What are the three steps of hemostasis in blood clotting?
Figure 1 summarizes the three steps of hemostasis. Figure 1. (a) An injury to a blood vessel initiates the process of hemostasis. Blood clotting involves three steps. First, vascular spasm constricts the flow of blood. Next, a platelet plug forms to temporarily seal small openings in the vessel.
What is the first step in the blood clotting process?
Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting.
What is the first response to a blood clot in leg?
Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall.
What is the function of hemostasis in the body?
It prevents activation of platelets and clotting factors. Hemostasis is the natural process in which blood flow slows and a clot forms to prevent blood loss during an injury, with hemo- meaning blood, and stasis meaning stopping. During hemostasis, blood changes from a fluid liquid to a gelatinous state.

What type of clot is formed in hemostasis?
Ultimately, the coagulation cascade forms a substance called fibrin. During this step, the platelet plug acts like bricks and the fibrin acts like mortar. Together, they form a solid, stable clot.
What is clotting in hemostasis?
Coagulation (or clotting) is the process through which blood changes from a liquid and becomes thicker, like a gel. Coagulation is part of a larger process called hemostasis, which is the way that the body makes bleeding stop when it needs to.
What occurs during hemostasis?
Definition. Hemostasis is the mechanism that leads to cessation of bleeding from a blood vessel. It is a process that involves multiple interlinked steps. This cascade culminates into the formation of a “plug” that closes up the damaged site of the blood vessel controlling the bleeding.
What is the process of forming a blood clot?
Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to a blood vessel. Platelets immediately begin to adhere to the cut edges of the vessel and release chemicals to attract even more platelets. A platelet plug is formed, and the external bleeding stops.
What is a fibrin clot?
fibrin, an insoluble protein that is produced in response to bleeding and is the major component of the blood clot. Fibrin is a tough protein substance that is arranged in long fibrous chains; it is formed from fibrinogen, a soluble protein that is produced by the liver and found in blood plasma.
What is hemostasis quizlet?
hemostasis. refers to the collection of events that STOPS the bleeding when a BLOOD VESSEL is damaged.
What are the steps of hemostasis quizlet?
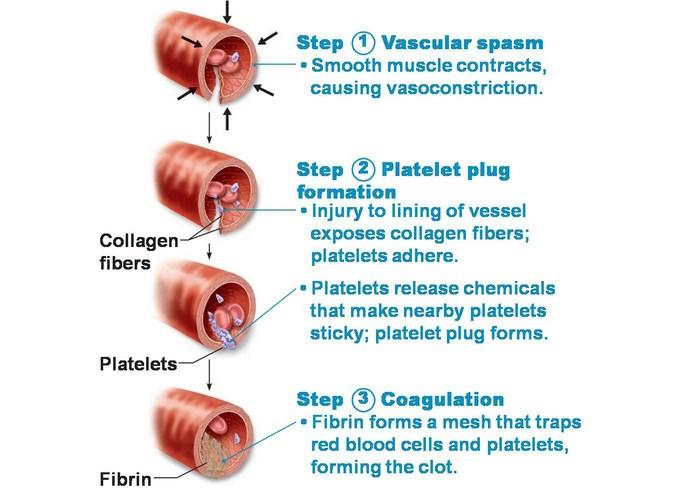
Hemostasis is the natural process that stops blood loss when an injury occurs.It involves three steps: (1) vascular spasm (vasoconstriction); (2) platelet plug formation; and (3) coagulation.
What are the 5 stages of hemostasis?
Terms in this set (16)1) Vessel Spasm. ... 2) Formation of Platelet Plug. ... 3) Blood Coagulation. ... 4) Clot Retraction. ... 5) Clot Dissolution (Lysis) ... Collagen. ... vWF. ... ADP.More items...
What happens during the clotting process of blood quizlet?
What is a blood clot? When a blood vessel is damaged, the body sets up a process to half the loss of blood. A temporary plug is formed by platelets. This plug is bound together by fibrin to form a clot.
What must occur in order for a blood clot to form quizlet?
What must occur in order for a blood clot to form? Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin.
What is blood clotting in biology?
Blood clotting, or coagulation, is an important process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. Platelets (a type of blood cell) and proteins in your plasma (the liquid part of blood) work together to stop the bleeding by forming a clot over the injury.
What are the 5 stages of hemostasis?
