Symptoms
Other indications that your child could be suffering from this condition include:
- Limited range of motion for their head
- Your baby not tracking you with their eyes because they don’t turn their head
- Your baby struggling to turn their head
- A soft lump in your baby’s neck muscle
- A flat spot on the side of their head from laying in the same position all the time
- Trouble breastfeeding on one side
Causes
Method 1 Method 1 of 2: Correcting Your Baby's Torticollis
- Stretch the tight side of your baby's neck very gently. ...
- Do gentle neck rotations to increase your baby’s range of motion. Lay your baby down flat and place your right hand on the front of their right shoulder.
- Feed your baby with their head turned away from the favored side. ...
- Put your baby’s favorite toys on their unfavored side. ...
How can you tell if your baby has torticollis?
It is usually discovered in the first 6 to 8 weeks of life, when a newborn begins to gain more control over the head and neck. Some babies with congenital torticollis also have developmental dysplasia of the hip—a condition in which the head of the thighbone is not held firmly in the hip socket.
What to do if your baby has torticollis?
- Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) and muscle relaxants
- Physical therapy and home stretching exercises
- Cervical collar
When your child has congenital muscular torticollis?
How can physical therapy help children with torticollis?

How do you fix torticollis in children?
Most babies with torticollis get better through position changes and stretching exercises. It might take up to 6 months to go away completely, and in some cases can take a year or longer. Stretching exercises to treat torticollis work best if started when a baby is 3–6 months old.
What happens when a child has torticollis?
Your child's head tilts to one side with their chin pointed to the opposite shoulder. In about 75% of babies with torticollis, the right side is affected. Their head doesn't turn side to side or up and down easily. You feel a soft lump in your baby's neck muscle.
What helps torticollis go away?
Most often, stretching exercises and position changes can treat congenital torticollis. Your baby's healthcare provider will teach you how to stretch your baby's neck muscles. You'll need to gently move your baby's head to the opposite side. You'll want to practice torticollis stretches several times a day.
What is torticollis associated with?
Certain syndromes are linked to an increased risk of torticollis such as Down syndrome, Morquio syndrome, Larsen syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and cervical spine arthritis, Eye impairment is another factor.
When should I worry about torticollis?
When to see your doctor. Make an appointment with your doctor if your baby's treatment for torticollis doesn't seem to be helping, or if they develop new symptoms. Additionally, if your child's torticollis develops after an injury or illness, see you doctor right away.
How serious is torticollis?
Acquired torticollis can be benign (not serious) or a sign of more serious health issues. Because the causes can be so different, it is very important to act quickly so that your child can get the proper care and treatment.
What happens if torticollis goes untreated?
If left untreated, a baby is at risk for learning to move with his head tilted. This causes a child to use one side of his body more than the opposite side. Torticollis can also cause a baby's head to flatten on one side, and if left untreated, a curve in the baby's spine may develop as he grows older.
Can torticollis be permanent?
Sometimes torticollis is permanent (fixed) because of a problem with muscles or bone structure. In rare cases, fixed torticollis is caused by an abnormal area in the back part of the brain or by a tumor in the spinal cord.
Does torticollis cause developmental delays?
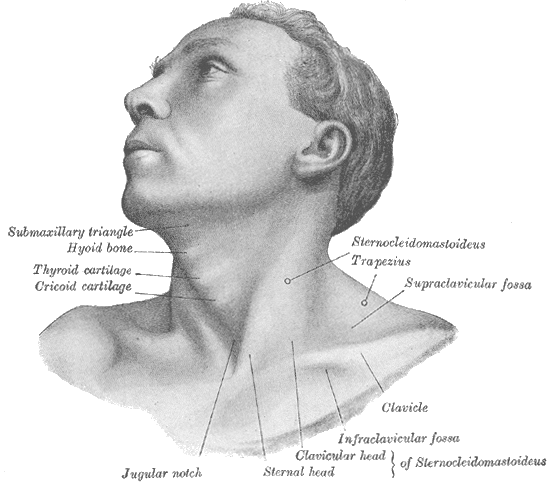
CMT is a result of excessive shortening of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which leads to an imbalance of muscle function around the neck. Previous studies found that postural torticollis may lead to motor development delay.
Is torticollis a neurological condition?
Cervical dystonia, also known as spasmodic torticollis, is a rare neurological disorder that originates in the brain. It is the most common form of focal dystonia in an office setting.
Is torticollis a birth defect?
Congenital torticollis is a birth defect in which the head becomes tilted at or soon after birth. To diagnose the defect, doctors do a physical examination. They may also do imaging tests to look for problems with the bones.
Can torticollis affect speech?
Speech and Feeding Torticollis can also affect speech development. If a baby doesn't have the proper trunk and head control, they might also have trouble getting the air that they need for speech production.
What are the long term effects of torticollis?
All 3 types of torticollis can lead to secondary changes in shape, such as deformational plagiocephaly (DP), facial scoliosis, and infantile scoliosis, and functional problems, including unilateral breastfeeding problems and asymmetrical use of the hands.
Does torticollis cause developmental delays?
CMT is a result of excessive shortening of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which leads to an imbalance of muscle function around the neck. Previous studies found that postural torticollis may lead to motor development delay.
Does torticollis affect speech?
Speech and Feeding Torticollis can also affect speech development. If a baby doesn't have the proper trunk and head control, they might also have trouble getting the air that they need for speech production.
What happens if torticollis goes untreated?
If left untreated, a baby is at risk for learning to move with his head tilted. This causes a child to use one side of his body more than the opposite side. Torticollis can also cause a baby's head to flatten on one side, and if left untreated, a curve in the baby's spine may develop as he grows older.