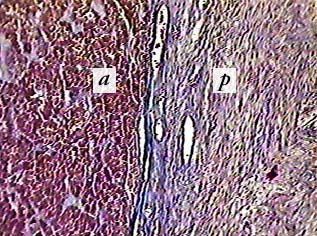
Pancreatic islets are home to three main types of cells, each producing a different endocrine product:
- Alpha cells (A cells) secrete the hormone glucagon.
- Beta cells (B cells) produce insulin and are the most abundant of the islet cells.
What cells are found inside the pancreas?
The pancreatic islets are small islands of cells that produce hormones that regulate blood glucose levels. Hormones produced in the pancreatic islets are secreted directly into the bloodstream by five different types of cells. The alpha cells produce glucagon, and make up 15–20% of total islet cells. The beta cells produce insulin and amylin ...
What are the endocrine cells of the pancreas called?
The pancreatic islets each contain four varieties of cells:
- The alpha cell produces the hormone glucagon and makes up approximately 20 percent of each islet. ...
- The beta cell produces the hormone insulin and makes up approximately 75 percent of each islet. ...
- The delta cell accounts for four percent of the islet cells and secretes the peptide hormone somatostatin. ...
What do alpha and beta cells do in the pancreas?
The key difference between Alpha and Beta cells is that the Alpha cells (or A cells) produce and secrete glucagon hormone whereas the Beta cells (or B cells) produce and secrete insulin hormone. The pancreas is one of the major organs located in the abdomen of our body. Pancreas fulfils two major functions namely endocrine (regulation of blood sugar) and exocrine (digestion of foods) functions.
Can the pancreas regenerate itself?
The pancreas can be triggered to regenerate itself through a type of fasting diet, say US researchers. Restoring the function of the organ - which helps control blood sugar levels - reversed symptoms of diabetes in animal experiments. The study, published in the journal Cell, says the diet reboots the body.
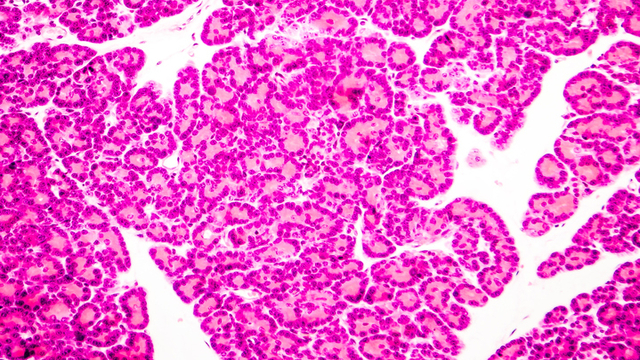
What type of cells make up the pancreas?
The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine functions. The pancreatic islet cell types include alpha cells, which produce glucagon; beta cells, which produce insulin; delta cells, which produce somatostatin; and PP cells, which produce pancreatic polypeptide.
What is a pancreas made of?
The pancreas is made up of 2 types of glands: Exocrine. The exocrine gland secretes digestive enzymes. These enzymes are secreted into a network of ducts that join the main pancreatic duct.
Can u live without a pancreas?
It's possible to live without a pancreas. But when the entire pancreas is removed, people are left without the cells that make insulin and other hormones that help maintain safe blood sugar levels. These people develop diabetes, which can be hard to manage because they are totally dependent on insulin shots.
What is glucagon made of?
Glucagon is a 29-amino acid peptide hormone predominantly secreted from the alpha cells of the pancreas. It is derived from the precursor proglucagon which can be processed into a number of related peptide hormones (Fig. 1).
What are the 4 main functions of the pancreas?
The pancreas contains exocrine glands that produce enzymes important to digestion. These enzymes include trypsin and chymotrypsin to digest proteins; amylase for the digestion of carbohydrates; and lipase to break down fats.
Is pancreas an organ or gland?
The pancreas is an organ in the back of your abdomen (belly). It is part of your digestive system. The pancreas is an organ and a gland. Glands are organs that produce and release substances in the body.
What is the main function of the pancreas?
During digestion, your pancreas makes pancreatic juices called enzymes. These enzymes break down sugars, fats, and starches. Your pancreas also helps your digestive system by making hormones. These are chemical messengers that travel through your blood.
What happens if the pancreas is damaged?
With repeated bouts of acute pancreatitis, damage to the pancreas can occur and lead to chronic pancreatitis. Scar tissue may form in the pancreas, causing loss of function. A poorly functioning pancreas can cause digestion problems and diabetes.
Where is the pancreas located?
The pancreas is located below the stomach and secretes its exocrine enzymes into the small intestine.
What is the function of the pancreas?
Due to its endocrine function, it helps in the maintenance of blood glucose levels and body growth. By its exocrine functions, it helps in digestion of food such ...
What are the functions of Langerhans cells?
These hormones act as agrowth hormone-inhibiting hormone and help in the regulation of our body height. F-cells: These cells secrete pancreatic polypeptides. These inhibit the contraction of gall bladder and secretion of digestive enzymes.
Which cell inhibits the secretion of glucagon and insulin?
Also, interestingly, somatostatin inhibits the secretion of glucagon and insulin from the respective cells while polypeptides from F-cells inhibit the secretion of somatostatin. Pancreatic stellate cells (PSC):These cells are located in the exocrine area of the pancreas. They comprise 4-7% of the total pancreatic cells.
How many Langerhans are there in the pancreas?
These cells perform the endocrine function. There are about 1 to 2 million islet s of Langerhans in the pancreas around small capillaries.
Which cells secrete glucagon?
