
How is the cell membrane involved in cell to cell recognition?
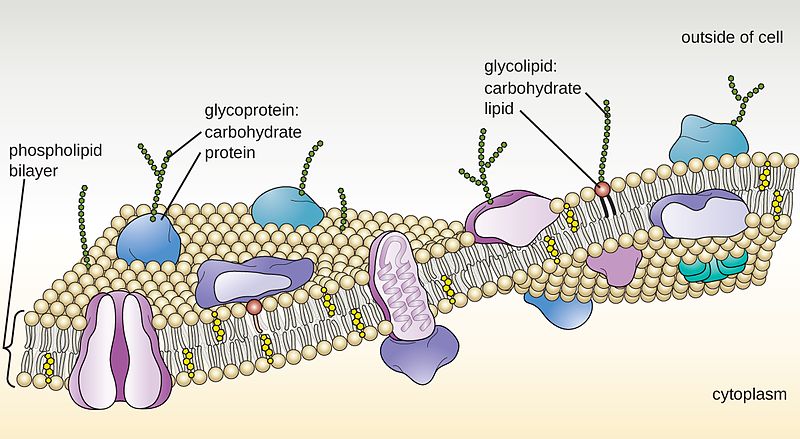
Cell membrane is Involved in Cell to Cell recognition This function is performed by glycolipids and glycoproteins present on the outer surface of cell membranes.
What is the function of the intracellular membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell, while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the cell wall in others.
What is the function of the membrane?
Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized.
Where is the cell membrane found in a cell?
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
What is the membrane of a cell?
Cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a physical barrier between a cell and the surrounding environment.
Which domain interacts with the molecules present in the cytoplasm of the cells?
A hydrophilic domain that is present on the cytosolic side of the membrane. This domain interacts with the molecules present in the cytoplasm of the cells.
How many layers are in a lipid bilayer?
The lipid bilayer is made up of two layers of phospholipids that are amphipathic compounds. Recall that a phospholipid molecule has a polar head and two nonpolar tails. The phospholipid molecules are arranged into two layers form a lipid bilayer. They are organized in such a way that the tails of the molecules in two layers face each other, while their heads are directed opposite. The heads are in contact with the water in the cytoplasm as well as in the extracellular fluid.
Why is the cytoskeleton important?
It provides structural and mechanical support to the cell. Cytoskeleton is anchored to the cell membrane via linker proteins such as integrin. The microfilaments and other components of the cytoskeleton are kept anchored to the cell membrane via these anchoring proteins.
Where is cholesterol found in the cell membrane?
Cholesterol molecules are present in the spaces among the hydrophobic tails of phospholipids in the lipid bilayer. The function of cholesterol is to regulate the fluidity of the cell membrane. According to the fluid mosaic model, the cell membrane is just like ...
What is the hydrophobic barrier around the cell?
Certain hydrophobic interactions develop among the tails of phospholipids, forming a spherical hydrophobic barrier around the cell. As a result, water and other dissolved substances in the cytoplasm or the extracellular fluid cannot enter or leave the cell. However, lipid-soluble compounds can easily cross this lipid bilayer. It is also impermeable to polar as well as charged compounds.
Why is the cytoplasm negative?
In a resting cell, the cytoplasm has more negative charges as compared to the extracellular fluid. It is due to the presence of organic anions in the cytoplasm. Also, potassium ions keep diffusing outside the cell down the concentration gradient. This further makes the cytoplasm negative as compared to the extracellular fluid.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoproteins, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning that there's a fat and a protein.
Is the cell wall tougher than the plasma membrane?
In fact, they have a cell wall outside of them, and that cell wall is much tougher and is structurally more sound than a plasma membrane is. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes from within the cell.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane (Plasma membrane) The outer thin membrane or the layer of the living cell is known as the cell membrane. It is also known as the plasma membrane in animal cells. In the plant cells, it is known as plasmalemma. The term cell membrane was given by Nageli and Cramer (1885) for the membrane covering of the protoplast.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Cell membrane helps to maintain homeostasis. It provides protection to all the internal organelles of the cell.
What are the three types of lipids in the cell membrane?
Most of the cell membrane is composed of 40-50 % protein and 50-60 % lipids. Membrane lipids are of three types: a) Phospholipids b) Glycolipids c) Steroids. In the different membrane, the proportion of the lipid varies:
Which model suggests that the cell membrane is a solid and stable structure?
It was proposed by James Danielli and Hugh Davsan in the year 1935. This model suggests the cell membrane as the solid and the stable structure. Four molecular layers are present in it i.e. two phospholipids and two protein layers. It consists of the phospholipid.
What is the interaction between lipids and proteins?
Between the lipids and the proteins, there is interaction which results in the fluidity of the membrane.
How many types of cell membranes are there?
There are two types of cell membrane. They are:
Which structure is present in the amoeba?
In the amoeba, pseudopodia are present for locomotion which is the modified structure of the cell membrane.
Introduction
Fluid Mosaic Model
- The structure of the cell membrane is described by the fluid mosaic model, a universally accepted model of the plasma membrane. According to this model, the cell membrane is considered as a liquid having two surfaces. It is composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. Let us study the detailed composition of this lipid bilayer and other substances found in the cell membr…
Membrane Polarity
- An important concept that must be understood in the context of cell membranes is membrane polarity. It means that the charges on the two sides of the cell membrane are not equal. In a resting cell, the cytoplasm has more negative charges as compared to the extracellular fluid. It is due to the presence of organic anions in the cytoplasm. Also, potassium ions keep diffusing out…
Functions
- In this section, we will discuss the several functions performed by cell membrane concerning a cell.
Summary
- Cell membrane is the barrier that separates a cell from the surrounding cells and the extracellular environment. It is the outermost part of the cell except in the case of cells having a cell wall. The structure of the cell membrane is described by the fluid mosaic model which states that the cell membrane is a fluid-structure made up of a lipid bi...
References
- Tom Herrmann1; Sandeep Sharma2. (March 2, 2019). “Physiology, Membrane”. StatPearls. 1 SIU School of Medicine 2 Baptist Regional Medical Center. PMID30855799.
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell(4th ed.). New York: Garland Science. ISBN978-0-8153-3218-3. Archivedfrom the original on 2017-12-20.
- Gorter E, Grendel F (March 1925). “On Bimolecular Layers of Lipoids on the Chromocytes of t…
- Tom Herrmann1; Sandeep Sharma2. (March 2, 2019). “Physiology, Membrane”. StatPearls. 1 SIU School of Medicine 2 Baptist Regional Medical Center. PMID30855799.
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell(4th ed.). New York: Garland Science. ISBN978-0-8153-3218-3. Archivedfrom the original on 2017-12-20.
- Gorter E, Grendel F (March 1925). “On Bimolecular Layers of Lipoids on the Chromocytes of the Blood”. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 41(4): 439–43. doi:10.1084/jem.41.4.439. PMC2130960. PMID...
- S J Singer and G L Nicolson.”The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes.” Science. (1972) 175. 720-731.