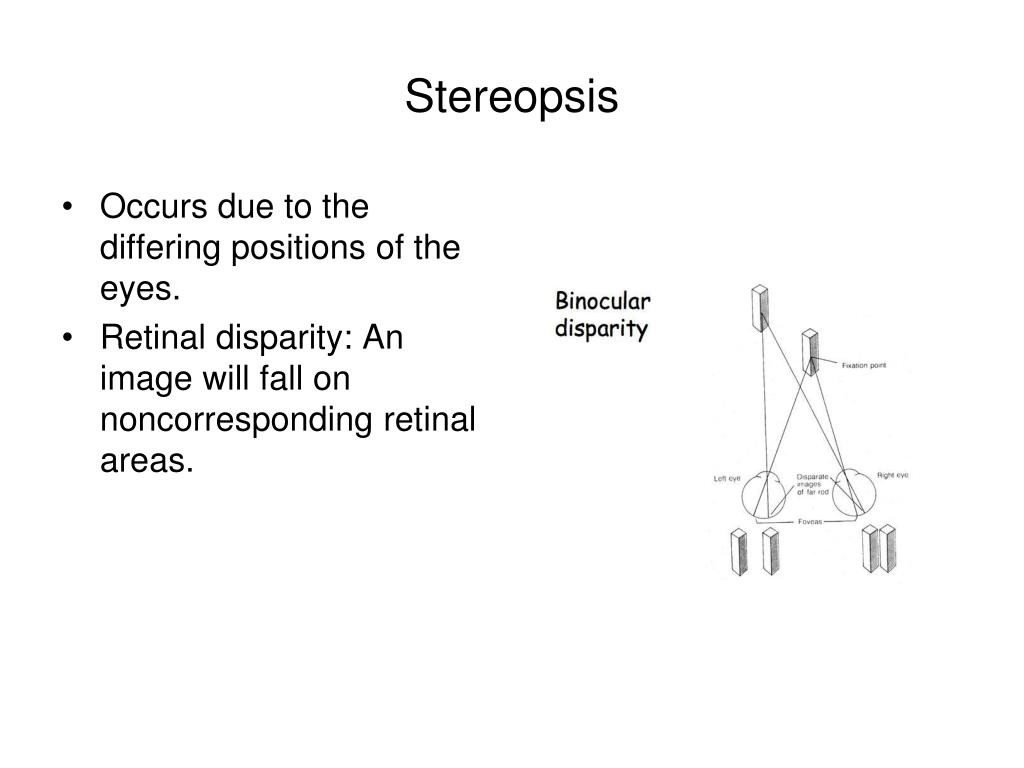
Stereopsis. Fusion occurs when the brain is able to bring together the two disparate images from both eyes and interpret them as one single image. This is what usually happens for normal eyes and normal visual processing systems in the brain. You need to have fusion first before you can have depth perception.
What is stereopsis (stereopsis)?
WHAT IS STEREOPSIS? Stereopsis, also known as stereoscopic depth perception, is the ability of both eyes to see the same object as one image and to create a perception of depth. It is a measure of binocular visual function, i.e. how well both eyes work together.
What can affect my stereopsis?
Finally, bear in mind too that disorders of the brain (particularly if the visual processing pathways are involved, such as in a stroke or head injury) will have an effect on your stereopsis. HOW IS STEREOPSIS PERCEIVED?
How to improve stereopsis with vision therapy?
The most effective way to improve stereopsis is with Vision Therapy for Lazy Eyes. Vision therapy teaches the eyes how to work together. For individuals whose poor stereopsis is caused by strabismus or amblyopia (lazy eye), vision therapy can help them regain good depth perception.
What causes poor or absent stereopsis?
Most of the time, poor or absent stereopsis is due to childhood amblyopia. However, stereopsis can also be affected later on in life by conditions that reduce your ability to see clearly, for example cataract, age-related macular degeneration and presbyopia.

What causes loss of stereopsis?