Terms in this set (16)1) Vessel Spasm. ... 2) Formation of Platelet Plug. ... 3) Blood Coagulation. ... 4) Clot Retraction. ... 5) Clot Dissolution (Lysis) ... Collagen. ... vWF. ... ADP.More items...
Which is another term for clotting factors?
Clotting factors have names, such as fibrinogen and prothrombin.
What is the process of forming a blood clot?
Coagulation is the process of forming a blood clot. The plasma protein fibrinogen is converted into a non-globular and insoluble protein called fibrin. Fibrin is created in threads, which results in a mesh that traps platelets and erythrocytes that travel through it. The final product is a gelatinous and durable clot.
What are the steps of hemostasis?
The process includes three main steps: the vascular spasm of the vessel damaged, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation.
How do platelets stick together?
As platelets pass by the area of the damaged vessel, they contact the normally covered layers of connective tissue and collagenous fibers. These layers are now exposed due to the vessel's damage, and the platelets start to stick together as they bind to the exposed collagen and endothelial lining. The clumping together of platelets is further stabilized by von Willebrand factor, a glycoprotein found within the blood plasma. As the clump grows, the platelets release various substances to reinforce the plug including ADP (to help additional platelets stick to the growing plug) and serotonin (to maintain vasoconstriction).
Why is it difficult to clot blood?
Another reason that could impair the blood's ability to clot is the inadequate production of functional amounts of one or more clotting factors. This is the case in the genetic disorder hemophilia. This disorder results in the inability to synthesize sufficient quantities of clotting factor VIII. The genetic roots of hemophilia are found in the X chromosome and are typically passed from a healthy (carrier) mother to her male offspring. Patients with hemophilia bleed from even minor internal and external wounds and leak blood into joint spaces after exercise and into urine and stool. Regular infusions of clotting factors isolated from healthy donors can help prevent bleeding in hemophiliac patients.
How long does hemostasis last?
The longitudinal layers pull the vessel away from its surrounding tissues; the circular layers act to constrict the flow of blood in general. This step of hemostasis may last several minutes to several hours.
What is the process of coagulation?
The process can be divided into the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. The extrinsic pathway is normally triggered by trauma; the intrinsic pathway is triggered by internal damage to the vessel walls. Both of these pathways merge into a third known as the common pathway. Each of the three pathways depends on the 12 known clotting factors.
What is the process of repairing a damaged blood vessel?
Hemostasis is the process in which the body repairs a damaged blood vessel to prevent the further loss of blood. This process is found with smaller wounds, as more serious wounds may require medical intervention to repair them. Hemostasis includes three separate steps: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation.
Why does hemostasis not clot?
The body’s hemostasis system requires careful regulation in order to work properly. If the blood does not clot sufficiently, it may be due to bleeding disorders such ashemophilia; this requires careful investigation.
How do clots form?
3. Blood coagulation – Clots form upon the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, and its addition to the platelet plug ( secondary hemostasis ). Coagulation: The third and final step in this rapid response reinforces the platelet plug. Coagulation or blood clotting uses fibrin threads that act as a glue for the sticky platelets. As the fibrin mesh begins to form the blood is also transformed from a liquid to a gel like substance through involvement of clotting factors and pro-coagulants. The coagulation process is useful in closing up and maintaining the platelet plug on larger wounds. The release of Prothrombin also plays an essential part in the coagulation process because it allows for the formation of a thrombus, or clot, to form. This final step forces blood cells and platelets to stay trapped in the wounded area. Though this is often a good step for wound healing, it has the ability to cause severe health problems if the thrombus becomes detached from the vessel wall and travels through the circulatory system; If it reaches the brain, heart or lungs it could lead to stroke, heart attack, or pulmonary embolism respectively. However, without this process the healing of a wound would not be possible.
What is the role of coagulation in hemostatic hemostasis?
Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a “molecular glue”. Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process. They allow for the creation of the “platelet plug” that forms almost directly after a blood vessel has been ruptured.
What is the first response to a vascular spasm?
Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting.
How do platelets help with hemostatic process?
This process is regulated through thromboregulation. Platelets play one of the biggest factors in the hemostatic process. Being the second step in the sequence they stick together (aggregation) to form a plug that temporarily seals the break in the vessel wall.
How does hemostasis occur?
