
Is amiodarone a dangerous drug?
The FDA has made it clear that this drug should only be prescribed for life-threatening heart rhythm abnormalities such as recurrent ventricular fibrillation. Amiodarone side effects can be life threatening. The drug can cause serious lung toxicity. It can also harm the liver and the thyroid gland.
Which drug is considered a class 1a antiarrhythmic drug?
Which drug is considered a Class 1a antiarrhythmic drug? Class I: lidocaine, procainamide, propafenone (quinidine: rarely used) Class II: propranolol, metoprolol. Class III: AMIODARONE, dronedarone, sotalol, ibutilide. Class IV: verapamil, diltiazem. Click to see full answer. Subsequently, one may also ask, what are Class 1a antiarrhythmics?
What class is amiodarone?
It is a class III antiarrhythmic medication. It works partly by increasing the time before a heart cell can contract again. Amiodarone was first made in 1961 and came into medical use in 1962 for chest pain believed to be related to the heart. It was pulled from the market in 1967 due to side effects.
Is amiodarone safe for arrhythmia?
Low-dose Amiodarone Is Safe: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Amiodarone is commonly used for a variety of arrhythmias and, in some parts of the world, is the only available antiarrhythmic drug (AAD). Yet, amiodarone is known to have a wide range of potential side effects, many of which are dose- and duration-dependent.
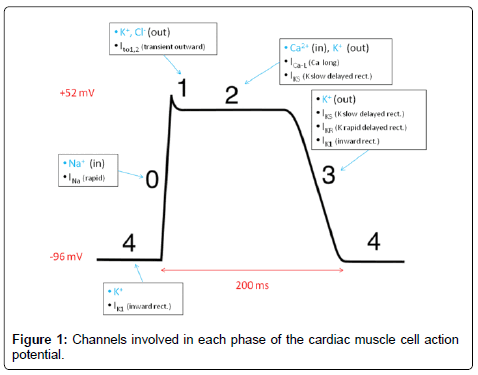
What are the 4 classes of antiarrhythmic drugs?
Antiarrhythmic drug classes:Class I - Sodium-channel blockers.Class II - Beta-blockers.Class III - Potassium-channel blockers.Class IV - Calcium-channel blockers.Miscellaneous - adenosine. - electrolyte supplement (magnesium and potassium salts) - digitalis compounds (cardiac glycosides)
What is a Class 2 antiarrhythmic drug?
Class 2 antiarrhythmics include beta-blockers, which competitively inhibit epinephrine. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the heart, and dilates bronchi and cerebral vessels.
Which is a class 3 antiarrhythmic drug?
Amiodarone, sotalol, dofetilide, and ibutilide are examples of class III drugs that are currently available. Amiodarone and sotalol have other antiarrhythmic properties in addition to pure class III action, which differentiates them from the others. However, all have potential serious adverse events.
What are the Class 1 antiarrhythmic drugs?
Quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide, lidocaine, mexiletine, flecainide, and propafenone are all class I antiarrhythmic drugs (table 1) used for the treatment of various atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
Is amiodarone a beta blocker?
Amiodarone is a coronary and peripheral vasodilator (1). Metoprolol is a selective beta1-blocker and exerts a slight vasoconstrictor effect on coronary arteries due to its lack of beta2 stimulation (1). The results of the present investigation were obtained in vitro.
What is a Class 5 antiarrhythmic?
Class 5 antiarrhythmic drugs are a miscellaneous group of medications that do not belong to a traditional class of antiarrhythmics. These drugs have varied mechanisms of action and uses. The medications in this class are digoxin. Digoxin has positive inotropic and negative chronotropic activity.
Is amiodarone a calcium channel blocker?
Abstract. Amiodarone possesses multiple pharmacologic properties, including peripheral and coronary vasodilatation, negative inotropy, and negative chronotropic and dromotropic effects. These properties are shared by the group of drugs termed calcium channel blockers.
Which of the following is an adverse effect of amiodarone?
Cardiac adverse reactions. Amiodarone could impair sinus beat formation and conduction and may induce significant bradycardia, especially in patients with pre-existing conduction disorders, and marked prolongation of the QT interval. These events are due to its effect in blocking the potassium channels.
Which medication is the drug of choice for a cardiac arrhythmia?
The most common arrhythmia is atrial fibrillation (AF), which is commonly treated with beta blockers such as atenolol, bisoprolol and metoprolol. Beta blockers may stop the arrhythmia occurring but, more often, are useful for slowing down the heart rate during the arrhythmia without actually terminating it.
What is the first drug of choice for atrial fibrillation?
Amiodarone as a first-choice drug for restoring sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation: a randomized, controlled study.
What is the safest antiarrhythmic drug?