The most common cause for loss of stereoscopic vision is amblyopia, in which one eye has failed to form an adequate input to the visual cortex, usually due to strabismus (deviating eye) or anisometropia.
What is the cause of stereoscopic vision in human?
Stereoscopic Vision In Humans Since our eyes are around 2 inches apart, two images are generated and sent to the brain for their processing, the disparity on the retina creates a combined overall image which also provides a sense of distance of an object.
Where does stereopsis happen?
Stereopsis appears to be processed in the visual cortex of mammals in binocular cells having receptive fields in different horizontal positions in the two eyes.
How is stereopsis achieved?
True stereopsis is dependent on disparities between the two images received by each eye, and therefore a certain number of points must fall on disparate points on the retina. It is also essential that these disparate points are fused like the corresponding points.
At what age does stereopsis develop?
The critical period for development of stereopsis in humans is well defined. After an abrupt onset at approximately 3 months of age, 1 2 3 4 5 there is a rapid period of maturation until 8 to 18 months of age, 6 followed by a continued gradual improvement until at least 3 years of age.
Why am I seeing 3D things?
Stereopsis, more commonly known as 3D depth perception, occurs when your brain combines the two images received from each eye and creates one single 3D image. This allows you to easily engage and interact with the world around you.
How do you know if you have a stereopsis?
The eye doctor will ask you to wear what looks like a pair of sunglasses, then show a book with images, often of a butterfly or reindeer, cartoon characters or circles and other shapes. These images are actually in 3D, and as you identify the 3D images 'popping out of the page' your 3D vision (stereopsis) is measured.
What part of the brain is responsible for depth perception?
visual cortexDepth is an illusion generated by the brain's visual cortex through a computation known as binocular disparity—in which visual input received separately from each eye is compared.
How do you fix depth perception problems?
There are several treatments available for problems of depth perception. Glasses can be prescribed to help people with strabismus. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to straighten the eyes. Wearing an eye patch has often been used to treat amblyopia.
What is an example of stereopsis?
Examples include the Randot stereotest, Random-dot E stereotest, TNO stereotest, Frisby stereotest and the Lang stereotest. All these tests require you to correctly identify the target or image that has stereoscopic depth at a set distance (usually 40 centimeters) from your eyes.
What is normal stereopsis?
For discerning the clinical significance the stereo acuity levels were categorized into normal (20 arc seconds or better), Borderline (25 arc seconds to 40 arc seconds) and Reduced stereopsis (50 arc seconds to 400 arc seconds).
How is stereopsis implemented in the brain?
External space is projected onto the retinae of both eyes as two-dimensional images. The brain fuses these two images, and because each is slightly displaced with respect to the other — a phenomenon known as retinal disparity — the relative and absolute depths of objects in space are perceived.
Do humans have stereoscopic vision?
Human stereo vision is capable of remarkably precise judgments, discriminating binocular disparities as small as 2 seconds of arc. Such performance requires good vision in both eyes, very precise oculomotor coordination and specialised sensory neurons in visual cortex.
How does the visual system create stereoscopic vision?
3D vision is the direct effect of our brains merging the images from both of our eyes together. Each of our eyes creates a single two-dimensional image, but the brain is able to interpret depth when it merges both two-dimensional images and understands the difference between them.
How do you do stereoscopic vision?
0:193:46Brain Games- Stereoscopic Vision - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow again bring your fingertips up like this. And while staring at your fingertips touch themMoreNow again bring your fingertips up like this. And while staring at your fingertips touch them together not as easy as it looks. Right.
What type of vision do humans have?
Each eye alone gives us roughly a 130-degree field of vision. With two eyes, we can see nearly 180 degrees. Most of that field is what's called a Cyclopean image -- the single mental picture that a Cyclops might see. But that single image, created by two eyes, has both range and depth.
Why is stereopsis important?
Having stereopsis allows you to judge distances and to see where objects are in relation to you and to each other.
What is stereovision test?