Hemostasis occurs when blood is present outside of the body or blood vessels. It is the instinctive response for the body to stop bleeding and loss of blood. During hemostasis three steps occur in a rapid sequence. Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting. Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a “molecular glue”. Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process. They allow for the creation of the “platelet plug” that forms almost directly after a blood vessel has been ruptured. Within seconds of a blood vessel’s epithelial wall being disrupted platelets begin to adhere to the sub-endotheliumsurface. It takes approximately sixty seconds until the first fibrin strands begin to intersperse among the wound. After several minutes the platelet plug is completely formed by fibrin. Hemostasis is maintained in the body via three mechanisms:
Why do people develop hemostasis?
Hemostasis disorders can develop for many different reasons. They may be congenital, due to a deficiency or defect in an individual’s platelets or clotting factors. A number of disorders can be acquired as well.
Why is my clotting time so slow?
A common cause of slow clotting time is vitamin k deficiency, which is required by the liver to make many clotting factors . Therefore, an injection of vitamin k is often given as a treatment for slow clotting times. This injection would not immediately improve clotting time because it takes time for the liver to absorb the vitamin k and to use it to synthesize the clotting factors
What happens if a thrombus blocks blood vessels?
Thrombus that totally block blood vessel will cause tissue hypoxia (lack of oxygen) and possible tissue death. If this happens in the heart it is called a_________ If it happens in the brain it is called a _________
What is the role of citric acid in blood?
Citric acid and EDTA bind calcium ions, which are required for formation of the clotting factor complexes. Because the presence of calcium ions in the blood is required for many life processes (including the beating of heart cells), EDTA and citric acid are only used as anticoagulants for blood samples in test tubes (in vitro), not as anticoagulants in living organisms (in vivo)
What is the molecule that makes platelets sticky?
Platelets release the molecule ADP. This causes platelets to become sticky, which allows them to cling together to form a platelet plug
What is the thick tissue layer in the wall of the arteries called?
Arteries have a thick tissue layer in their wall called the tunica media. What type of tissue is the tunica media and what is its main function?
What causes the tunica media smooth muscle to contract?
Releasing throboxane and serotonin, which cause the tunica media smooth muscle to contract.
Does leather sand help with clotting?
In the lab exercise on bleeding time, blood samples with leather shavings or sand added usually had faster clotting times than blood samples without leather or sand added.
What is the process of blood clotting?
Hemostasis is the natural process in which blood flow slows and a clot forms to prevent blood loss during an injury, with hemo- meaning blood, and stasis meaning stopping. During hemostasis, blood changes from a fluid liquid to a gelatinous state.
How many factors are involved in the process of blood clotting?
First, blood changes from a liquid to a gel. At least 12 substances called clotting factors or tissue factors take part in a cascade of chemical reactions that eventually create a mesh of fibrin within the blood. Each of the clotting factors has a very specific function.
What is the role of intact blood vessels in coagulation?
Intact blood vessels are central to moderating blood’s clotting tendency. The endothelial cells of intact vessels prevent clotting by expressing a fibrinolytic heparin molecule and thrombomodulin, which prevents platelet aggregation and stops the coagulation cascade with nitric oxide and prostacyclin. When endothelial injury occurs, the endothelial cells stop secretion of coagulation and aggregation inhibitors and instead secrete von Willebrand factor, which causes platelet adherence during the initial formation of a clot. The vasoconstriction that occurs during hemostasis is a brief reflexive contraction that causes a decrease in blood flow to the area.
What are the steps of hemostasis?
Steps of Hemostasis. Hemostasis includes three steps that occur in a rapid sequence: (1) vascular spasm, or vasoconstriction , a brief and intense contraction of blood vessels; (2) formation of a platelet plug; and (3) blood clotting or coagulation, which reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin mesh that acts as a glue to hold the clot together.
What is the process of slowing and stopping the flow of blood to initiate wound healing?
hemostasis : The process of slowing and stopping the flow of blood to initiate wound healing. coagulation: The process by which blood forms gelatinous clots. heparin: A fibrinolytic molecule expressed on endothelial cells or produced as a blood thinner medicine. It prevents activation of platelets and clotting factors.
How long does it take for a platelet to form?
Within twenty seconds of an injury in which the blood vessel’s epithelial wall is disrupted, coagulation is initiated. It takes approximately sixty seconds until the first fibrin strands begin to intersperse among the wound. After several minutes, the platelet plug is completely formed by fibrin.
What causes clotting of skin?
