
What color is a CSF leak?
The classic presentation of CSF leaks is the expression of clear, watery drainage from the nose. This occurs usually on one side; however if fluid drains into the back of the throat there may be a salty taste. Drainage also tends to increase when bending over or straining.
Is CSF fluid yellow?
Cerebrospinal Fluid The color of CSF is most usefully described as (1) pink or orange, (2) yellow, or (3) brown. These colors correspond to the major pigments derived from red cells: oxyhemoglobin, bilirubin, and methemoglobin. Oxyhemoglobin is red in color, but after dilution in the CSF it appears pink or orange.
What does normal CSF look like?
Normal Results Appearance: clear, colorless. CSF total protein: 15 to 60 mg/100 mL. Gamma globulin: 3% to 12% of the total protein.
What does CSF leak fluid look like?
Clear, watery drainage from the nose or ear (on one side) Hearing loss. A metallic taste in the mouth.
What does it mean if spinal fluid is yellow?
Xanthochromia, from the Greek xanthos (ξανθός) "yellow" and chroma (χρώμα) "colour", is the yellowish appearance of cerebrospinal fluid that occurs several hours after bleeding into the subarachnoid space caused by certain medical conditions, most commonly subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Is CSF fluid sticky?
Unlike mucus, which is thick and sticky, CSF is clear and watery.
How do you know if your brain fluid is leaking from your nose?
For patients with cranial CSF leaks, the most common indicators are: Drainage from the nose (rhinorrhea) Salty or metallic taste in the mouth. Sense of drainage down back of throat.
How do you check for CSF leak?
CT myelography. This test is considered the gold standard for diagnosing and locating CSF leaks. It uses a CT scan and a contrast dye to locate CSF leaks anywhere in the skull base. It provides the most precise location of a CSF leak and helps to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
How can you tell the difference between nasal discharge and CSF?
Identifying of CSF leakage Handker chief test: When the discharge from the nose is buried in a handkerchief or dry gauze, the CSF is more likely to be clear if it is not sticky The Handker chief test is a test to determine the nasal discharge, which is unclear and sticky due to mucin secretion from the nose.
What does a CSF leak headache feel like?
The classic symptom is a headache that becomes severe when the patient is upright and quickly disappears when the patient is lying flat. So, the headaches are typically absent first thing in the morning, and start or worsen shortly after getting out of bed.
Are CSF leaks common?
How common is a CSF leak? Spontaneous CSF leaks (ones that are not triggered by a medical procedure such as a lumbar puncture, or by a serious injury such as a gunshot wound) occur in at least five in 100,000 people per year, making them fairly rare.
How long does a CSF leak last?
Most of posttraumatic CSF leakage resolves within six months after trauma. CSF fistula should be closely evaluated because of fatal complication.
What is yellow fluid from nose?
Yellow mucus is a sign that whatever virus or infection you have is taking hold. The good news? Your body is fighting back. The yellow color comes from the cells — white blood cells, for example — rushing to kill the offending germs.
Can you leak brain fluid from your nose?
Cranial CSF leaks occur in the head and are associated with CSF rhinorrhea, in which the cerebrospinal fluid escapes through the nasal passages (runny nose). Spinal CSF leaks develop due to tears in the soft tissues surrounding the spinal cord.
Why would there be bilirubin in CSF?
Xanthochromia is the term used for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) stained yellow with bilirubin. This is the result of a recent subarachnoid or cerebral bleed, head injury, or previous bloody tap. Bilirubin is formed ONLY in vivo, and not after CSF has been taken.
Where is CSF found?
Cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates. It replaces the body fluid found outside the cells of all bilateral animals. The CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, ...
How is CSF produced?
Firstly, a filtered form of plasma moves from fenestrated capillaries in the choroid plexus into an interstitial space , with movement guided by a difference in pressure between the blood in the capillaries and the interstitial fluid. This fluid then needs to pass through the epithelium cells lining the choroid plexus into the ventricles, an active process requiring the transport of sodium, potassium and chloride that draws water into CSF by creating osmotic pressure. Unlike blood passing from the capillaries into the choroid plexus, the epithelial cells lining the choroid plexus contain tight junctions between cells, which act to prevent most substances flowing freely into CSF. Cilia on the apical surfaces of the ependymal cells beat to help transport the CSF.
