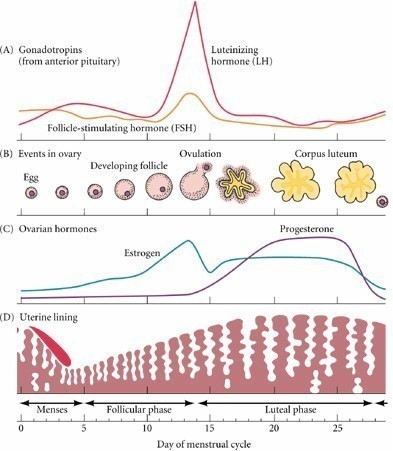
Endometrial hyperplasia most often is caused by excess estrogen without progesterone. If ovulation does not occur, progesterone is not made, and the lining is not shed. The endometrium may continue to grow in response to estrogen.
How to thicken the endometrium lining naturally?
Tips to improve endometrial thickness
- Foods to eat. A balanced diet can help women increase endometrial receptivity thanks to the action of estrogen, balanced hormones, and blood flow.
- Rest. Sleeping has a direct effect on reproductive hormones and causes them to be properly balanced. ...
- Doing exercise. ...
- Femoral massage. ...
- Acupuncture. ...
- Castor oil packs. ...
What causes the thickening of the endometrium?
Risk factors connected with endometrial thickening include:
- Age > 35 years
- Racial aspects: White women are most likely to be affected
- Women who have never been pregnant are more likely to have thick endometrium
- Reaching menopause at an older age increases your risk.
- Early menarche (when menstruation started).
- Weight problems is typically connected with thick endometrium.
Is thickening of the uterine lining always cancer?
This is thickening of the uterine lining and it is not always a sign of cancer, even though, as Dr. Schink points out, it can eventually lead to malignancy.
What is the treatment for thickened endometrium?
What is the treatment for thickened endometrium? The most common treatment is progestin. This can be taken in several forms, including pill, shot, vaginal cream, or intrauterine device. Atypical types of endometrial hyperplasia, especially complex, increase your risk of getting cancer. If you have these types, you might consider a hysterectomy.
What causes the uterine lining to shed?
The uterine lining, also called the endometrium, is the layer of tissue lining the inside of your uterus. It consists of epithelial cells, the same types of cells that make up your skin and cover your entire body. They protect your internal organs from the world outside.
Why do we shed our uterus?
The lining of your uterus sheds in response to hormones that reduce the blood flow to the endometrial tissue. Most people with uteruses shed their uterine lining roughly every 28 days. It seems natural to be a little concerned about shedding a body part, but that’s the way the human body was designed to function.
What hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle?
This is what most people refer to as “ getting your period ” and is the final step in the menstrual cycle. During menstruation, the reproductive organs are regulated by hormones. The sex hormones estrogen, progesterone, and androgen work together to keep your menstrual cycle repeating every month or so. Reproductive hormones are synthesized in ...
What happens on day 25 of the cycle?
The endometrial tissue shrinks and blood flow is restricted. This causes the uterus to contract to shed this tissue that’s no longer receiving adequate oxygen.
What are the two parts of the reproductive system that make up the ovaries?
Reproductive hormones are synthesized in a complex cycle involving two parts of the brain called the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary , as well as the ovaries. The functions of the ovaries are one half of the menstrual cycle. The other half of the menstrual cycle takes place in the uterus and concludes with the shedding of the uterine lining.
What is the first half of the cycle?
The first half of your cycle is called the proliferative phase. During this phase, the cells of the endometrium respond to increases in estrogen by lengthening and linking to one another. During ovulation, the secretory phase begins.
How to study endometrium?
Researchers have studied endometriums in a few ways. One way is to take a biopsy of the uterus, which is the process of removing a tiny bit of tissue and studying it under a microscope. Doctors can now use a specialized camera called a hysteroscope to study the ways in which hormones affect this tissue. .
What Causes Thickened Endometrium?
Aside from the normal changes associated with the menstrual cycle, hormonal changes during perimenopausal stage may also cause endometrial thickening. Chronic disorders like obesity, diabetes, or PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome) may also be associated with thick endometrium.Aside from these, endometrial hyperplasia may also be associated with uterine cancer.
What changes are associated with the hormonal changes that occur during the period?
