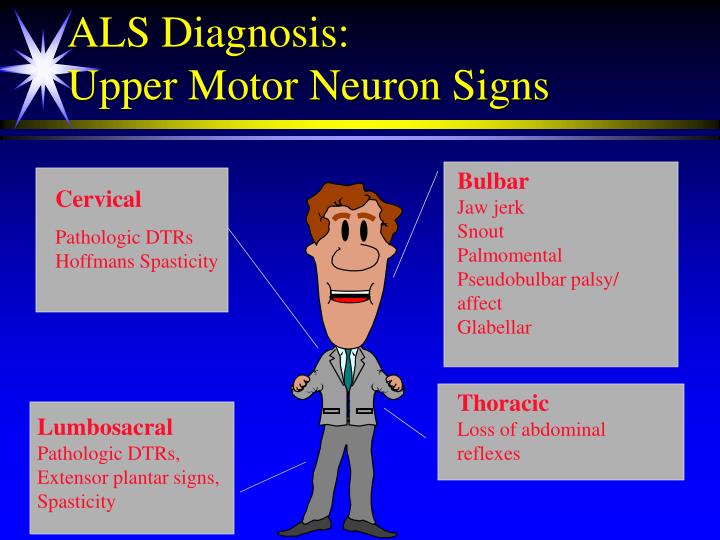
What are the signs of an upper motor neuron lesion?
Signs of Upper Motor Neuron Lesions (UMNL) 1. Paralysis or weakness of movements of the affected side but gross movements may be produced. No muscle atrophy is seen initially but later on some disuse atrophy may occur. 2.
What are the symptoms of upper motor neuron syndrome?
- weakness (decreased ability for the muscle to generate force)
- decreased motor control including decreased speed, accuracy and dexterity
- altered muscle tone (hypotonia or hypertonia) – a decrease or increase in the baseline level of muscle activity
- decreased endurance
What diseases are caused by upper motor neurons?
Types of Motor Neuron Diseases-
- Classical Motor Neuron Disease-. Classical Motor neuron disease affects both the upper and lower motor neurons. ...
- Upper Motor Neuron Disease (Primary Lateral Sclerosis or PLS)-. Upper motor neuron disease is also known as primary motor neuron disease when disease affects upper motor neuron and upper motor ...
- Lower Motor Neuron Disease-. ...
What are upper and lower neurons?
Upper motor neuron refers to the motor neurons of the cerebral cortex and their axons which terminate at the brainstem and spinal cord while the lower motor neuron refers to the motor nuclei of cranial nerves and their axons as well as the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord and their axons.
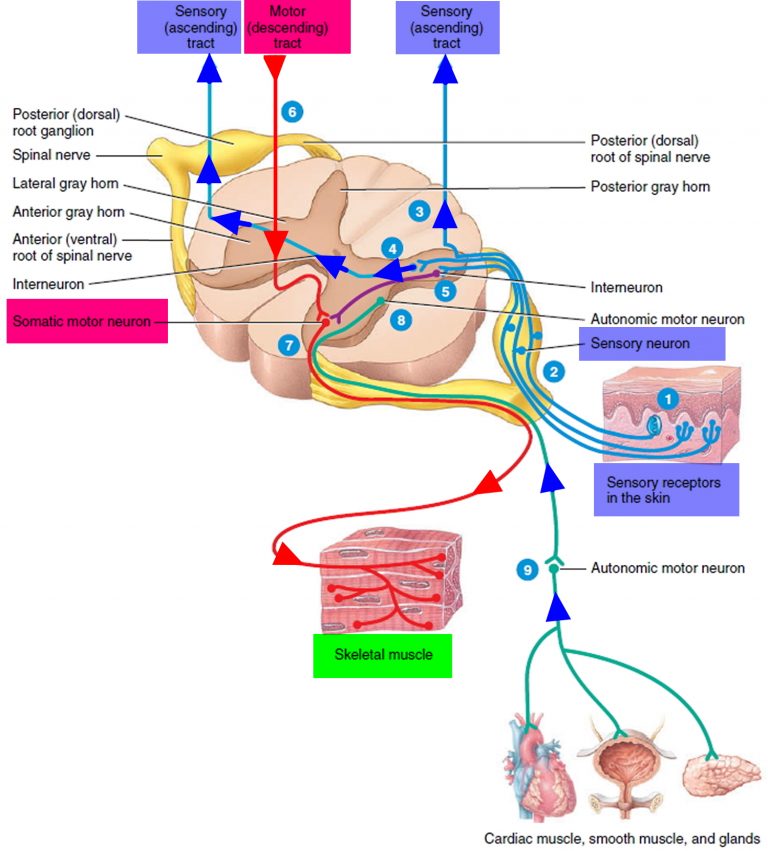
What causes UMN signs?
