| Type | Colour | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Fibrinous | Cloudy | Contains fibrin protein strands. |
| Serosanguinous | Clear, pink | Normal. |
| Sanguinous | Red | Trauma to blood vessels. |
| Seropurulent | Murky, yellow, cream-coffee | Infection |
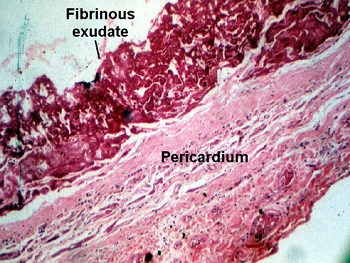
What is fibrin exudate?
Collection of fluid in a body cavity is an effusion. It is called a transudate if there are few cells and/or protein. If this fluid is protein-rich and/or has many cells within it, then it becomes an exudate. The large amount of fibrin in such fluid can form a fibrinous exudate on body cavity surfaces.
What is fibrinous exudate in wound?
fibrin stands (fibrinous exudate. — a response to inflammation) or infection (purulent exudate. containing white blood cells and. bacteria)
What color is exudate?
Exudate is usually amber or straw coloured, similar to plasma (Davies, 2012). Any change in colour can indicate a possible problem. Green usually indicates bacterial infection practice.
What are the 4 types of exudate?
Types of ExudateSerous – a clear, thin and watery plasma. ... Sanguinous – a fresh bleeding, seen in deep partial- and full-thickness wounds. ... Serosanguineous – thin, watery and pale red to pink in color.Seropurulent – thin, watery, cloudy and yellow to tan in color.More items...•
What is the difference between serous and fibrinous exudates?
Serous: a transudate with mainly edema fluid and few cells. Serosanguinous: an effusion with red blood cells. Fibrinous (serofibrinous): fibrin strands are derived from a protein-rich exudate.
Is fibrinous exudate an infection?
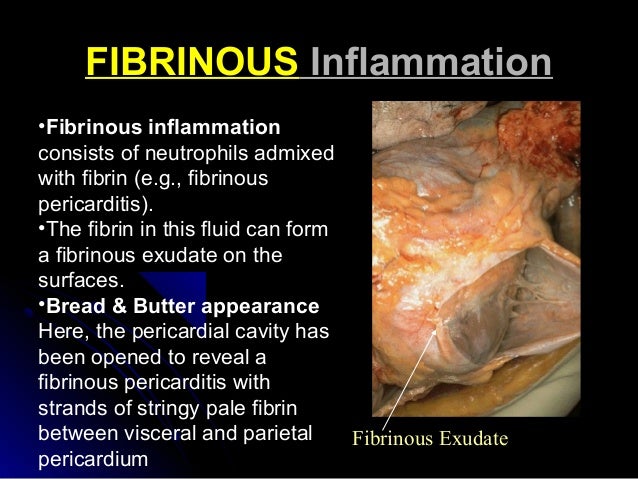
This kind of exudate is consistent with more severe infections, and is commonly referred to as pus. Fibrinous exudate is composed mainly of fibrinogen and fibrin. It is characteristic of rheumatic carditis, but is seen in all severe injuries such as strep throat and bacterial pneumonia.
What does fibrin look like in a wound?
What may this material look like? Depending on the amount of moisture in the wound, the colour of this material can vary from whitish to yellow or brown. It often turns grey when silver dressings are used. It may be firmly attached to the wound bed or easily removed.
Does yellow exudate mean infection?
Exudate that becomes a thick, milky liquid or a thick liquid that turns yellow, tan, gray, green, or brown is almost always a sign that infection is present. This drainage contains white blood cells, dead bacteria, wound debris, and inflammatory cells.
What does wound exudate look like?
Serosanguinous drainage is the most common type of exudate that is seen in wounds. It is thin, pink, and watery in presentation. Purulent drainage is milky, typically thicker in consistency, and can be gray, green, or yellow in appearance. If the fluid becomes very thick, this can be a sign of infection.
What color is serous drainage?
Serous drainage is composed mainly of plasma. It is often thin and watery and will usually have a clear to yellowish or brownish appearance. Small amounts of serous drainage are normal during the first stages of healing.