Of all antiarrhythmic agents, dofetilide and amiodarone have been proven safe in patients with heart failure.
Which of the following is an example of a class 2 antiarrhythmic drug?
Class II agents include atenolol, esmolol, propranolol, and metoprolol.
Which of the following is the example of class 2 antiarrhythmic drugs?
Class II agents include atenolol, esmolol, propranolol, and metoprolol.
Which of the following is an adverse effect of the class II antiarrhythmics?
Class II Antiarrhythmic Drugs Beta-blockers are generally well tolerated; adverse effects include lassitude, sleep disturbance, and gastrointestinal upset. These drugs are contraindicated in patients with asthma.
What is the safest antiarrhythmic drug?
Of all antiarrhythmic agents, dofetilide and amiodarone have been proven safe in patients with heart failure.
What is the best medication for irregular heartbeat?
There are 4 main types of medicines for treating irregular heartbeats:sodium channel blockers like flecainide.beta blockers like propranolol and atenolol.potassium blockers like sotalol and amiodarone.calcium channel blockers like verapamil.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not use this medicine if you are allergic to amiodarone or iodine, or if you have: 1. a serious heart condition called "AV block" (2nd o...
How Should I Take Amiodarone?
Take amiodarone exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not take this medicine in larger or smal...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to...
What Happens If I Overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. An overdose of amiodarone can be fatal.Overdose symptoms may inclu...
What Should I Avoid While Taking Amiodarone?
Grapefruit and grapefruit juice may interact with amiodarone and lead to unwanted side effects. Avoid the use of grapefruit products while taking t...
Amiodarone Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Arrhythmias:IV:Initial dose: 1000 mg over the first 24 hours of therapy, delivered by the following infusion regimen:-Loading...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Amiodarone?
Amiodarone takes a long time to completely clear from your body. Drug interactions are possible for up to several months after you stop using this...
What to do before taking Amiodarone?
Periodic blood work will need to be done to test your liver and thyroid function. You may also be asked to perform a breathing test to measure your pulmonary (lung) function.
What is the best medicine for irregular heartbeat?
Amiodarone (Cordarone) is used to treat and prevent an irregular heartbeat. It slows down nerve activity in the heart and relaxes an overactive heart.
Does amiodarone come in tablets?
Amiodarone comes in tablets. Your prescription label tells you how much to take at each dose. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription.
Does caffeine affect amiodarone?
Cigarettes and beverages that contain caffeine may increase the irritability of your heart and interfere with the action of amiodarone. Always have enough of this medication on hand. Check your supply before vacations, holidays, and other times when you may be unable to get more medication.
Can amiodarone burn your skin?
If are pregnant or breastfeeding, or if you plan to become pregnant. This medication can make your skin more sensitive than usual to sunlight and sunlamps, which could cause a serious burn. This effect may continue for weeks or months after you stop taking amiodarone.
Can Amiodarone keep you from taking other medications?
The names of all vitamins, herbals, dietary supplements, nonprescription (over the counter) and other prescription medications you take. Amiodarone can keep many medications from working they way they should.
What is amiodarone?
Amiodarone affects the rhythm of your heartbeats. It is used to help keep the heart beating normally in people with life-threatening heart rhythm disorders of the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart that allow blood to flow out of the heart).
What other drugs will affect amiodarone?
Sometimes it is not safe to use certain medications at the same time. Some drugs can affect your blood levels of other drugs you take, which may increase side effects or make the medications less effective.
How long does it take for amiodarone to clear?
Amiodarone takes a long time to completely clear from your body. Drug interactions are possible for up to several months after you stop using amiodarone. Talk to your doctor before taking any medication during this time. Keep track of how long it has been since your last dose of amiodarone.
Does amiodarone cause swelling?
Amiodarone side effects. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to amiodarone: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Amiodarone takes a long time to completely clear from your body.
Can you take Amiodarone if you have AV block?
Before taking this medicine. You should not use amiodarone if you have: a serious heart condition called "AV block" (2nd or 3rd degree), unless you have a pacemaker; a history of slow heartbeats that have caused you to faint; or. if your heart cannot pump blood properly.
Can grapefruit interact with amiodarone?
Your reactions could be impaired. Grapefruit may interact with amiodarone and lead to unwanted side effects.
Does amiodarone affect your heart?
Amiodarone can cause dangerous side effects on your heart, liver, lungs, or vision.
What is amiodarone used for?
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of irregular heartbeats. This includes ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF), and wide complex tachycardia, as well as atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Evidence in cardiac arrest, however, is poor.
Where did amiodarone come from?