CausesLou Gehrig's disease (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS)Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS)Traumatic brain injury.Spinal cord injury.Multiple sclerosis.Stroke.Huntington's disease.
What are upper motor neuron signs?
Upper motor neuron syndrome refers to a combination of resulting symptoms such as muscle weakness, decreased muscle control, easy fatigability, altered muscle tone and exaggerated deep tendon reflexes (also known as spasticity), all of which can occur after a brain or spinal cord injury.
What causes upper motor neuron disease?
The motor tract. Upper motor neuron lesions occur in the brain or the spinal cord as the result of stroke, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, cerebral palsy, atypical parkinsonisms, multiple system atrophy, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
What causes upper motor neuron weakness?
Some diseases that can damage upper motor neurons include cerebrovascular accidents, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, primary lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Brown-Sequard Syndrome, vitamin B12 deficiency.
How can you tell the difference between UMN and LMN lesions?
Although both upper and motor neuron lesions result in muscle weakness, they are clinically distinct due to various other manifestations. Unlike UMNs, LMN lesions present with muscle atrophy, fasciculations (muscle twitching), decreased reflexes, decreased tone, negative Babinsky sign, and flaccid paralysis.
What toxins can cause motor neurone disease?
An algal toxin called BMAA has long been associated with the increased incidence of a motor neurone disease called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
What are usually the first signs of motor neurone disease?
The first signs of MND vary from person to person. Some people we talked to first noticed weakness or stiffness in their legs or feet, while others found their arms or hands were affected. These symptoms are typical of the most common form of MND, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Can stress cause motor neuron disease?
Some people with motor neurone disease have additional symptoms that aren't directly caused by the condition but are related to the stress of living with it.
How do you test for motor neurone disease?
Tests that may be requested by the medical team to help diagnose MND include:Blood tests. There is no blood test to diagnose MND. ... Nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG) ... Magnetic Resonance Scanning (MRI) ... Lumbar Puncture.
What is the target of an upper motor neuron?
The target of the upper motor neuron is the dendrites of the lower motor neuron in the gray matter of the spinal cord. (8) The axon of the lower motor neuron emerges from the spinal cord in a nerve and connects to a muscle through a neuromuscular junction to cause contraction of the target muscle.
What are upper and lower motor neuron signs?
Upper motor neuron disease causes stiffness, which is called "spasticity". Lower motor neuron disease causes weakness, loss of muscle ("atrophy") and muscle twitching ("fasciculations").
What is the difference between an upper and lower motor neuron?
The upper motor neurons originate in the cerebral cortex and travel down to the brain stem or spinal cord, while the lower motor neurons begin in the spinal cord and go on to innervate muscles and glands throughout the body.
How do you test for upper motor neurons?
0:391:42Hoffmann's Sign or Reflex | Upper Motor Neuron Lesion - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd a specificity of 49%. To test for the hoffmans sign the patient isn't sitting or standing.MoreAnd a specificity of 49%. To test for the hoffmans sign the patient isn't sitting or standing. Position. Support the patient's hand so that it is completely relaxed with the fingers partially flexed
What are examples of upper motor neurons?
PathwaysTractPathwaycorticospinal tractfrom the motor cortex to lower motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cordcorticobulbar tractfrom the motor cortex to several nuclei in the pons and medulla oblongatacolliculospinal tract (tectospinal tract)from the superior colliculus to lower motor neurons3 more rows
What is the sign of upper motor neuron syndrome?
