Factors to Consider
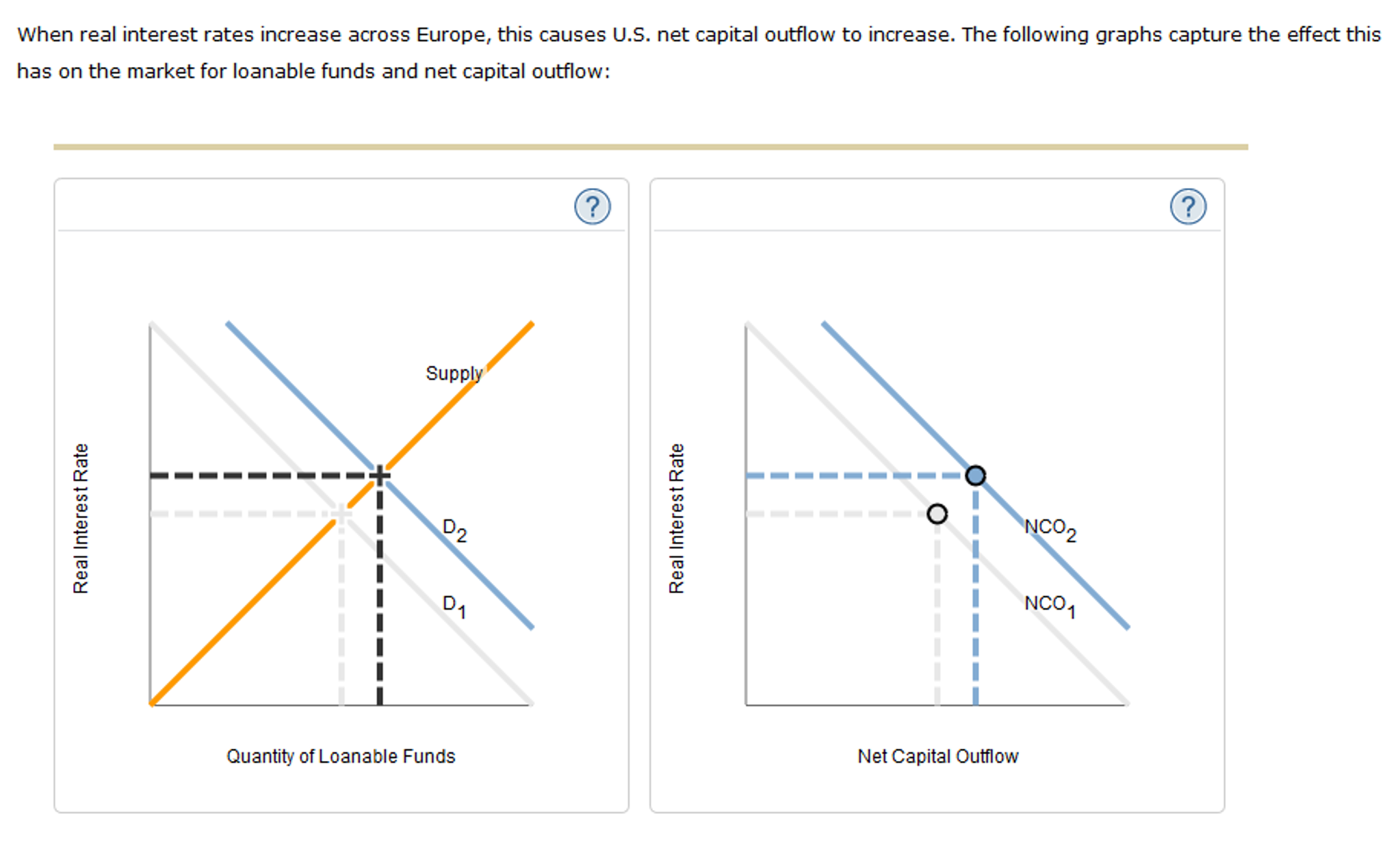
- Economic Growth. The most important factor in determining why interest rates change is the supply of funds available from lenders and the demand from borrowers.
- Fiscal Policy. The same logic applies to the credit markets as a whole. ...
- Monetary Policy. Another major factor affecting why interest rates change is Monetary Policy. ...
- Inflation. ...
Why should fed cut interest rates?
Oct 25, 2020 · Interest is simply the cost of borrowing money. As with any good or service in a free market economy, price ultimately boils down to supply and demand. When demand is weak, lenders charge less to ...