Stereovision tests are primarily used in children, as a vision screening tool for amblyopia and binocular vision defects, and also as a way of monitoring the progress of amblyopia treatment. There are 2 groups of clinical tests (also called stereotests) that are used to measure stereopsis: contour stereotests and random-dot stereograms.
What is contour stereotest?
Contour stereotests use two horizontally disparate images to evaluate stereopsis. An example is the Titmus Fly stereotest (left). After wearing polarizing spectacles (so that each eye sees a different image), you will need to determine which of the images have depth.
Which random dot stereograms do not require glasses?
The 2 random dot stereograms that do not require glasses are the Frisby and Lang stereotests. Both use different principles to avoid the need for glasses during testing. The Frisby stereotest uses a series of squares containing geometric shapes painted on perspex of different thicknesses. The Lang stereotest uses a combination of random dots and cylinder gratings.
How many seconds of arc is stereoscopic depth perception?
Stereoscopic depth perception is measured in seconds of arc. In general, you are considered to have gross stereoscopic vision at 3,600 seconds of arc. The smaller the number (some people can achieve stereovision better than 20 seconds of arc), the better your stereopsis.
What are the two aspects of stereopsis?
There are two distinct aspects to stereopsis: coarse stereopsis and fine stereopsis, and provide depth information of different degree of spatial and temporal precision.
Where is stereopsis processed?
Stereopsis appears to be processed in the visual cortex of mammals in binocular cells having receptive fields in different horizontal positions in the two eyes. Such a cell is active only when its preferred stimulus is in the correct position in the left eye and in the correct position in the right eye, making it a disparity detector.
Why is stereopsis possible with double vision?
Because each eye is in a different horizontal position, each has a slightly different perspective on a scene yielding different retinal images. Normally two images are not observed, but rather a single view of the scene, a phenomenon known as singleness of vision. Nevertheless, stereopsis is possible with double vision. This form of stereopsis was called qualitative stereopsis by Kenneth Ogle.
Why is coarse stereopsis important?
Coarse stereopsis is important for orientation in space while moving, for example when descending a flight of stairs. Fine stereopsis is mainly based on static differences.
How many perceptual mechanisms are involved in stereoscopic processes?
There are strong indications that the stereoscopic mechanism consists of at least two perceptual mechanisms, possibly three. Coarse and fine stereopsis are processed by two different physiological subsystems, with a coarse stereopsis being derived from diplopic stimuli (that is, stimuli with disparities well beyond the range of binocular fusion) and yielding only a vague impression of depth magnitude. Coarse stereopsis appears to be associated with the magno pathway which processes low spatial frequency disparities and motion, and fine stereopsis with the parvo pathway which processes high spatial frequency disparities. The coarse stereoscopic system seems to be able to provide residual binocular depth information in some individuals who lack fine stereopsis. Individuals have been found to integrate the various stimuli, for example stereoscopic cues and motion occlusion, in different ways.
What is fine stereopsis?
Fine stereopsis is mainly based on static differences. It allows the individual to determine the depth of objects in the central visual area ( Panum's fusional area) and is therefore also called quantitative stereopsis. It is typically measured in random-dot tests; persons having coarse but no fine stereopsis are often unable to perform on random-dot tests, also due to visual crowding which is based on interaction effects from adjacent visual contours. Fine stereopsis is important for fine-motor tasks such as threading a needle.
How many minutes of arc can you see with stereopsis?
Not everyone has the same ability to see using stereopsis. One study shows that 97.3% are able to distinguish depth at horizontal disparities of 2.3 minutes of arc or smaller, and at least 80% could distinguish depth at horizontal differences of 30 seconds of arc.
What are the two types of stereopsis?
Types of Stereopsis. Stereopsis can be broadly classified into two types - coarse stereopsis and fine stereopsis . Coase stereopsis is large, more easily distinguishable amounts of depth using retinal disparity cues. Fine stereopsis is often what is tested in an eye exam - this is very fine amounts of depth between objects.