What is the purpose of a CSF test?
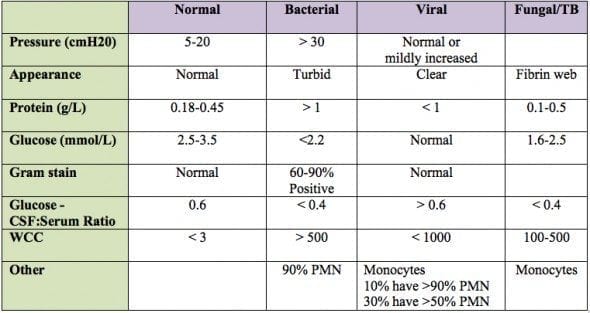
Testing often includes observing the colour of the fluid, measuring CSF pressure , and counting and identifying white and red blood cells within the fluid; measuring protein and glucose levels; and culturing the fluid. The presence of red blood cells and xanthochromia may indicate subarachnoid hemorrhage; whereas central nervous system infections such as meningitis, may be indicated by elevated white blood cell levels. A CSF culture may yield the microorganism that has caused the infection, or PCR may be used to identify a viral cause. Investigations to the total type and nature of proteins reveal point to specific diseases, including multiple sclerosis, paraneoplastic syndromes, systemic lupus erythematosus, neurosarcoidosis, cerebral angiitis; and specific antibodies such as Aquaporin 4 may be tested for to assist in the diagnosis of autoimmune conditions. A lumbar puncture that drains CSF may also be used as part of treatment for some conditions, including idiopathic intracranial hypertension and normal pressure hydrocephalus.
What causes CSF to leak?
CSF can leak from the dura as a result of different causes such as physical trauma or a lumbar puncture, or from no known cause when it is termed a spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak. It is usually associated with intracranial hypotension: low CSF pressure. It can cause headaches, made worse by standing, moving and coughing, as the low CSF pressure causes the brain to "sag" downwards and put pressure on its lower structures. If a leak is identified, a beta-2 transferrin test of the leaking fluid, when positive, is highly specific and sensitive for the detection for CSF leakage. Medical imaging such as CT scans and MRI scans can be used to investigate for a presumed CSF leak when no obvious leak is found but low CSF pressure is identified. Caffeine, given either orally or intravenously, often offers symptomatic relief. Treatment of an identified leak may include injection of a person's blood into the epidural space (an epidural blood patch ), spinal surgery, or fibrin glue.
How does CSF protect the brain?
Protection: CSF protects the brain tissue from injury when jolted or hit, by providing a fluid buffer that acts as a shock absorber from some forms of mechanical injury. Prevention of brain ischemia: The prevention of brain ischemia is aided by decreasing the amount of CSF in the limited space inside the skull.
How much cerebrospinal fluid is produced in the brain?
The brain produces roughly 500 mL of cerebrospinal fluid per day , at a rate of about 25 mL an hour. This transcellular fluid is constantly reabsorbed, so that only 125–150 mL is present at any one time. CSF volume is higher on a mL/kg basis in children compared to adults.
What test is used to detect a CSF leak?
If a leak is identified, a beta-2 transferrin test of the leaking fluid, when positive, is highly specific and sensitive for the detection for CSF leakage. Medical imaging such as CT scans and MRI scans can be used to investigate for a presumed CSF leak when no obvious leak is found but low CSF pressure is identified.
What is a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless liquid found in your brain and spinal cord. The brain and spinal cord make up your central nervous system. Your central nervous system controls and coordinates everything you do including, muscle movement, organ function, and even complex thinking and planning. CSF helps protect this system by acting like a cushion against sudden impact or injury to the brain or spinal cord. CSF also removes waste products from the brain and helps your central nervous system work properly.
What is the CSF test for?
CSF tests for infections look at white blood cells, bacteria, and other substances in the cerebrospinal fluid. Autoimmune disorders, such as Guillain-Barré Syndrome and multiple sclerosis (MS). CSF tests for these disorders look for high levels of certain proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid. These tests are called albumin protein and igG/albumin.