Contrary to popular belief, clotting of a skin injury is not caused by exposure to air, but by platelets adhering to and being activated by collagen in the blood vessels’ endothelium. The activated platelets then release the contents of their granules, which contain a variety of substances that stimulate further platelet activation and enhance the hemostatic process.
How do stabilized clots work?
The stabilized clot is acted upon by contractile proteins within the platelets. As these proteins contract, they pull on the fibrin threads, bringing the edges of the clot more tightly together, somewhat as we do when tightening loose shoelaces (see Figure 1a). This process also wrings out of the clot a small amount of fluid called serum, which is blood plasma without its clotting factors.
What are the clotting factors?
clotting factors: group of 12 identified substances active in coagulation. coagulation: formation of a blood clot; part of the process of hemostasis. common pathway: final coagulation pathway activated either by the intrinsic or the extrinsic pathway, and ending in the formation of a blood clot.
What is the physiological process by which bleeding ceases?
Chapter Review. Hemostasis is the physiological process by which bleeding ceases. Hemostasis involves three basic steps: vascular spasm, the formation of a platelet plug, and coagulation, in which clotting factors promote the formation of a fibrin clot.
How does the coagulation cascade restore hemostasis?
The coagulation cascade restores hemostasis by activating coagulation factors in the presence of an injury. How does the endothelium of the blood vessel walls prevent the blood from coagulating as it flows through the blood vessels?
What is the role of platelets in hemostasis?
Platelets are key players in hemostasis, the process by which the body seals a ruptured blood vessel and prevents further loss of blood. Although rupture of larger vessels usually requires medical intervention, hemostasis is quite effective in dealing with small, simple wounds. There are three steps to the process: vascular spasm, ...
How does a thrombolytic agent help a patient?
A class of drugs collectively known as thrombolytic agents can help speed up the degradation of an abnormal clot. If a thrombolytic agent is administered to a patient within 3 hours following a thrombotic stroke, the patient’s prognosis improves significantly. However, some strokes are not caused by thrombi, but by hemorrhage. Thus, the cause must be determined before treatment begins. Tissue plasminogen activator is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, the primary enzyme that breaks down clots. It is released naturally by endothelial cells but is also used in clinical medicine. New research is progressing using compounds isolated from the venom of some species of snakes, particularly vipers and cobras, which may eventually have therapeutic value as thrombolytic agents.
What happens to platelets in the second step of the blood vessel?
In the second step, platelets, which normally float free in the plasma, encounter the area of vessel rupture with the exposed underlying connective tissue and collagenous fibers. The platelets begin to clump together, become spiked and sticky, and bind to the exposed collagen and endothelial lining. This process is assisted by a glycoprotein in the blood plasma called von Willebrand factor, which helps stabilize the growing platelet plug. As platelets collect, they simultaneously release chemicals from their granules into the plasma that further contribute to hemostasis. Among the substances released by the platelets are:
Introduction
- Hemostasis or haemostasis is a process which causes bleeding to stop, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage). It is the first stage of wound healing. This involves blood changing from a liquid to a gel. Intact blood vessels are central to moderating bloods tendency to clot. The endothelial cel...
Mechanism
- Hemostasis occurs when blood is present outside of the body or blood vessels. It is the instinctive response for the body to stop bleeding and loss of blood. During hemostasis three steps occur in a rapid sequence. Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stic…
Function
- 2. Platelet plug formation Platelets adhere to damaged endothelium to form platelet plug (primary hemostasis) and then degranulate. This process is regulated through thromboregulation. Platelets play one of the biggest factors in the hemostatic process. Being the second step in the sequence they stick together (aggregation) to form a plug that temporarily seals the break in th…
Pathophysiology
- The second stage of hemostasis involves platelets that move throughout the blood. When the platelets find an exposed area or an injury, they begin to form what is called a platelet plug. The platelet plug formation is activated by a glycoprotein called the Von Willebrand factor (vWF), which are found in the bodys blood plasma. When the platelets in the blood are activated, they t…
Clinical significance
- DISORDERS The bodys hemostasis system requires careful regulation in order to work properly. If the blood does not clot sufficiently, it may be due to bleeding disorders such ashemophilia; this requires careful investigation. Over-active clotting can also cause problems; thrombosis, where blood clots form abnormally, can potentially causeembolisms, where blood clots break off and s…
Causes
- Hemostasis disorders can develop for many different reasons. They may be congenital, due to a deficiency or defect in an individuals platelets or clotting factors. A number of disorders can be acquired as well.