F-cells or PP cells. Alpha cells: These cells secrete glucagon. They constitute about 17-25% of the total pancreatic islets of Langerhans cells. The secreted glucagon hormone helps in the conversion of glycogen into glucose.
Which type of cells have an exocrine function and arranged as lobules?
Pancreatic stellate cells. Pancreatic cells. Acinar cells: These cells have an exocrine function and arranged as lobules. They synthesize the digestive enzymes and secrete them into the intestine through the pancreatic duct. In general, they secrete enzymes like pancreatic amylase, trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypolypeptidase, pancreatic lipase, ...
What are the two types of cells that make up the pancreas?
Most of the remaining cells are endocrine cells , and make up portions of the pancreas called “islets of Langerhans;” these are associated with hormone production that can access the bloodstream directly.
What is the pancreas?
The pancreas produces insulin and other enzymes essential to digestion. Mark Gurarie is a freelance writer, editor, and adjunct lecturer of writing composition at George Washington University. Rochelle Collins, DO, is a board-certified family medicine doctor currently practicing in Bloomfield, Connecticut. Located in the upper abdomen between the ...
What is the main duct of the pancreas?
It’s also important to understand the pancreas’s system of ducts as these are essential to its function. Along the length of the organ—from head to tail—is the main pancreatic duct (also known as the “Wirsung duct”), which connects with the bile duct in the head to form the ampulla of Vater, which opens into the duodenum. 1 Movement of bile through this duct is regulated by a smooth muscle structure called the sphincter of Oddi, which prevents material from the intestines from accessing the pancreas. The other ducts also have sphincters that control the outflow of hormones and enzymes.
What are the most common diseases that affect the pancreas?
Diseases or disorders of the pancreas can be dangerous, disruptive, and require serious medical attention. The most common of these are pancreatitis (an inflammation of this organ), pancreatic cancer, and perforation (in which digestive enzymes cause holes in the surface).
What are the most common variations of the pancreas?
3 By far the most commonly observed of these is a condition called “pancreas divisum, ” in which there is abnormal or absent fusion of pancreatic ducts, a case which is estimated to affect between 3% and 14% of the general population. Furthermore, in about 3% to 5% of cases, pancreatic tissue is erroneously found in the stomach or small intestine, though this rarely leads to health problems. 2
How long is the pancreas?
The pancreas is an elongated organ that’s approximately 15 centimeters (cm) long and has a tapered shape. Anatomically speaking, it’s divided into four sections: 1 . Head: The head of the pancreas is, as the name implies, the widest portion of the organ.
Where is the tail located in the pancreas?
Tail: The narrowing end of the pancreas represents its tail, which lies just in front of the left kidney. It’s here that you find the primary pancreatic duct that secretes insulin and digestive enzymes.
Parts of the Pancreas
Your pancreas is shaped like an elongated pear that extends horizontally across your abdomen. The widest part, called the head, is near the center of the abdomen, the point where the stomach meets the small intestine.
What Does the Pancreas Do?
Your pancreas makes about 8 ounces of digestive juices every day. These juices contain enzymes to break down your food. These enzymes empty into the upper part of your small intestine and include:
What Are Some Diseases of the Pancreas?
There are several common problems that can affect your pancreas, including:
What is the term for pancreatic tissue that is outside the normal pancreas?
When pancreatic tissue occurs AWAY from pancreas (like endometriosis of the stomach) Heterotopic pancreas is pancreatic tissue outside the bounds of the normal pancreas without anatomic or vascular connections to the pancreas itself. Heterotopic pancreas occurs in 0.5% to 14% of autopsy series.
Which organs are directly connected to the posterior surface of the pancreas?
The posterior surface of the pancreatic body is not peritonealized and directly contacts the aorta, left adrenal gland, left kidney, and left renal artery and vein.
What is the annular pancreas?
People with annular pancreas have a thin band of normal pancreatic parenchyma completely surrounding the second portion of the duodenum. This band is in continuity with the head of the pancreas and causes variable degrees of duodenal compression and stenosis (Fig. 51.4). In 1910, Lecco postulated that annular pancreas resulted from abnormal fusion of the ventral pancreatic bud to the duodenum, leading to improper rotation of the ventral bud around the duodenum.14
What causes congenital anomalies in the pancreas?
Congenital anomalies of the pancreas largely result from failure of rotation or fusion of the ventral and dorsal pancreatic buds.
When pancreatic tissue occurs AWAY from pancreas (like endometriosis of the stomach?
When pancreatic tissue occurs AWAY from pancreas (like endometriosis of the stomach) Heterotopic pancreas is pancreatic tissue outside the bounds of the normal pancreas without anatomic or vascular connections to the pancreas itself. Heterotopic pancreas occurs in 0.5% to 14% of autopsy series.
Which duct forms the head, body, and tail of the pancreas?
The dorsal bud forms first and is larger. It ultimately forms much of the head, body, and tail of the pancreas. As the duodenum grows and rotates, the ventral bud rotates clockwise (Fig. 51.2) and fuses with the dorsal bud, forming the uncinate process and inferior head of the pancreas. In the majority of cases, the duct in the ventral bud fuses with the duct in the dorsal bud to become the main pancreatic duct (duct of Wirsung), which drains the majority of the pancreas into the duodenum through the major papilla, or ampulla of Vater. The proximal duct of the dorsal bud forms the lesser or minor pancreatic duct (duct of Santorini), which drains into the duodenum through the minor papilla superior to the major papilla.
Which organ is composed of islets of Langerhans?
The endocrine pancreas is composed of islets of Langerhans. The islets secrete hormones including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin directly into the bloodstream in endocrine fashion. These hormones regulate glucose homeostasis and also play a role in the complex regulation of pancreatic secretion and digestion.