammatory, infective, and malignant states. [ 6, 7, 8, 9] Elevated levels of IL-1, IL-6, C-reactive protein (CRP), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) lead to megakaryocyte growth and increased production of platelets as part of secondary thrombocytosis.
How many children have secondary thrombocytosis?
Overall, secondary thrombocytosis occurs in 3-13% of hospitalized children. However, in a Greek study of children 10 days to 8 years old who were hospitalized with viral pneumonia, [ 9] and an Italian study of children 1 to 24 months old who were hospitalized for community-acquired infections, [ 16] approximately half had thrombocytosis.
Is secondary thrombocytosis asymptomatic?
Secondary thrombocytosis is usually identified on routine laboratory evaluation, as most patients are asymptomatic, However, patients may have symptoms related to the primary condition that may have precipitated the thrombocytosis (see Presentation ).