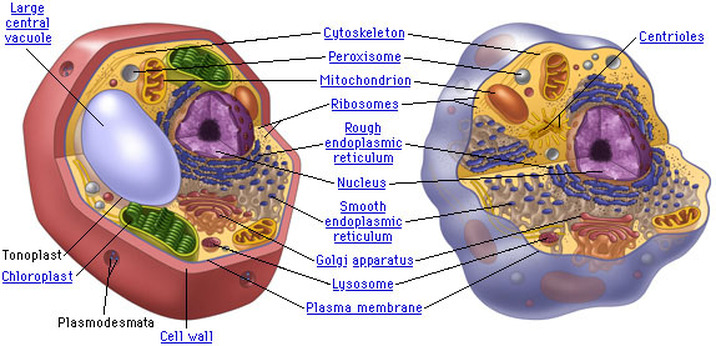
The following are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
- cell membrane
- nuclear material
- ribosomes
- cytoplasm
- exons
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic?
A prokaryotic cell is a primitive type of cell that is characterized by the absence of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes do not possess membrane-bound cellular organelles. Prokaryotes are exclusively unicellular. What is a Eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles.
Do both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have ribosomes?
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have ribosomes. Ribosomes are small organelles used to synthesize proteins as the cell needs them. They can either float freely in the cell or sit on the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells, (giving it the designation of "rough," in comparison to its smooth sibling that lacks ribosomes).
Are mitochondria found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
a) Mitochondria are found in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. b) There tend to be more mitochondria in fat cells than in liver cells.
Are cell walls found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Cell walls are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, the only eukaryotes with cell walls are plant cells. How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells alike? Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells both have ribosome, plasma membrane, and cytoplasm. Also both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the two main types of cells.

What is a Prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell is a primitive type of cell that is characterized by the absence of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes do not possess membrane-...
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells?
The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucle...
Define Cell?
The cell is the basic functional and structural unit of life. Cell plays a vital role in all biological activities and include membrane-bound organ...
What is Ribosome?
The ribosome is a multi-component cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein. Therefore, it is called the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes ar...
List out the unique features of Animal and Plant Cells.
Both animal and plant cells have several unique features. Listed below are some important features: In structure, both animal and plant cells are q...
List out the functions of Chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are the plastids found in all plant cells. These cell organelles comprise the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll and are involv...
Who discovered Cell and Cell Theory?
The cell was first discovered in the year 1665 by an English natural philosopher Robert Hooke. The Cell Theory was explained by Theodor Schwann and...
What is the meaning of eukaryotic cell?
The term “ Eukaryotes ” is derived from the Greek word “ eu “, (meaning: good) and “ karyon ” (meaning: kernel), therefore, translating to “ good or true nu clei .”. Eukaryotes are more complex and much larger than the prokaryotes. They include almost all the major kingdoms except kingdom monera.
Which is smaller, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Scientists speculate that these organisms gave rise to the eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are comparatively smaller and much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The other defining characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that it does not possess membrane-bound cell organelles such as a nucleus.
What are the structures that help in cellular respiration?
It is also one of the smallest components within the cell. Some prokaryotic cells contain special structures called mesosomes which assist in cellular respiration.
What is the nucleus of a cell?
The nucleus contains DNA, which is responsible for storing all genetic information. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Within the nucleus exists the nucleolus, and it plays a crucial role in synthesising proteins. Eukaryotic cells also contain mitochondria, which are responsible for the creation of energy, which is then utilized by the cell.
Which type of cell has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the smallest part of a cell?
Right below the protective coating lies the cell wall, which provides strength and rigidity to the cell. Further down lies the cytoplasm that helps in cellular growth, and this is contained within the plasma membrane, which separates the interior contents of the cell from the outside environment. Within the cytoplasm, ribosomes exist and it plays an important role in protein synthesis. It is also one of the smallest components within the cell.
What are the biotic components of the environment?
Biotic components of the environment include all forms of life from minute bacteria to towering giant Sequoias. However, at the microscopic level, all living organisms are made up of the same basic unit – the cell.
What allows a cell to survive environmental changes?
B) Endospores allow a cell to survive environmental changes.
Is DNA enclosed in a membrane?
A) Their DNA is not enclosed within a membrane.
Does sucrose move into the cell?
A) Sucrose will move into the cell from a higher to a lower concentration .
Which type of cell can exhibit both asexual and sexual reproduction?
c) Prokaryotic cells can exhibit both asexual and sexual reproduction, whereas eukaryotes only carry out asexual reproduction.
Which organelle is responsible for generating the most ATP?
a) Mitochondria and chloroplasts have similar function in that they are responsible for generating most of the cell's ATP.
What is the name of the series of disc-like, flattened sacs that stack upon one another?
a series of disc-like, flattened sacs called cisternae that stack upon one another.
Do prokaryotes have a single chromosome?
a) Most prokaryotes have a single circular chromosome, as compared to a eukaryote's larger genome spread across multiple linear chromosomes.
