
What is Wilson disease caused by?
Wilson disease is caused by an inherited defect in the ATP7B gene. It is an autosomal recessive disorder. This means that both parents must pass on the same abnormal gene to the child. Many times parents, who have only one abnormal gene, show no signs of the disease but are carriers of the disease.
Is Wilson disease autosomal recessive or dominant?
The defective gene in Wilson disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. For an individual to have Wilson disease they must have inherited a defective gene from each parent. A person who has one defective gene and one normal gene is termed a “ carrier ” and will lead a perfectly healthy life.
What is the prevalence of Wilson disease?
At least one in 30,000 people of all known races and nationalities has the disease. Of the 23 different human chromosomes, the gene responsible for Wilson disease is located on chromosome 13.
Is Wilson's disease hereditary in dogs?
The genetic basis of Wilson's disease, and its linkage to ATP7B mutations, was elucidated by several research groups in the 1980s and 1990s. Hereditary copper accumulation has been described in Bedlington Terriers, where it generally only affects the liver.
What is Wilson disease?
What is the cause of death from Wilson's disease?
How is Wilson disease diagnosed?
What is the name of the disease that causes copper to be lost?
How early can you get Wilson's disease?
How many copies of a gene do you need to inherit to develop Wilson disease?
Why do women with Wilson disease get lower doses of Wilson's disease?
See more
About this website
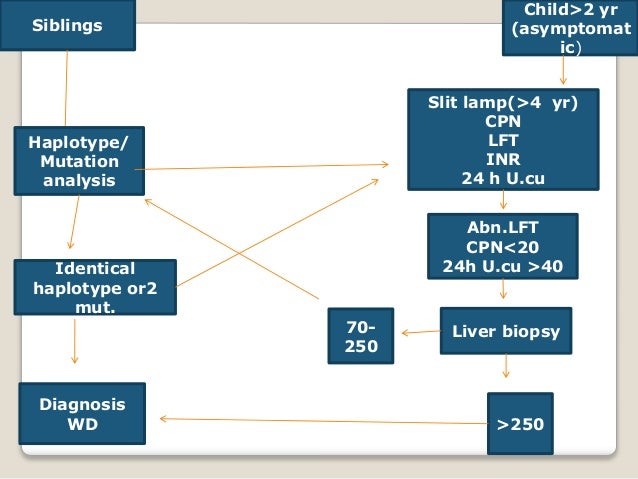
Is Wilson's disease a gene or chromosome?
Wilson disease (WD) is an Autosomal-Recessive disorder due to mutations of ATP7B gene on chromosome 13q14.
What is the function of chromosome 13?
Chromosome 13 likely contains 300 to 400 genes that provide instructions for making proteins. These proteins perform a variety of different roles in the body.
Is Wilson disease autosomal dominant?
Wilson disease is an autosomal-recessive disorder of hepatocellular copper deposition caused by pathogenic variants in the copper-transporting gene, ATP7B.
What is responsible for Wilson's disease?
What causes Wilson disease? Mutations link of a gene called ATP7B cause Wilson disease. These gene mutations prevent the body from removing extra copper. Normally, the liver releases extra copper into bile.
What does the 14th chromosome do?
Chromosome 14 likely contains 800 to 900 genes that provide instructions for making proteins. These proteins perform a variety of different roles in the body.
What does the 21st chromosome do?
Researchers believe that having extra copies of genes on chromosome 21 disrupts the course of normal development, causing the characteristic features of Down syndrome and the increased risk of health problems associated with this condition.
What chromosome is hemochromatosis on?
Many mutations in the body's iron transport system can cause hemochromatosis; however, most cases are caused by mutations in the HFE gene. This is located on chromosome 6, and one mutation leads to the substitution of the 282nd amino acid.
Is Wilson's disease dominant or recessive?
Wilson's disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait, which means that to develop the disease you must inherit one copy of the defective gene from each parent.
What gene mutation causes Wilson's disease?
Researchers have determined that Wilson disease is caused by disruption or changes (mutations) of the ATP7B gene, which plays an important role in the movement of excess copper from the liver to the bile to eventually be excreted from the body through the intestines.
What is the genetic test for Wilson's disease?
The Invitae Wilson Disease Test analyzes the ATP7B gene, pathogenic variants in which can cause decreased biliary excretion of copper, reduced incorporation of copper into apoceruloplasmin, and the overall accumulation of copper in the body.
What blood test shows Wilson's disease?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose Wilson's disease include: Blood and urine tests. Blood tests can monitor your liver function and check the level of a protein that binds copper in the blood (ceruloplasmin) and the level of copper in your blood.
Is Wilson disease an autoimmune disease?
In Wilson's disease presenting as autoimmune hepatitis, fatigue, malaise, and rashes may occur; laboratory findings included greatly elevated IgG, ANA, and ASMA levels. Wilson disease must be specifically investigated because treatment of the 2 diseases is entirely different.
What happens when chromosome 13 is missing?
Features that often occur in people with Chromosome 13q deletion include developmental delay, intellectual disability, behavioral problems and distinctive facial features. Chromosome testing of both parents can provide more information on whether or not the deletion was inherited.
