Table 1
| CHARACTERISTICS | SYMMETRICAL IUGR | ASYMMETRICAL IUGR |
| Period of insult | Earlier gestation | Later gestation |
| Incidence of total IUGR cases | 20% to 30% | 70% to 80% |
| Etiology | Genetic disorder or infection intrinsic ... | Utero-placental insufficiency |
| Antenatal scan Head circumference, Abdom ... | All are proportionally reduced | Abdominal circumference-decreased Bipari ... |
When to induce For IUGR?
- A difficult time handling the stress of vaginal delivery.
- Increased risk of being stillborn.
- Low blood sugar level at birth.
- Lower resistance to infection.
- Trouble maintaining body temperature.
- An abnormally high red blood cell count.
Does IUGR mean birth defects?
Intrauterine growth restriction, formerly retardation, (IUGR) is a medical condition affecting infants who fail to grow as expected during pregnancy. These infants weigh less than the 10th percentile of the normal weight range. The abdominal circumference is typically less than the 2.5 percentile. During the prenatal period, physicians are responsible for monitoring the baby’s growth.
What causes intrauterine growth restriction?
What causes intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)? The restricted growth associated with IUGR is caused by the baby not receiving enough nutrients and oxygen in the uterus to grow at a normal rate. Many factors can lead to an insufficient flow of nutrients and oxygen.
How is IUGR diagnosed?
What are the risks to a baby born with IUGR?
- Increased risk for cesarean delivery
- Increased risk for hypoxia (lack of oxygen when the baby is born)
- Increased risk for meconium aspiration, which is when the baby swallows part of the first bowel movement. ...
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- Polycythemia (increased number of red blood cells)

What causes asymmetric fetal growth restriction?
Asymmetric growth restriction implies a fetus who is undernourished and is directing most of its energy to maintaining growth of vital organs, such as the brain and heart, at the expense of the liver, muscle and fat. This type of growth restriction is usually the result of placental insufficiency.
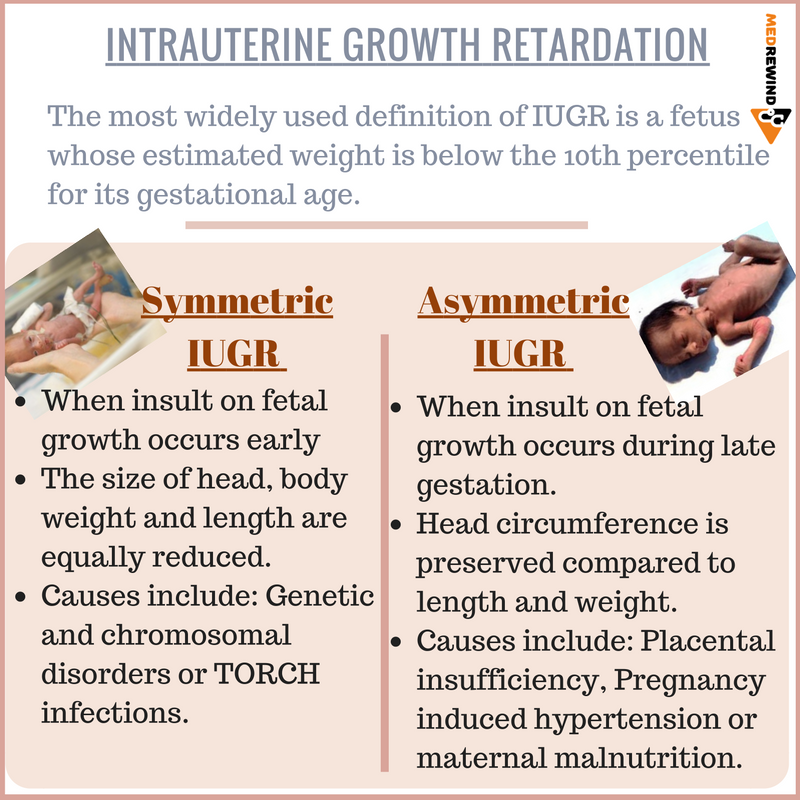
What does symmetrical IUGR mean?
This timing is known as an unborn baby's "gestational age." The two types of IUGR are: symmetrical IUGR: all parts of the baby's body are similarly small in size. asymmetrical IUGR: the baby's head and brain are the expected size, but the rest of the baby's body is small.
What is the most common cause of IUGR?