What is fine stereopsis?
Fine stereopsis is often what is tested in an eye exam - this is very fine amounts of depth between objects. What is interesting is that the human visual system appears to have developed two different neural mechanisms to extract these different forms of depth information from the visual world.
Why is stereopsis important?
The phenomenon of stereopsis is important for several reasons. In the animal kingdom, having a spare eye if one is damaged is necessary for survival. In addition, certain animals have eyes on opposite sides of the head, allowing a 360° visual field from the combined fields of view and protection from potential pred ators.
What is stereopsis in children?
Stereopsis is not present at birth and develops in a child at 3-6 months of age. Any interference in the process of perceiving depth results in defective stereopsis, which can occur at any point from the infantile period to the elderly period of life. These interferences are known as binocular vision impairments. For example, a child with a congenital cataract will not be able to develop simultaneous perception if the cataract is not corrected early enough. Another possibility is a newborn with a unilateral refractive error, known as anisometropia, which can lead to anisometric amblyopia. As a result of anisometropia, the newborn cannot fuse the images from both eyes but rather produces two separate images in the brain. Depending on the difference in visual acuity, the brain can then either suppress visual capacity in the eye with greater refractive error or maintain stereopsis. Yet another common visual impediment affecting children is strabismus. Patients with strabismus exhibit tropias, which manifest as binocular misalignments. If these tropias are present from an early age, stereopsis would be expected, only shifted and with receptive fields of visual neurons offset on the retinae by the degree of shift. With misalignment, however, normal stereopsis is not possible, as the images on the retinae are too far apart for the brain to fuse. In addition, not only is eye position misaligned in strabismus, but it may also be variable. When the difference in visual acuity between the two eyes is greater than the brain can overcome or when the visual fields are dissimilar, the brain chooses to suppress the bad eye, resulting in amblyopia. Although stereopsis is lost, amblyopia serves to protect the eyes from diplopia. Any interruption in vision, no matter the severity or duration, in the first 8 years of life can hinder the development of visual perception. If interruptions in vision occur after this time, stereopsis is not lost, but adaptive changes occur. Adults can acquire strabismus as part of these adaptive changes. In order to avoid diplopia, the brain deviates one eye so that the visual fields are not overlapping.
What are tropias in strabismus?
Patients with strabismus exhibit tropias, which manifest as binocular misalignments. If these tropias are present from an early age, stereopsis would be expected, only shifted and with receptive fields of visual neurons offset on the retinae by the degree of shift.
How to test for stereopsis?
As the haploscope is not used often for diagnostic purposes, newer techniques were sought out to test for stereopsis while maintaining the line of sight. The anaglyph utilizes different colors, such as red and cyan, while presenting the two images to the eyes. When the images are viewed, the visual cortex of the brain fuses the images to produce one integrated stereoscopic image. Wilhelm Rollmann was the first to develop a method to view anaglyph images in 1852. Using camera filters, two images from the left-sided and right-sided perspectives were projected as a single image through a red filter on one side and a contrasting color on the other side, such as blue or green. Now, however, image-processing computer programs can simulate the effect of color filters.
How does a haploscope work?
A haploscope is a device that delivers different images to each eye simultaneously. This optical device in its earliest stages consisted of a pair of mirrors with the shiny surfaces facing away from each other and placed at 45-degree angles. The mirror on the right corresponded to images on the absolute right, and the mirror on the left corresponded to those on the absolute left. Depending on the difference between the images perceived, the brain will attempt to fuse the images. If the images are extremely dissimilar, confusion results. If the images are only slightly dissimilar, the brain will be able to process them. When the brain is able to fuse the images, stereopsis results and depth and distance can both be perceived. The modern haploscope, also known as a stereoscope, is composed of prisms instead of mirrors, and in order to downscale on its size, lenses as eye pieces were eventually introduced .
What is the basis of stereopsis testing?