What is yellow fluid from wound?
Purulent drainage is a sign of infection. It's a white, yellow, or brown fluid and might be slightly thick in texture. It's made up of white blood cells trying to fight the infection, plus the residue from any bacteria pushed out of the wound. There may be an unpleasant smell to the fluid, as well.
What color should wound drainage be?
Color is generally clear to pale yellow (normal), red (fresh blood), brown (dried or old blood), white (see above), or blue-green (usually indicative of Pseudomonas infection and should be cultured). The amount of drainage is generally documented as absent, scant, minimal, moderate, large, or copious.
What does Fibrinous mean?
fibrinous (not comparable) Of, pertaining to, characteristic of, resembling or having the nature of fibrin.
What is Fibrinous tissue?
The widespread name “fibrinous tissue” is due to its clinical resemblance to fibrin. However, in its composition, in addition to fibrin, there are other substances. The term “slough“ would be the most appropriate to refer to this devitalized tissue, which normally consists of: Denatured proteins (collagen, fibrin)
What type of exudate indicates infection?
Exudate that becomes a thick, milky liquid or a thick liquid that turns yellow, tan, gray, green, or brown is almost always a sign that infection is present. This drainage contains white blood cells, dead bacteria, wound debris, and inflammatory cells.
What is Fibrinous inflammation?
Fibrinous inflammation is a form of inflammation which is characterised by fibrin deposition. It may be acute, but more often it is a chronic response. It results from the exudation of a high concentration of the plasma protein fraction. There is activation of the coagulation cascade and depostion of fibrin locally.
Why do we use alginates?
Alginates are highly absorbent and are indicated when a wound is very exudative. They release calcium ions, which help haemostasis so are useful applied to a surgical wound in a patient with excessive bleeding. In chronic wounds, the exudate combines with the alginate gel to form green or yellowish goo. The alginates are nonadherent unless the wound dries out. They can be soaked off to avoid unnecessarily debriding the wound.
What is transudate fluid?
Transudate is a clear fluid with low protein concentration and a limited number of white blood cells. An imbalance between the hydrostatic and oncotic pressure within the capillaries causes a transudate effusion. Light’s criteria 1) can be used to determine if the fluid is an exudate versus transudate.
What is the term for an alteration of the local inflammatory factors that precipitate a fluid accumulation?
An alteration of the local inflammatory factors that precipitate a fluid accumulation represents an exudative effusion. Exudate has a higher than normal protein content and may be cloudy due to increased numbers of white blood cells and is also called pus.
What is the fluid that leaks out of blood vessels into a body cavity or nearby tissues?
Exudate is fluid that leaks out of blood vessels into a body cavity or nearby tissues as a result of injury or inflammation. Exudate is made of cells, proteins, and solid materials. Exudate may ooze from cuts or from areas of infection or inflammation. An alteration of the local inflammatory factors that precipitate a fluid accumulation represents ...
Why does transudate leak out of blood vessels?
Transudate is fluid that leaks out of blood vessels into a body cavity or nearby tissues, due to an imbalance between the pressure within blood vessels (which drives fluid out) and the amount of protein in blood (which keeps fluid in). Transudate is a clear fluid with low protein concentration and a limited number of white blood cells. An imbalance between the hydrostatic and oncotic pressure within the capillaries causes a transudate effusion.
How long can you wear hydrophilic foam dressing?
In addition, they absorb mild to moderate wound exudate so they can be worn for three to seven days without changing. Hydrophilic foam dressings are permeable to oxygen and water vapour.
What is the color of serosanguineous exudate?
Serosanguineous exudate – thin, watery and pale red to pink in color.
What is the color of wound drainage?
It is made up of blood and serous fluid and is typically pink-red and thin . This drainage is common in many wounds. 1. Serous: This is thin, watery, clear drainage.
Why is it important to make an accurate assessment of wound drainage and color?
Accurate assessment of wound drainage and color is sometimes difficult because of the timing of the dressing changes, the products used, and extrinsic variables . It is important to make an accurate assessment and to use descriptive documentation to paint a picture of what is going on with the wound and the entire patient. Certain types of topical treatments can cause a change in wound drainage consistent with what is expected when that particular treatment is used.