Chronic hypertension is the most common cause of IUGR. Moreover, the infants of hypertensive mothers have a three-fold increase in perinatal mortality compared with infants with IUGR who are born of normotensive mothers.
What is asymmetric IUGR?
Asymmetrical intrauterine growth restriction is a type of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) where some fetal biometric parameters are disproportionately lower than others, as well as falling under the 10th percentile. The parameter classically affected is the abdominal circumference (AC).
Is asymmetrical or symmetrical IUGR worse?
These neonates have clinical features of both symmetrical and asymmetrical IUGR at birth....Table 1.CHARACTERISTICSSYMMETRICAL IUGRASYMMETRICAL IUGRCell numberReducedNormalCell sizeNormalReducedPonderal IndexNormal (more than 2)Low (less than 2)8 more rows
Can you have a healthy baby with IUGR?
It's important to know that IUGR only means slowed growing. These small babies aren't mentally slow or retarded. Most small babies grow up to be healthy children and adults.
Can stress cause IUGR?
Intrauterine fetal growth restriction (FGR or IUGR), defined as weight below the 10th percentile, has been associated with excessive maternal stress.
What causes restricted fetal growth?
Intrauterine growth restriction results when a problem or abnormality prevents cells and tissues from growing or causes cells to decrease in size. This may occur when the fetus does not receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen needed for growth and development of organs and tissues, or because of infection.
How often is IUGR misdiagnosed?
The preterm elective cesarean section rate was 12.7% among newborns for whom IUGR was erroneously diagnosed, compared to 1.2% among those for whom IUGR was not diagnosed.
Which of the following maternal conditions may place an infant at risk for asymmetric intrauterine growth restriction?
Pregnancies that have any of the following conditions may be at a greater risk at developing IUGR: Maternal weight less than 100 pounds. Poor nutrition during pregnancy. Birth defects or chromosomal abnormalities.
Do IUGR babies have birth defects?
The prenatal management of IUGR depends on a variety of factors, including the severity of the baby's growth restriction, the timing of when during the pregnancy the IUGR began, the mother's health, and the presence of any birth defects or genetic anomalies. Babies with IUGR are at increased risk of stillbirth.
Does bed rest help with IUGR?
Once IUGR is diagnosed, various treatments such as bed rest, increased or supplemental food intake to increase the baby's weight, and treatment of any medical condition, may be recommended. Bed rest may improve circulation to the baby in some cases, though evidence is weak.
Why does IUGR happen?
Often, IUGR happens because the fetus doesn't get enough nutrients and nourishment. This can happen if there is a problem with: the placenta, the tissue that brings nutrients and oxygen to the developing baby. the blood flow in the umbilical cord, which connects the baby to the placenta. Intrauterine growth restriction also can happen ...
What is IUGR in pregnancy?
Intrauterine growth restriction, or IUGR, is when a baby in the womb (a fetus) does not grow as expected. The baby is not as big as would be expected for the stage of the mother's pregnancy. This timing is known as an unborn baby's "gestational age.". The two types of IUGR are:
How to check if a baby has iugr?
Before babies are born, doctors check their growth by measuring the mother's belly from the top of the pubic bone to the top of the uterus. This is called the uterine fundal height. They also can do a prenatal ultrasound, which is how IUGR often is diagnosed.
What are the problems with intrauterine growth restriction?
Other problems that can be related to intrauterine growth restriction include: problems with breathing and feeding.
What tests are done to check for IUGR?
Doctors will also use ultrasounds to check the blood flow to the placenta and through the umbilical cord. If they think a baby has IUGR, doctors also might do such tests as: fetal monitoring to track the baby's heart rate and movements. screening the mother for infections that could affect the baby.
What causes IUGR?
Causes of IUGR. IUGR is the common end result of maternal, placental, fetal, or genetic factors , and IUGR can also result due to a combination of any of these factors (Fig. 1).
What are the endocrine factors that contribute to IUGR?
Endocrine Basis of IUGR. The fetal growth depends on various hormones, namely, insulin, thyroid, adrenal hormones, and pituitary hormones. These hormones promote the growth and development of the fetus and any disruption in these hormonal levels leads to IUGR.
What is IUGR in fetal development?
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR ), a condition that occurs due to various reasons, is an important cause of fetal and neonatal morbidity and mortality. It has been defined as a rate of fetal growth that is less than normal in light of the growth potential of that specific infant. Usually, IUGR and small for gestational age (SGA) ...