The basis of testing for stereopsis resides in delivering dissimilar images to the eyes in a phenome non called methodology of dissociation, and these tests utilize various methodologies of dissociation.
How is stereopsis quantified?
Stereopsis, the third grade of binocular vision, is quantified by a unit known as seconds of arc. When one thinks of a circle, which consists of 360 degrees, each degree is divided into 60 minutes of arc, and each minute is divided into 60 seconds of arc.
What causes stereopsis problems?
There are a number of factors that can contribute to problems with depth perception.
What is stereopsis?
Stereopsis is the visual ability to see your surroundings in three dimensions (3D), allowing a person to judge the distance between themselves and objects around them. Poor stereopsis could indicate a serious eye condition, known as Amblyopia (lazy eye)
How does stereopsis impact daily life?
Here are some examples of how poor depth perception may create some challenges in your life:
What is stereopsis in eye exam?
Fine stereopsis is often what is tested in an eye exam – this is, very fine amounts of depth between objects. It’s important for fine-motor tasks such as threading a needle.
Why is stereopsis important?
Stereopsis is also crucial to judge the flight of a ball or the movement of players around you. Consider depth perception needed in baseball: accurate depth perception is vital when the batter needs to identify the difference between a fastball and a curveball, or for an outfielder making the game-winning catch. 4.
What does it mean when a car has poor stereopsis?
Having poor stereopsis means that a driver might be unable to tell the distance between their car and other cars, or from the back of their car to the curb.
Why do children squint?
Children may not have the ability to articulate their visual problem, or may not know that a problem exists. If you notice them moving their head or squinting in an effort to try to get a better view, the problem could be their vision. .
Why is stereopsis important?
Stereopsis is a critical component of human vision and is a visual trait shared by animals with front-facing eyes. The spacing between our eyes gives us an advantage. This slight offset causes our visual system to see an image from a slightly different perspective (try it now by looking at something far away and moving your hand back and forth between each eye!) The combination of these slightly different images allows the visual system to judge fine depth and create a 3-dimensional interpretation of the image. This becomes important when objects are close to one another or the task requires the visual system to provide exact information on where the body is relative to an object (thing threading a needle).
What are the two main components of stereopsis?
Stereopsis is divided into two main components - coarse ( or gross) stereopsis, which is important for large amounts of depth, and fine stereopsis, which is important for very small amounts of depth. Most stereo tests check both.
What is a stereo target?
There are different methods of stereo testing targets. Random dot targets at first glance look like a bunch of scattered dots. These targets require the patient to combine the images to see a shape or pattern. Countour targets have a distinct shape but use smaller and smaller offsets of the shape to measure stereo ability. Most tests require some form of dissociation, either with polarized lenses or with red/green or red/blue glasses.
How is stereopsis measured?
Stereopsis is measured in the value seconds of arc - this is actually a very small value. To understand how small, first think of a circle that is made of up 360 degrees all the way around - the other way to think of this is a circle is made of 360 individual 1-degree segments. So, one degree of a circle represents 1/360th of the circle.
How does stereovision help with binocular function?
When patients have good stereovision, it can be an indicator of their binocular function as well. We need both eyes together to see in stereopsis. Otherwise, items in the world appear flat or 2D and we must use adaptations to see what others can see by just looking at an item. Shadows, size, and other indicators help us to determine how close and how far something is from us both when we have 3D vision and when we do not. The biggest difference is that the 3D vision can be more precise and accurate compared to the 2D visual cues that we might use to understand the depth of objects around us. The concept of stereopsis makes us realise the importance of two eyes in our lives and the aim in treating the bad eye with almost care even if the patient has another good eye. It’s the quality of life we are talking about.
Why do my eyes see different perspectives?
The slightly different perspective each eye sees is due to images falling on slightly different points on the retina of the eye. This is termed disparity and is the critical item that is measured in a stereopsis test.
What are the two types of stereopsis?
There are two types of stereopsis – coarse stereopsis and fine stereopsis.
What is stereopsis in eye exam?