What is dry cell wound?
Wound exudate or drainage gives us significant information about what is going on with the wound, all the way down to a cellular level, and it is one of the wound components that guide our topical treatments. As mentioned in prior blogs, a dry cell is a dead cell , but a wound with too much moisture will also have delayed healing. Additionally, infection, poor nutrition, impaired mobility, impaired sensory perception, and even malignancy in the wound can impair the healing process.
Why does drainage decrease over time?
Additionally, infection, poor nutrition, impaired mobility, impaired sensory perception, and even malignancy in the wound can impair the healing process. In acute wounds, drainage typically decreases over several days while the wound heals, whereas in chronic wounds, a large amount of drainage is suggestive of prolonged inflammation ...
What is clinical judgment in wound documentation?
Clinical judgment in terms of wound documentation requires training, knowledge, and experience. Additionally, knowledge of absorptive properties of the topical treatment along with suggested wear times is important. If you’re ever unsure, consult with your wound care specialist prior to documenting.
Why is it important to understand the way the topical treatment works and application guidelines?
Understanding the way the topical treatment works and application guidelines is important here, especially when it comes to accurately documenting and understanding what is going on with the wound. As the expert clinician, it is imperative to be aware that wound drainage is often one of the most difficult features for a patient with a wound.
Why is it important to document wounds?
Accurate and clear documentation is a key factor in appropriate wound assessment and treatment. Painting an accurate picture of what is going on with a particular wound and patient through documentation is important for many reasons. In addition to the tips and knowledge shared here, your wound care specialist and the interprofessional team are great resources to manage the whole patient (not just the hole in the patient!).
Types of Wound Exudates
Wound exudate is not simply an inert liquid. It can help provide valuable clinical information to wound care specialists and podiatrists regarding etiology, the progression of a wound, and the presence of infection. The biochemical properties of wound exudate are altered depending on the wound microenvironment.
Characteristics of Acute And Chronic Wound Exudate
Chronic wounds result from persistent inflammation that fails to promote wound healing. The characteristics of wound exudate can help podiatrists and wound care specialists differentiate between acute and chronic wounds.
Management of Wound Exudate
Excessive wound exudate can considerably impact a patient’s well-being and quality of life. Many patients experience discomfort related to leakage, soiling of clothes, and malodor. The presence of excessive exudate can also have social, economical, and psychological implications for the patient.
Selecting A Wound Dressing
While selecting a dressing, it should be kept in mind that the properties of the wound dressing should be favorable towards wound healing. Simply wiping off the excess exudate is not going to optimize wound healing. It is also important for wound care specialists to consider the type of wound exudate when selecting a dressing.
Use of Skin Barriers And Ointments
Excess exudate can cause maceration of the surrounding skin. Macerated skin is also at increased risk of infection.6 Therefore, skin barriers and ointments should be considered to avoid additional damage to the fragile peri-wound skin. However, before prescribing skin ointments, allergies to the ointment material should be ruled out.
Conclusion
Wound exudate provides critical information regarding wound etiology and the health status of the wound. Wound exudate is an essential component of wound healing, but excess can contribute to patient discomfort. In addition, excessive exudate can also be a signal of infection.
Why is serosanguinous fluid pink?
Serosanguinous fluid appears pink due to a small number of blood cells mixing with serous drainage. “World Wide Wounds” describe a consistency of thin and watery for serosanguinous fluid. Serosanguinous fluid appears normally in the healing of wounds and is typically a pinkish color due to the yellow liquid combining with small blood droplets.
What is the name of the fluid that comes out of a wound when infection invades the area?
When the wound is infected, the volume of the purulent exudate increases. Purulent effluent refers to a thick yellow, gray or green drainage that comes out of a wound when infection invades the area. The fluid contains pathogenic microorganisms along with white cells, inflammatory cells and dead or dying bacteria.
What is purulent effluent?