Increased muscle tone- spasticity, is also a common sign of the upper motor neuron syndrome. The stretching reflexes and muscle response to stretching is also present. If the upper motor neuron lesion is extensive, muscle rigidity in the leg extensors and arm flexor muscles can also be seen.
What is the term for damage to the upper motor neuron?
Damage to the upper motor neuron pathway results in group of symptoms called the upper motor neuron syndrome.
What is the term for the loss of superficial reflexes?
Upper motor neuron syndrome is also characterized by hyporeflexia of superficial reflexes. This includes loss or diminishing of: Corneal reflex-. Superficial abdominal reflex- tensing of abdominal muscles when the overlaying skin is stroked.
Why are my arms flaccid?
This occurs due to the remaining pathways from the brain to the spinal cord or due to bilateral projection of the nerve pathways.
What happens when a lesion involves descending pathways of the upper motor neuron that control the lower motor neurons of?
When the lesion involves descending pathways of the upper motor neuron that control the lower motor neurons of the libs, there is a loss of motor function. This means losing the ability to execute fine movements, like the movement of the fingers [5].
How rare is motor neuron disease?
Motor neuron diseases are rare, affecting around 2 out of 100,000 people per year. the risk factors of this disorder include genetic predisposition, age over 50 years and male gender. The symptoms differ according to stage. In the initial stage, besides the previously mentioned signs, there is also: Clumsiness. Fatigue.
Which neuron provides impulses to move the muscles?
Lower motor neuron is a nerve cells that extends from the spinal cord to the skeletal muscles and provides nerve impulses to move the muscles [1,2].
What happens if you have a motor neuron lesions?
If you have upper motor neuron lesions, you have damage to certain nerve cells that help you move. Medicines and therapy can help control symptoms like muscle spasms and help you walk and talk more easily.
How many types of motor neurons are there?
You have two types of motor neurons:
What is the cause of muscle stiffness?
Upper motor neuron lesions prevent signals from traveling from your brain and spinal cord to your muscles. Your muscles can't move without these signals and become stiff and weak.
What tests can a doctor do for motor neuron disease?
Your doctor can do blood and urine tests to check for infections, muscle diseases, and other conditions that have symptoms similar to those of motor neuron diseases.
What are lesions in the brain?
Lesions are areas of damage to motor neurons. Damage to upper motor neurons stops the signals your muscles need to move.
What is nerve conduction?
Nerve conduction study. This test measures how quickly an electrical current moves through your nerve. It can show how well your nerves are sending signals to your muscles and if you have nerve damage.
What is a spinal tap?
Spinal tap or lumbar puncture. It removes a small amount of fluid from your spine to show whether MS or an infection is causing your symptoms.
What is upper motor neuron syndrome?
The upper motor neuron syndrome signs are seen in conditions where motor areas in the brain and/or spinal cord are damaged or fail to develop normally. These include spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis and acquired brain injury including stroke. The impact of impairment of muscles for an individual is problems with movement, ...
What is the meaning of the saying "upper lower motor neuron syndrome"?
In neuroanatomical circles, it is often joked, for example, that hemisection of the cervical spinal cord leads to an "upper lower motor neuron syndrome and a lower upper motor neuron syndrome". The saying refers to lower motor neuron symptoms in the upper extremity (arm) and upper motor neurons symptoms in the lower extremity (leg).
What is UMNS in skeletal muscle?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. Upper motor neuron syndrome ( UMNS) is the motor control changes that can occur in skeletal muscle after an upper motor neuron lesion . Following upper motor neuron lesions, affected muscles potentially have many features of altered performance including:
What is the imbalance of muscle activity?
While multiple muscles in a limb are usually affected in the Upper Motor Neuron Syndrome, there is usually an imbalance of muscle activity (muscle tone), such that there is a stronger pull on one side of a joint, such as into elbow flexion. Decreasing the degree of this imbalance is a common focus of muscle strengthening programs.