Fine stereopsis — that is, very small quantities of depth between objects – is frequently assessed during an eye exam. Fine motor tasks like threading a needle require it.
Why is my vision blurry?
Blurry vision: From eye problems, glaucoma, and corneal abrasions to nearsightedness and diabetic retinopathy, there are dozens of possible causes of blurry vision. Any ailment that produces blurry vision, even if just temporarily, can impair your ability to accurately judge distances and depth.
What is it called when your eyes turn?
Strabismus (eye turn): This condition occurs when your eyes are misaligned, leading each eye to focus in a slightly different direction.
What is stereopsis in biology?
Stereopsis refers to the cues about the relative distance of an object given by the disparity in the location of its images on the two retinas (only if the object is at the same distance as the location of current fixation there is no sense of disparity;
How to measure stereopsis?
Stereopsis can be measured via stereoacuity tasks (which rely primarily on high spatial frequency, local correspondences) or via detection of random-dot stereograms (which rely primarily on low frequency, global correspondences).
Why do humans develop strabismus?
New knowledge of stereopsis development in the 1980s bolstered the rationale in favor of early surgery. 62,63 This prompted a gradual re-examination of old data and inspired important case studies – on the efficacy of early strabismus surgery. 64-67 These reports showed that, if stable binocular alignment was not achieved until age 24 months, the chances of repairing stereopsis were nil. If stable alignment was achieved by age 6 months, the chances of repairing stereopsis were good. A substantial percentage of infants regained robust stereopsis, i.e. random dot stereopsis with thresholds in the order of 60–400 arc sec.
When does stereopsis peak?
Fusion and stereopsis are absent before 2 months of age but develop rapidly between 3 and 5 months of age. 13 Forced-choice preferential looking and visual evoked potential stereoacuity both reach adult levels by 6–7 months of age. 75 Infants with a recent onset of strabismus that had been corrected with prisms had similar stereoacuity to normal infants of the same age 76,77 ( Fig. 74.8 ). The critical period for disruption of stereopsis in IET peaks at 4.3 months of age so the time window for correction of IET with the aim of obtaining high grade stereopsis may be very narrow. 78 Wong reviewed the published data in favor of early surgery. 33 She showed there was a clear trend of declining stereopsis outcomes with increasing age at surgery ( Fig. 74.9 ).
What is stereoscopic vision?
Taken literally, stereoscopic vision describes the ability of the visual brain to register a sense of three-dimensional shape and form from visual inputs. In current usage, stereoscopic vision often refers uniquely to the sense of depth derived from the two eyes. This usage excludes a number of things that might be considered stereoscopic vision, such as the sense of depth arising from the motion parallax generated when subjects translate themselves through the visual environment. This article is primarily concerned with binocular stereoscopic vision.
How much shift is required for stereoscopic imaging?
A good rule of thumb is that the shift should be 10% of the target-film distance (i.e., a 4-inch shift for a 40-inch target-film distance). The 10% shift will produce an angle of approximately 6°.
Is left-right bias adaptive?
Indeed, given the lack of ecological differences between visual input to the left versus right visual fields (in contrast to the clear differences between upper and lower), it would not appear to be evolutionarily adaptive for an organism to exhibit strong left-right biases in stereo scopic vision.

Overview
Stereopsis (from Ancient Greek: στερεο-, romanized: stereo-, lit. 'solid', and ὄψις, opsis, 'appearance, sight') is the perception of depth and three-dimensional structure through binocular vision, the combined visual information from two eyes. Because the eyes of humans, and many animals, are located at different lateral positions on the head, binocular vision results in two slightly different images projected to the retinas of the eyes. The differences are mainly in the rela…
Distinctions
There are two distinct aspects to stereopsis: coarse stereopsis and fine stereopsis, and provide depth information of different degree of spatial and temporal precision.
