Common Causes
Trouble swallowing causes
- Oropharyngeal. ...
- Esophageal. ...
- Acid reflux disease (gerd) GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) in infants refers to the passage of stomach contents into the throat causing troublesome symptoms, such as feeding intolerance, inadequate oral intake ...
Related Conditions
Causes of weak pelvic floor muscles include: • age – changes in your body as you become older • menopause – changes in women’s hormones during and after menopause • heavy lifting – constant heavy lifting at work or in the gym • high-impact exercises – for example, running or aerobics
What is the cause of difficulty swallowing?
Symptoms of a Weak Pelvic Floor
- Leaking Pee. ...
- Fecal Incontinence. ...
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse. ...
- Painful Sex. ...
- Vaginal Flatulence (Queefing) Flatulence or a farting sound coming out of your vagina, otherwise known as “ queefing ,” is another lesser-known symptom that can be attributed to a weak ...
- A Frequent Urge To Pee. ...
- Vaginal Dryness. ...
What are the causes of weak pelvic floor muscles?
- Swallowing difficulties can be a degenerative disorder of weakened cervical neck ligaments
- Weakened cervical neck ligaments cause neck instability
- Neck instability causes abnormal motion in the cervical vertebrae
- Abnormal motion causes bone spurs
- Bone spurs cause swallowing difficulties.
What are the symptoms of weak pelvic floor muscles?
What can cause swallowing problems?

What causes throat muscles to weaken?
The muscles and nerves that help move food through the throat and esophagus are not working right. This can happen if you have: Had a stroke or a brain or spinal cord injury. Certain problems with your nervous system, such as post-polio syndrome, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, or Parkinson's disease.
How do I strengthen my muscles for swallowing?
Extend your tongue to the bumpy part on the top of your mouth right behind your teeth. Then curl your tongue back toward the back of your mouth as far as possible. Hold for a few seconds. Repeat 5 times.
What is the most common cause of swallowing disorders?
Neurological conditions that can cause swallowing difficulties are: stroke (the most common cause of dysphagia); traumatic brain injury; cerebral palsy; Parkinson disease and other degenerative neurological disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig's disease), multiple sclerosis, ...
How do you treat weak swallowing?
Treatment options include:Medication.Swallowing retraining.Botulinum toxin.Dilation.Enteral feeding.Esophageal stent placement.Surgery.Treatment for specific swallowing disorders.
When should I be worried about trouble swallowing?
You should see your doctor to determine the cause of your swallowing difficulties. Call a doctor right away if you're also having trouble breathing or think something might be stuck in your throat. If you have sudden muscle weakness or paralysis and can't swallow at all, call 911 or go to the emergency room.
What are the 4 stages of dysphagia?
There are 4 phases of swallowing:The Pre-oral Phase. – Starts with the anticipation of food being introduced into the mouth – Salivation is triggered by the sight and smell of food (as well as hunger)The Oral Phase. ... The Pharyngeal Phase. ... The Oesophageal Phase.
What are the warning signs of swallowing problems?
Other signs of dysphagia include:coughing or choking when eating or drinking.bringing food back up, sometimes through the nose.a sensation that food is stuck in your throat or chest.persistent drooling of saliva.being unable to chew food properly.a gurgly, wet-sounding voice when eating or drinking.
What cancers cause difficulty swallowing?
Cancers likely to cause swallowing problems mouth and tongue (oral cancer) throat (pharynx) nasal cavity and sinuses. melanoma or other skin cancer on the face.
What does trouble swallowing indicate?
Sour taste in the mouth. Difficulty swallowing only solids (may indicate a tumor or stricture) suggests a physical blockage such as a stricture or a tumor. Difficulty swallowing liquids but not solids (may indicate nerve damage or spasm of the esophagus).
Can swallowing problems be fixed?
In some cases, treating the underlying cause, such as mouth cancer or oesophageal cancer, can help relieve swallowing problems. Treatment for dysphagia may be managed by a group of specialists that may include a speech and language therapist (SLT), a dietitian and, possibly, a surgeon.
What kind of doctor do you see for swallowing problems?
Gastroenterologists are trained to provide the best care for even the most difficult swallowing problems. Treatment for a swallowing problem depends on the condition that's causing it as well as the severity of the symptoms. Treatment options include medicine, speech therapy and surgery.
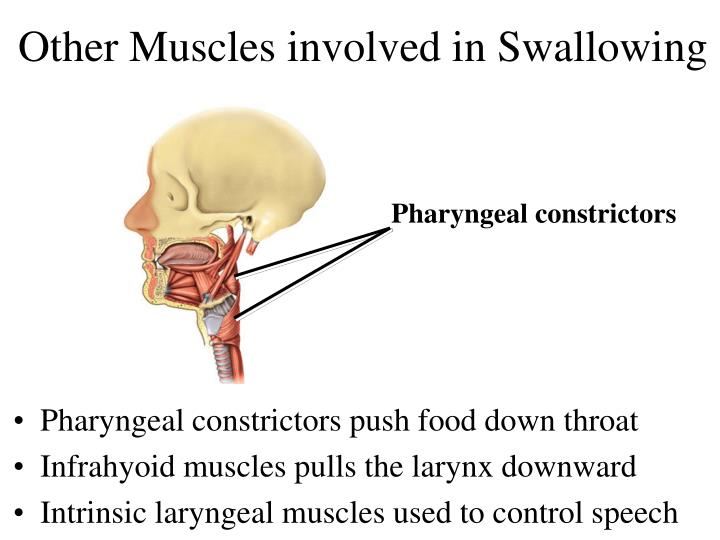
What muscles control swallowing?
These muscles include the omohyoid, sternohyoid, and sternothyroid muscles (ansa cervicalis), and the thyrohyoid muscle (CN XII). [17] The longitudinal pharyngeal muscles function to condense and expand the pharynx as well as help elevate the pharynx and larynx during swallowing.
Can throat muscles be strengthened?
Swallowing exercises can improve the strength, mobility, and control of these muscles. Over time, they may help you to swallow normally again. A speech-language pathologist (SLP) may prescribe swallowing exercises to improve your swallowing. The exact exercises will depend on why you are having trouble swallowing.
How can elderly improve their swallowing?
Larynx-lifting exercises are done to help improve swallowing. They are a type of treatment when you have trouble swallowing (dysphagia). The exercises may help you increase the strength and mobility of the muscles of your larynx (voice box) over time. This may help the ability to swallow.
How do you strengthen your neck and throat muscles?
Place the elbows, forearms and the backs of the hands and fingers on the wall with wrists about shoulder height. Keeping the arms, hands, head and fingers all touching the wall as best possible, slowly slide the hands up above the head and slowly back down. Repeat this 10 times, 3 to 5 times per day.
How can I strengthen my upper esophagus?
By lifting and holding the neck from a supine position for 60 seconds at a time, you create enough tension in the muscle associated with the upper esophageal sphincter that it can strengthen the valve.
Why is it so hard to swallow?
An infection or irritation can cause narrowing of the esophagus. Finally, for people with dementia , memory loss and cognitive decline may make it difficult to chew and swallow.
What causes dysphagia?
Dysphagia has many possible causes and happens most frequently in older adults. Any condition that weakens or damages the muscles and nerves used for swallowing may cause dysphagia. For example, people with diseases of the nervous system, such as cerebral palsy or Parkinson’s disease, often have problems swallowing. Additionally, stroke or head injury may weaken or affect the coordination of the swallowing muscles or limit sensation in the mouth and throat.
What is dysphagia?
People with dysphagia have difficulty swallowing and may even experience pain while swallowing (odynophagia). Some people may be completely unable to swallow or may have trouble safely swallowing liquids, foods, or saliva. When that happens, eating becomes a challenge. Often, dysphagia makes it difficult to take in enough calories and fluids to nourish the body and can lead to additional serious medical problems.
How does dysphagia occur?
Dysphagia occurs when there is a problem with the neural control or the structures involved in any part of the swallowing process. Weak tongue or cheek muscles may make it hard to move food around in the mouth for chewing. A stroke or other nervous system disorder may make it difficult to start the swallowing response, a stimulus that allows food and liquids to move safely through the throat. Another difficulty can occur when weak throat muscles, such as after cancer surgery, cannot move all of the food toward the stomach. Dysphagia may also result from disorders of the esophagus.
What are some problems caused by dysphagia?
Dysphagia can be serious. Someone who cannot swallow safely may not be able to eat enough of the right foods to stay healthy or maintain an ideal weight.
What research is being done on dysphagia?
Every aspect of the swallowing process is being studied in people of all ages, including those who do not have dysphagia, to give researchers a better understanding of how normal and disordered processes compare.
Where can I find additional information about dysphagia?
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, taste, smell, voice, speech, and language.
Why is it so hard to swallow?
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) means it takes more time and effort to move food or liquid from your mouth to your stomach. Dysphagia may also be associated with pain. In some cases, swallowing may be impossible. Occasional difficulty swallowing, which may occur when you eat too fast or don't chew your food well enough, ...
Why is it difficult to swallow food?
Aspiration pneumonia. Food or liquid entering your airway when you try to swallow can cause aspiration pneumonia, because the food can introduce bacteria to the lungs.
What does it mean when food sticks to your throat?
Esophageal dysphagia refers to the sensation of food sticking or getting caught in the base of your throat or in your chest after you've started to swallow. Some of the causes of esophageal dysphagia include:
How do you know if you have dysphagia?
Signs and symptoms associated with dysphagia may include: Having pain while swallowing (odynophagia) Being unable to swallow. Having the sensation of food getting stuck in your throat or chest or behind your breastbone (sternum) Drooling. Being hoarse. Bringing food back up (regurgitation) Having frequent heartburn.
Why does my stomach bring food back up?
Some of the causes of esophageal dysphagia include: Achalasia. When your lower esophageal muscle (sphincter) doesn't relax properly to let food enter your stomach, it may cause you to bring food back up into your throat .
What causes oropharyngeal dysphagia?
Causes of oropharyngeal dysphagia include: Neurological disorders. Certain disorders — such as multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy and Parkinson's disease — can cause dysphagia. Neurological damage. Sudden neurological damage , such as from a stroke or brain or spinal cord injury, can affect your ability to swallow.
What is the esophagus?
Overview. The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects your mouth and your stomach. Rings of muscle (sphincters) in the upper and lower portions contract and relax to allow food and liquid to pass. Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) means it takes more time and effort to move food or liquid from your mouth to your stomach.
What causes stomach pain when swallowing?
In other words, there are lots of things that can go wrong and lead to problems swallowing. Some conditions include: Acid reflux and GERD: Acid reflux symptoms are caused when stomach contents flow up from the stomach back into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn, stomach pain, and burping.
Why is it so hard to swallow without choking?
Oropharyngeal dysphagia is caused by disorders of the nerves and muscles in the throat. These disorders weaken the muscles, making it difficult for a person to swallow without choking or gagging. The causes of oropharyngeal dysphagia are conditions that primarily affect the nervous system such as: multiple sclerosis.
What is the inflammation of the esophagus that can be caused by acid reflux?
Esophagitis: Esophagitis is inflammation of the esophagus that can be caused by acid reflux or certain medications. Learn more about the types of esophagitis and their treatments.
What is it called when you feel something stuck in your throat?
Esophageal dysphagia is the feeling that something is stuck in your throat. This condition is caused by: spasms in the lower esophagus, such as diffuse spasms or the inability of the esophageal sphincter to relax. tightness in the lower esophagus due to an intermittent narrowing of the esophageal ring.
What is the name of the condition where you can't swallow?
People who have a hard time swallowing may choke on their food or liquid when trying to swallow. Dysphagia is a another medical name for difficulty swallowing. This symptom isn’t always indicative of a medical condition.
What are the phases of swallowing?
Types of dysphagia. Swallowing occurs in four phases: oral preparatory, oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal. Swallowing difficulty can be broken down into two categories: oropharyngeal (which includes the first three phases) and esophageal.
Can swallowing cause dehydration?
However, if swallowing problems are persistent, they can result in malnutrition and dehydration, especially in the very young and in older adults. Recurrent respiratory infections and aspiration pneumonia are also likely. All of these complications are serious and life-threatening and must be treated definitively.
What is swallowing disorder?
Swallowing Disorders. Swallowing is a set of coordinated muscle movements that control the mouth, the back of the throat (pharynx) and the food tube (esophagus). Swallowing occurs without us even thinking about it, yet it is a complex and vital function, as it is very important to eating and social interaction.
What does it mean when you cough after swallowing?
Coughing during or immediately after swallowing. Choking — a feeling of food or liquid sticking in the throat or esophagus followed by coughing. Regurgitation — the return of food or liquid back to the mouth or pharynx after it successfully passed.
What is the procedure for swallowing disorders?
Endoscopy. Gastroenterologists at Johns Hopkins routinely perform endoscopies, a frequently used diagnostic procedure for swallowing disorders. Their vast experience with these tools allows for an accurate diagnosis. Your doctor may perform an endoscopy to examine the esophagus and stomach.
What is the name of the disorder where food sticks to the stomach?
Johns Hopkins gastroenterologists can quickly and accurately diagnose any swallowing disorder you may have. Symptoms of swallowing disorders include: Dysphagia — a sense of food "sticking" on the way down and difficulty passing food or liquid from the mouth to the esophagus to the stomach. Choking — a feeling of food or liquid sticking in ...
What is the sensation of food or fluid being regurgitated or stuck in the chest?
Dysphagia — the sensation of food or fluid being regurgitated or stuck in the chest; also any throat discoordination leading to coughing or choking during swallowing
Which muscle controls the emptying of food from the esophagus to the stomach?
Strength and relaxation function of the upper and lower esophageal sphincters. A sphincter is a muscle that opens and closes; the lower esophageal sphincter is the muscle that controls the emptying of foods from the esophagus to the stomach.
Does Johns Hopkins have swallowing disorders?
Treatment of Swallowing Disorders at Johns Hopkins. Swallowing disorders encompass a wide variety of conditions and causes, so treatment for a swallowing disorder needs to be individualized. Your doctor will create a treatment plan based on the severity of your symptoms and how they affect your quality of life.
What causes muscle weakness and fatigue?
Sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy and insomnia, can result in daytime muscle weakness and fatigue.
What are some examples of neurological conditions that can cause muscle weakness?
Examples of neurological conditions that can cause muscle weakness include: Cervical spondylosis: Age-related changes to the cushioning spinal disks in the neck can cause cervical spondylosis.
What are the symptoms of polio?
Symptoms can include fatigue, headaches, agitation, confusion, and seizures, as well as muscle weakness and spasms. 11. Neurological conditions.
Why do my muscles feel tired?
Some chronic medical conditions can cause the muscles to wear out more quickly or cause a person to feel fatigued. In other cases, an infection may cause the muscles to falter. If a person has a sudden, severe onset of muscle weakness, they should talk to a doctor. 1.
What causes headaches, fatigue, low grade fever, and seizures?
Toxoplasmosis: Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic infection that causes headaches, fatigue, a low-grade fever, and seizures.
What are some examples of electrolyte disorders?
Examples of electrolyte disorders include hypokalemia or hyperkalemic periodic paralysis.
Can diabetes cause muscle weakness?
Diabetes can also lead to a variety of other symptoms related to muscle weakness, including:
What causes muscle weakness in the elderly?
One of the contributing factors to the development of muscular weakness in the elderly is a reduction in physical activity. Inactivity and aging result in a significant increase in the endo- and perimysial connective tissue, which leads to alterations in the mechanical characteristics of the skeletal muscle as a result of these changes.
Why is my throat so hard to swallow?
In Scleroderma, the immune system (the body’s natural defense mechanism) targets healthy tissue, causing the muscles of the neck and oesophagus to stiffen, resulting to difficulty swallowing. With aging, the muscles that are utilized for swallowing might get weaker.
What causes dysphagia in the elderly?
In Scleroderma, the immune system (the body’s natural defense mechanism) targets healthy tissue, causing the muscles of the neck and oesophagus to stiffen, resulting to difficulty swallowing. With aging, the muscles that are utilized for swallowing might get weaker. This may help to explain why dysphagia is so widespread among the older population.
What causes stiffening of the throat and oesophagus?
Scleroderma is a condition in which the immune system (the body’s natural defense mechanism) destroys healthy tissue, resulting in a hardening of the muscles of the neck and oesophagus. It is characterized by the loss of the capacity to relax and open muscles of the oesophagus, which prevents food or fluids from entering the stomach.
Do throat muscles weaken with age?
The size of the aperture may shrink as a result of aging. If this is the case, solid meals, pills or tablets, or even a big gulp of liquid may become ″stuck,″ making it difficult to swallow. Fourth, the throat (pharynx) is longer and more dilated in elderly people compared to their younger counterparts.
What causes elderly to have trouble swallowing?
It is possible for seniors to suffer from a variety of conditions that might result in dysphagia. These conditions include the following: Poor dental health or ill-fitting dentures are two examples. Acid reflux is a condition that occurs when the stomach produces too much acid. Some drugs have side effects that might be harmful.
What is the most common cause oropharyngeal dysphagia in elderly?
One-third of all stroke patients experience oropharyngeal dysphagia, which is the most prevalent cause of this condition in the senior population. Esophageal dysphagia can be caused by a variety of different motor or mechanical factors (Table 2 and Figure 2).
What Causes Muscle Weakness?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ( ALS): Also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, ALS is a disorder that causes damage to the nerves that control muscles and voluntary movement. Symptoms of ALS include muscle weakness, atrophy (wasting), stiffening, spasticity, twitches, and cramping. 1
How to help muscle weakness?
Improving your diet and taking supplements can help improve electrolyte imbalances and nutritional deficiencies that can cause muscle weakness. Depending on your doctor’s recommendations, you may have to increase your intake of iron, magnesium, or potassium.
What is the term for muscle weakness and muscle pain?
Hyperthyroidism: Myalgia, or muscle pain, and muscle weakness are commonly associated with hyperthyroidism , or too much thyroid hormones. Often, these symptoms occur with treatment to reduce thyroid hormone levels, which results in a rapid decrease in levels and relative hypothyroidism and associated symptoms. 13
What is the effect of magnesium deficiency on muscle strength?
Hypomagnesemia: Magnesium deficiency, or hypomagnesemia, can lead to an electrolyte imbalance between magnesium and potassium levels. This can result in fatigue and muscle weakness. 11
What causes muscle and joint pain?
Chronic fatigue syndrome: Chronic fatigue syndrome is a disorder of unknown cause, but may be triggered by an infection, immune system change, or stress, resulting in extreme fatigue, muscle weakness, and muscle and joint pain. 28
What is it called when you can't contract your muscles?
Hypokalemia: In order for muscles to contract properly, they require adequate levels of the electrolyte potassium, which passes through the cell membrane of nerve and muscle cells. When there is not enough potassium in the blood, called hypokalemia, muscles may not be able to contract properly, leading to muscle weakness. 10
Why do muscles need iron?
Anemia: Muscles require adequate levels of iron to function properly due to their high energy demand. With anemia, levels of red blood cells that carry iron are significantly reduced, leading to muscle dysfunction and weakness. 26
How to build swallowing muscle?
This exercise will help you build swallowing muscle strength and control. Place a few small pieces of paper (about one inch in diameter) over a blanket or a towel. Then place a straw in your mouth and suck one of the pieces of paper to its tip.
How to improve swallowing ability?
Shaker Exercise. This simple exercise can strengthen muscles to improve your swallowing ability. To perform this exercise, lie flat on your back and raise your head as though you were trying to fixate your gaze on your toes. While you do this, make sure not to raise your shoulders.
What is swallowing 2021?
on February 25, 2021. While swallowing is considered an effortless, reflexive action, it's actually quite a complicated and coordinated maneuver involving many muscles and nerves. As a result, neurological conditions characterized by damage to the brain, spinal cord or nerves can often result in difficulties swallowing, called dysphagia.
How to get rid of a swollen throat?
This exercise consists of three simple steps: 1 First, take a deep breath 2 Hold your breath, as you swallow 3 Cough to clear any residues of saliva or food which might have gone down past your vocal cords 3
What is the purpose of the exercise "Effortful Swallow"?
Effortful Swallow. The purpose of this exercise is to improve the contact and coordination between the different muscles used during the act of swallowing. In essence, the exercise consists of swallowing. But as you do it, you must try to squeeze all of the muscles of swallowing as hard as you can.
What is the super supraglottic swallow maneuver?
Super Supraglottic Swallow Maneuver. This exercise is just like the supraglottic maneuver described above, but with an extra twist. After you take that deep breath, bear down while swallowing. The pressure generated helps with swallowing and increases the strength of your swallowing muscles. 3 .
Why is dysphagia important after stroke?
The American Heart Association recommends early screening for dysphagia after stroke to help reduce the risk of developing adverse health consequences, including weight loss, dehydration, malnutrition , pneumonia and overall quality of life concerns. 2 .
What is the protein that causes myasthenia gravis?
This protein is involved in forming the nerve-muscle junction. Antibodies against this protein can lead to myasthenia gravis. Antibodies against another protein, called lipoprotein-related protein 4 (LRP4), can play a part in the development of this condition.
What are the symptoms of myasthenia gravis?
In more than half of people who develop myasthenia gravis, their first signs and symptoms involve eye problems, such as: Drooping of one or both eyelids (ptosis) Double vision (diplopia), which may be horizontal or vertical, and improves or resolves when one eye is closed.
What is the name of the muscle-specific receptor that blocks acetylcholine?
Some people have myasthenia gravis that isn't caused by antibodies blocking acetylcholine or the muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase. This type of myasthenia gravis is called antibody-negative myasthenia gravis. Antibodies against another protein, called lipoprotein-related protein 4, can play a part in the development of this condition.
Can myasthenia gravis cause muscle weakness?
Muscle weakness caused by myasthenia gravis worsens as the affected muscle is used. Because symptoms usually improve with rest, muscle weakness can come and go. However, the symptoms tend to progress over time, usually reaching their worst within a few years after the onset of the disease.
Can myasthenia gravis be caused by antibodies?
Other antibodies have been reported in research studies and the number of antibodies involved will likely expand over time. Some people have myasthenia gravis that isn't caused by antibodies blocking acetylcholine, MuSK or LRP4.

Overview
Burning or pain while swallowing due to inflammation, erosion or irritation in the tissues.
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- Signs and symptoms associated with dysphagia can include: 1. Pain while swallowing 2. Inability to swallow 3. A sensation of food getting stuck in the throat or chest or behind the breastbone (sternum) 4. Drooling 5. Hoarseness 6. Food coming back up (regurgitation) 7. Frequent heartburn 8. Food or stomach acid backing up into the throat 9. Weight loss 10. Coughing or gag…
Prevention
- Swallowing is complex, involving many muscles and nerves. Any condition that weakens or damages the muscles and nerves used for swallowing or leads to a narrowing of the back of the throat or esophagus can cause dysphagia. Dysphagia generally falls into one of the following categories.