What is altered muscle tone?
altered muscle tone (hypotonia or hypertonia) – a decrease or increase in the baseline level of muscle activity. decreased endurance. exaggerated deep tendon reflexes including spasticity, and clonus (a series of involuntary rapid muscle contractions) Such signs are collectively termed the "upper motor neuron syndrome".
What are secondary changes in muscle?
Other secondary changes such as loss of muscle fibres following acquired muscle weakness are likely to compound the weakness arising from the upper motor neuron lesion. In severely affected muscles, there may be marked secondary changes, such as muscle contracture, particularly if management has been delayed or absent.
What are secondary effects of muscle lengthening?
Secondary effects are likely to impact on assessment of impaired muscles. If muscle tone is assessed with passive muscle lengthening, increased muscle stiffness may affect the feeling of resistance to passive stretch, in addition to neurological resistance to stretch. Other secondary changes such as loss of muscle fibres following acquired muscle ...
Where are the upper motor neurons located?
Upper motor neurons of the pyramidal tract have the majority of their cell bodies located in the precentral motor cortex (Brodmann area 4) and the premotor area (Brodmann area 6). Cell bodies are also present in the supplementary motor area, primary somatosensory cortex, and the superior parietal lobe.
Why do patients have abnormally brisk reflexes?
Patients can be seen to have abnormally brisk reflexes which are due to decreased modulation by descending inhibitory pathways. Radiation of reflexes is a regular observation with the hyperreflexia of UMN lesions. For example, tapping of the supra-patellar tendon would elicit a knee-jerk reflex.
What are the symptoms of a UMN lesion?
Knowledge about the pathways of the pyramidal tracts is paramount to understanding the clinical presentation of UMN lesions. Lesions above or below the pyramidal decussation will have symptoms on different parts of the body. UMN lesions rostral to the pyramidal decussation will result in symptoms contralateral to the site of the lesion. For example, a unilateral lesion on the right corticospinal tract before the pyramidal decussation would cause weakness and spasticity of musculature on the left side of the body. UMN lesions caudal to the decussation will cause symptoms ipsilateral to the site of the lesion. This presentation would generally be with lesions to the spinal cord. For example, left-sided lesions of the corticospinal tract in the spinal cord will cause left-sided weakness and spasticity. Unilateral UMN lesions innervating cranial nerves do not manifest with clinically significant symptoms due to their bilateral innervation from the left and right motor areas. Hence, only bilateral lesions to the UMN of cranial nerves would create deficits. Lesions of UMN’s to CN VII and XII are the exceptions because of their unilateral innervation from contralateral motor areas. For example, a right-sided UMN lesion to the motor area that controls CN VII would manifest as a weakness on the left lower face. [5]
What is Brown-Sequard syndrome?
Brown-Sequard Syndrome is a spinal cord lesion caused by a hemisection injury to the spinal cord. The most common etiology is from penetrating trauma to the spine. However, other etiologies include blunt trauma, hematoma, tumors, or disc herniation. As a result of the hemisection of the spinal cord, the symptoms are manifestations of damage to the lateral corticospinal tract, dorsal column, and the lateral spinothalamic tract. Patients present with upper motor neuron signs ipsilateral and below the level of the lesion. Patients will also present with ipsilateral loss of fine touch, vibration, and proprioception in addition to the contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation. [14]
Which cranial nerves innervate the tongue?
CN VII and CN XII innervate muscles of the lower face and the tongue, respectively. These cranial nerves receive unilateral innervation from the pyramidal tract. Unilateral lesions of UMN’s to CN VII or CN XII would manifest as a lower facial droop or tongue deviation away from the side of the lesion, respectively.
Which part of the brain controls movement?
A vast network of nerve tracts in the central nervous system (CNS) which spans the cerebral corte x, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord control the initiation and modulation of movements.
What is a UMN lesion?