The original observation that amiodarone's progenitor molecule, khellin, had cardioactive properties, was made by the Russian physiologist Gleb von Anrep while working in Cairo in 1946. Khellin is obtained from a plant extract of Khella or Ammi visnaga, a common plant in north Africa. Anrep noticed that one of his technicians had been cured of anginal symptoms after taking khellin, then used for various, non-cardiac ailments. This led to efforts by European pharmaceutical industries to isolate an active compound. Amiodarone was initially developed in 1961 at the Labaz company, Belgium, by chemists Tondeur and Binon, who were working on preparations derived from khellin. It became popular in Europe as a treatment for angina pectoris.
How long does amiodarone stay in your system?
Excretion is primarily via the liver and the bile duct with almost no elimination via the kidney and it is not dialyzable. Elimination half-life average of 58 days (ranging from 25–100 days [Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy 21st edition]) for amiodarone and 36 days for the active metabolite, desethylamiodarone (DEA). There is 10-50% transfer of amiodarone and DEA in the placenta as well as a presence in breast milk. Accumulation of amiodarone and DEA occurs in adipose tissue and highly perfused organs (i.e. liver, lungs), therefore, if an individual was taking amiodarone on a chronic basis, if it is stopped it will remain in the system for weeks to months.
How does amiodarone work?
Amiodarone potentiates the action of warfarin by inhibiting the clearance of both (S) and (R) warfarin. Individuals taking both of these medications should have their warfarin doses adjusted based on their dosing of amiodarone, and have their anticoagulation status (measured as prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR)) measured more frequently. Dose reduction of warfarin is as follows: 40% reduction if amiodarone dose is 400 mg daily, 35% reduction if amiodarone dose is 300 mg daily, 30% reduction if amiodarone dose is 200 mg daily, and 25% reduction if amiodarone dose is 100 mg daily. The effect of amiodarone on the warfarin concentrations can be as early as a few days after initiation of treatment; however, the interaction may not peak for up to seven weeks.
How to administer amiodarone IV?
Amiodarone IV should be administered via a central venous catheter. It has a pH of 4.08. If administered outside of the standard concentration of 900 mg/500mL it should be administered using a 0.22 micron filter to prevent precipitate from reaching the patient. Amiodarone IV is a known vesicant. For infusions of longer than 1 hour, concentrations of 2 mg/mL should not be exceeded unless a central venous catheter is used.
What is the name of the drug Tachyra?
In India, amiodarone is marketed (produced by Cipla Pharmaceutical) under the brand name Tachyra. It is also available in intravenous ampules and vials.
What is the name of the blocker of potassium?
Amiodarone is a blocker of voltage gated potassium ( KCNH2) and voltage gated calcium channels ( CACNA2D2 ).
What is amiodarone hydrochloride used for?
Amiodarone hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of documented, life-threatening recurrent ventricular fibrillation and life-threatening recurrent hemodynamically unstable tachycardia in adults who have not responded to adequate doses of other available antiarrhythmics or when alternative agents cannot be tolerated.
How many tablets are in Amiodarone Hydrochloride?
Amiodarone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP are available in bottles of 60 tablets and 500 tablets as follows:
What enzymes are used to metabolize amiodarone?
Amiodarone is metabolized to DEA by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme group, specifically CYP3A and CYP2C8. The CYP3A isoenzyme is present in both the liver and intestines. In vitro, Amiodarone and DEA exhibit a potential to inhibit CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A, CYP2A6, CYP2B6 and CYP2C8. Amiodarone and DEA have also a potential to inhibit some transporters such as P-glycoprotein and organic cation transporter (OCT2).
What is the U over score on Amiodarone Hydrochloride?
Amiodarone Hydrochloride Tablets USP, 200 mg are white to off white round-shaped flat faced beveled edged tablets debossed with "U" over score on one side and "359" on other side.
How long does it take for amiodarone to be absorbed?
The bioavailability of Amiodarone hydrochloride is approximately 50%. Maximum plasma concentrations are attained 3 to 7 hours after a single dose. Plasma concentrations with chronic dosing at 100 to 600 mg/day are approximately dose proportional, with a mean 0.5 mg/L increase for each 100 mg/day. These means, however, include considerable individual variability.
How many adverse reactions does amiodarone cause?
At the usual maintenance dose (400 mg/day) and above, Amiodarone hydrochloride causes adverse reactions in about three-fourths of all patients, resulting in discontinuation in 7 to 18%.
How long does amiodarone last?
Because of the long half-life of Amiodarone (15 to 142 days) and its active metabolite desethylAmiodarone (14 to 75 days), adverse reactions and drug interactions can persist for several weeks following Amiodarone discontinuation [see Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3 )].
Is amiodarone a broad spectrum antiarrhythmic?
Amiodarone is useful in wide range of atrial and ventricular arrhythmias and it is a so called broad spectrum antiarrhythmic agent and widely used.
Is amiodarone a K+ channel blocker?