Purulent effluent refers to a thick yellow, gray or green drainage that comes out of a wound when infection invades the area. The fluid contains pathogenic microorganisms along with white cells, inflammatory cells and dead or dying bacteria. When the wound is infected, the volume of the purulent exudate increases.
What is serous wound fluid?
Serous wound fluid occurs as a normal process of healing. Serous wound drainage looks clear or straw colored. The serous drainage supports the healing process and contains protein, electrolytes, sugar, white cells and some microorganisms.
What is serous drainage?
Serous wound drainage looks clear or straw colored. This serous material arises from protein and fluid in the tissue. At times, serous material will leak through swollen skin when a person suffers a critical illness. The serous drainage supports the healing process and contains protein, electrolytes, sugar, white cells and some microorganisms. Platelets and fibrin used in the clotting process appear in the fluid in the first 48 to 72 hours of formation of a wound to prevent bleeding. Serous wound fluid occurs as a normal process of healing.
What is sanguinous fluid?
Sanguinous. Sanguinous liquid means red drainage from trauma to a blood vessel that may occur with the cleaning of a wound or excessive movement of the individual with a wound immediately after a wound emerges. The consistency appears thin and watery with sanguinous fluid. Sanguinous represents an infrequent finding in a wound.
What does hemorrhaging mean?
Hemorrhaging indicates a leaking blood vessel putting out blood. The consistency is thicker than sanguinous fluid. This situation may constitute an emergency requiring a physician’s assistance to control bleeding if large amounts of blood flow from the wound site. Hemorrhaging represents an abnormal discovery in a wound.
What may this material look like?
Depending on the amount of moisture in the wound, the colour of this material can vary from whitish to yellow or brown. It often turns grey when silver dressings are used. It may be firmly attached to the wound bed or easily removed. Its consistency may be fibrinous, viscous, gelatinous.
What is the purpose of sharp debridement?
However, in this type of wound it is essential to control both oedema and exudate with the choice of the appropriate dressing but, above all, with an adequate COMPRESSION THERAPY. This will have a direct impact on the improvement of the perilesional skin, the reduction of nutrients for the biofilm and pro-inflammatory cells and molecules.
How long does it take for biofilm to reappear?
Biofilm is a material that is rapidly reorganized and can reappear in the wound within 24 hours. Therefore, cleansing and debridement, the use of dressings that protect the wound from new germs and decrease metalloproteinase activity, and the use of products with antimicrobial activity are important. In a nutshell, it seems an easy task. However, biofilm control is a real therapeutic challenge. It is necessary to better understand the behaviour of these bacterial armies in order to develop specific weapons to attack them. We have to bear in mind that biofilm is one of the main factors involved in promoting chronicity of wounds.
What is the difference between a slough and a gel?
Some authors point out that gel-like consistency and gloss are characteristics of biofilm, while slough normally form an opaque layer over the wound. Blue, green or black colour is also typical of overproduction of certain bacteria.
Why is biofilm important?
Clinical identification of biofilm is important because conventional culture methods are not useful for detecting these organized bacteria in complex structures. Advanced microscopy methods or specialized culture techniques, which are normally only used in research studies, are needed.
What is a slough?
The term “slough“ would be the most appropriate to refer to this devitalized tissue, which normally consists of: Denatured proteins (collagen, fibrin) Inflammatory cells (neutrophils, macrophages) Bacteria. Cellular debris.
What is a biofilm?
Biofilms are communities of bacteria organized in a complex way. They synthesize a nutritive and protective matrix (polysaccharides, proteins and cellular detritus) in which they are embedded and which allows them to live adhered to the wound bed.
What is exudate in wounds?
Most frequently referred to as wound “drainage,” exudate is a liquid produced by the body in response to tissue damage. It bathes the wound continuously, keeping it moist, supplying nutrients, and providing the best conditions for migration of new tissue to heal the wound. Open wounds should be moist, but not overly moist.
What causes a clear amber exudate?
• Clear/amber—serous exudate, often considered “normal,” but may be associated with infection by fibrinolysin-producing bacteria such as Staphyloccocus auerus; may also be due to fluid from a urinary or lymphatic fistula.
What Do You Think?
