Notably, thymosin β4 is secreted from platelets and aids in the formation of crosslinks with fibrin in a time- and calcium-dependent manner in the process of clot formation. This crosslinking is mediated by factor XIIIa, a transglutaminase that is released with thymosin β4 from stimulated platelets.
Does Thymosin Fraction 5 influence pituitary hormone release?
Thymosin fraction 5, a partially purified extract of calf thymus, can influence pituitary hormone release. We have studied the effects of thymosin alpha 1 (T alpha 1), the first peptide isolated from thymosin fraction 5, on thyrotropin (TSH), adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), prolactin (Prl) and growth hormone (GH) release.
What does thymosin do to T cells?
Researchers think thymosin acts upon the T cells that have matured in the thymus and prepares them for use throughout the body. When T cells mature within the thymus, they are not capable of fighting viruses, bacteria, and foreign antigens. After the T cells leave the thymus, thymosin ensures they undergo complete maturation.
What is the function of thymosin beta 4?
Thymosin is a 5-Da polypeptide hormone secreted by the thymus gland. Thymosin α1 stimulates the development of precursor T cells in the thymus to mature T cells. Of the thymosin peptide family, thymosin β4, is the most abundant member and is also expressed in many cell types.
What hormone is secreted from the thymus gland?
Thymosin Thymosin is a 5-Da polypeptide hormone secreted by the thymus gland. Thymosin α1 stimulates the development of precursor T cells in the thymus to mature T cells. Of the thymosin peptide family, thymosin β4, is the most abundant member and is also expressed in many cell types.
What stimulates the thymus gland?
Vitamin A supports the thymus and stimulates the immune response. Daily supplementation with high dose vitamin C maintains the size and weight of the thymus and increases the number of T cells. You also need enough selenium for immunity against viruses and cancer.
What stimulates the release of thymosin and thymopoietin?
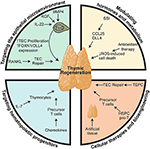
Endocrine-Immune Modulation The release of these peptides, which include thymopoietin, thymulin, and thymosin, is influenced by various hormones. The existence of a specific thymus-stimulating hormone has been suspected but not demonstrated.
What gland releases thymosin?
thymusYour thymus produces and releases several hormones including: Thymopoietin: fuels the production of T-cells and tells the pituitary gland to release hormones. Thymosin and thymulin: help make specialized types of T-cells. Thymic humoral factor: keeps your immune system working properly.
What is thymosin controlled by?
Thus, thymosin β4 is regulated by cell proliferation, but it is not a cell cycle-regulated gene.
How do you activate the thymus gland?
Using your fingertips or side of your fist, tap up and down about 2-3 inches along your sternum, between and above your breasts. The thymus is located behind the third rib, but any vibrations along the length of the upper sternum will stimulate it. Do this for 15-20 seconds and continue to take regular slow breaths.
What is the function of thymosin quizlet?
- Thymosin is a hormone secreted by thymus for the stimulation of T-cells. Function: Aids with social bonding, sexual reproduction in both sexes, and during and after childbirth.
Where is thymosin produced?
The thymus produces all our T cells before we become teenagers. It gradually becomes less active and eventually gets smaller and is replaced by fat tissue. The thymus also produces a hormone called thymosin that helps make and develop T cells.
What is the action of thymosin?
Introduction. Thymosin is a hormone secreted from the thymus. Its primary function is to stimulate the production of T cells, which are an important part of the immune system. Thymosin also assists in the development of B cells to plasma cells to produce antibodies.
Where does the thymus develop from?
third pharyngeal pouchThe thymus develops from the third pharyngeal pouch, which gives rise to endodermal-derived thymic cortical epithelium, and the third pharyngeal cleft, which is thought to give rise to ectodermal-derived medullary thymic epithelium.
Where are hormones secreted in the thymus?
Effects of hormones and cytokines on thymus hormone secretion and actions. Three major thymus hormones, thymosin, thymopoietin, and thymulin, are thought to reside in the cytoplasm of the thymus epithelial cell.
Where is Thymopoietin produced?
Thymus The thymusThymus. The thymus is an immune organ controlling the development of lymphocytes. It also produces thymopoietins and thymosins, which are hormones important to the immune system (Wilson, 2009).
Where is Thymopoietin secreted?
the thymusThymopoietin is secreted by epithelial cells of the thymus and is pleiotropic in action, affecting neuromuscular transmission, induction of early T cell differentiation and immune regulation.
What stimulates the release of antidiuretic hormone ADH or vasopressin )?
A decrease in blood volume or low blood pressure, which occurs during dehydration or a haemorrhage, is detected by sensors (baroreceptors) in the heart and large blood vessels. These stimulate anti-diuretic hormone release.
What produces oxytocin and ADH?
These hormones are stored or released into the blood via the capillary plexus. The posterior pituitary gland does not produce hormones, but rather stores and secretes hormones produced by the hypothalamus. The paraventricular nuclei produce the hormone oxytocin, whereas the supraoptic nuclei produce ADH.
What is thymosin fraction 5?
Thymosin fraction 5 has been used in most clinical trials reported to date, including children with immunodeficiency disease and patients with autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Is thymosin fraction 5 purified?
Using a partially purified preparation, thymosin fraction 5, we have documented that thymosin can correct many of the immunological deficiencies resulting from the lack of thymosin function in animal models and in humans. Ongoing studies indicate that there is a family of biologically active peptide …. Using a partially purified preparation, ...