What is the 13th gene?
Trisomy 13 is a genetic disorder that your baby gets when they have an extra 13th chromosome. In other words, they have three copies of their chromosome 13 when they should have just two. It happens when cells divide abnormally during reproduction, and create extra genetic material on chromosome 13.
What happens when you have an extra 13 chromosome?
Each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, which carry the genes you inherit from your parents. But a baby with Patau's syndrome has 3 copies of chromosome 13, instead of 2. This severely disrupts normal development and, in many cases, results in miscarriage, stillbirth or the baby dying shortly after birth.
What is another name for trisomy 13?
Trisomy 13 (also called Patau syndrome) is a genetic disorder in which a person has 3 copies of genetic material from chromosome 13, instead of the usual 2 copies. Rarely, the extra material may be attached to another chromosome (translocation).
Wilson's disease - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
Wilson's disease, an inherited disorder, causes copper to accumulate in vital organs. It's treatable when diagnosed early.
Symptoms & Causes of Wilson Disease | NIDDK
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public.
Wilson disease - About the Disease - Genetic and Rare Diseases ...
Wilson disease is a rare inherited disorder that is characterized by the accumulation of copper in the body. Because high levels of copper are toxic to tissues and organs, this buildup can lead to damage of the liver, brain and eyes.
Wilson Disease | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Wilson disease is a rare genetic disorder that is passed from parents to children (inherited). It prevents your body from getting rid of extra copper in your system.
What is Wilson disease?
Wilson disease is a rare inherited disorder that is characterized by the accumulation of copper in the body. Because high levels of copper are toxic to tissues and organs, this buildup can lead to damage of the liver, brain and eyes. Signs and symptoms of Wilson disease include chronic liver disease, central nervous system abnormalities, and psychiatric (mental health-related) disturbances. [1] [2] It is caused by a mutation of the ATP7B gene and is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. [3] [4] Although there is no cure for Wilson disease, therapies exist that aim to reduce or control the amount of copper that accumulates in the body. [1] [4]
What are the symptoms of Wilson's disease?
About a third of those with Wilson disease will also experience psychiatric (mental health-related) symptoms such as abrupt personality changes, depression accompanied by suicidal thoughts, anxiety, and/or psychosis. [5] [1] [2]
How to make a diagnosis for a genetic disorder?
Healthcare professionals typically look at a person’s medical history, symptoms, physical exam, and laboratory test results in order to make a diagnosis. The following resources provide information relating to diagnosis and testing for this condition. If you have questions about getting a diagnosis, you should contact a healthcare professional.
How does Wilson disease affect the body?
Wilson disease can affect many different systems of the body. Affected people often develop signs and symptoms of chronic liver disease in their teenaged years or early twenties. These features may include jaundice; abnormal fluid retention which can lead to swelling of the legs and/or abdomen; weight loss; nausea and vomiting; and/or fatigue. Unfortunately, some people may not experience any signs until they suddenly develop acute liver failure. [5] [1] [2]
Is there a cure for Wilson's disease?
There is currently no cure for Wilson disease; however, therapies exist that aim to reduce or control the amount of copper that accumulates in the body. Affected people require lifelong treatment, which may include certain medications and/or dietary modifications. If treatment is not effective or if liver failure develops, a liver transplant may be necessary. [5] [1] [2]#N#For more specific information on the treatment and management of Wilson disease, please visit the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease's (NIDDK) website and/or GeneReviews. Click the link to view these resources.
Is Wilson disease autosomal recessive?
Wilson disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means that to be affected, a person must have a mutation in both copies of the responsible gene in each cell. The parents of an affected person usually each carry one mutated copy of the gene and are referred to as carriers.
Is Wilson disease a long term disease?
The long-term outlook ( prognosis) for people with Wilson disease varies and largely depends on timely diagnosis and treatment. If the condition is detected early and treated appropriately, people with Wilson disease can usually enjoy normal health and a normal lifespan. Unfortunately, untreated Wilson disease is associated with severe brain damage, liver failure, and death. [6]
How rare is Wilson disease?
Wilson disease is a rare disorder that affects approximately 1 in 30,000 individuals.
What are the symptoms of Wilson disease?
Signs and symptoms of these problems can include clumsiness, tremors, difficulty walking, speech problems, impaired thinking ability, depression, anxiety, and mood swings.
What is the PRNP gene?
Research indicates that a normal variation in the PRNP gene may modify the course of Wilson disease. The PRNP gene provides instructions for making prion protein, which is active in the brain and other tissues and appears to be involved in transporting copper. Studies have focused on the effects of a PRNP gene variation that affects position 129 ...
What is inherited gene?
Inheritance. This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
What age does Wilson disease start?
The signs and symptoms of Wilson disease usually first appear between the ages of 6 and 45, but they most often begin during the teenage years. The features of this condition include ...
Does copper cause Wilson disease?
With a shortage of functional protein, excess copper is not removed from the body. As a result, copper accumulates to toxic levels that can damage tissues and organs, particularly the liver and brain. Research indicates that a normal variation in the PRNP gene may modify the course of Wilson disease. The PRNP gene provides instructions ...
When was Wilson's disease discovered?