The endometrium normally changes in thickness and appearance throughout your menstrual cycle. These changes are associated with the hormonal changes that occur during the cycle. Early in the menstrual cycle, estrogen, which is produced by the ovaries, causes the uterine lining to grow, to prepare the uterus for possible pregnancy.
What to do if endometrial thickening is recurrent?
Postmenopausal women who are taking replacement hormones causing recurrent endometrial thickening should discuss with their gynecologists options which include either supplementing their therapy with progesterone or stopping therapy .
What are the risk factors for endometrial thickening?
Anemia (low blood count) may also occur. Risk factors associated with endometrial thickening include: Age > 35 years. Racial factors: White women are more likely to be affected. Women who have never been pregnant are more likely to have thick endometrium. Reaching menopause at an older age increases your risk.
Why is my endometrium thick?
The endometrial thickening often reflects estrogen stimulation, which may be due to hormone replacement therapy or from intake of breast cancer drug, tamoxifen, or continuous estrogen production resulting from obesity . A rare cause is ovarian tumor, which may be producing excess estrogen.
How to reduce endometrial cancer risk?
Take birth control pills containing estrogen and progestin if your menstrual periods are irregular. Lose weight if you are obese or overweight. This may also reduce your risk of endometrial cancer.
What is the inner lining of the uterus?
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. Its thickness varies with a woman’s age, reproductive stage and specific point of her menstrual cycle. A thickened endometrium may or may not be a normal finding, depending on various factors of a woman’s menstrual stage.
How do the symptoms of a decidual cast differ from those of a miscarriage?
The symptoms for miscarriage and decidual cast can be similar. Both can lead to cramping, pain, or vaginal bleeding and the loss of large pieces of tissue. Contact your doctor if you think you might be pregnant and experience these symptoms.
What are the side effects of taking hormonal contraceptives?
Some other side effects of hormonal contraceptives can include spotting as well as vomiting and nausea.
What is decidual cast?
Prevention. Outlook. A decidual cast occurs when a large piece of tissue passes through your vaginal canal. Once outside your body, you may notice that it looks like the shape of your uterus. This condition can affect menstruating women. It can cause extreme discomfort as well as vaginal bleeding as it leaves your body.
Why does a decidual cast go away?
Generally, symptoms related to this condition go away after the decidual cast exits the body if it’s not related to another condition. There isn’t a single known cause of a decidual cast, but it may be related to hormonal contraception or ectopic pregnancies.
What to ask a doctor before a decidual cast?
Before or after you pass a decidual cast, your doctor may conduct some imaging tests. These can help your doctor diagnose the condition.
Why does the decidual cast appear fleshy?
This is because the entire lining exited as one piece. The decidual cast will also appear fleshy because it’s made up of tissue. It’s possible that the decidual cast will also come out in fragments instead of as a single piece of tissue.
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs when an egg is fertilized outside the uterus. This isn’t a viable pregnancy and is considered a medical emergency. Contact your doctor or your local emergency services if you suspect ectopic pregnancy, as it can be life threatening.
What is the cause of endometrial hyperplasia?
Hyperplasia: Hyperplasia is caused by a hormonal imbalance of estrogen and progesterone. Too much estrogen can overstimulate the endometrial lining to become overly thick. 4
How long does it take for a woman to go through menopause?
Menopause is the period of time 12 consecutive months after a woman's last menstrual cycle. This can occur with age (typically between ages 45 and 55), or be triggered by a hysterectomy (surgery to remove the uterus) or surgery that removes the ovaries. Because there is no cyclical rise and fall of the reproductive hormones estrogen and progesterone during menopause, the uterine lining is relatively stable during this time. 5
What is the inner lining of the uterus?
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. The uterine lining changes throughout the month, along with the menstrual cycle. During a woman's reproductive years, the lining thickens to prepare for pregnancy to occur.
What is the endometrium?
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. It plays an important role in women's reproductive health. The uterine lining changes throughout the month, along with the menstrual cycle, in response to your body's reproductive hormones, estrogen and progesterone.
Why is endometrial lining important?
Your endometrial lining is important to your health, whether you are trying to get pregnant, notice changes to your menstrual cycle, or experience bleeding after menopause. You may try lifestyle or natural treatments to help with managing symptoms of thick endometrial lining or be a candidate for medical treatment to improve your chances of getting pregnant.
What is the purpose of the endometrial lining?