UMN lesions can arise from a variety of injuries to the brain or spinal cord. These include cerebrovascular accidents, traumatic brain injury, anoxic brain injury, malignancy, infections, inflammatory disorders, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic disorders. The clinical manifestation of a UMN lesion is known as upper motor neuron syndrome. The symptoms of UMN damage require differentiation from damage to lower motor neurons which would manifest with weakness, muscle atrophy, hypotonia, hyporeflexia, fasciculations, and fibrillation. [7]
What is the effect of Alpha motor neuron on UMNL?
In UMNL mainly Extrapyramidal tract got damaged so INHIBITORY EFFECT is lost & ALPHA MOTOR NEURON shows its exaggerated activity in the form of SPASTICITY & HYPERREFLEXIA.
What happens if you damage a lower motoneuron?
If the "lower motoneuron" is damaged, you might as well have damaged the muscle itself, because you get a limp, flaccid, completely paralyzed limb.
What is the term for a brief spontaneous contraction that affects a small number of muscle fibres, causing?
Fasciculation represents a brief spontaneous contraction that affects a small number of muscle fibres, causing a flicker of movement under the skin. Fasciculations derive from ectopic (meaning, other than the normal site) activity generated in the motor system.
Why does the spinal cord lose contact with the CNS?
Due to upper motor neuron lesions, spinal cord loses it's contact from CNS.
What is the term for a motor disorder characterized by a speed-dependent increase in the muscle stretch reflex?
A motor disorder characterized by a speed-dependent increase in the muscle stretch reflex, also called myotatic, with exaggerated movements in the tendons, which is accompanied by hyperreflexia and hypertonia, due to neuronal hyperexcitability being one of the signs of upper motor neuron syndrome ”.
What is spasticity in motor?
Spasticity is part of a spectrum of involuntary motor activity, with broad features of spastic hypertonia. It can present multiarticular spasms, simultaneous contraction of muscles agonists and antagonists, and dystonia or abnormal postures.
Can spinal muscular atrophy be ignored?
Signs of spinal muscular atrophy can be easily ignored. Look for spinal muscular atrophy symptoms.
Which is weaker, the extensors or the flexors?
weakness - the extensors are weaker than the flexors in the arms, but the reverse is true in the legs
Do fasciculations occur in lower motor neurone lesion?
no fasciculations - fasciculations occur in a lower motor neurone lesion
What causes lower motor neuron lesions?
Some of the likely causes of lower motor neuron lesions are motor neuron disease, peripheral neuropathy, poliomyelitis, and spinal cord injury with nerve root compression. Lower motor neurons control movement in the arms, legs, chest, face, throat, and tongue. Mixed upper and lower motor neuron diseases include multiple sclerosis.
What is the difference between upper and lower motor neuron lesion?
An upper motor neuron lesion is a lesion of the neural pathway above the anterior horn of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. A Lower motor neuron lesion is a lesion which affects nerve fibers traveling from the anterior horn of the spinal cord to the associated muscle (s). 1. When the spinal cord develops, ...
What is the Hoffmann sign?
Hoffmann’s sign is positive if flexion and sudden release of the terminal phalanx of the middle finger result in reflex flexion of all the digits. This is a sign of the presence of reflex activity. It is positive in, but not specific to, upper motor neuron lesions.
What is EMG/NCV used for?
EMG/NCV: Used to diagnose disorders of lower motor neurons, as well as disorders of muscles and peripheral nerves. Nerve conduction studies help to differentiate lower motor neuron diseases from peripheral neuropathy and can detect abnormalities in sensory nerves.
What are the nerve cells that send messages between the brain and the peripheral nervous system?
The nerve cells that are responsible for relaying messages between the brain and the peripheral nervous system are called motor neurons. The nerves that send messages between the cerebral cortex and the spine are called upper motor neurons, and those that relay messages from the spine to the muscles are called lower motor neurons.
Which part of the spinal cord is responsible for sensation?
Advertisement. When the spinal cord develops, the posterior part becomes responsible for managing most aspects of sensation, and the anterior is more responsible for movement. When you move, the cells of your cerebral cortex send a message to cells in the spinal cord.
Can a motor neuron lesion be a result of cervical spine injury?
However, an upper motor neuron lesion can also occur as a result of cervical spine injury.