• Coarse stereopsis (also called gross stereopsis) appears to be used to judge stereoscopic motion in the periphery. It provides the sense of being immersed in one's surroundings and is therefore sometimes also referred to as qualitative stereopsis. Coarse stereopsis is important for orientati…
Prevalence and impact of stereopsis in humans
Not everyone has the same ability to see using stereopsis. One study shows that 97.3% are able to distinguish depth at horizontal disparities of 2.3 minutes of arc or smaller, and at least 80% could distinguish depth at horizontal differences of 30 seconds of arc.
Stereopsis has a positive impact on exercising practical tasks such as needle-threading, ball-catching (especially in fast ball games ), pouring liquids, and others. Professional activity may in…
History of investigations into stereopsis
Stereopsis was first explained by Charles Wheatstone in 1838: “… the mind perceives an object of three dimensions by means of the two dissimilar pictures projected by it on the two retinæ …”. He recognized that because each eye views the visual world from slightly different horizontal positions, each eye's image differs from the other. Objects at different distances from the eyes proje…
Human stereopsis in popular culture
A stereoscope is a device by which each eye can be presented with different images, allowing stereopsis to be stimulated with two pictures, one for each eye. This has led to various crazes for stereopsis, usually prompted by new sorts of stereoscopes. In Victorian times it was the prism stereoscope (allowing stereo photographs to be viewed), while in the 1920s it was red-green glasses (allowing stereo movies to be viewed). In 1939 the concept of the prism stereoscope wa…
Geometrical basis
Stereopsis appears to be processed in the visual cortex of mammals in binocular cells having receptive fields in different horizontal positions in the two eyes. Such a cell is active only when its preferred stimulus is in the correct position in the left eye and in the correct position in the right eye, making it a disparity detector.
When a person stares at an object, the two eyes converge so that the object appears at the cent…
Interaction of stereopsis with other depth cues
Under normal circumstances, the depth specified by stereopsis agrees with other depth cues, such as motion parallax (when an observer moves while looking at one point in a scene, the fixation point, points nearer and farther than the fixation point appear to move against or with the movement, respectively, at velocities proportional to the distance from the fixation point), and pictorial cues such as superimposition (nearer objects cover up farther objects) and familiar size …
Computer stereo vision
Computer stereo vision is a part of the field of computer vision. It is sometimes used in mobile robotics to detect obstacles. Example applications include the ExoMars Rover and surgical robotics.
Two cameras take pictures of the same scene, but they are separated by a distance – exactly like our eyes. A computer compares the images while shifting the two images together over top of e…
Monocular Depth Cues
- What's very interesting about vision is that crudedepth perceptiondoes not require the use of both eyes. Take a moment to perform a quick experiment. Cover one eye with your hand and look around. Are you able to tell what items in the room are closer to you? Farther away? The answer should be yes! Even someone with one eye is able to use single-eye cues to depth.
Binocular Depth Cues
- Binocular depth cues are more complicated and required a coordinated effort from both eyes.The eyesmust both move in the correct direction so that the visual axis of each eye is pointing at the same object of interest, and the images must be able to be fused.
Types of Stereopsis
- Stereopsis can be broadly classified into two types - coarse stereopsis and fine stereopsis. Coase stereopsis is large, more easily distinguishable amounts of depth using retinal disparity cues. Finestereopsis is often what is tested in an eye exam - this is very fine amounts of depth between objects. What is interesting is that the humanvisual sys...
Testing Stereopsis
- Random Dot vs. Contour TestsThere are different methods of stereo testing targets. Random dot targets at first glance look like a bunch of scattered dots. These targets require the patient to combine the images to see a shape or pattern. Countour targets have a distinct shape but use smaller and smaller offsets of the shape to measure stereo ability. Most tests require some form …
References
- Michael Kalloniatis and Charles Luu. The Perception of Depth. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK11512/ Deborah Giaschi. Sathyasri Narasimhan, Aliya Solski, Emily Harrison, and Laurie M.Wilcox. On the typical development ofstereopsis: Fine and coarse processing. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_perception https://www.sciencedirect.co…