When it comes to documenting exudate, do you see one type being identified more than others – like the well-known serosanguineous? And what about the amount of drainage – do you use the terms listed above, or does your clinic use percentages instead? We would love to hear how your facility typically documents exudate, and if you encounter any specific challenges or successes with identifying or treating wounds based on exudate. Please leave your comments below.
What are the different types of exudates?
First, let’s start with the types of exudate we most commonly see in our patients’ wounds. They are: 1 Serous – a clear, thin and watery plasma. It’s normal during the inflammatory stage of wound healing, and smaller amounts are considered normal. However, a moderate to heavy amount may indicate a high bioburden. 2 Sanguinous – a fresh bleeding, seen in deep partial- and full-thickness wounds. A small amount is normal during the inflammatory stage. 3 Serosanguineous – thin, watery and pale red to pink in color. 4 Seropurulent – thin, watery, cloudy and yellow to tan in color. 5 Purulent – a thick and opaque exudate that is tan, yellow, green or brown in color. It’s never normal in a wound bed, and is often associated with infection or high bacteria levels.
What is the difference between sanguinous and serosanguineous?
A small amount is normal during the inflammatory stage. Serosanguineous – thin, watery and pale red to pink in color. Seropurulent – thin, watery, cloudy and yellow to tan in color.
What is Wound Care Education Institute?
Wound Care Education Institute® provides online and onsite courses in the fields of Skin, Wound, Diabetic and Ostomy Management. Health care professionals who meet the eligibility requirements may sit for the prestigious WCC®, DWC® and OMS national board certification examinations through the National Alliance of Wound Care and Ostomy® (NAWCO®). For more information see wcei.net.
How much of a bandage is exudate?
Small or minimal amount on the dressing – exudate covers less than 25% of the bandage. Moderate amount – wound tissues are wet, and exudate involves 25% to 75% of the bandage. Large or copious amount – wound tissue is filled with fluid, and exudate covers more than 75% of the bandage.
What is the term for the drainage of wounds?
Ooze. Pus. Secretion. The drainage that seeps out of wounds can be called many things, but as wound care clinicians know, the technical term is exudate. This liquid, which is produced by the body in response to tissue damage, can tell us what we need to know about the wound. And while we want wounds to be moist, we don’t want them to be overly moist. Finding that balance can sometimes be a bit tricky – which is why it’s so important to know all about exudate.
What is a seropurulent?
Seropurulent – thin, watery, cloudy and yellow to tan in color.
Introduction
Common Colors and Consistencies of Wound Drainage
- Serosanguineous: Serosanguineous drainage is typically seen in a normal, non-infected wound. It is made up of blood and serous fluid and is typically pink-red and thin. This drainage is common in many wounds.1 Serous: This is thin, watery, clear drainage. It is also common in many wounds throughout the healing process and may also be seen in vascul...
A Few Tips When Documenting Wound Exudate
- Remove the old dressing; note the drainage in the wound bed itself and on the old dressing when making an assessment (is the wound bed wet, dry, scabbed? How much drainage is present on the old dre...
- What type of dressing was on the wound previously (hydrogel [moist] vs. hydrofiber or alginate [absorptive])? It is important to recall the properties of the topical treatment in use and what t…
- Remove the old dressing; note the drainage in the wound bed itself and on the old dressing when making an assessment (is the wound bed wet, dry, scabbed? How much drainage is present on the old dre...
- What type of dressing was on the wound previously (hydrogel [moist] vs. hydrofiber or alginate [absorptive])? It is important to recall the properties of the topical treatment in use and what they’...
- How long has the previous dressing been in place? If you’re removing it just a few hours after the treatment was applied for an assessment, wound drainage could be underreported.
- Cleanse the wound prior to documenting the presence of an odor. Many chronic wounds will have a “wound odor,” from old drainage, that goes away after cleansing. This would not be do…
Conclusion
- Accurate and clear documentation is a key factor in appropriate wound assessment and treatment. Painting an accurate picture of what is going on with a particular wound and patient through documentation is important for many reasons. In addition to the tips and knowledge shared here, your wound care specialist and the interprofessional team are great resources to m…