Why does the Federal Reserve decrease interest rates?
Sep 19, 2019 · On May 4, 2022, the Federal Reserve announced that it would raise interest rates by 0.50%, shifting the target range to 0.75% to 1.00%. During the Covid-18 pandemic the interest rate was kept at a near-zero range, but in December 2021 the Fed announced an anticipated rate hike to combat inflation.
What causes interest rates to change?
Jan 06, 2016 · Interest rate changes spill over to many facets of the economy, including mortgage rates and home sales, consumer credit and consumption, and stock market movements. 1:46 Forces Behind Interest Rates
Why do mortgage interest rates change so often?
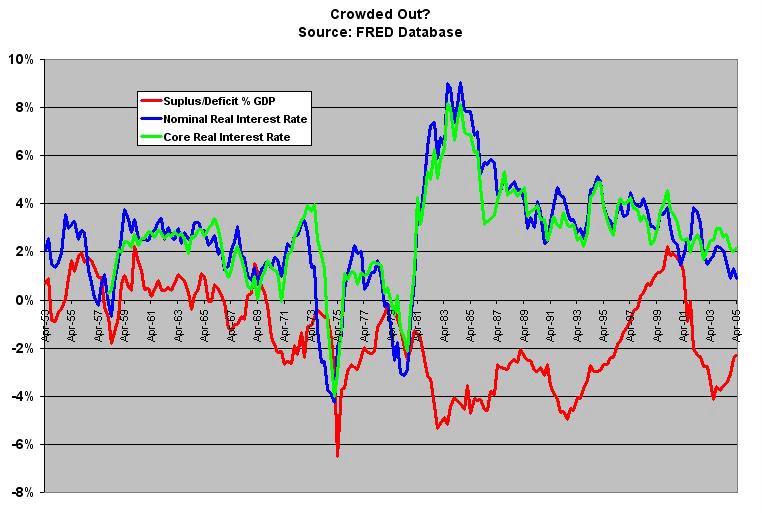
The real interest rate is calculated as the difference between the nominal interest rate and the inflation rate. The chart above displays the nominal interest rate of a 1-year US Treasury bond, the US inflation rate, and the resulting one-year real interest rate . Inflation is defined as the yearly percentage change of the Consumer Price Index (CPI).

What causes real interest rates to decrease?
What are the 4 factors that influence interest rates?
What are the 3 main factors that affect interest rates?
- Credit score. Your credit score is a three-digit number that generally carries the most weight when it comes to determining your individual creditworthiness. ...
- Loan-to-value ratio. ...
- Debt-to-income.
What are the 6 factors that affect nominal interest rates?
What is interest rate?
An interest rate is the cost of borrowing money. Interest provides a certain compensation for bearing risk. Interest rate levels are a factor of the supply and demand of credit. The interest rate for each different type of loan depends on the credit risk, time, tax considerations, and convertibility of the particular loan.
How does inflation affect interest rates?
Inflation. Inflation will also affect interest rate levels. The higher the inflation rate, the more interest rates are likely to rise. This occurs because lenders will demand higher interest rates as compensation for the decrease in purchasing power of the money they are paid in the future.
Who is Michael Boyle?
Her writing covers a wide array of large-scale financial topics. Michael Boyle is an experienced financial professional with more than 9 years working with financial planning, derivatives, equities, fixed income, project management, and analytics.
What happens if a loan is not paid back?
A greater chance that the loan will not be repaid leads to higher interest rate levels. If, however, the loan is "secured," meaning there is some sort of collateral that the lender will acquire in case the loan is not paid back (i.e., such as a car or a house), the rate of interest will probably be lower.
What is the Federal Funds Rate for 2021?
Updated June 17, 2021. On June 16, 2021, the Federal Reserve maintained its target for the federal funds rate (the benchmark for most interest rates) at a range of 0% to 0.25%. 1 This was no different from its April 2021 announcement that the target rate would remain unchanged.
What is fed funds rate?
The fed funds rate is the interest rate banks charge each other to lend Federal Reserve funds overnight. The nation's central bank relies on it to promote economic stability by raising or lowering the cost of borrowing.
What is reserve requirement?
The reserve requirement is also set by the Fed. It is a percentage of deposits a bank must keep on hand each night. Banks that don't have enough to meet the requirement borrow fed funds from banks that have excess. They charge the borrower the fed funds rate.
How often does the Federal Open Market Committee meet?