The genetic basis of Wilson's disease, and its linkage to ATP7B mutations, was elucidated by several research groups in the 1980s and 1990s.
How many people have Wilson's disease?
Wilson's disease occurs in about 1 in 30,000 people. Symptoms usually begin between the ages of 5 and 35 years. It was first described in 1854 by German pathologist Friedrich Theodor von Frerichs and is named after British neurologist Samuel Wilson.
How many mutations are there in ATP7B?
Most (60%) are homozygous for ATP7B mutations (two abnormal copies), and 30% have only one abnormal copy. Ten percent have no detectable mutation. Although 300 mutations of ATP7B have been described, in most populations the cases of Wilson's disease are due to a small number of mutations specific for that population.
Where is ATP7B expressed?
The Wilson's disease gene ( ATP7B) is on chromosome 13 (13q14.3) and is expressed primarily in the liver, kidney, and placenta. The gene codes for a P-type (cation transport enzyme) ATPase that transports copper into bile and incorporates it into ceruloplasmin. Mutations can be detected in 90% of cases. Most (60%) are homozygous for ATP7B mutations (two abnormal copies), and 30% have only one abnormal copy. Ten percent have no detectable mutation.
Which protein is found in liver cells?
Liver cells also carry the CMT1 protein, and metallothionein and ATOX1 bind it inside the cell, but here it is ATP7B that links copper to ceruloplasmin and releases it into the bloodstream, as well as removing excess copper by secreting it into bile. Both functions of ATP7B are impaired in Wilson's disease.
How does PRNP affect the disease?
A normal variation in the PRNP gene can modify the course of the disease by delaying the age of onset and affecting the type of symptoms that develop. This gene produces prion protein, which is active in the brain and other tissues and also appears to be involved in transporting copper. A role for the ApoE gene was initially suspected but could not be confirmed.
What are the complications of Wilson's disease?
Complications of Wilson's disease can include liver failure, liver cancer and kidney problems. A liver transplant may be helpful in those in whom other treatments are not effective or if liver failure occurs. Wilson's disease occurs in about 1 in 30,000 people. Symptoms usually begin between the ages of 5 and 35 years.
What is Wilson disease?
Wilson disease is a rare genetic condition that affects about one in 30,000 people. Wilson disease causes a person's body to store too much of the mineral copper. Many foods contain copper, and it is important for people to have a small amount of copper in the body. However, high levels of copper can damage organs in the body.
What is the cause of death from Wilson's disease?
In Wilson disease, copper builds up in the liver, brain, eyes and other organs. Over time, the extra copper can lead to organ damage that may cause death. Other names for Wilson disease include copper storage disease, hepatolenticular degeneration syndrome, WD and Wilson's disease.
How is Wilson disease diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose Wilson disease through a physical exam and laboratory tests. The physical examination focuses on signs of liver disease as well as neurologic function.
What is the name of the disease that causes copper to be lost?
Other names for Wilson disease include copper storage disease, hepatolenticular degeneration syndrome, WD and Wilson's disease .
How early can you get Wilson's disease?
Either the liver or the brain can be harmed first, with signs as early as 4 years, or as late as 70 years of age. Symptoms of liver disease include: Jaundice, which is when the skin or the white part of the eye turns yellow.
How many copies of a gene do you need to inherit to develop Wilson disease?
In this pattern of inheritance, a person needs to inherit two altered (mutated) copies of a gene - one from each parent - to develop the disease. The parents of a person with Wilson disease each carry one mutated copy of the gene and one normal copy of the gene, so they do not show signs or symptoms of the disease.
Why do women with Wilson disease get lower doses of Wilson's disease?
If they are pregnant, women with Wilson disease are given lower doses of these drugs to reduce the risk of having a baby with birth defects. Lower doses also improve the body's ability to heal if surgery is done during childbirth.

Overview
Genetics
Signs and symptoms
Pathophysiology
Diagnosis
Treatment
The Wilson's disease gene (ATP7B) is on chromosome 13 (13q14.3) and is expressed primarily in the liver, kidney, and placenta. The gene codes for a P-type (cation transport enzyme) ATPase that transports copper into bile and incorporates it into ceruloplasmin. Mutations can be detected in 90% of cases. Most (60%) are homozygous for ATP7B mutations (two abnormal copies), and 30% have only one abnormal copy. Ten percent have no detectable mutation.
Prognosis
The main sites of copper accumulation are the liver and the brain, and consequently liver disease and neuropsychiatric symptoms are the main features that lead to diagnosis. People with liver problems tend to come for medical attention earlier, generally as children or teenagers, than those with neurological and psychiatric symptoms, who tend to be in their twenties or older. Some are identified only because relatives have been diagnosed with Wilson's disease; many of these, wh…
History
Copper is needed by the body for a number of functions, predominantly as a cofactor for a number of enzymes such as ceruloplasmin, cytochrome c oxidase, dopamine β-hydroxylase, superoxide dismutase and tyrosinase.
Copper enters the body through the digestive tract. A transporter protein on the cells of the small bowel, copper membrane transporter 1 (Ctr1; SLC31A1), carries copper inside the cells, where so…