Why do I need a CSF analysis?
You may need a CSF analysis if you have symptoms of an infection of the brain or spinal cord, or of an autoimmune disorder, such as multiple sclerosis (MS).
What happens during a CSF analysis?
Your cerebrospinal fluid will be collected through a procedure called a spinal tap, also known as a lumbar puncture. A spinal tap is usually done in a hospital. During the procedure:
How long does it take for a cerebrospinal fluid to be withdrawn?
Your provider will withdraw a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid for testing. This will take about five minutes. You'll need to stay very still while the fluid is being withdrawn. Your provider may ask you to lie on your back for an hour or two after the procedure.
Where is CSF manufactured?
CSF is manufactured continuously in areas of the brain called ventricles and is absorbed by the bloodstream. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.
How rare are CSF leaks?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks are a rare event. Researchers estimate that they occur in about 5 in every 100,000 people. However, they also believe that this is an underestimate and that the true number of people affected remains unknown. They are mostly found in people in their 30s and 40s.
What is the best treatment for spinal CSF leaks?
Spinal CSF leaks. After conservative treatments have been tried, an epidural blood patch is the most common treatment for spinal CSF leaks. In this procedure, your own blood is injected into the spinal canal. The blood clot that forms creates a seal to stop the leak.
What causes cerebrospinal fluid to leak?
The following are other possible common causes: Head trauma or spine injury. Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) History of epidurals or spinal catheters. Certain head and spine surgeries.
What is the process of leaking cerebrospinal fluid?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs when CSF escapes through a small tear or hole in the outermost layer of connective tissue (called the dura mater) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord and holds in the CSF. The tear or hole allows the CSF to leak out.
How to repair cranial CSF leak?
Repair of cranial CSF leaks depend on the size and the location of the leak. CSF leaks from your nose can usually be repaired using nasal endoscopy (using a camera and a thin long lens through your nostril). CSF leaks into your ear will usually need the use of a microscope.
How to tell if a nose leak is cerebrospinal fluid?
Your doctor may also ask you to lean forward for several minutes to see if drainage comes out your nose. If the drainage can be collected, it is often sent for laboratory testing to confirm that it is cerebrospinal fluid. Your ears will also be examined. One or more of the following other tests may be ordered to determine the location of the leak as well as changes in structures and features in the brain or spinal cord area:
What is CSF used for?
How is it used? Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis may be used to help diagnose a wide variety of diseases and conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
What is CSF testing?
What is being tested? Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, watery liquid that flows around the brain and spinal cord, surrounding and protecting them. A CSF analysis is a group of tests that evaluate substances in CSF in order to diagnose conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
Why is CSF protein small?
CSF protein – only a small amount is normally present in CSF because proteins are large molecules and do not cross the blood/brain barrier easily. Decreases in CSF protein are not generally considered significant. Increases in protein are most commonly seen with:
How many ounces of CSF are produced in a day?
About 17 ounces (500 mL) are produced each day. This rate of production means that all of the CSF is replaced every few hours. A protective blood-brain barrier separates the brain from the bloodstream and regulates the distribution of substances between the blood and the CSF.
How is CSF produced?
CSF is formed and secreted by the choroid plexus, a special tissue that has many blood vessels and that lines the small cavities or chambers (ventricles) in the brain. It is continually produced, circulated, and then absorbed into the blood. About 17 ounces (500 mL) are produced each day.
When can you measure CSF pressure?
Pressure of the CSF can be measured when opening (starting) and closing (finishing) the collection.
When is CSF analysis ordered?
CSF analysis may be ordered when a health practitioner suspects that a person has a condition or disease involving their central nervous system. A person's medical history may prompt the request for CSF analysis. It may be ordered when someone has suffered trauma to the brain or spinal cord, has been diagnosed with cancer that may have spread into the central nervous system, or has signs or symptoms suggestive of central nervous system involvement.
How to identify CSF?
A healthcare professional can often identify CSF just by looking at a sample on a handkerchief or piece of gauze. Unlike mucus, which is thick and sticky, CSF is clear and watery.