What is SGA in infants?
SGA has been defined as having birth weight less than two standard deviations below the mean or less than the 10th percentile of a population-specific birth weight for specific gestational age. These infants have many acute neonatal problems that include perinatal asphyxia, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, and polycythemia.
Why does insulin affect cell number?
Insulin controls the cell number because it has direct mitogenic effects on cellular development. It leads to glucose uptake and consumption by body tissues and decreases protein breakdown. Fetal insulin acts as a signal of nutrient availability for growth and insulin deficiency will lead to IUGR.
Does growth hormone affect fetal growth?
Growth hormone, which is the major hormonal regulator of postnatal growth, has no demonstrable effect on fetal growth.22. Antenatal Diagnosis of Growth Retardation. The goal of antenatal monitoring is early detection of IUGR, so that antenatal management can be optimized for better neonatal outcome.
Is IUGR higher in developed countries?
The incidence of IUGR is six times higher in underdeveloped/developing countries when compared to that in developed countries, and this incidence can be further high in lower- and middle-income countries, as many infants are born in home with no birth records.
Introduction
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), also known as foetal growth restriction (FGR), is when a foetus does not grow to its genetic potential in the uterus. IUGR is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality.
Aetiology
Asymmetrical IUGR refers to disproportionate growth restriction with a greater decrease in foetal body and limbs compared to head circumference. It is caused by extrinsic factors such as placental insufficiency.
Risk factors
Risk factors for IUGR can be divided into maternal , uteroplacental and foetal risk factors.
Clinical features
A thorough obstetric history is crucial to identify any risk factors for IUGR.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of IUGR is made from serial ultrasound scans and umbilical artery Doppler (UA Doppler) showing estimated foetal weight <10th centile, oligohydramnios, abnormal UA Doppler and/or poor interval growth velocity and/or EFW <3rd centile. 1
Management
Conservative management involves optimising modifiable risk factors during pregnancy, including smoking cessation, drug counselling, and healthy diet and exercise.
What causes a fetus to have symmetrical iugr?
Common causes include: Early intrauterine infections, such as cytomegalovirus, rubella or toxoplasmosis. Chromosomal abnormalities.
What are the causes of IUGR?
Hypothermia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hypocalcemia, and bleeding in the lungs are often results of IUGR. If the cause of IUGR is intrinsic to the fetus, growth is restricted due to genetic factors or as a sequela of infection.IUGR is associated with a wide range of short- and long-term neurodevelopmental disorders.
What is IUGR in micrograph?
Intrauterine growth restriction. Micrograph of villitis of unknown etiology, a placental pathology associated with IUGR. H&E stain. Intrauterine growth restriction ( IUGR) refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the mother's womb during pregnancy. The causes can be many, but most often involve poor maternal nutrition or lack ...
How many babies have IUGR?
By definition, IUGR affects 10% of pregnancies, however when corrected for several factors such as low maternal weight it is estimated only around 3% of pregnancies are affected by true IUGR. 20% of stillborn infants have IUGR. Perinatal mortality rates are 4-8 times higher for infants with IUGR, and morbidity is present in 50% of surviving infants.
What is the SGA of a baby?
Intrauterine growth restriction can result in a baby being small for gestational age (SGA), which is most commonly defined as a weight below the 10th percentile for the gestational age. At the end of pregnancy, it can result in a low birth weight.
What is asymmetrical iugr?
In asymmetrical IUGR, there is restriction of weight followed by length. The head continues to grow at normal or near-normal rates (head/brain sparing). A lack of subcutaneous fat leads to a thin and small body out of proportion with the liver. Normally at birth the brain of the fetus is 3 times the weight of its liver. In IUGR, it becomes 5-6 times. In these cases, the embryo /fetus has grown normally for the first two trimesters but encounters difficulties in the third, sometimes secondary to complications such as pre-eclampsia. Other symptoms than the disproportion include dry, peeling skin and an overly-thin umbilical cord. The baby is at increased risk of hypoxia and hypoglycemia. This type of IUGR is most commonly caused by extrinsic factors that affect the fetus at later gestational ages. Specific causes include:
What causes low birth weight?
At least 60% of the 4 million neonatal deaths that occur worldwide every year are associated with low birth weight (LBW), caused by intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, and genetic abnormalities, demonstrating that under-nutrition is already a leading health problem at birth. Intrauterine growth restriction can result in ...