
Quark Composition: Protons & Neutrons
- Protons and neutrons are not fundamental particles. They are each made up of three quarks
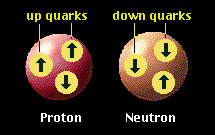
- Protons are made up of two up quarks and a down quark
- Neutrons are made up of two down quarks and an up quark
How many quarks are in a neutron and a proton?
How many quarks are in a neutron? Protons and neutrons each contain three quarks . A proton is composed of two 'Up' quarks and one 'Down' quark while neutrons are composed of one 'Up' quark and two 'Down' quarks.
Which is smaller a proton or a quark?
The most simple, concise answer is that quarks are smaller than protons and neutrons. Electrons seem to be the same 'size' as quarks. Considering this, is there anything smaller than protons neutrons and electrons? As of right now, the only thing smaller than a proton, neutron, or electron is called a quark.
How do quarks make protons and neutrons?
The researchers combined the data with an idea that is well accepted by physicists - the idea that a symmetry exists between protons and neutrons. Both particles are built of different combinations of up- and down-flavored valence quarks. The proton has two up quarks and one down quark, while the neutron sports the symmetrically opposite two down quarks and one up quark.
What are quarks in protons or neutrons made of?
What was the old name for the Top and Bottom quark? Protons are made of two Up and one Down quark. The neutron is made of two Down and one Up quark. The Up quarks have a 2/3 positive charge and the Down has a 1/3 negative charge.
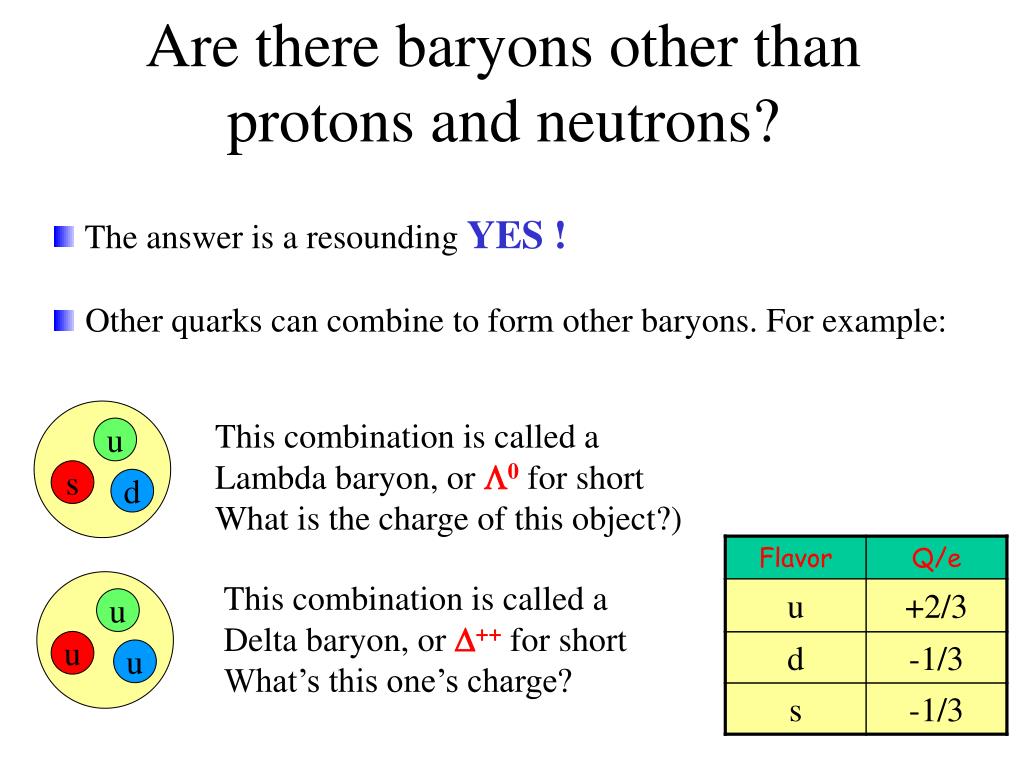
What 3 quarks make a proton?
Although we usually say that a proton contains three quarks (up, up and down), there are many more quark-antiquark pairs at fine scales. Matter is made of molecules, which are made of atoms, which are primarily made of protons and neutrons, which are made of quarks.
What combinations of up and down quarks make up the neutron?
Both particles are built of different combinations of up- and down-flavored quarks. The proton has two up quarks and one down quark, while the neutron sports the symmetrically opposite two down quarks and one up quark.
What is the combination of quarks?
Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks, down quarks and electrons.
What are the quark combination for proton and electron?
A proton and a neutron consist of three quarks each. Two types of quarks, the so-called 'up' quark (denoted by u) of charge + (2/3) e, and the 'down' quark (denoted by d) of charge (-1/3) e, together with electrons build up ordinary matter.
What is a proton made from?
A proton consists of three quarks bound together by a field of gluons.
What quarks make up a electron?
Unlike the electron, hadrons are not fundamental - they are made up of even smaller particles called quarks. Quarks are fundamental. They make up one family of fundamental particles. The other family is the leptons (the electron's family)....FamilyParticleFundamentalleptonelectronyeshadronprotonnoneutronno
How many quarks are in a photon?
A photon has zero quarks. Quarks are elementary or subatomic particles having a mass. They combine in different ratios to form protons and neutrons that in turn form elements around us.
How many combinations of quarks are there?
Quarks are observed to occur only in combinations of two quarks (mesons), three quarks (baryons). There was a recent claim of observation of particles with five quarks (pentaquark), but further experimentation has not borne it out....Quarks.QuarkDownSymbolDB0T0Mass*4.1-5.8 MeV5 more columns
What are the 6 types of quarks?
Quarks were eventually found to come in six types, called up, down, charm, strange, top and bottom. Gell-Mann predicted that some known particles, such as the pion, were made up of two quarks, and others, such as the proton and neutron, were made up of three quarks.
Are protons and neutrons made of quarks?
Quarks and gluons are the building blocks of protons and neutrons, which in turn are the building blocks of atomic nuclei. Scientists' current understanding is that quarks and gluons are indivisible—they cannot be broken down into smaller components.
What are the 7 quarks?
Read a brief summary of this topicquark typebaryon numberchargeup (u)1/3+(2/3)estrange (s)1/3−(1/3)echarm (c)1/3+(2/3)ebottom (b)1/3−(1/3)e4 more rows•Aug 31, 2022
How many quarks does a neutron have?
A neutron is made of 3 quarks, one up quark, and 2 down quarks and many many "intermediate particles" called gluons which carry the interaction between the quarks. These gluons are exchanged very often, so the quarks feel each of other. Neutrons do not always decay.
Which combination of three quarks will produce a neutron?
Protons and neutrons each contain three quarks. A proton is composed of two 'Up' quarks and one 'Down' quark while neutrons are composed of one 'Up' quark and two 'Down' quarks.
How many quarks make up a neutron?
Within the theoretical framework of Standard Model for particle physics, the neutron is composed of two down quarks and an up quark.
Are neutrons made of quarks?
Quarks and gluons are the building blocks of protons and neutrons, which in turn are the building blocks of atomic nuclei. Scientists' current understanding is that quarks and gluons are indivisible—they cannot be broken down into smaller components.
What particle is made up of two down antiquarks and one up antiquark?
The neutron, on the other hand, is built from one up quark and two down quarks, so that it has a net charge of zero.
How do quarks interact?
As described by quantum chromodynamics, the strong interaction between quarks is mediated by gluons, massless vector gauge bosons. Each gluon carries one color charge and one anticolor charge. In the standard framework of particle interactions (part of a more general formulation known as perturbation theory ), gluons are constantly exchanged between quarks through a virtual emission and absorption process. When a gluon is transferred between quarks, a color change occurs in both; for example, if a red quark emits a red–antigreen gluon, it becomes green, and if a green quark absorbs a red–antigreen gluon, it becomes red. Therefore, while each quark's color constantly changes, their strong interaction is preserved.
What are the colors of proton?
The color assignment of individual quarks is arbitrary, but all three colors must be present; red, blue and green are used as an analogy to the primary colors that together produce a white color.
What is the charge of a quark?
Unlike leptons, quarks possess color charge, which causes them to engage in the strong interaction. The resulting attraction between different quarks causes the formation of composite particles known as hadrons (see " Strong interaction and color charge " below).
What is the name of the element that is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter?
1. /. 2. Baryon number. 1. /. 3. A quark ( / kwɔːrk, kwɑːrk /) is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei.
How many gluons are there in the Quark pattern?
The pattern of strong charges for the three colors of quark, three antiquarks, and eight gluons (with two of zero charge overlapping).
How many generations of elementary fermions are there?
Elementary fermions are grouped into three generations, each comprising two leptons and two quarks. The first generation includes up and down quarks, the second strange and charm quarks, and the third bottom and top quarks. All searches for a fourth generation of quarks and other elementary fermions have failed, and there is strong indirect evidence that no more than three generations exist. Particles in higher generations generally have greater mass and less stability, causing them to decay into lower-generation particles by means of weak interactions. Only first-generation (up and down) quarks occur commonly in nature. Heavier quarks can only be created in high-energy collisions (such as in those involving cosmic rays ), and decay quickly; however, they are thought to have been present during the first fractions of a second after the Big Bang, when the universe was in an extremely hot and dense phase (the quark epoch ). Studies of heavier quarks are conducted in artificially created conditions, such as in particle accelerators.
Where did the quark originate?
The word quark is an outdated English word meaning to croak and the above-quoted lines are about a bird choir mocking king Mark of Cornwall in the legend of Tristan and Iseult. Especially in the German-speaking parts of the world there is a widespread legend however that Joyce had taken it from the word Quark, a German word of Slavic origin which denotes a dairy product, but is also a colloquial term for "rubbish". In the legend it is said that he had heard it on a journey to Germany at a peasant market in Freiburg. Some authors however defend a possible German origin of Joyce's word quark. Gell-Mann went into further detail regarding the name of the quark in his 1994 book The Quark and the Jaguar:
Overview
Properties
Quarks have fractional electric charge values – either (−1/3) or (+2/3) times the elementary charge (e), depending on flavor. Up, charm, and top quarks (collectively referred to as up-type quarks) have a charge of +2/3 e; down, strange, and bottom quarks (down-type quarks) have a charge of −1/3 e. Antiquarks have the opposite charge to their corresponding quarks; up-type an…
Classification
The Standard Model is the theoretical framework describing all the known elementary particles. This model contains six flavors of quarks ( q ), named up ( u ), down ( d ), strange ( s ), charm ( c ), bottom ( b ), and top ( t ). Antiparticles of quarks are called antiquarks, and are denoted by a bar over the symbol for the corresponding quark, such as u for an up antiquark. As with antimatter in gener…
History
The quark model was independently proposed by physicists Murray Gell-Mann and George Zweig in 1964. The proposal came shortly after Gell-Mann's 1961 formulation of a particle classification system known as the Eightfold Way – or, in more technical terms, SU(3) flavor symmetry, streamlining its structure. Physicist Yuval Ne'eman had independently developed a scheme similar to the …
Etymology
For some time, Gell-Mann was undecided on an actual spelling for the term he intended to coin, until he found the word quark in James Joyce's 1939 book Finnegans Wake:
– Three quarks for Muster Mark! Sure he hasn't got much of a bark And sure any he has it's all beside the mark.
The word quark is an outdated English word meaning to croak and the above-quoted lines are ab…
Interacting quarks
As described by quantum chromodynamics, the strong interaction between quarks is mediated by gluons, massless vector gauge bosons. Each gluon carries one color charge and one anticolor charge. In the standard framework of particle interactions (part of a more general formulation known as perturbation theory), gluons are constantly exchanged between quarks through a virtual emi…
See also
• Color–flavor locking
• Koide formula
• Nucleon magnetic moment
• Preons
• Quarkonium
Explanatory notes
1. ^ There is also the theoretical possibility of more exotic phases of quark matter.
2. ^ The main evidence is based on the resonance width of the Z boson, which constrains the 4th generation neutrino to have a mass greater than ~45 GeV/c . This would be highly contrasting with the other three generations' neutrinos, whose masses cannot exceed 2 MeV/c .