The main function of the endometrial lining is during a woman's reproductive years. This inner lining of the uterus begins to thi cken to prepare for an embryo to implant, or for pregnancy to occur. If pregnancy occurs, the lining helps to maintain the pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the lining sheds (you get your period), and the process begins again for the following cycle. 1
What is the thickest part of the endometrium?
Uterine lining thickness is the thickest part of the endometrium. Thickness varies depending on the stage of a person's menstrual cycle. It is the thinnest after menstruation and thickest after ovulation.
What Is Endometrial Hyperplasia?
Your endometrium is the lining of your uterus (womb). During your menstrual cycle, your endometrium changes. The estrogen that your ovaries produce makes your endometrium thicken. This prepares your uterus for possible pregnancy.
Are There Risk Factors for Getting Endometrial Hyperplasia?
You’re at a higher risk for endometrial hyperplasia if you have these risk factors:
What is the medical term for a woman who has excessive body fat?
Obesity: A condition characterized by excessive body fat. Obstetrician–Gynecologist (Ob-Gyn): A doctor with special training and education in women’s health. Ovaries: Organs in women that contain the eggs necessary to get pregnant and make important hormones, such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone.
What is the first day of a menstrual cycle?
A menstrual cycle is defined as the first day of menstrual bleeding of one cycle to the first day of menstrual bleeding of the next cycle. Menstrual Periods: The monthly shedding of blood and tissue from the uterus.
What is the procedure to remove the uterus?
Hysterectomy: Surgery to remove the uterus. Hysteroscopy: A procedure in which a lighted telescope is inserted into the uterus through the cervix to view the inside of the uterus or perform surgery. Intrauterine Device (IUD): A small device that is inserted and left inside the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
What hormones are released during ovulation?
In the middle of the cycle, an egg is released from one of the ovaries ( ovulation ). Following ovulation, levels of another hormone called progesterone begin to increase. Progesterone prepares the endometrium to receive and nourish a fertilized egg.
What is the term for a condition in which the lining of the uterus grows too thick?
Endometrial Hyperplasia: A condition in which the lining of the uterus grows too thick. Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia (EIN): A precancerous condition in which areas of the lining of the uterus grow too thick. Endometrium: The lining of the uterus. Estrogen: A female hormone produced in the ovaries.
What does it mean when your endometrium is thick?
Sound waves from the device are converted into images of the pelvic organs. If the endometrium is thick, it may mean that endometrial hyperplasia is present.
What are the different types of endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia (EIN) —precancerous changes in the lining. Endometrial adenocarcinoma, endometrioid type, well differentiated—cancerous changes in the lining.
What causes endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial hyperplasia is caused by too much estrogen or not enough progesterone . Both of these hormones play roles in the menstrual cycle. Estrogen makes the cells grow, while progesterone signals the shedding of the cells. A hormonal imbalance can produce too many cells or abnormal cells.
Can endometrial hyperplasia be prevented or avoided?
You are more likely to have endometrial hyperplasia if you have gone through menopause. This is because your body’s hormones and menstrual cycles change. Other risk factors for this condition are:
What does it mean when your uterus is bleeding?
Abnormal uterine bleeding can be a symptom for many things. Your doctor can perform an exam and tests to diagnose the main condition. A transvaginal ultrasound measures your endometrium. It uses sound waves to see if the layer is average or too thick. A thick layer can indicate endometrial hyperplasia. Your doctor will take a biopsy of your endometrium cells to determine if cancer is present.
What is the term for a condition in which the lining of the uterus is abnormally thick?
Endometri al hyperplasia is a condition in which the endometrium (lining of the uterus) is abnormally thick. There are four types of endometrial hyperplasia. The types vary by the amount of abnormal cells and the presence of cell changes.
Can endometrial hyperplasia cause cancer?
Atypical types of endometrial hyperplasia, especially complex, increase your risk of getting cancer. If you have these types, you might consider a hysterectomy. This is a surgery to remove your uterus. Doctors recommend this if you no longer want to become pregnant.
Is endometrial hyperplasia a treatable condition?
In most cases, endometrial hyperplasia is very treatable. Work with your doctor to create a treatment plan. If you have a severe type or if the condition is ongoing, you might need to see your doctor more often to monitor any changes.
Does the 'General Overview' apply to everyone?
This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject.