Causes of Wound Dehiscence
- Infection.
- Pressure on sutures.
- Poor suture technique.
- Decreased blood flow.
What is the difference between wound dehiscence and wound evisceration?
May 09, 2021 · The causes of dehiscence are similar to the causes of poor wound healing and include ischemia, infection, increased abdominal pressure, diabetes, malnutrition, smoking, and obesity.[1] Superficial dehiscence is when the wound edges begin to separate and by increased bleeding or drainage at the site.
How to deal with Wound dehiscence?
May 09, 2021 · The causes of dehiscence are similar to the causes of poor wound healing and include ischemia, infection, increased abdominal pressure, diabetes, malnutrition, smoking, and obesity. Superficial dehiscence is when the wound edges begin to separate and by increased bleeding or drainage at the site.
What causes delayed healing of wound?
Causes of Wound Dehiscence Infection. Pressure on sutures. Poor suture technique. Decreased blood flow.
What causes a wound to become infected?
healing of a wound. Since we do not know how to accelerate the healing of wounds, it is more pragmatic to deal with those factors that may interfere with proper healing of the wound and hence predispose toward dehiscence. Factors can be divided into three groups: (1) systemic, such as severe anemia; (2) local, such as infection, or

What are five possible causes of wound dehiscence?
The causes of dehiscence are similar to the causes of poor wound healing and include ischemia, infection, increased abdominal pressure, diabetes, malnutrition, smoking, and obesity.9 May 2021
When does wound dehiscence most commonly occur?
Dehiscence is most likely to take place within the first two weeks after surgery, but it can occur as late as one month after surgery.9 Jul 2020
How can dehiscence be prevented?
SYSTEMIC STRATEGIES TO PREVENT DEHISCENCEmaintaining blood volume through adequate fluid replacement.maintaining warmth (to prevent vasoconstriction)aggressively managing pain (to prevent vasoconstriction)using supplemental oxygen when needed to maintain normal oxygen levels.
What do you do when a wound dehiscence?
Treatment for wound dehiscence can involve medicines to fight pain and treat infection, and surgery to remove dead tissue and repair the wound.
What medications increase the risk for wound dehiscence?
The medications most likely to impair wound healing and damage skin integrity include antibiotics, anticonvulsants, angiogenesis inhibitors, steroids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Conversely, drugs such as ferrous sulfate, insulin, thyroid hormones, and vitamins may facilitate wound healing.3 Mar 2017
What does dehiscence look like?
A dehisced wound can appear fully open – the tissue underneath is visible – or it can be partial, where just the top portion of the skin has torn open. The wound could be red around the wound margins, have drainage, or it could be bleeding or seeping, where only a thin trickle of blood is coming out.8 Mar 2016
Why is there a hole in my incision?
A clean wound will have minimal space between the edges of the wound and will commonly form a straight line. If your stitches, staples, or surgical glue have split apart, or if you see any holes forming in the wound, you're experiencing dehiscence.19 Dec 2019
How common is wound dehiscence?
Wound dehiscence is estimated to occur in 0.5–3.4% of abdominopelvic surgeries, and carries a mortality of up to 40%. Postoperative wound dehiscence has been adopted as a surrogate safety outcome measure since it impacts morbidity, length of stay, healthcare costs and readmission rates.1 Mar 2016
How do nurses treat dehiscence?
Managing dehiscence• Call medical and nursing assistance immediately. Stay with the patient.• Assist the patient into a position which reduces intra-abdominal pressure to prevent further strain on the wound and evisceration. ... • Cover the wound with a sterile pad soaked.
Can you Restitch a wound?
Complications of Removing Stitches Wound reopening: If sutures are removed too early, or if excessive force is applied to the wound area, the wound can reopen. The doctor may restitch the wound or allow the wound to close by itself naturally to lessen the chances of infection.
Is it better to keep wounds moist or dry?
Wet or moist treatment of wounds has been shown to promote re-epithelialization and result in reduced scar formation, as compared to treatment in a dry environment. The inflammatory reaction is reduced in the wet environment, thereby limiting injury progression.22 Jan 2013
How long does it take wound dehiscence to heal?
The most evident feature of wound dehiscence is the visible opening of the wound (Fig. 2), healing poorly following the operation; this typically happens around 5-7 days post-operatively.
How long does it take for a wound to dehisce?
Signs of Wound Dehiscence. Wound disruption is most common within 3 to 10 days after a surgery. Symptoms at the incision site start getting worse instead of better and may include: You may also have a fever. You or your doctor might be able to see broken stitches or a gap where the edge of the incision used to meet.
What is partial dehiscence?
Partial dehiscence means that the edges of an incision have pulled apart in one or more small areas. Complete dehiscence is when the entire cut reopens through all layers of skin and muscle.
What are the phases of wound healing?
Wound healing involves three phases: 1 Inflammatory: The body rushes fluid and healing cells to the incision site, causing swelling, redness, and pain. The goal is to clear out dead cells and bacteria so that repair of the wound can begin. 2 Proliferative: Special cells called fibroblasts pull the edges of the wound together. The body makes new tissue to repair the cut. 3 Maturation: The new tissue gets stronger and less fragile.
Why do sutures separate?
Sometimes wound separation will occur when sutures are removed too early in the healing process. Decreased blood flow. Good blood flow is important to move oxygen and healing cells to the wound and to clear away bacteria and dead cells. Anything that decreases blood flow puts you at a higher risk of wound breakdown.
What is NPWT therapy?
Negative pressure wound therapy. Negative pressure wound therapy ( NPWT) is used to treat wounds that are not healing well, especially if there is a lot of fluid draining from the wound. It can help prevent infection, increase blood flow, remove extra fluid, and encourage the growth of new tissue.
Can a wound be closed with stitches?
The doctor may close the wound separation with new stitches, or they may allow it to heal as it is. If a wound disruption is deep or complete, you may need another surgery to repair the wound. If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
Can an open wound be infected?
An open wound is easily infected, and infection can lead to further separation. Complete wound dehiscence is a medical emergency, as it can lead to evisceration, where internal organs protrude through the wound. Treatment for Wound Dehiscence. Call your doctor if you notice signs of wound breakdown.
What is wound disruption?
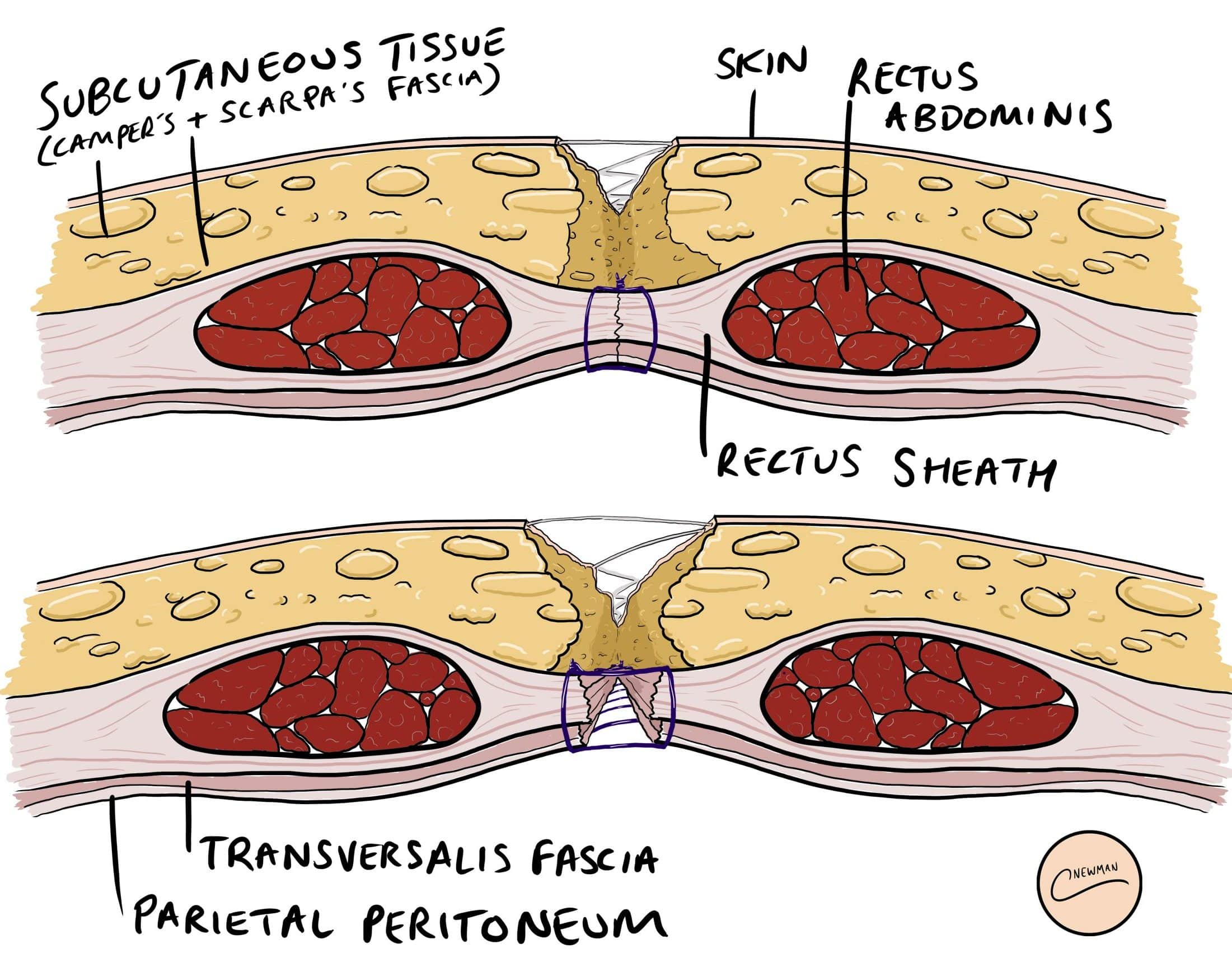