How to tell if CSF is leaking?
The symptoms of a CSF leak include fluid drainage from the ears or nose and a headache that worsens when the head is upright.
What is a CSF leak that does not improve with conservative treatment?
a CSF leak that does not improve with conservative treatment. a severe CSF leak that is unlikely to heal on its own. blood clotting in the brain or spinal cord. herniated brain tissue that pushes into the ears or nose. meningitis. Surgery involves suturing — or stitching— any tear to prevent further CSF leakage.
What causes CSF leaks?
Blunt force head injuries can fracture bones in the face or the temporal bones on either side of the skull. These fractures can also tear the dura mater, causing a CSF leak. Other causes of a CSF leak. Trusted Source.
What does it mean when you have a CSF leak?
An individual with a CSF leak may also notice clear , watery fluid draining from their nose or ears when they move their head, especially when bending forward . CSF may also drain down the back of the throat. People describe the taste as salty and metallic. Other symptoms of a CSF leak include:
What is the role of CSF in the brain?
Its role is to supply nutrients to these areas and to cushion the brain inside the skull. The brain is covered in thin layers of tissue collectively called the dura mater, and CSF can escape through a tear in this tissue.
How to diagnose a CSF leak?
A doctor can use a number of tests to diagnose a CSF leak. One test involves placing a sample of what the doctor suspects to be CSF discharge on a piece of filter paper. Once in contact with the paper, any CSF will separate from any blood or mucus.
Overview
Clinical significance
CSF pressure, as measured by lumbar puncture, is 10–18 cmH2O (8–15 mmHg or 1.1–2 kPa) with the patient lying on the side and 20–30 cmH2O (16–24 mmHg or 2.1–3.2 kPa) with the patient sitting up. In newborns, CSF pressure ranges from 8 to 10 cmH2O (4.4–7.3 mmHg or 0.78–0.98 kPa). Most variations are due to coughing or internal compression of jugular veins in the neck. When lying down, the CSF pressure as estimated by lumbar puncture is similar to the intracrania…
Structure
There is about 125–150 mL of CSF at any one time. This CSF circulates within the ventricular system of the brain. The ventricles are a series of cavities filled with CSF. The majority of CSF is produced from within the two lateral ventricles. From here, CSF passes through the interventricular foramina to the third ventricle, then the cerebral aqueduct to the fourth ventricle. From the fourth ventricle, the fluid passes into the subarachnoid space through four openings – the central canal o…
Development
At around the third week of development, the embryo is a three-layered disc, covered with ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. A tube-like formation develops in the midline, called the notochord. The notochord releases extracellular molecules that affect the transformation of the overlying ectoderm into nervous tissue. The neural tube, forming from the ectoderm, contains CSF prior to the development of the choroid plexuses. The open neuropores of the neural tube close after the …
Physiology
CSF serves several purposes:
1. Buoyancy: The actual mass of the human brain is about 1400–1500 grams; however, the net weight of the brain suspended in CSF is equivalent to a mass of 25-50 grams. The brain therefore exists in neutral buoyancy, which allows the brain to maintain its density without being impaired by its own weight, which would cut off blood supply and kill neurons in the lower sections without C…
History
Various comments by ancient physicians have been read as referring to CSF. Hippocrates discussed "water" surrounding the brain when describing congenital hydrocephalus, and Galen referred to "excremental liquid" in the ventricles of the brain, which he believed was purged into the nose. But for some 16 intervening centuries of ongoing anatomical study, CSF remained unmentioned in the literature. This is perhaps because of the prevailing autopsy technique, whic…
Other animals
During phylogenesis, CSF is present within the neuraxis before it circulates. The CSF of Teleostei fish is contained within the ventricles of the brains, but not in a nonexistent subarachnoid space. In mammals, where a subarachnoid space is present, CSF is present in it. Absorption of CSF is seen in amniotes and more complex species, and as species become progressively more complex, the system of absorption becomes progressively more enhanced, and the role of spinal epidural …
See also
• Neuroglobin
• Pandy's test
• Reissner's fiber
• Syrinx (medicine)