The nation's central bank uses its Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) to make these decisions. It meets eight times per year. At its July 2021 meeting, the FOMC had said it intends to keep the benchmark rate at current rock-bottom levels until inflation is at 2% for the long term.
Why is FOMC important?
Its importance is psychological as well as financial. The FOMC targets a specific level for the fed funds rate. It determines the interest rates banks charge one another for overnight loans. Banks use these loans, called the fed funds, to help them meet the cash reserve requirement .
What is FOMC rate?
The FOMC targets a specific level for the fed funds rate. It determines the interest rates banks charge one another for overnight loans. Banks use these loans, called the fed funds, to help them meet the cash reserve requirement . The reserve requirement is also set by the Fed.
What is the goal of the FOMC?
The FOMC's goal is to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. 5 . The Fed uses interest rates as a lever to grow the economy or put the brakes on it. If the economy is slowing, the FOMC lowers interest rates to make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, invest, and create jobs.
What happens if interest rates fall?
But if interest rates fall, the same home for the same purchase price will result in lower monthly payments and less total interest paid over the life of the mortgage. As mortgage rates fall, the same home becomes more affordable—and so buyers should be more eager to make purchases.
How do bond prices affect interest rates?
Bond prices move inversely to interest rates, so as interest rates fall, the price of bonds rise. Likewise, an increase in interest rates sends the price of bonds lower, negatively impacting fixed-income investors.
When did the Fed cut interest rates?
On September 18, 2019 , the Federal Reserve —also called the Fed—cut the target range for its benchmark interest rate by 0.25%. It was the second time the Fed had cut rates in 2019, and part of an ongoing attempt to keep the economic expansion from slowing amid many signs that a slowdown had already begun (and, in fact, was already well underway).
What is prime rate?
The prime rate represents the credit rate that banks extend to their most credit-worthy customers.
Why are credit cards affected by prime rate?
Rates will be affected for credit cards and other loans because both require extensive risk-profiling of consumers seeking credit to make purchases. Short-term borrowing will have higher rates than those considered long-term.
Does the Fed have a zero interest rate on auto loans?
Auto Loan Rates. Auto companies have benefited immensely from the Fed’s zero-interest-rate policy, but rising benchmark rates will have an incremental impact. Surprisingly, auto loans have not shifted much since the Federal Reserve's announcement because they are long-term loans.
Why do CD rates increase?
Savings. Money market and certificate of deposit (CD) rates increase because of the tick-up of the prime rate. In theory, that should boost savings among consumers and businesses because they can generate a higher return on their savings.
What is the difference between nominal and real interest rates?
A real interest rate is an interest rate that has been adjusted to remove the effects of inflation to reflect the real cost of funds to the borrower and the real yield to the lender or to an investor. A nominal interest rate refers to the interest rate before taking inflation into account. Nominal can also refer to the advertised ...
What is nominal interest rate?
A nominal interest rate refers to the interest rate before taking inflation into account. It is the interest rate quoted on bonds and loans. The nominal interest rate is a simple concept to understand. If you borrow $100 at a 6% interest rate, you can expect to pay $6 in interest without taking inflation into account.
How to calculate nominal rate?
To calculate the real interest rate, you need to subtract the actual or expected rate of inflation from the nominal interest rate.
Lenders and Borrowers
How Interest Rates Are Determined
- Supply and Demand
Interest rate levels are a factor of the supply and demand of credit: an increase in the demand for money or credit will raise interest rates, while a decrease in the demand for credit will decrease them. Conversely, an increase in the supply of credit will reduce interest rates while a decrease i… - Inflation
Inflation will also affect interest rate levels. The higher the inflation rate, the more interest rates are likely to rise. This occurs because lenders will demand higher interest rates as compensation for the decrease in purchasing power of the money they are paid in the future.
Types of Loans
- Of the factors detailed above, supply and demandare, as we implied earlier, the primary forces behind interest rate levels. The interest rate for each different type of loan, however, depends on the credit risk, time, tax considerations (particularly in the U.S.), and convertibility of the particular loan. Risk refers to the likelihood of the loan being repaid. A greater chance that the loan will no…
The Bottom Line
- As interest rates are a significant factor of the income you can earn by lending money, of bond pricing and of the amount you will have to pay to borrow money, it is important that you understand how prevailing interest rates change: primarily by the forces of supply and demand, which are also affected by inflation and monetary policy. Of course, when you are deciding whet…