This is the group of voltage dependent K+ channel blockers. It is a nonselective K+ channel blocker. Another drug in class IIIa is dronedarone, which is a related drug free of iodine atoms and hence the thyroid related adverse effects of amiodarone.
Is amiodarone an antianginal?
It may be noted that amiodarone was originally introduced as an antianginal agent and its antiarrhythmic potential was noted later.
What is the mechanism of action of amiodarone?
Amiodarone is a Class III antiarrhythmic agent [ 7, 8] that prolongs the duration of action potential and hence increases the refractory period of atrial, nodal and ventricular tissues, thereby has a very broad spectrum of activity.
How much iodine is in amiodarone?
Amiodarone contains two atoms of iodine per molecule ( Figure 1 ). This amounts to 37.5% of organic iodine by molecular weight, of which 10% is deiodinated to yield free iodine. It has the potential to cause thyroid dysfunction because of the two iodine atoms two iodine atoms [ 22, 23 ].
What are the different types of antiarrhythmic drugs?
The classification includes five major groups of antiarrhythmic drugs, classes I, II, III, IV and V ( Table 1 ). Class I agents are sodium channel blockers, class II are beta blockers, class III are potassium channel blockers, class IV are calcium channel blockers and class V agents work by unknown mechanisms. The class I agents are classified into class Ia, Ib and Ic. Ia class includes Quinidine, Procainamide and Dispopyramide. They slow the rate of rise of phase 0, lengthen the refractory period and the width of the monophasic action potential. Quinidine is one of the oldest antiarrhythmic agents derived from the cinchona tree bark and has anti malarial, antipyretic and antiarrhythmic effects. Procainamide and its main metabolite, N-acetyl Procainamide are effective for treating supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias. Disopyramide has three important side effects. It is vagolytic causing urinary retention, constipation and dry mouth. The class 1b agents are pure sodium channel blockers. This class includes Lidocaine, Phenytoin Mexiletine and Tocainide. Class Ib antiarrhythmic agents used only for the management of ventricular tachyarrhythmia. The class Ic agents are strong sodium channel blockers. This class comprises of Flecainide, Encainide, Propafenone and Moricizine. They are being used to treat ventricular and supraventricular tachyarrhythmia. They are contraindicated in patients with structural heart disease due to the risk of precipitating life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. Class II drugs include Metoprolol, Carvedilol, Atenolol, Propranolol and Bisoprolol. They antagonize beta-receptors inhibiting the effect of the sympathetic nervous system resulting in decreased heart rate, contractility and conductivity. The class III agents are drugs that block the potassium channel as their main anti arrhythmic effect. This class includes Sotalol, Dofetilide, Ibutilide, and Amiodarone. They exert their effect by prolonging the refractory period. Sotalol is a nonspecific beta adrenergic receptor blocker with potassium channel blocking properties that is used in managing ventricular arrhythmias and atrial fibrillation. Dofetilide is a potassium channel blocker and excreted by the kidneys. Ibutilide is a short-acting intravenous potassium channel blocker that is used only for the acute termination of atrial fibrillation or flutter. Class IV drugs are Verapamil and Diltiazem. These drugs are known as nondihydropyridine and act by blocking cardiac calcium uptake. They are used to slow AV nodal conduction by decreasing heart rate. Class V agents include Adenosine, Digoxin, magnesium and sulphate are used in supraventricular arrhythmias, especially heart failure with atrial fibrillation, contraindicated in patients with ventricular arrhythmias [ 1 – 3 ]. Amiodarone is considered one of the most effective antiarrhythmic drugs which is widely prescribed. Here, its clinical uses as well as its side effects are reviewed.
How long does amiodarone last?
The half-life of Amiodarone is long and with chronic oral dosing can be from 14 to 110 days but is usually in the range of 14–59 days. The principal metabolite of Amiodarone, which has been detected in the plasma and other tissues, is Desethylamiodarone [ 16, 18 ].
Where do arrhythmias occur?
Arrhythmias may occur in the atria or ventricles [ 5] and is one of the most common signs of anomaly in heart function. Amiodarone as an iodinated benzofuran derivative ( Figure 1) is a potent antiarrhythmic drug that is being used for the treatment of a wide variety of cardiac arrhythmias [ 6 ].
What is the class IV drug for flutter?
Ibutilide is a short-acting intravenous potassium channel blocker that is used only for the acute termination of atrial fibrillation or flutter. Class IV drugs are Verapamil and Diltiazem. These drugs are known as nondihydropyridine and act by blocking cardiac calcium uptake.
Is amiodarone safe for long term use?
Therefore the effectiveness of Amiodarone in long-term treatment of patients with heart arrhythmia is limited because of the development of its adverse side effects.