Wound disruption is a serious com-plication that may follow any laparot-omy, and may vary in extent from a separation of the wound edges to evisceration with bowel and other ab-dominal contents protruding through the wound. In an unselected series the incidence of wound disruption gen-erally occurs in about 1% of all laparotomies; in patients with late malignant diseases or other serious ill-nesses the incidence may be much greater. Factors predisposing toward dehiscence include systemic abnormal-ities such as anemia and hypopro-teinemia, local influences such as poor technique in construction and closure of the incision, and postoperative com-plications that increase the tension on the wound (such as coughing, vomit-ing, and abdominal distension). The method used in the closure of the wound has some significance, although dehiscence with evisceration may fol-low any type of closure except one em-ploying retention sutures through all layers. We prefer a mass closure of fascia, muscle, and peritoneum with interrupted No. 30 stainless steel wire for the primary incision, and aresu-42 Cleveland Clinic Quarterly
What are the factors that affect wound healing?
Local factors adversely affecting wound healing include such obvious conditions as postirradiation changes, scars of previous incisions near the operative site, and infection in the skin. We have nevertheless noted the sound healing of an incision unavoid-ably placed through a psoriatic lesion. A good blood supply must be avail-able to any wounded area if proper healing is to take place.13 Fortunately, the problem of blood supply in the abdominal incision rarely arises unless a new incision is placed parallel to a previous one, and then only the skin and subcutaneous fat may suffer ische-mic necrosis. The muscles and fascia revascularize promptly after abdomi-nal surgery.
When does disruption occur?
Disruption can take place at any time in the postoperative period but most often occurs between the fifth and twelfth postoperative days. In pa-tients with healing problems the dis-ruption may occur much later. It may occur shortly after the skin sutures have been removed. In about half the cases disruption will be heralded by the appearance of a serosanguinous discharge on the dressing.1-2 If this occurs before the seventh day, it may be considered pathognomonic of dehis-cence. The patient should be taken immediately to the operating room to undergo exploration of the wound under an anesthetic. When the dis-charge is the result of a hematoma, it can be evacuated and the superficial portions of the wound resutured with-out harm, but if there is in fact a disruption, the wound can be immedi-ately resutured with minimal risk and discomfort to the patient. In the absence of infection a resutured wound heals more rapidly than the primary wound, presumably because some metabolic preparation of the tissues has already taken place.15 In a few patients the disruption is violent and sudden, with protrusion of the intestines through the wound onto the surface of the abdomen.1 Ap-propriate treatment at the bedside in-cludes protecting the intestines with sterile towels, promptly administering
